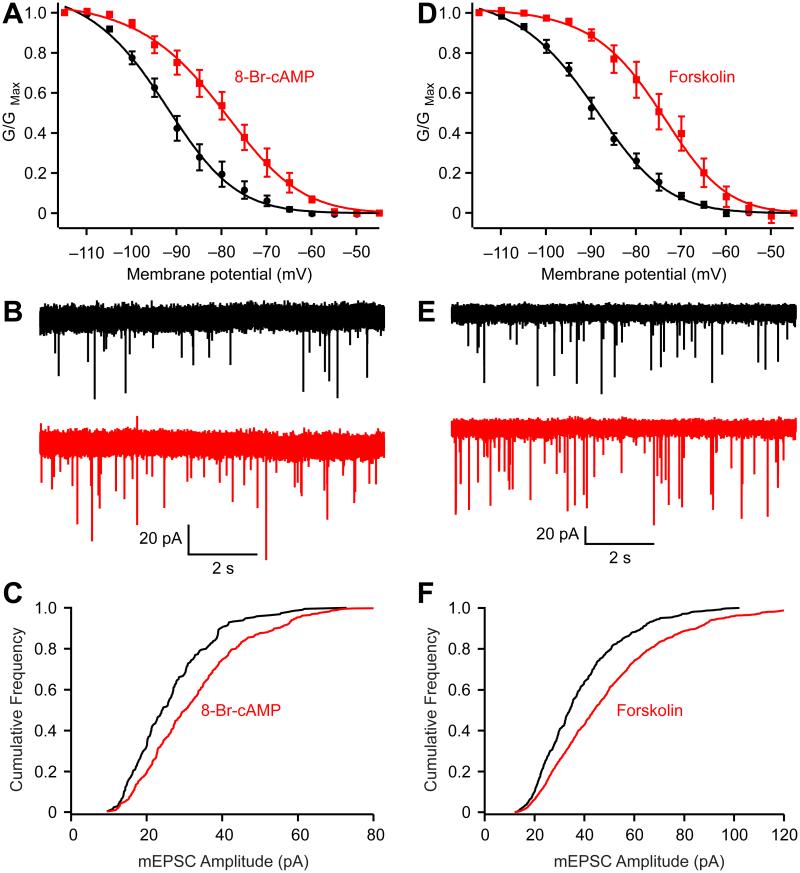
Figure 4.
Enhancing presynaptic HCN channel activation increases mEPSC amplitude. (A) 8-Br-cAMP (200-500 μM) right-shifted the activation curve of HCN channels (Control: Vhalf = −93.3 ± 0.7 mV and slope = 11.1 ± 0.6 mV; 8-Br-cAMP: Vhalf = −80.5 ± 0.5 and slope = 8.7 ± 0.4 mV. n = 5). (B-C) 8-Br-cAMP increased the mEPSC amplitudes (B) and right-shifted the cumulative probability histograms (C). (D-F) Forskolin (20 μM) also right-shifted the activation curve (Control: Vhalf of = −90.0 ± 0.5 mV and slope = 11.5 ± 0.4 mV; Forskolin Vhalf = −74.9 ± 0.5 mV and slope of 9.9 ± 0.5 mV. n = 5), increased the mEPSC amplitudes (E) and right-shifted the cumulative probability histogram (F). The voltage dependence of HCN activation was measured from HCN tail currents (TTX and XE991 were added to block Na+ and KCNQ currents, respectively). Error bars, ± S.E.M.