Abstract
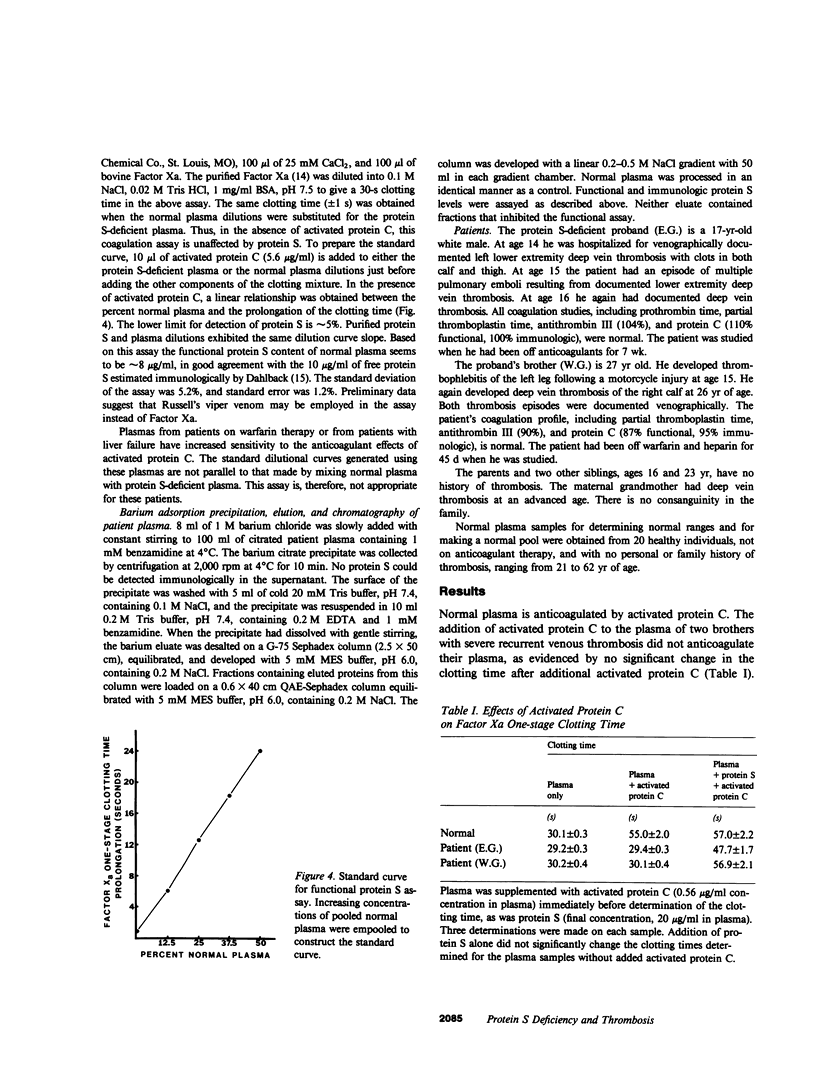
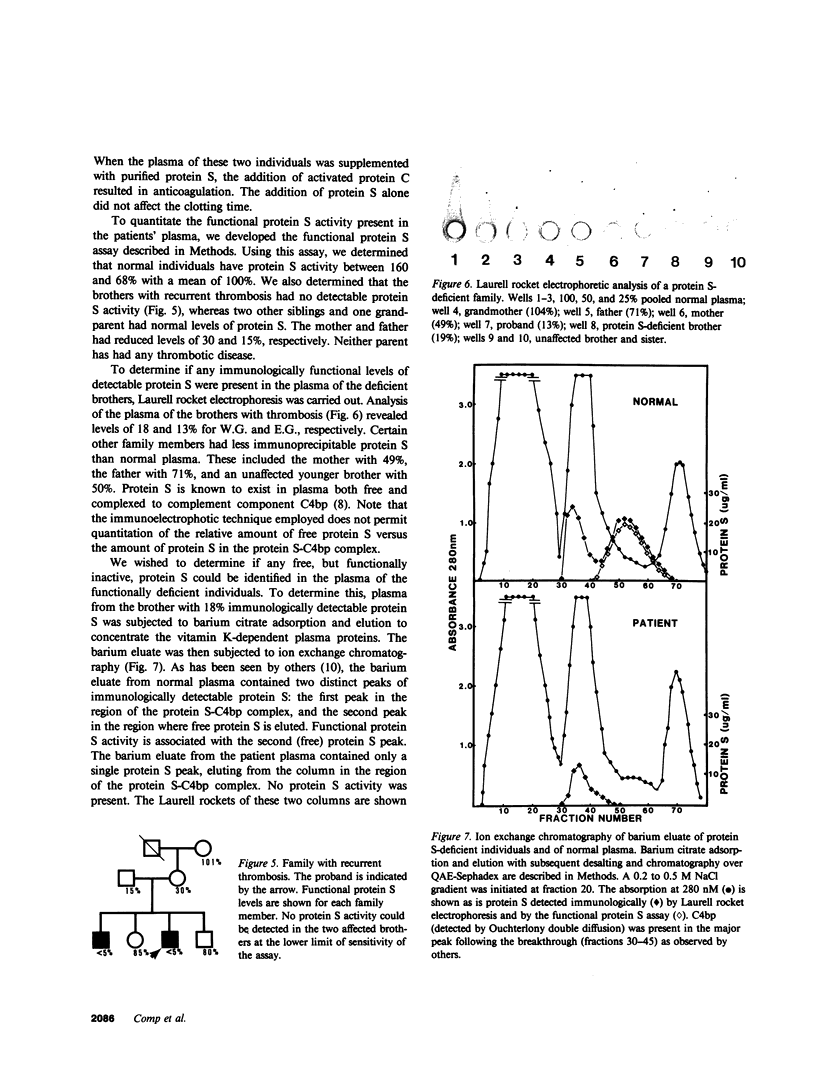
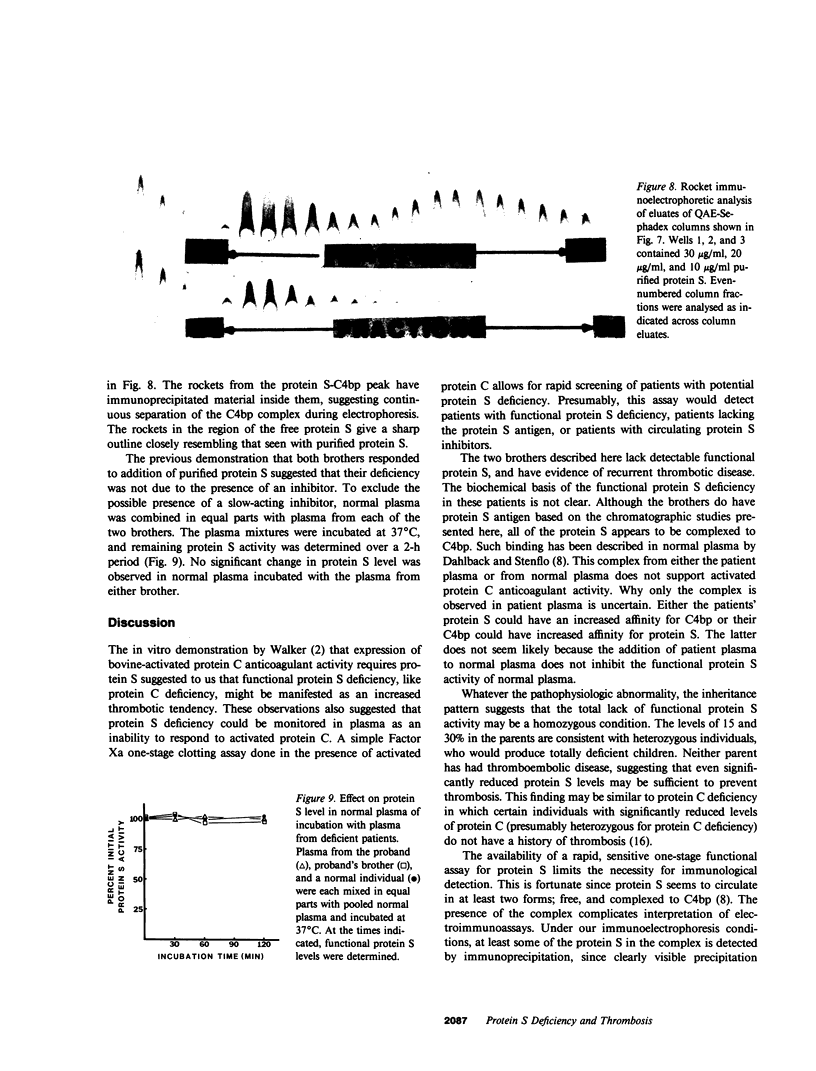
Recent studies have demonstrated that protein C deficiency is associated with recurrent familial thrombosis. In plasma, activated protein C functions as an anticoagulant. This anticoagulant response requires a vitamin K-dependent plasma protein cofactor, referred to as protein S. Since the anticoagulant activity of activated protein C is dependent on protein S, we hypothesized that patients lacking functional protein S might have associated thrombotic disease. Two related individuals with otherwise normal coagulation tests are described whose plasma is not effectively anticoagulated with activated protein C. Addition of purified human protein S to their plasma restores a normal anticoagulant response to activated protein C. We have developed a rapid one-stage clotting assay for protein S to quantitate the level of protein S in their plasma. Plasma is depleted of protein S by immunoadsorption with immobilized antiprotein S antibodies. The resultant plasma responds poorly to activated protein C, but is effectively anticoagulated in a dose-dependent fashion upon addition of purified protein S or small quantities of plasma. The affected individuals possess less than 5% protein S activity. Using Laurell rockets, protein S antigen was detected in the plasma but was at reduced levels of 13 and 18% in the two individuals. When the barium eluate of the patient plasma was chromatographed on quaternary aminoethyl Sephadex, a single peak of protein S antigen devoid of protein S anticoagulant cofactor activity was detected early in the chromatogram. In contrast, the barium eluate from normal donors separated into two peaks, one emerging early and also devoid of anticoagulant cofactor, and the second peak with anticoagulant activity emerging later. The first peak of protein S antigen, from both the normal donor and the patient, chromatographed in the region of the complement component C4-binding protein-protein S complex. These studies suggest that protein S deficiency may result in recurrent thrombotic disease.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aoki N., Moroi M., Sakata Y., Yoshida N., Matsuda M. Abnormal plasminogen. A hereditary molecular abnormality found in a patient with recurrent thrombosis. J Clin Invest. 1978 May;61(5):1186–1195. doi: 10.1172/JCI109034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BACHMANN F., DUCKERT F., KOLLER F. The Stuart-Prower factor assay and its clinical significance. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1958 May 1;2(1-2):24–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertina R. M., Broekmans A. W., van der Linden I. K., Mertens K. Protein C deficiency in a Dutch family with thrombotic disease. Thromb Haemost. 1982 Aug 24;48(1):1–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branson H. E., Katz J., Marble R., Griffin J. H. Inherited protein C deficiency and coumarin-responsive chronic relapsing purpura fulminans in a newborn infant. Lancet. 1983 Nov 19;2(8360):1165–1168. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91216-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comp P. C., Nixon R. R., Esmon C. T. Determination of functional levels of protein C, an antithrombotic protein, using thrombin-thrombomodulin complex. Blood. 1984 Jan;63(1):15–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlbäck B., Hildebrand B. Degradation of human complement component C4b in the presence of the C4b-binding protein-protein S complex. Biochem J. 1983 Mar 1;209(3):857–863. doi: 10.1042/bj2090857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlbäck B. Purification of human C4b-binding protein and formation of its complex with vitamin K-dependent protein S. Biochem J. 1983 Mar 1;209(3):847–856. doi: 10.1042/bj2090847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlbäck B. Purification of human vitamin K-dependent protein S and its limited proteolysis by thrombin. Biochem J. 1983 Mar 1;209(3):837–846. doi: 10.1042/bj2090837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlbäck B., Stenflo J. High molecular weight complex in human plasma between vitamin K-dependent protein S and complement component C4b-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2512–2516. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Scipio R. G., Hermodson M. A., Yates S. G., Davie E. W. A comparison of human prothrombin, factor IX (Christmas factor), factor X (Stuart factor), and protein S. Biochemistry. 1977 Feb 22;16(4):698–706. doi: 10.1021/bi00623a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EGEBERG O. INHERITED ANTITHROMBIN DEFICIENCY CAUSING THROMBOPHILIA. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1965 Jun 15;13:516–530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon C. T., Grant G. A., Suttie J. W. Purification of an apparent rat liver prothrombin precursor: characterization and comparison to normal rat prothrombin. Biochemistry. 1975 Apr 22;14(8):1595–1600. doi: 10.1021/bi00679a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon C. T. The subunit structure of thrombin-activated factor V. Isolation of activated factor V, separation of subunits, and reconstitution of biological activity. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 10;254(3):964–973. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin J. H., Evatt B., Zimmerman T. S., Kleiss A. J., Wideman C. Deficiency of protein C in congenital thrombotic disease. J Clin Invest. 1981 Nov;68(5):1370–1373. doi: 10.1172/JCI110385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seligsohn U., Berger A., Abend M., Rubin L., Attias D., Zivelin A., Rapaport S. I. Homozygous protein C deficiency manifested by massive venous thrombosis in the newborn. N Engl J Med. 1984 Mar 1;310(9):559–562. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198403013100904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skogen W. F., Esmon C. T., Cox A. C. Comparison of coagulation factor Xa and des-(1-44)factor Xa in the assembly of prothrombinase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2306–2310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki K., Nishioka J., Hashimoto S. Regulation of activated protein C by thrombin-modified protein S. J Biochem. 1983 Sep;94(3):699–705. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker F. J. Regulation of activated protein C by a new protein. A possible function for bovine protein S. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 25;255(12):5521–5524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker F. J. Regulation of activated protein C by protein S. The role of phospholipid in factor Va inactivation. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):11128–11131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]