Abstract
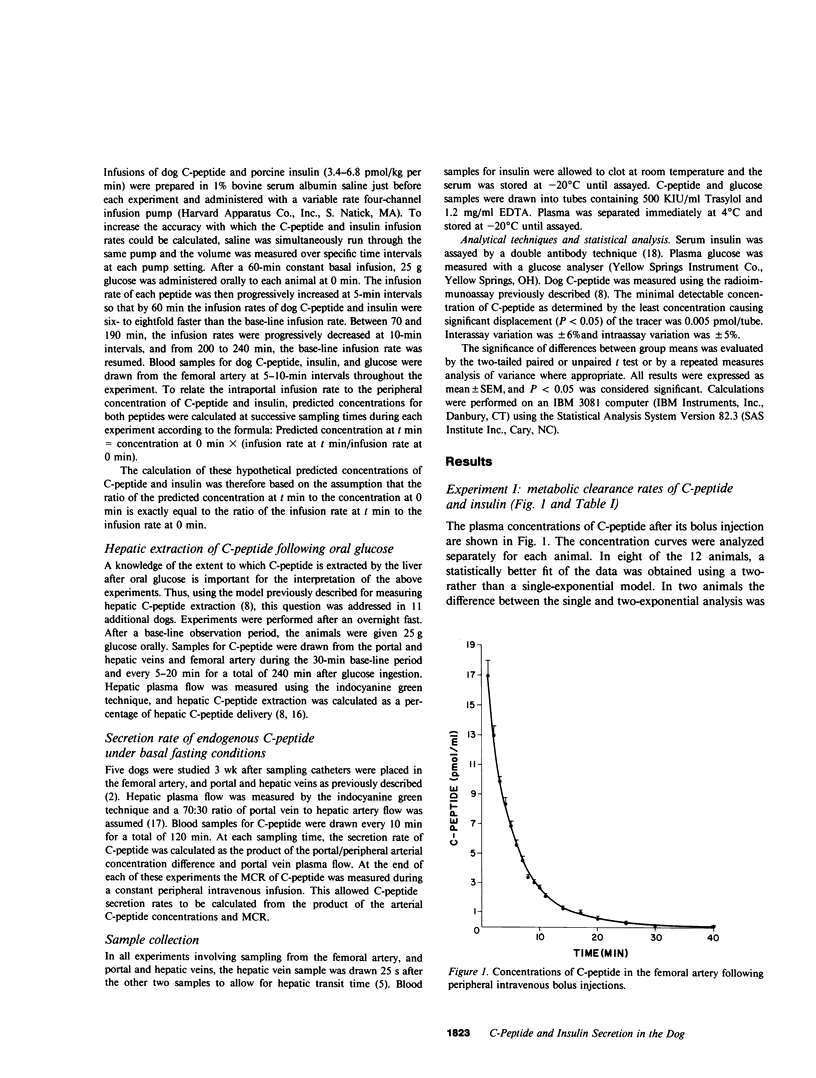
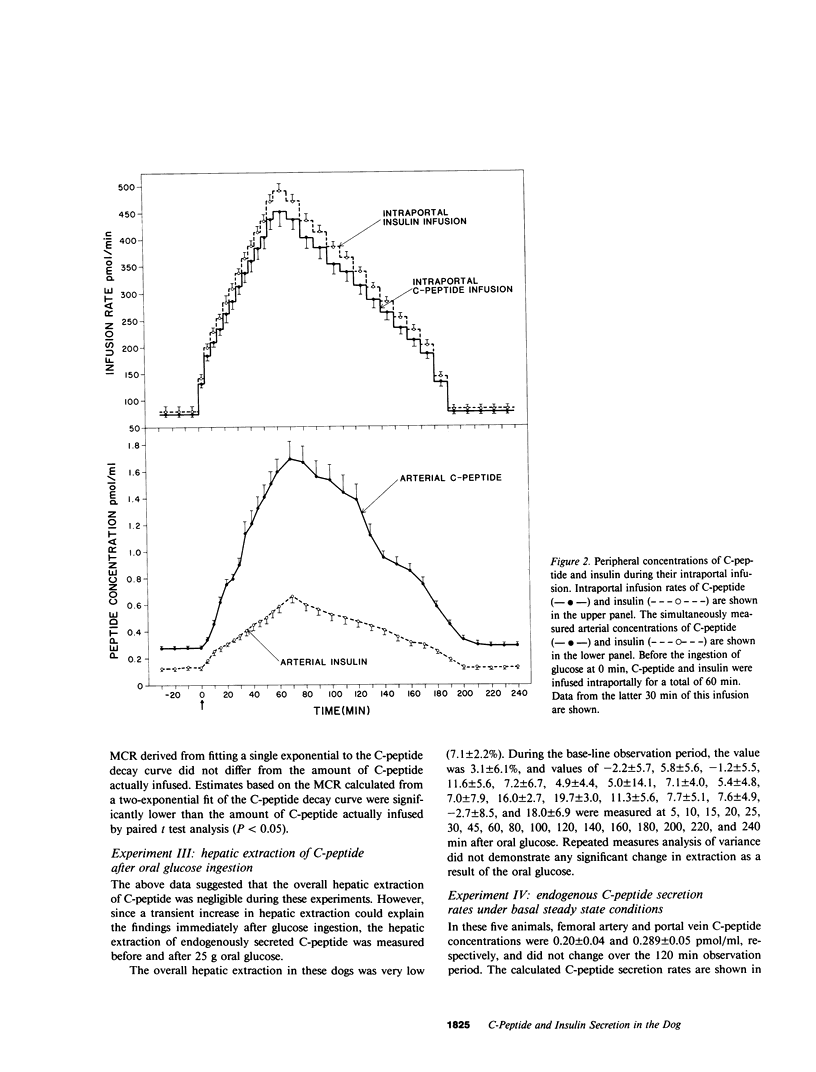
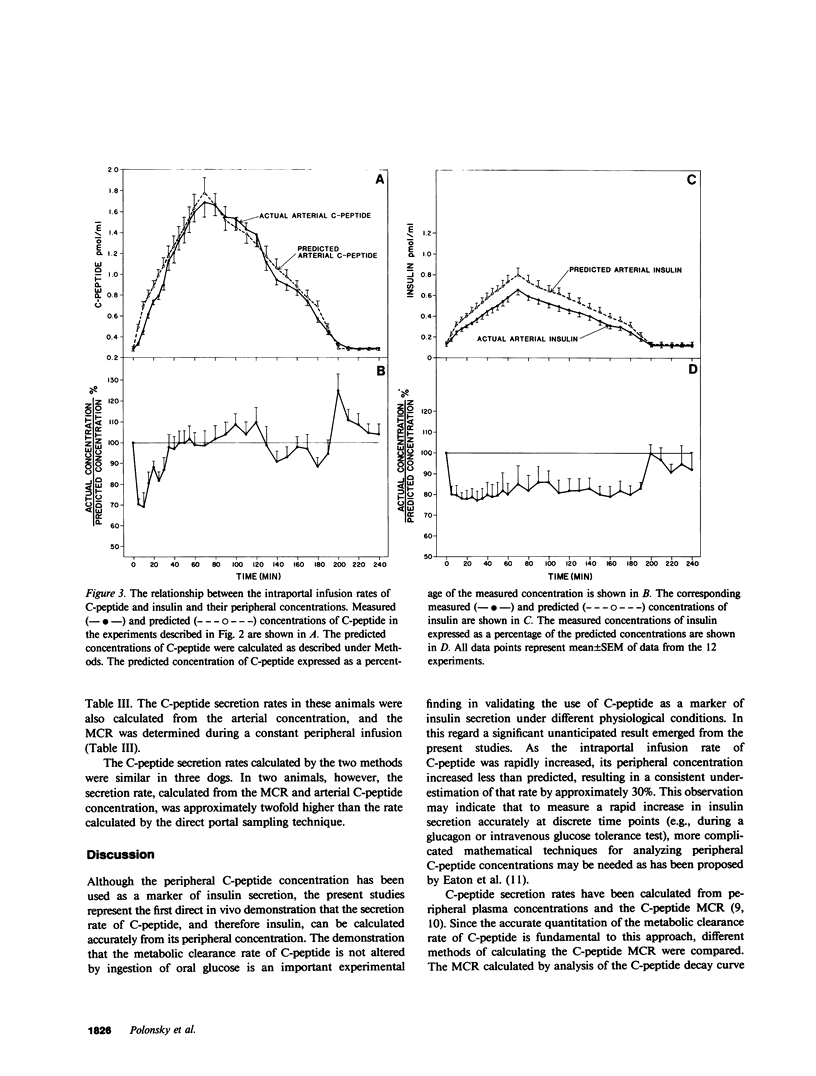
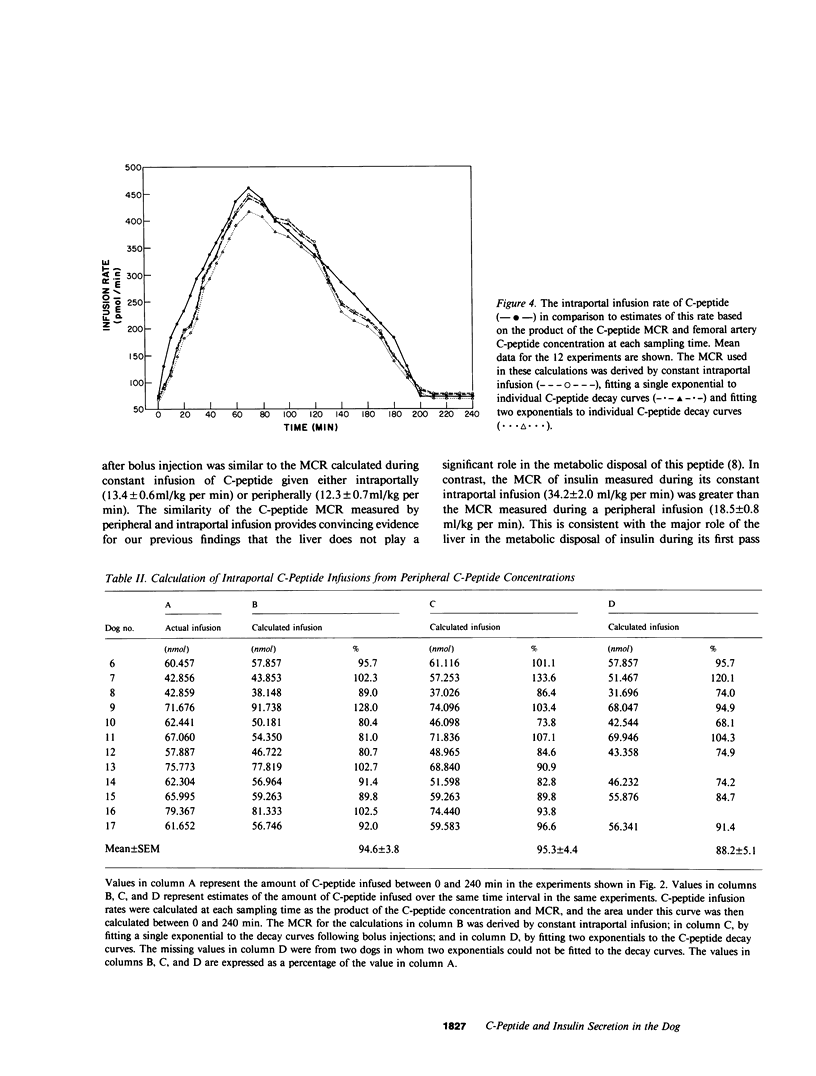
Estimation of the insulin secretory rate from peripheral C-peptide concentrations depends upon the following characteristics of C-peptide kinetics: (a) equimolar secretion of insulin and C-peptide by pancreatic beta cells; (b) negligible hepatic extraction of C-peptide; (c) constant metabolic clearance rate (MCR) of C-peptide over a physiological and pathophysiological range of plasma levels; and (d) proportional changes in the secretion rate of C-peptide and its peripheral concentrations under varying physiological conditions. In the present experiments, the relationship between a variable intraportal infusion of C-peptide and its concentration in the femoral artery was explored in 12 pancreatectomized dogs. As the infusion of C-peptide was rapidly increased, the magnitude of its peripheral concentration initially increased less than the infusion rate by 20-30%. After an equilibration period of approximately 30 min, however, further increases and decreases in the intraportal infusion were accompanied by nearly proportional changes in its peripheral concentration. Estimates of the amount of C-peptide infused during the experiment based on the steady state C-peptide MCR and its peripheral concentration were within 20% of the amount of C-peptide actually infused. These experiments demonstrate that the portal delivery rate of C-peptide can be calculated from its MCR and peripheral concentration in the dog. They also provide a basis for testing the validity of more complicated models of insulin secretion based on peripheral C-peptide concentrations in the dog as well as other species, including man. Finally, we have shown that the hepatic extraction of endogenously secreted C-peptide is negligible in the basal state (3.1 +/- 6.1%), and does not change after oral glucose ingestion. The MCR of exogenous dog C-peptide was similar whether measured by constant peripheral intravenous infusion (12.3 +/- 0.7 ml/kg per min), constant intraportal infusion (13.4 +/- 0.6 ml/kg per min), or analysis of the decay curve after a bolus injection (13.5 +/- 0.7 ml/kg per min).
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Eaton R. P., Allen R. C., Schade D. S., Erickson K. M., Standefer J. Prehepatic insulin production in man: kinetic analysis using peripheral connecting peptide behavior. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1980 Sep;51(3):520–528. doi: 10.1210/jcem-51-3-520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton R. P., Allen R. C., Schade D. S. Hepatic removal of insulin in normal man: dose response to endogenous insulin secretion. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983 Jun;56(6):1294–1300. doi: 10.1210/jcem-56-6-1294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faber O. K., Hagen C., Binder C., Markussen J., Naithani V. K., Blix P. M., Kuzuya H., Horwitz D. L., Rubenstein A. H., Rossing N. Kinetics of human connecting peptide in normal and diabetic subjects. J Clin Invest. 1978 Jul;62(1):197–203. doi: 10.1172/JCI109106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding P. E., Bloom G., Field J. B. Effect of infusion of insulin into portal vein on hepatic extraction of insulin in anesthetized dogs. Am J Physiol. 1975 May;228(5):1580–1588. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.228.5.1580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honey R. N., Price S. The determinants of insulin extraction in the isolated perfused rat liver. Horm Metab Res. 1979 Feb;11(2):111–117. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1092691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaspan J., Polonsky K. Glucose ingestion in dogs alters the hepatic extraction of insulin. In vivo evidence for a relationship between biologic action and extraction of insulin. J Clin Invest. 1982 Mar;69(3):516–525. doi: 10.1172/JCI110477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KETTERER S. G., WIEGAND B. D., RAPAPORT E. Hepatic uptake and biliary excretion of indocyanine green and its use in estimation of hepatic blood flow in dogs. Am J Physiol. 1960 Sep;199:481–484. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1960.199.3.481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaden M., Harding P., Field J. B. Effect of intraduodenal glucose administration on hepatic extraction of insulin in the anesthetized dog. J Clin Invest. 1973 Aug;52(8):2016–2028. doi: 10.1172/JCI107386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meistas M. T., Rendell M., Margolis S., Kowarski A. A. Estimation of the secretion rate of insulin from the urinary excretion rate of C-peptide. Study in obese and diabetic subjects. Diabetes. 1982 May;31(5 Pt 1):449–453. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.5.449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meistas M. T., Zadik Z., Margolis S., Kowarski A. A. Correlation of urinary excretion of C-peptide with the integrated concentration and secretion rate of insulin. Diabetes. 1981 Aug;30(8):639–643. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.8.639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polonsky K. S., Jaspan J. B., Berelowitz M., Emmanouel D. S., Dhorajiwala J. Hepatic and renal metabolism of somatostatin-like immunoreactivity. Simultaneous assessment in the dog. J Clin Invest. 1981 Nov;68(5):1149–1157. doi: 10.1172/JCI110359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polonsky K., Jaspan J., Emmanouel D., Holmes K., Moossa A. R. Differences in the hepatic and renal extraction of insulin and glucagon in the dog: evidence for saturability of insulin metabolism. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1983 Mar;102(3):420–427. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1020420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polonsky K., Jaspan J., Pugh W., Cohen D., Schneider M., Schwartz T., Moossa A. R., Tager H., Rubenstein A. H. Metabolism of C-peptide in the dog. In vivo demonstration of the absence of hepatic extraction. J Clin Invest. 1983 Sep;72(3):1114–1123. doi: 10.1172/JCI111036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubenstein A. H., Pottenger L. A., Mako M., Getz G. S., Steiner D. F. The metabolism of proinsulin and insulin by the liver. J Clin Invest. 1972 Apr;51(4):912–921. doi: 10.1172/JCI106886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



