Abstract
Development of bacteriophage T4 in Escherichia coli requires the sequential recognition of three classes of promoters: early, middle, and late. Recognition of middle promoters is known to require the motA gene product, a protein that binds specifically to the "Mot box" located at the -30 region of these promoters. In vivo, the asiA gene product is as critical for middle mode RNA synthesis as is that of the motA gene. In vitro, AsiA protein is known to loosen the sigma 70-core RNA polymerase interactions and to inhibit some sigma 70-dependent transcription, presumably through binding to the sigma 70 subunit. Here we show that, in vitro, purified MotA and AsiA proteins are both necessary and sufficient to activate transcription initiation at T4 middle promoters by the E. coli RNA polymerase in a sigma 70-dependent manner. AsiA is also shown to inhibit recognition of T4 early promoters and may play a pivotal role in the recognition of all three classes of phage promoters.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Daniels D., Zuber P., Losick R. Two amino acids in an RNA polymerase sigma factor involved in the recognition of adjacent base pairs in the -10 region of a cognate promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):8075–8079. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.8075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dombroski A. J., Walter W. A., Record M. T., Jr, Siegele D. A., Gross C. A. Polypeptides containing highly conserved regions of transcription initiation factor sigma 70 exhibit specificity of binding to promoter DNA. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):501–512. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90174-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardella T., Moyle H., Susskind M. M. A mutant Escherichia coli sigma 70 subunit of RNA polymerase with altered promoter specificity. J Mol Biol. 1989 Apr 20;206(4):579–590. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90567-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guild N., Gayle M., Sweeney R., Hollingsworth T., Modeer T., Gold L. Transcriptional activation of bacteriophage T4 middle promoters by the motA protein. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jan 20;199(2):241–258. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90311-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinton D. M. Transcription from a bacteriophage T4 middle promoter using T4 motA protein and phage-modified RNA polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 25;266(27):18034–18044. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar A., Grimes B., Fujita N., Makino K., Malloch R. A., Hayward R. S., Ishihama A. Role of the sigma 70 subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase in transcription activation. J Mol Biol. 1994 Jan 14;235(2):405–413. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malik S., Zalenskaya K., Goldfarb A. Competition between sigma factors for core RNA polymerase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8521–8530. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattson T., Van Houwe G., Epstein R. H. Isolation and characterization of conditional lethal mutations in the mot gene of bacteriophage T4. J Mol Biol. 1978 Dec 15;126(3):551–570. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90058-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen L. H., Jensen D. B., Burgess R. R. Overproduction and purification of sigma 32, the Escherichia coli heat shock transcription factor. Protein Expr Purif. 1993 Oct;4(5):425–433. doi: 10.1006/prep.1993.1056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orsini G., Ouhammouch M., Le Caer J. P., Brody E. N. The asiA gene of bacteriophage T4 codes for the anti-sigma 70 protein. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jan;175(1):85–93. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.1.85-93.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ouhammouch M., Orsini G., Brody E. N. The asiA gene product of bacteriophage T4 is required for middle mode RNA synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1994 Jul;176(13):3956–3965. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.13.3956-3965.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt R. P., Kreuzer K. N. Purified MotA protein binds the -30 region of a bacteriophage T4 middle-mode promoter and activates transcription in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 5;267(16):11399–11407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegele D. A., Hu J. C., Walter W. A., Gross C. A. Altered promoter recognition by mutant forms of the sigma 70 subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1989 Apr 20;206(4):591–603. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90568-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens A. Deoxyribonucleic acid dependent ribonucleic acid polymerases from two T4 phage-infected systems. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 29;13(3):493–503. doi: 10.1021/bi00700a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens A., Rhoton J. C. Characterization of an inhibitor causing potassium chloride sensitivity of an RNA polymerase from T4 phage-infected Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1975 Nov 18;14(23):5074–5079. doi: 10.1021/bi00694a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
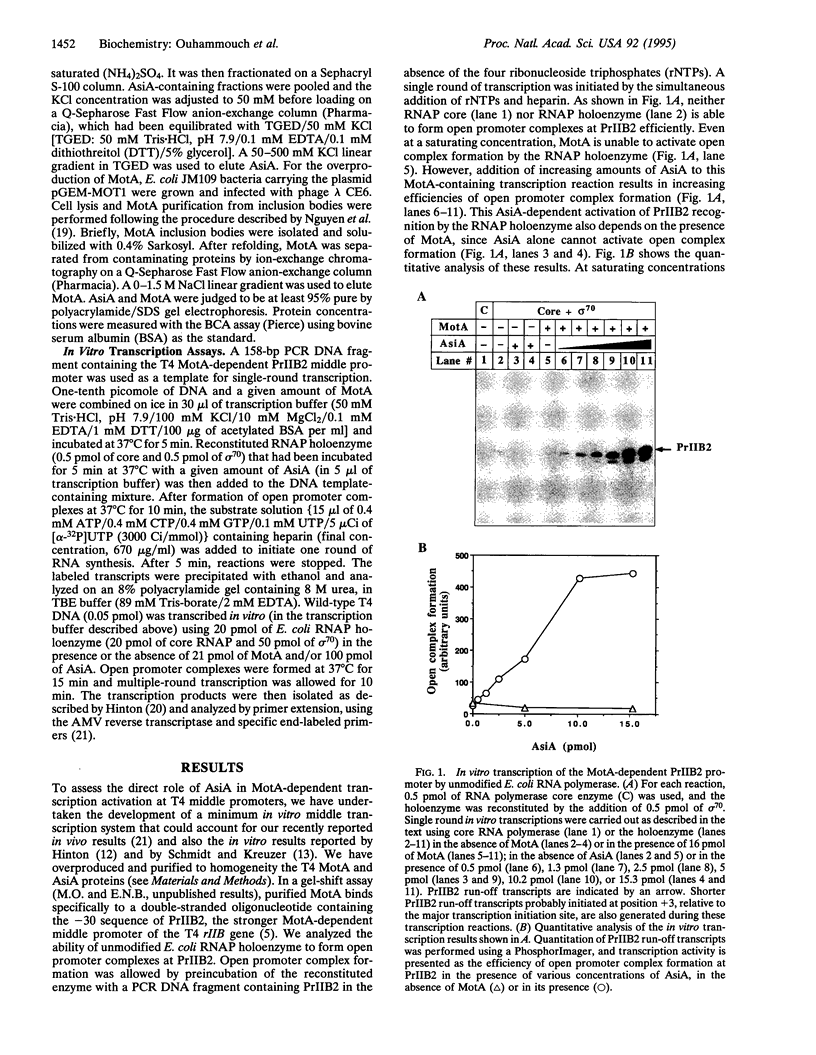
- Uzan M., Brody E., Favre R. Nucleotide sequence and control of transcription of the bacteriophage T4 motA regulatory gene. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Sep;4(9):1487–1496. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb02059.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldburger C., Gardella T., Wong R., Susskind M. M. Changes in conserved region 2 of Escherichia coli sigma 70 affecting promoter recognition. J Mol Biol. 1990 Sep 20;215(2):267–276. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(05)80345-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams K. P., Kassavetis G. A., Geiduschek E. P. Interactions of the bacteriophage T4 gene 55 product with Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Competition with Escherichia coli sigma 70 and release from late T4 transcription complexes following initiation. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 5;262(25):12365–12371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zograff Y. N. On the role of the Escherichia coli RNA polymerase sigma factor in T4 phage development. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;183(3):557–558. doi: 10.1007/BF00268782. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]