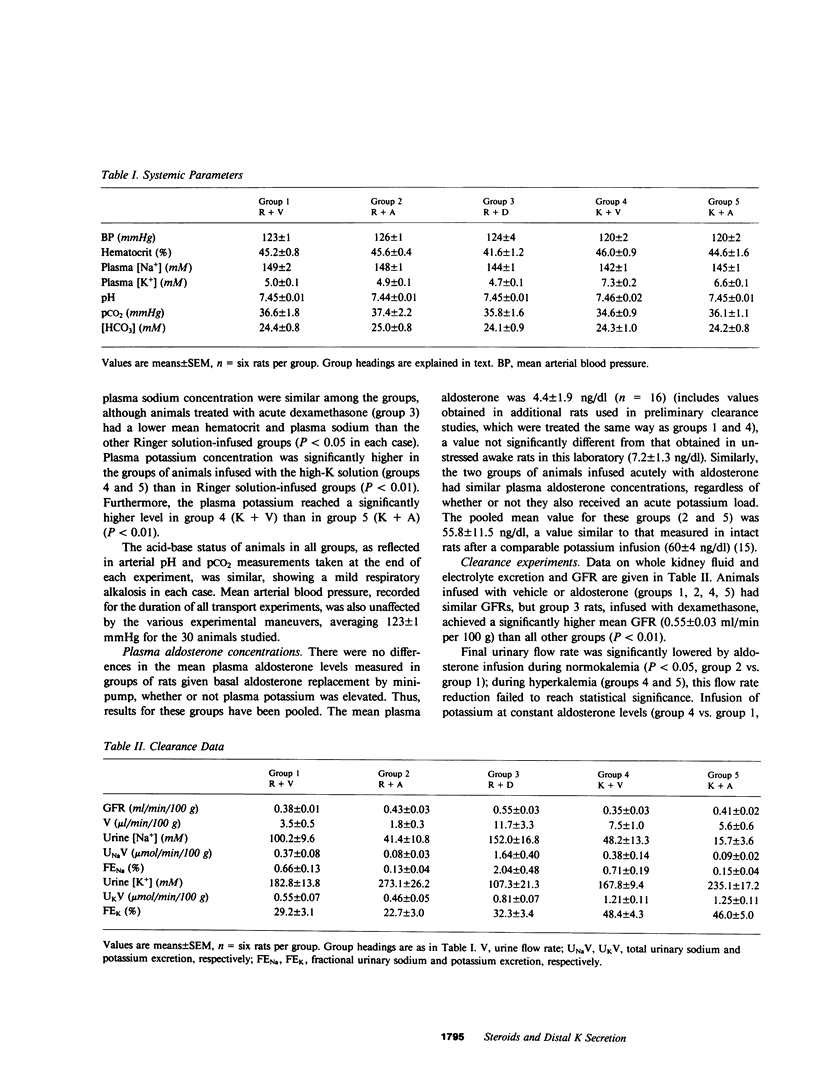
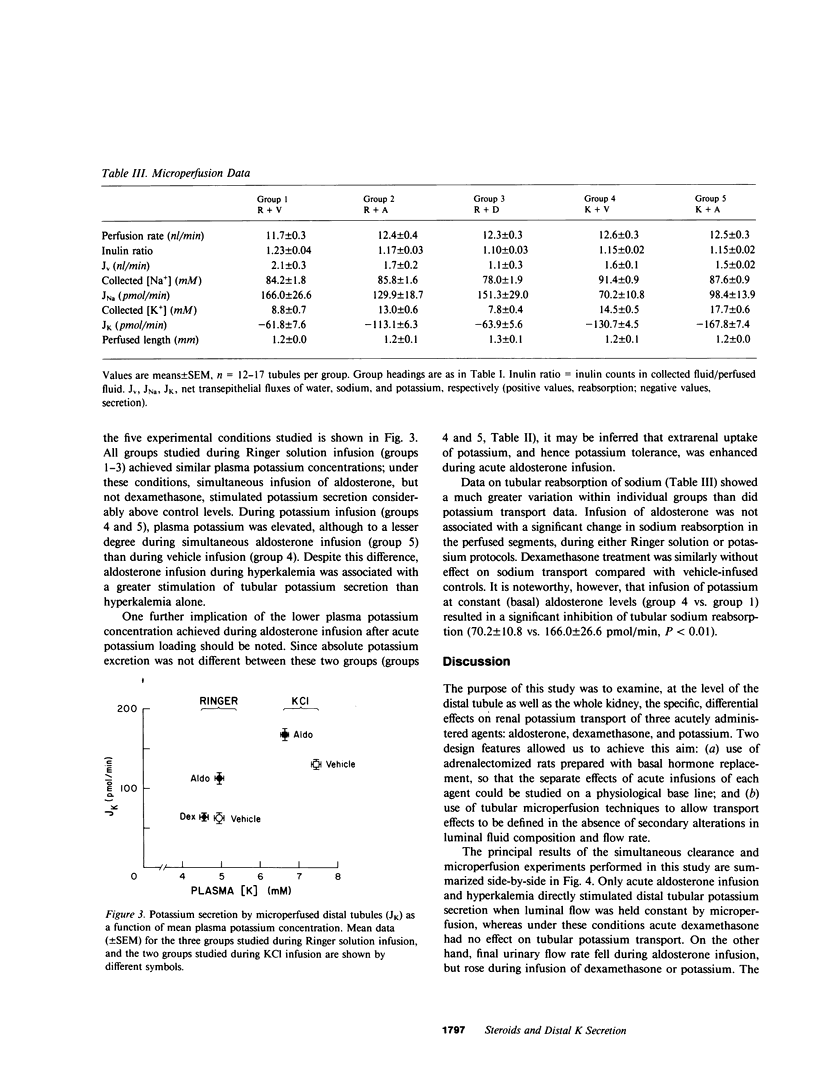
Abstract
To determine the specific effects on renal potassium transport of acute elevations in plasma aldosterone, dexamethasone, and potassium concentrations, we studied adrenalectomized rats prepared such that each factor could be varied independently. Clearance data alone could not be used to deduce the underlying tubular transport effects, however, since infusion of each of these agents was associated with a marked change in urinary flow rate, which may itself have influenced potassium excretion. We therefore used a technique of continuous microperfusion, in vivo, of single superficial distal tubules to evaluate potassium secretion at constant luminal flow rate during each experimental maneuver. Acute aldosterone infusion was associated with a 90% stimulation of potassium secretion by microperfused tubules. However, total kidney sodium excretion and urinary flow rate were markedly reduced, and these factors opposed the direct tubular action of aldosterone, resulting in no net change in the amount of potassium excreted into the final urine. Conversely, dexamethasone had no direct effect on potassium secretion by single microperfused tubules, but it caused a sharp increase in urinary flow and sodium excretion, and secondarily enhanced urinary potassium excretion by 50%. Hyperkalemia per se stimulated renal potassium excretion both via a direct tubular effect and by increasing urinary flow rate. We conclude that urinary potassium excretion after infusion of each of these agents represents the net result of direct tubular effects and secondary flow-mediated changes.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen G. G., Barratt L. J. Effect of aldosterone on the transepithelial potential difference of the rat distal tubule. Kidney Int. 1981 May;19(5):678–686. doi: 10.1038/ki.1981.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bia J. M., Tyler K., DeFronzo R. A. The effect of dexamethasone on renal electrolyte excretion in the adrenalectomized rat. Endocrinology. 1982 Sep;111(3):882–888. doi: 10.1210/endo-111-3-882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bia M. J., Tyler K. A., DeFronzo R. A. Regulation of extrarenal potassium homeostasis by adrenal hormones in rats. Am J Physiol. 1982 Jun;242(6):F641–F644. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1982.242.6.F641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bia M. J., Tyler K., DeFronzo R. The effect of dexamethasone on renal potassium excretion and acute potassium tolerance. Endocrinology. 1983 Nov;113(5):1690–1696. doi: 10.1210/endo-113-5-1690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campen T. J., Vaughn D. A., Fanestil D. D. Mineralo- and glucocorticoid effects on renal excretion of electrolytes. Pflugers Arch. 1983 Oct;399(2):93–101. doi: 10.1007/BF00663903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claire M., Oblin M. E., Steimer J. L., Nakane H., Misumi J., Michaud A., Corvol P. Effect of adrenalectomy and aldosterone on the modulation of mineralocorticoid receptors in rat kidney. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 10;256(1):142–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cortney M. A. Renal tubular transfer of water and electrolytes in adrenalectomized rats. Am J Physiol. 1969 Mar;216(3):589–598. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.216.3.589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman I. S. Receptors and effectors in hormone action on the kidney. Am J Physiol. 1981 Oct;241(4):F333–F339. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.241.4.F333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El Mernissi G., Doucet A. Short-term effect of aldosterone on renal sodium transport and tubular Na-K-ATPase in the rat. Pflugers Arch. 1983 Oct;399(2):139–146. doi: 10.1007/BF00663910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanestil D. D., Park C. S. Steroid hormones and the kidney. Annu Rev Physiol. 1981;43:637–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.43.030181.003225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farman N., Bonvalet J. P. Aldosterone binding in isolated tubules. III. Autoradiography along the rat nephron. Am J Physiol. 1983 Nov;245(5 Pt 1):F606–F614. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1983.245.5.F606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field M. J., Stanton B. A., Giebisch G. H. Influence of ADH on renal potassium handling: a micropuncture and microperfusion study. Kidney Int. 1984 Mar;25(3):502–511. doi: 10.1038/ki.1984.46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fimognari G. M., Fanestil D. D., Edelman I. S. Induction of RNA and protein synthesis in the action of aldosterone in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1967 Oct;213(4):954–962. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1967.213.4.954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARROD O., DAVIES S. A., CAHILL G., Jr The action of cortisone and desoxycorticosterone acetate on glomerular filtration rate and sodium and water exchange in the adrenalectomized dog. J Clin Invest. 1955 Jun;34(6):761–776. doi: 10.1172/JCI103131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garg L. C., Knepper M. A., Burg M. B. Mineralocorticoid effects on Na-K-ATPase in individual nephron segments. Am J Physiol. 1981 Jun;240(6):F536–F544. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.240.6.F536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George J. M., Wright L., Bell N. H., Bartter F. C. The syndrome of primary aldosteronism. Am J Med. 1970 Mar;48(3):343–356. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(70)90065-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Good D. W., Velázquez H., Wright F. S. Luminal influences on potassium secretion: low sodium concentration. Am J Physiol. 1984 May;246(5 Pt 2):F609–F619. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1984.246.5.F609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Good D. W., Wright F. S. Luminal influences on potassium secretion: sodium concentration and fluid flow rate. Am J Physiol. 1979 Feb;236(2):F192–F205. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1979.236.2.F192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOWELL D. S., DAVIS J. O. Relationship of sodium retention to potassium excretion by the kidney during administration of desoxycorticosterone acetate to dogs. Am J Physiol. 1954 Nov;179(2):359–363. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1954.179.2.359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiatt N., Chapman L. W., Davidson M. B., Sheinkopf J. A. Adrenal hormones and the regulation of serum potassium in potassium-loaded adrenalectomized dogs. Endocrinology. 1979 Jul;105(1):215–219. doi: 10.1210/endo-105-1-215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horisberger J. D., Diezi J. Effects of mineralocorticoids on Na+ and K+ excretion in the adrenalectomized rat. Am J Physiol. 1983 Jul;245(1):F89–F99. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1983.245.1.F89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khuri R. N., Strieder W. N., Giebisch G. Effects of flow rate and potassium intake on distal tubular potassium transfer. Am J Physiol. 1975 Apr;228(4):1249–1261. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.228.4.1249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lan N. C., Graham B., Bartter F. C., Baxter J. D. Binding of steroids to mineralocorticoid receptors: implications for in vivo occupancy by glucocorticoids. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 Feb;54(2):332–342. doi: 10.1210/jcem-54-2-332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. S., Jones W. J., Hayslett J. P. Animal model to study the effect of adrenal hormones on epithelial function. Kidney Int. 1983 Sep;24(3):386–391. doi: 10.1038/ki.1983.171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mujais S. K., Chekal M. A., Jones W. J., Hayslett J. P., Katz A. I. Regulation of renal Na-K-ATPase in the rat. Role of the natural mineralo- and glucocorticoid hormones. J Clin Invest. 1984 Jan;73(1):13–19. doi: 10.1172/JCI111183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möhring J., Möhring B. Reevaluation of DOCA escape phenomenon. Am J Physiol. 1972 Nov;223(5):1237–1245. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.223.5.1237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson L. N., Wright F. S. Effect of sodium intake on renal potassium excretion. Am J Physiol. 1977 Sep;233(3):F225–F234. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1977.233.3.F225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petty K. J., Kokko J. P., Marver D. Secondary effect of aldosterone on Na-KATPase activity in the rabbit cortical collecting tubule. J Clin Invest. 1981 Dec;68(6):1514–1521. doi: 10.1172/JCI110405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz G. J., Burg M. B. Mineralocorticoid effects on cation transport by cortical collecting tubules in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1978 Dec;235(6):F576–F585. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1978.235.6.F576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanton B. A., Biemesderfer D., Wade J. B., Giebisch G. Structural and functional study of the rat distal nephron: effects of potassium adaptation and depletion. Kidney Int. 1981 Jan;19(1):36–48. doi: 10.1038/ki.1981.5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanton B. A., Giebisch G. H. Potassium transport by the renal distal tubule: effects of potassium loading. Am J Physiol. 1982 Nov;243(5):F487–F493. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1982.243.5.F487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes J. B. Potassium secretion by cortical collecting tubule: relation to sodium absorption, luminal sodium concentration, and transepithelial voltage. Am J Physiol. 1981 Oct;241(4):F395–F402. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.241.4.F395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiederholt M., Behn C., Schoormans W., Hansen L. Effect of aldosterone on sodium and potassium transport in the kidney. J Steroid Biochem. 1972 Feb;3(2):151–159. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(72)90045-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiederholt M., Schoormans W., Fischer F., Behn C. Mechanism of action of aldosterone on potassium transfer in the rat kidney. Pflugers Arch. 1973 Dec 12;345(2):159–178. doi: 10.1007/BF00585838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiederholt M., Wiederholt B. Der Einfluss von Dexamethason auf die Wasser- und Elektrolytausscheidung adrenalektomierter Ratten. Pflugers Arch. 1968;302(1):57–78. doi: 10.1007/BF00586782. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox C. S., Cemerikic D. A., Giebisch G. Differential effects of acute mineralo- and glucocorticosteroid administration on renal acid elimination. Kidney Int. 1982 Apr;21(4):546–556. doi: 10.1038/ki.1982.61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodhall P. B., Tisher C. C. Response of the distal tubule and cortical collecting duct to vasopressin in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1973 Dec;52(12):3095–3108. doi: 10.1172/JCI107509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright F. S., Knox F. G., Howards S. S., Berliner R. W. Reduced sodium reabsorption by the proximal tubule of Doca-escaped dogs. Am J Physiol. 1969 Apr;216(4):869–875. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.216.4.869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young D. B., Jackson T. E. Effects of aldosterone on potassium distribution. Am J Physiol. 1982 Nov;243(5):R526–R530. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1982.243.5.R526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



