Abstract
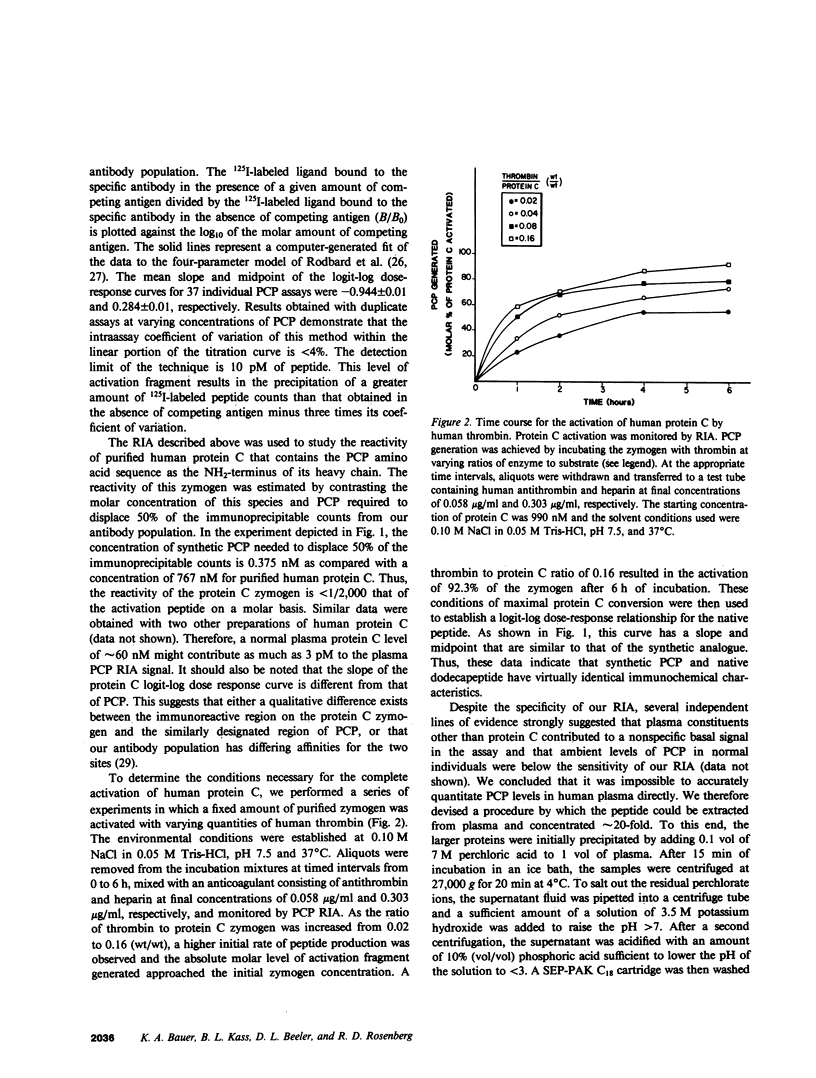
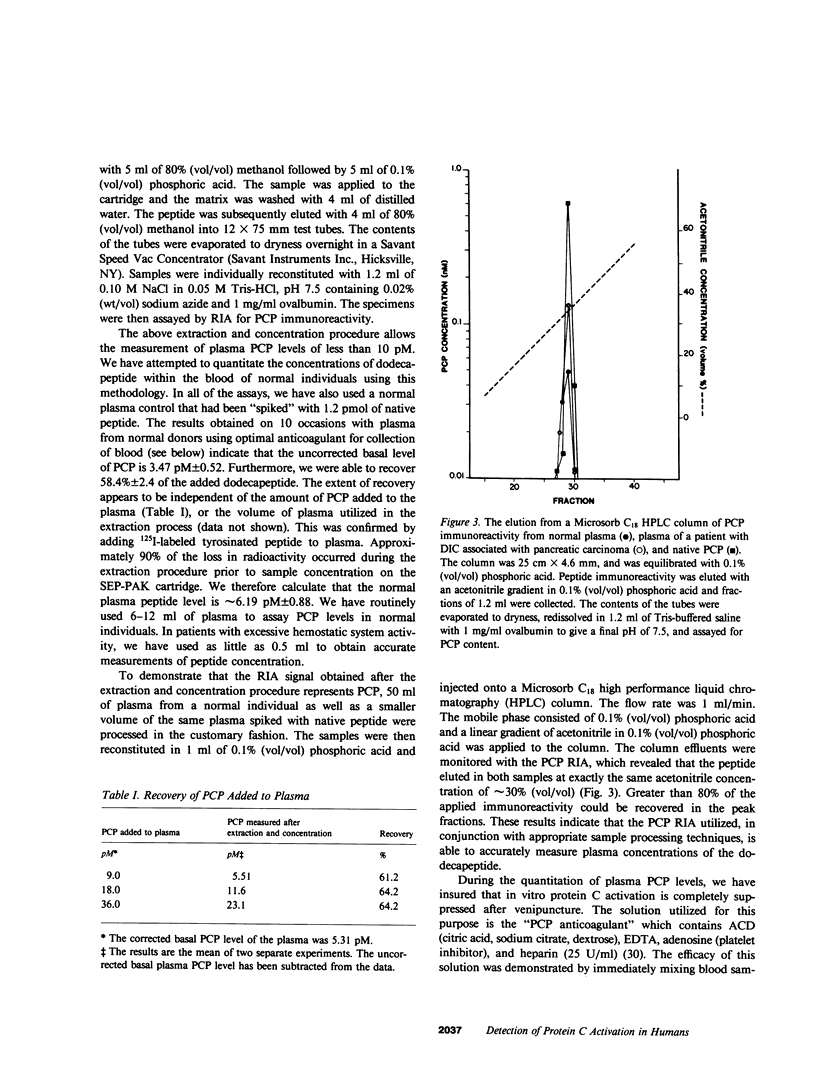
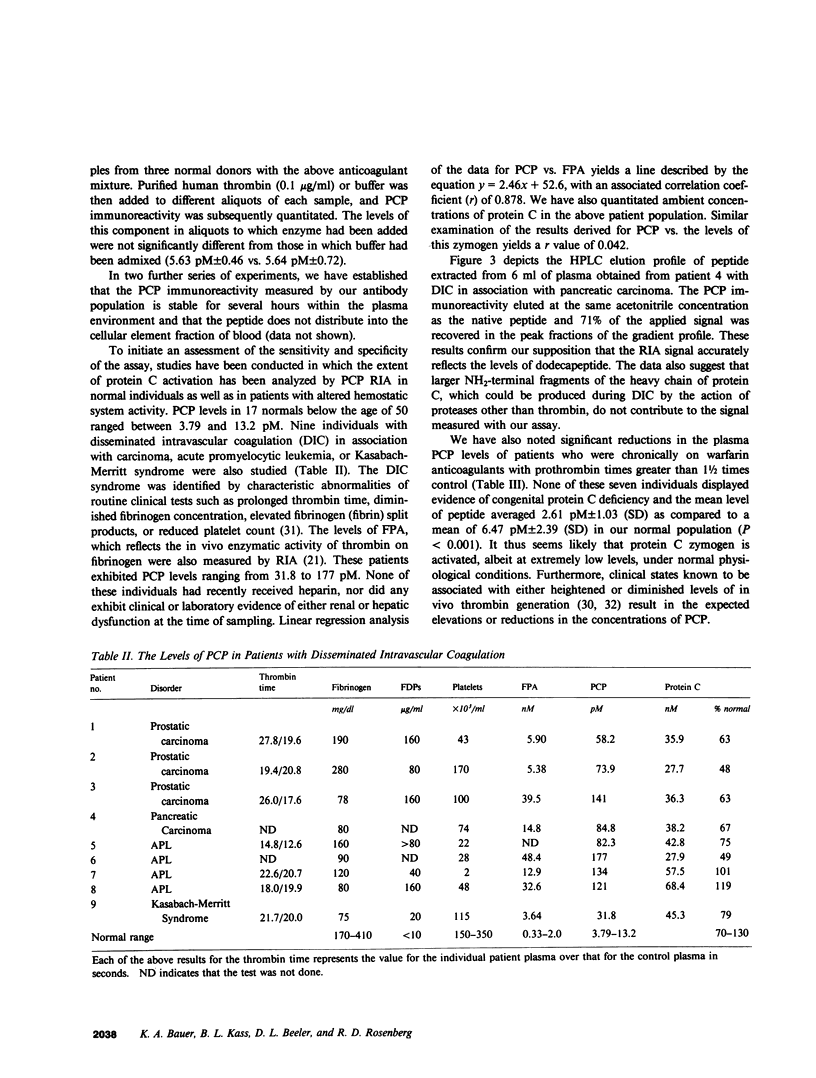
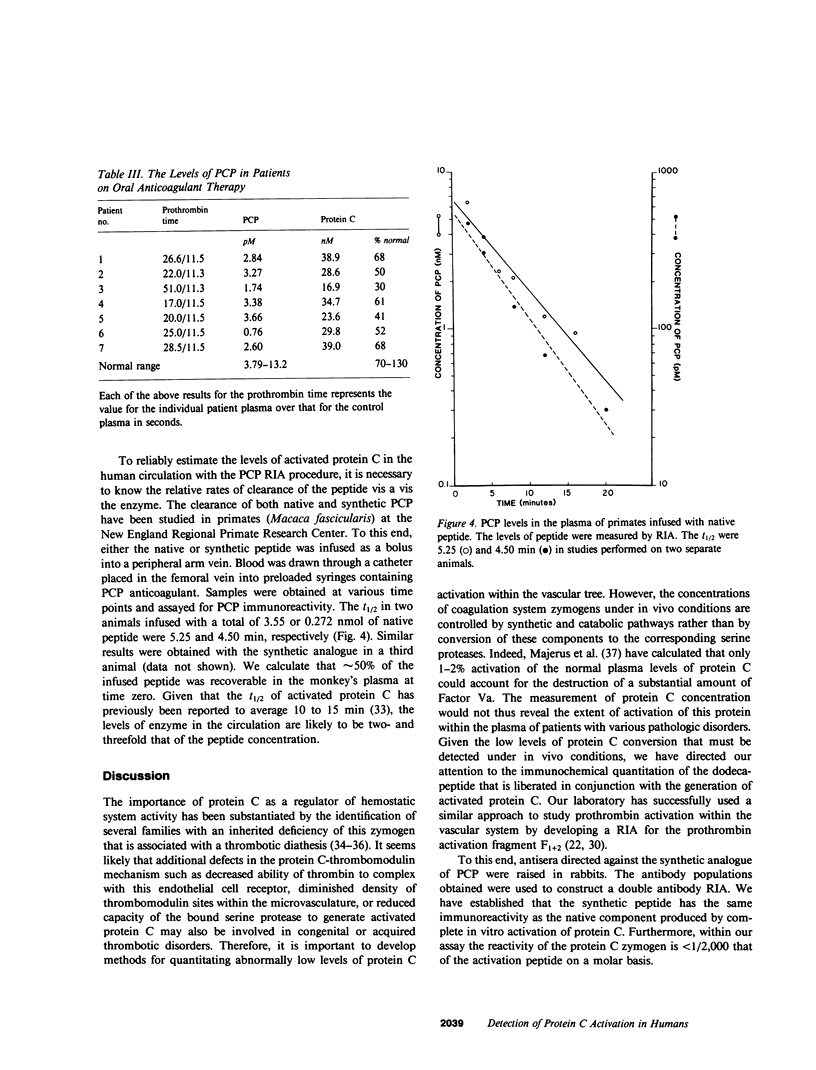
We have developed a radioimmunoassay (RIA) for the dodecapeptide that is liberated from protein C when this zymogen is activated by thrombin bound to thrombomodulin present on the vascular endothelium. The protein C activation peptide (PCP) was synthesized using the solid-phase method of Merrifield. Antisera were raised in rabbits to the synthetic analogue coupled to bovine serum albumin with glutaraldehyde. The antibody population obtained was used together with a 125I-labeled tyrosinated ligand and various concentrations of unlabeled PCP to construct a double antibody RIA capable of measuring as little as 10 pM of this component. We have established that the synthetic dodecapeptide has the same immunoreactivity as the native peptide and that the reactivity of protein C is less than 1/2,000 that of PCP on a molar basis. The extremely low levels of peptide in normal individuals as well as the nonspecific contributions of plasma constituents to the immunoreactive signal, necessitated the development of a procedure by which the PCP could be reproducibly extracted from plasma and concentrated approximately 20-fold. This methodology permitted us to demonstrate that the plasma PCP levels in 17 normal donors averaged 6.47 pM, and that elevations up to 180 pM were observed in individuals with evidence of disseminated intravascular coagulation. The validity of these measurements of protein C activation is supported by the fact that, in both of these situations, the RIA signal migrates on reverse-phase high pressure liquid chromatography in a manner identical to that of the native dodecapeptide. We have also noted that the mean PCP concentration in seven patients fully anticoagulated with warfarin averaged 2.61 pM. Our studies also show that PCP is cleared from the plasma of primates with a t1/2 of approximately 5 min. Given that the t1/2 of activated protein C is estimated to be 10-15 min, the latter enzyme appears to exert its effects on the activated cofactors of the coagulation system at concentrations considerably less than 1.0 nM.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Björk I., Nordenman B. Acceleration of the reaction between thrombin and antithrombin III by non-stoichiometric amounts of heparin. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Sep 15;68(2):507–511. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10838.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broekmans A. W., Veltkamp J. J., Bertina R. M. Congenital protein C deficiency and venous thromboembolism. A study of three Dutch families. N Engl J Med. 1983 Aug 11;309(6):340–344. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198308113090604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comp P. C., Esmon C. T. Activated protein C inhibits platelet prothrombin-converting activity. Blood. 1979 Dec;54(6):1272–1281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comp P. C., Jacocks R. M., Ferrell G. L., Esmon C. T. Activation of protein C in vivo. J Clin Invest. 1982 Jul;70(1):127–134. doi: 10.1172/JCI110584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damus P. S., Rosenberg R. D. Antithrombin-heparin cofactor. Methods Enzymol. 1976;45:653–669. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(76)45056-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon C. T., Owen W. G. Identification of an endothelial cell cofactor for thrombin-catalyzed activation of protein C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2249–2252. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOODFRIEND T. L., LEVINE L., FASMAN G. D. ANTIBODIES TO BRADYKININ AND ANGIOTENSIN: A USE OF CARBODIIMIDES IN IMMUNOLOGY. Science. 1964 Jun 12;144(3624):1344–1346. doi: 10.1126/science.144.3624.1344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin J. H., Evatt B., Zimmerman T. S., Kleiss A. J., Wideman C. Deficiency of protein C in congenital thrombotic disease. J Clin Invest. 1981 Nov;68(5):1370–1373. doi: 10.1172/JCI110385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin J. H., Mosher D. F., Zimmerman T. S., Kleiss A. J. Protein C, an antithrombotic protein, is reduced in hospitalized patients with intravascular coagulation. Blood. 1982 Jul;60(1):261–264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hruby V. J., Muscio F., Gronginsky C. M., Gitu P. M., Saba D., Chan W. Y. Solid-phase synthesis of (2-isoleucine, 4-leucine) oxytocin and (2-phenylalanine, 4-leucine) oxytocin and some their pharmacological properties. J Med Chem. 1973 Jun;16(6):624–629. doi: 10.1021/jm00264a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kisiel W., Canfield W. M., Ericsson L. H., Davie E. W. Anticoagulant properties of bovine plasma protein C following activation by thrombin. Biochemistry. 1977 Dec 27;16(26):5824–5831. doi: 10.1021/bi00645a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kisiel W. Human plasma protein C: isolation, characterization, and mechanism of activation by alpha-thrombin. J Clin Invest. 1979 Sep;64(3):761–769. doi: 10.1172/JCI109521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau H. K., Rosenberg J. S., Beeler D. L., Rosenberg R. D. The isolation and characterization of a specific antibody population directed against the prothrombin activation fragments F2 and F1 + 2. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):8751–8761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau H. K., Rosenberg R. D. The isolation and characterization of a specific antibody population directed against the thrombin antithrombin complex. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 25;255(12):5885–5893. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannucci P. M., Vigano S. Deficiencies of protein C, an inhibitor of blood coagulation. Lancet. 1982 Aug 28;2(8296):463–467. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)90494-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrifield R. B. Solid-phase peptide synthesis. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1969;32:221–296. doi: 10.1002/9780470122778.ch6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merskey C., Johnson A. J., Kleiner G. J., Wohl H. The defibrination syndrome: clinical features and laboratory diagnosis. Br J Haematol. 1967 Jul;13(4):528–549. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1967.tb00762.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myrmel K. H., Lundblad R. L., Mann K. G. Characteristics of the association between prothrombin fragment 2 and alpha-thrombin. Biochemistry. 1976 Apr 20;15(8):1767–1773. doi: 10.1021/bi00653a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossel H. L., Yudelman I., Canfield R. E., Butler V. P., Jr, Spanondis K., Wilner G. D., Qureshi G. D. Measurement of fibrinopeptide A in human blood. J Clin Invest. 1974 Jul;54(1):43–53. doi: 10.1172/JCI107749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen W. G., Esmon C. T. Functional properties of an endothelial cell cofactor for thrombin-catalyzed activation of protein C. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 10;256(11):5532–5535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepper D. S., Prowse C. Chromatography of human prothrombin complex or dextran sulphate agarose. Thromb Res. 1977 Nov;11(5):687–692. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(77)90026-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plow E. F., Edgington T. S. A cleavage-associated neoantigenic marker for a gamma chain site in the NH2-terminal aspect of the fibrinogen molecule. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 10;250(9):3386–3392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbard D., Lenox R. H., Wray H. L., Ramseth D. Statistical characterization of the random errors in the radioimmunoassay dose--response variable. Clin Chem. 1976 Mar;22(3):350–358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbard D. Statistical quality control and routine data processing for radioimmunoassays and immunoradiometric assays. Clin Chem. 1974 Oct;20(10):1255–1270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg J. S., Beeler D. L., Rosenberg R. D. Activation of human prothrombin by highly purified human factors V and X-a in presence of human antithrombin. J Biol Chem. 1975 Mar 10;250(5):1607–1617. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg R. D., Waugh D. F. Multiple bovine thrombin components. J Biol Chem. 1970 Oct 10;245(19):5049–5056. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salem H. H., Broze G. J., Miletich J. P., Majerus P. W. Human coagulation factor Va is a cofactor for the activation of protein C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(6):1584–1588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.6.1584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seligsohn U., Berger A., Abend M., Rubin L., Attias D., Zivelin A., Rapaport S. I. Homozygous protein C deficiency manifested by massive venous thrombosis in the newborn. N Engl J Med. 1984 Mar 1;310(9):559–562. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198403013100904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teitel J. M., Bauer K. A., Lau H. K., Rosenberg R. D. Studies of the prothrombin activation pathway utilizing radioimmunoassays for the F2/F1 + 2 fragment and thrombin--antithrombin complex. Blood. 1982 May;59(5):1086–1097. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vehar G. A., Davie E. W. Preparation and properties of bovine factor VIII (antihemophilic factor). Biochemistry. 1980 Feb 5;19(3):401–410. doi: 10.1021/bi00544a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viganò S., Mannucci P. M., Solinas S., Bottasso B., Mariani G. Decrease in protein C antigen and formation of an abnormal protein soon after starting oral anticoagulant therapy. Br J Haematol. 1984 Jun;57(2):213–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



