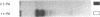Abstract
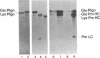
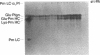
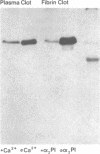
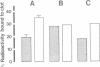
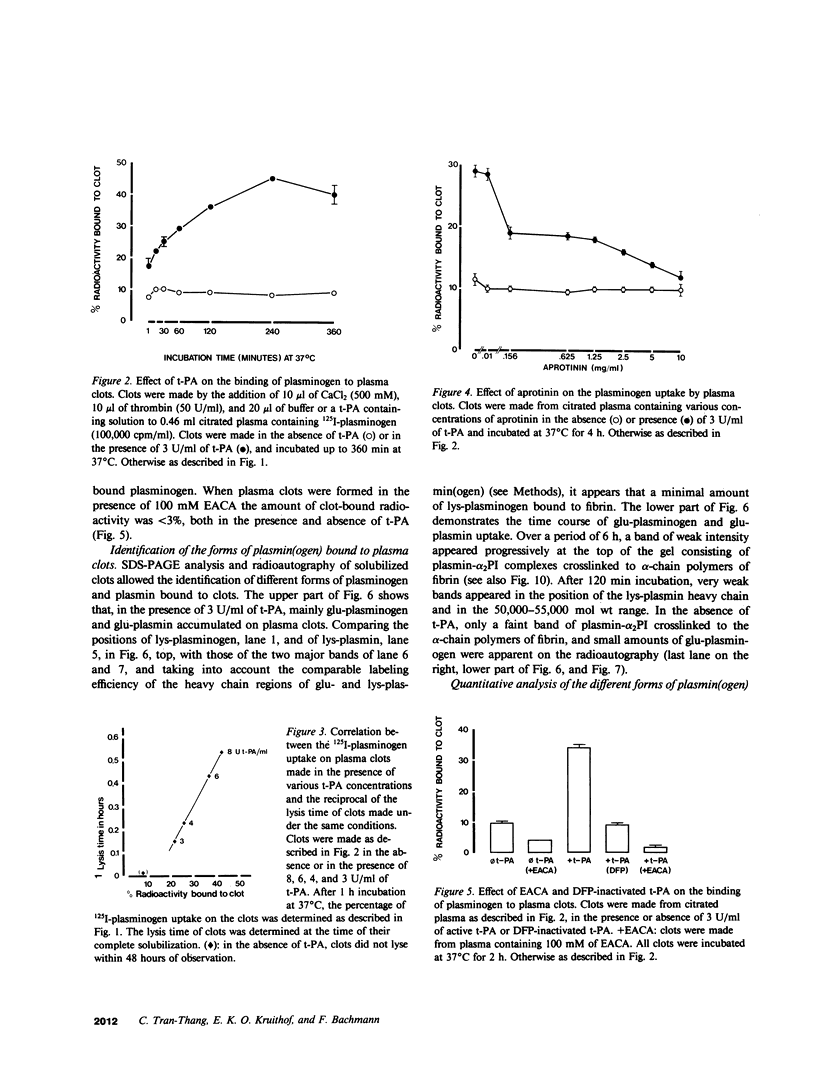
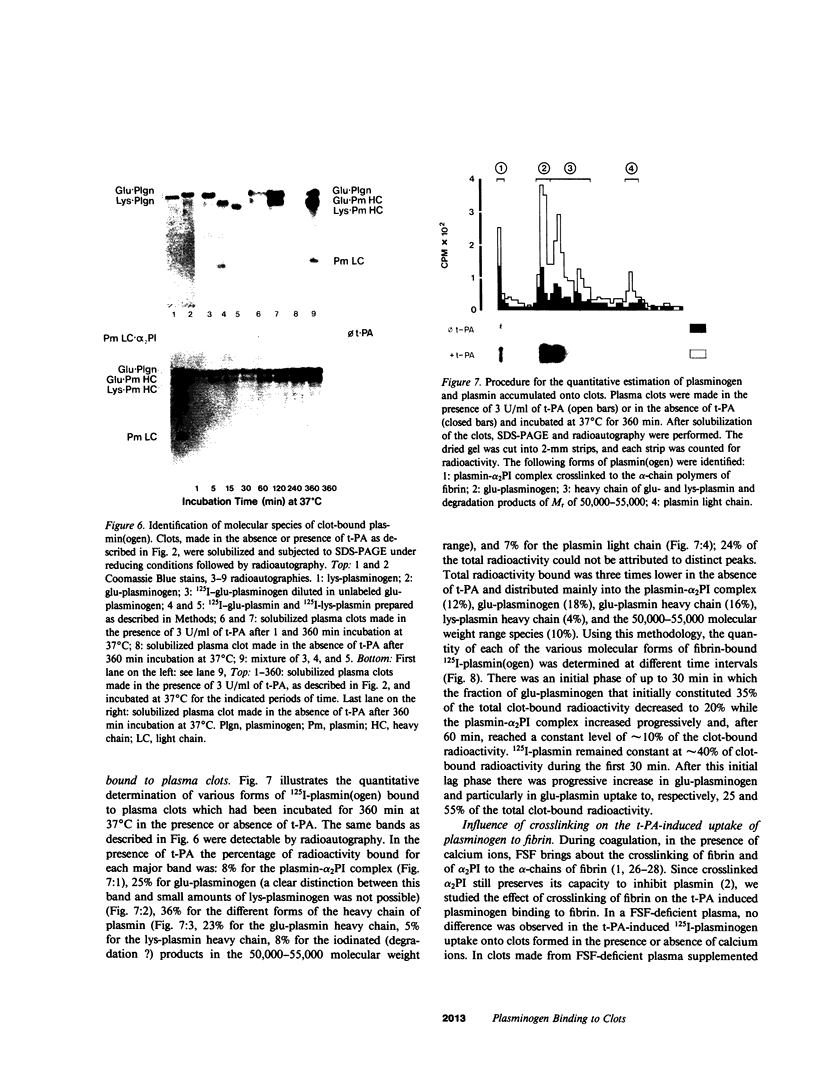
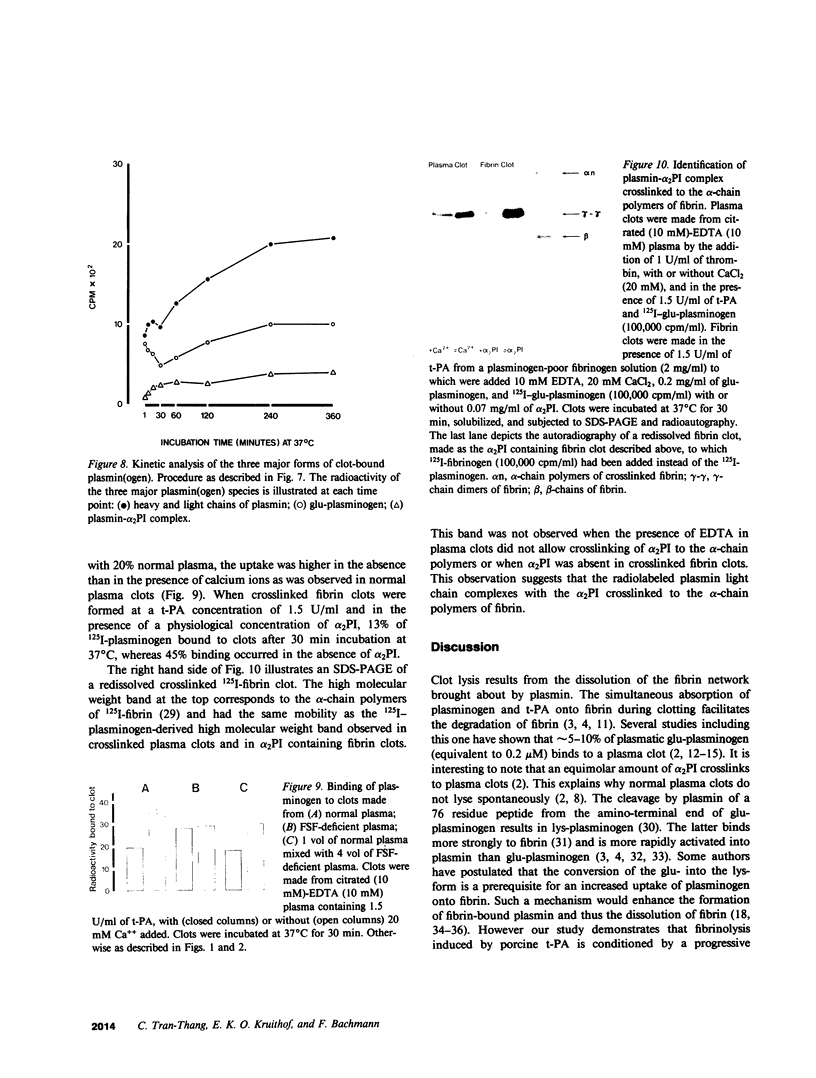
Porcine tissue-type plasminogen activator (t-PA) increases the binding of 125I-glu-plasminogen to clots made from human plasma or purified fibrinogen in a time and t-PA concentration dependent fashion. The accumulation of plasminogen was faster and greater on noncrosslinked plasma clots than on clots which had been crosslinked by Factor XIIIa. Furthermore, the uptake of plasminogen to crosslinked fibrin clots occurred at a slower rate in the presence of alpha 2-plasmin inhibitor (alpha 2 PI) than in its absence. The kinetics of the uptake of 125I-plasminogen were analyzed using SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and radioautography of solubilized plasma clots formed in the presence of t-PA. During the initial phase there was a decrease of clot-bound glu-plasminogen; simultaneously, there was a slight increase in clot-bound glu-plasmin and in plasmin complexed to alpha 2 PI that was crosslinked to alpha-chain polymers of fibrin. This was followed by a marked increase in clot-bound plasminogen having glutamic acid as NH2-terminal (glu-plasminogen) and gluplasmin. t-PA-induced enhancement of glu-plasminogen uptake appears to be mediated by plasmin but does not require the conversion of glu-plasminogen to plasminogen having lysine or methionine as NH2-terminal. The described mechanism assures an adequate supply of clot-bound plasmin, which is the enzyme ultimately involved in the degradation of fibrin.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Deutsch D. G., Mertz E. T. Plasminogen: purification from human plasma by affinity chromatography. Science. 1970 Dec 4;170(3962):1095–1096. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3962.1095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaffney P. J., Brasher M., Lord K., Kirkwood T. B. Activation of plasminogen as a feature in its assay. Haemostasis. 1977;6(1):72–88. doi: 10.1159/000214167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gladner J. A., Nossal R. Effects of crosslinking on the rigidity and proteolytic susceptibility of human fibrin clots. Thromb Res. 1983 May 1;30(3):273–288. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(83)90081-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granelli-Piperno A., Reich E. A study of proteases and protease-inhibitor complexes in biological fluids. J Exp Med. 1978 Jul 1;148(1):223–234. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.1.223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoylaerts M., Rijken D. C., Lijnen H. R., Collen D. Kinetics of the activation of plasminogen by human tissue plasminogen activator. Role of fibrin. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):2912–2919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korninger C., Matsuo O., Suy R., Stassen J. M., Collen D. Thrombolysis with human extrinsic (tissue-type) plasminogen activator in dogs with femoral vein thrombosis. J Clin Invest. 1982 Mar;69(3):573–580. doi: 10.1172/JCI110483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lijnen H. R., Van Hoef B., Collen D. On the role of the carbohydrate side chains of human plasminogen in its interaction with alpha 2-antiplasmin and fibrin. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Nov;120(1):149–154. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05682.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas M. A., Fretto L. J., McKee P. A. The binding of human plasminogen to fibrin and fibrinogen. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 10;258(7):4249–4256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas M. A., Fretto L. J., McKee P. A. The relationship of fibrinogen structure to plasminogen activation and plasmin activity during fibrinolysis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1983 Jun 27;408:71–91. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1983.tb23235.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas M. A., Straight D. L., Fretto L. J., McKee P. A. The effects of fibrinogen and its cleavage products on the kinetics of plasminogen activation by urokinase and subsequent plasmin activity. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12171–12177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuo O., Rijken D. C., Collen D. Comparison of the relative fibrinogenolytic, fibrinolytic and thrombolytic properties of tissue plasminogen activator and urokinase in vitro. Thromb Haemost. 1981 Jun 30;45(3):225–229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattsson C., Nyberg-Arrhenius V., Wallén P. Dissolution of thrombi by tissue plasminogen activator, urokinase and streptokinase in an artificial circulating system. Thromb Res. 1981 Mar 15;21(6):535–545. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(81)90254-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rákóczi I., Wiman B., Collen D. On the biological significance of the specific interaction between fibrin, plasminogen and antiplasmin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 May 3;540(2):295–300. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90142-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rånby M., Bergsdorf N., Nilsson T. Enzymatic properties of the one- and two-chain form of tissue plasminogen activator. Thromb Res. 1982 Jul 15;27(2):175–183. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(82)90197-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rånby M. Studies on the kinetics of plasminogen activation by tissue plasminogen activator. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Jun 24;704(3):461–469. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(82)90068-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakata Y., Aoki N. Cross-linking of alpha 2-plasmin inhibitor to fibrin by fibrin-stabilizing factor. J Clin Invest. 1980 Feb;65(2):290–297. doi: 10.1172/JCI109671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakata Y., Aoki N. Significance of cross-linking of alpha 2-plasmin inhibitor to fibrin in inhibition of fibrinolysis and in hemostasis. J Clin Invest. 1982 Mar;69(3):536–542. doi: 10.1172/JCI110479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakata Y., Mimuro J., Aoki N. Differential binding of plasminogen to crosslinked and noncrosslinked fibrins: its significance in hemostatic defect in factor XIII deficiency. Blood. 1984 Jun;63(6):1393–1401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakata Y., Tateno K., Tamaki T., Aoki N. Calcium-dependent binding of alpha 2-plasmin inhibitor to fibrin. Thromb Res. 1979;16(1-2):279–282. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(79)90291-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suenson E., Lützen O., Thorsen S. Initial plasmin-degradation of fibrin as the basis of a positive feed-back mechanism in fibrinolysis. Eur J Biochem. 1984 May 2;140(3):513–522. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08132.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suenson E., Thorsen S. Secondary-site binding of Glu-plasmin, Lys-plasmin and miniplasmin to fibrin. Biochem J. 1981 Sep 1;197(3):619–628. doi: 10.1042/bj1970619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takada A., Ito T., Takada Y. Interaction of plasmin with tranexamic acid and alpha 2 plasmin inhibitor in the plasma and clot. Thromb Haemost. 1980 Feb 29;43(1):20–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaki T., Aoki N. Cross-linking of alpha 2-plasmin inhibitor and fibronectin to fibrin by fibrin-stabilizing factor. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Oct 13;661(2):280–286. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(81)90016-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaki T., Aoki N. Cross-linking of alpha 2-plasmin inhibitor to fibrin catalyzed by activated fibrin-stabilizing factor. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):14767–14772. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorsen S., Clemmensen I., Sottrup-Jensen L., Magnusson S. Adsorption to fibrin of native fragments of known primary structure from human plasminogen. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 May 29;668(3):377–387. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(81)90171-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorsen S. Differences in the binding to fibrin of native plasminogen and plasminogen modified by proteolytic degradation. Influence of omega-aminocarboxylic acids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 May 30;393(1):55–65. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(75)90216-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tran-Thang C., Kruithof E. K., Bachmann F. The mechanism of in vitro clot lysis induced by vascular plasminogen activator. Blood. 1984 Jun;63(6):1331–1337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Violand B. N., Castellino F. J. Mechanism of the urokinase-catalyzed activation of human plasminogen. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jul 10;251(13):3906–3912. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Váli Z., Patthy L. Location of the intermediate and high affinity omega-aminocarboxylic acid-binding sites in human plasminogen. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 25;257(4):2104–2110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitaker A. N., Rowe E. A., Masci P. P., Joe F., Gaffney P. J. The binding of glu- and lys-plasminogens to fibrin and their subsequent effects on fibrinolysis. Thromb Res. 1980 Aug 1;19(3):381–391. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(80)90266-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiman B., Collen D. Molecular mechanism of physiological fibrinolysis. Nature. 1978 Apr 6;272(5653):549–550. doi: 10.1038/272549a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiman B., Collen D. On the kinetics of the reaction between human antiplasmin and plasmin. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Mar 15;84(2):573–578. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12200.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wohl R. C., Summaria L., Robbins K. C. Kinetics of activation of human plasminogen by different activator species at pH 7.4 and 37 degrees C. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 10;255(5):2005–2013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]