Abstract
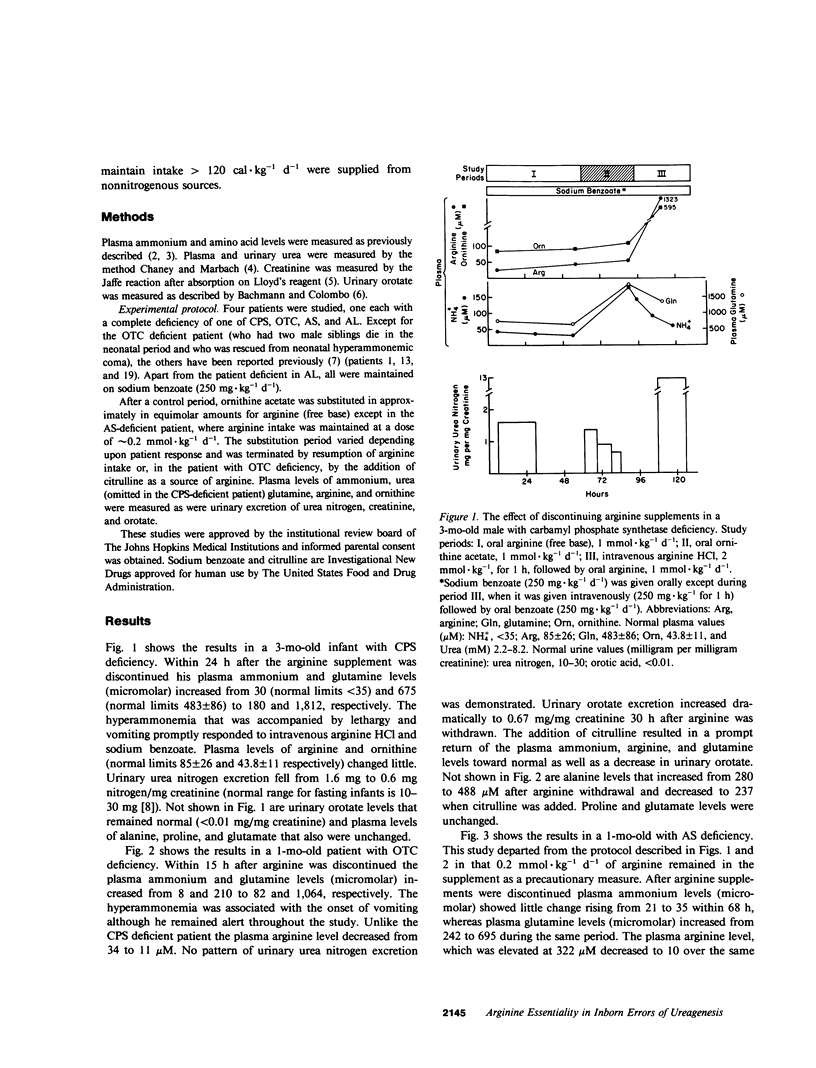
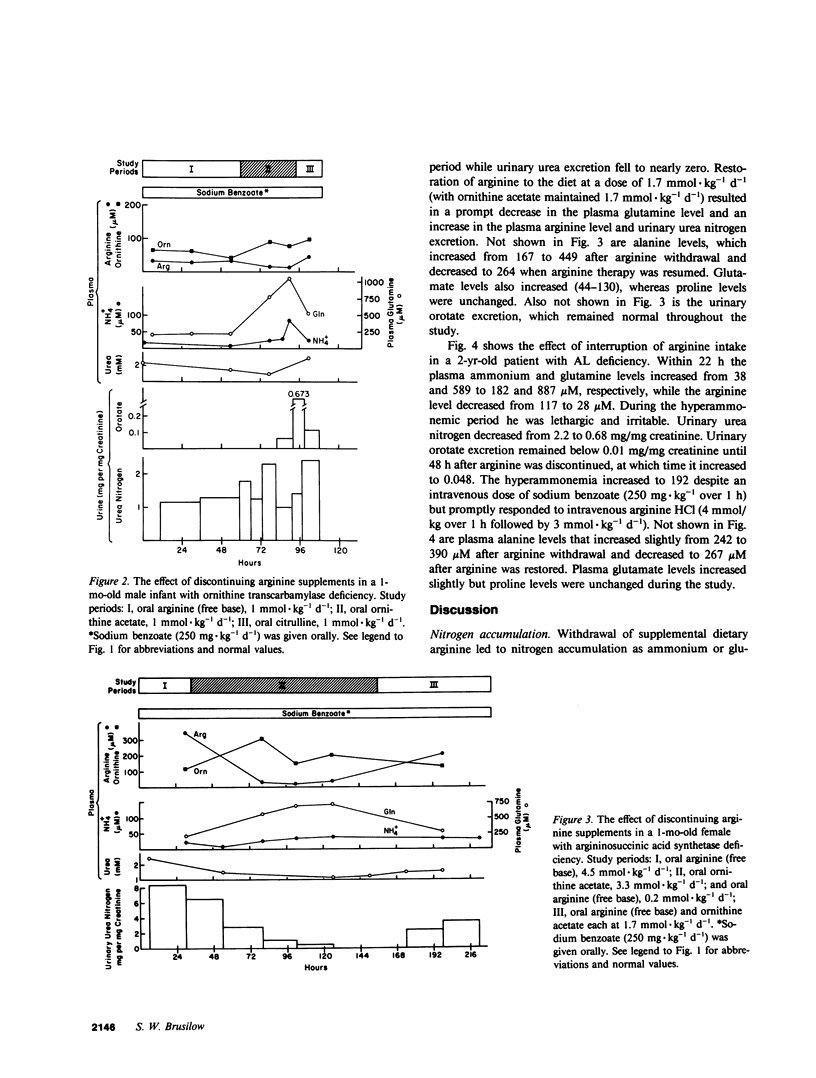
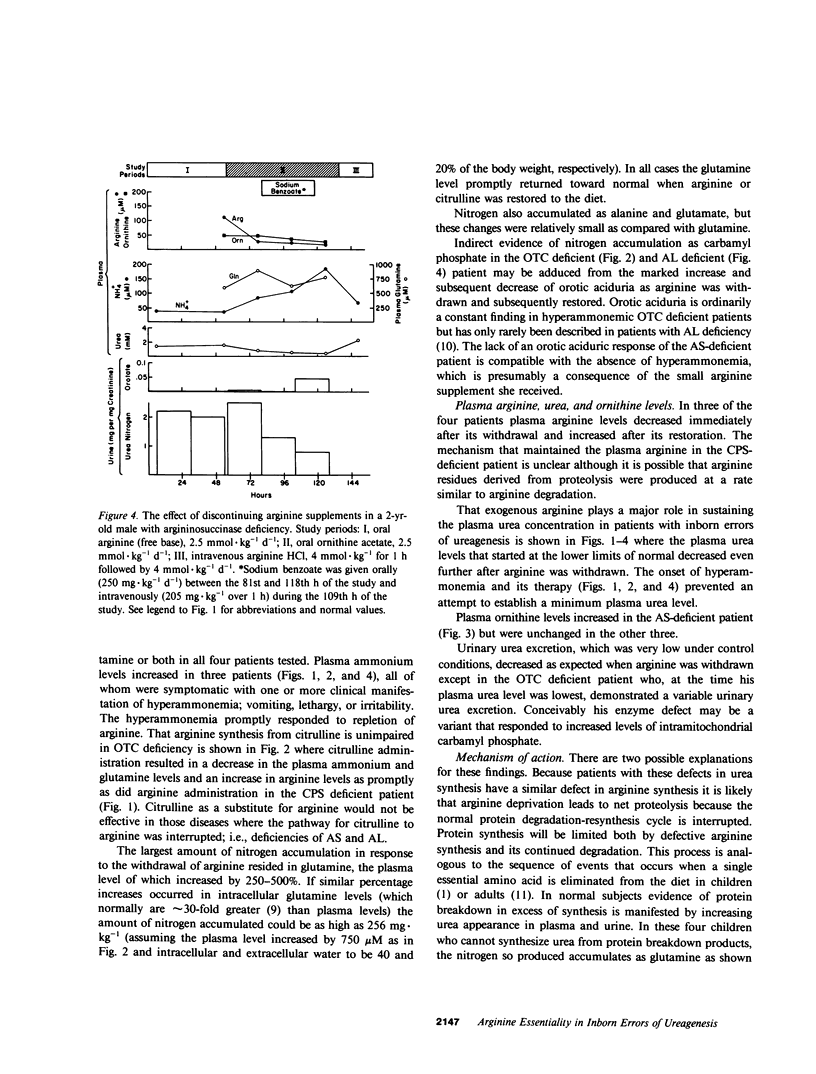
The role of arginine as an essential amino was evaluated in four children with one of the deficiencies of carbamyl phosphate synthetase, ornithine transcarbamylase, argininosuccinate synthetase, and argininosuccinase. Within 15-68 h after arginine deprivation nitrogen accumulated as ammonium or glutamine or both, but glutamine was quantitatively the largest nitrogen accumulation product. Concomitantly plasma and urinary urea levels decreased. Resumption of arginine intake (or citrulline in the case of ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency) promptly led to correction of the hyperammonemia, hyperglutaminemia and hypoargininemia. Ornithine was an unsatisfactory substitute for arginine. Arginine deprivation did not interfere with carbamyl phosphate synthesis as manifested by orotic aciduria. It is concluded that arginine is an indispensable amino acid for children with inborn errors of ureagenesis and its absence results in the rapid onset of symptomatic hyperammonemia.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachmann C., Colombo J. P. Determination of orotic acid in children's urine. J Clin Chem Clin Biochem. 1980 May;18(5):293–295. doi: 10.1515/cclm.1980.18.5.293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann C., Colombo J. P. Diagnostic value of orotic acid excretion in heritable disorders of the urea cycle and in hyperammonemia due to organic acidurias. Eur J Pediatr. 1980 Aug;134(2):109–113. doi: 10.1007/BF01846026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batshaw M. L., Brusilow S., Waber L., Blom W., Brubakk A. M., Burton B. K., Cann H. M., Kerr D., Mamunes P., Matalon R. Treatment of inborn errors of urea synthesis: activation of alternative pathways of waste nitrogen synthesis and excretion. N Engl J Med. 1982 Jun 10;306(23):1387–1392. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198206103062303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergström J., Fürst P., Norée L. O., Vinnars E. Intracellular free amino acid concentration in human muscle tissue. J Appl Physiol. 1974 Jun;36(6):693–697. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1974.36.6.693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brusilow S. W., Batshaw M. L., Waber L. Neonatal hyperammonemic coma. Adv Pediatr. 1982;29:69–103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brusilow S., Tinker J., Batshaw M. L. Amino acid acylation: a mechanism of nitrogen excretion in inborn errors of urea synthesis. Science. 1980 Feb 8;207(4431):659–661. doi: 10.1126/science.6243418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANEY A. L., MARBACH E. P. Modified reagents for determination of urea and ammonia. Clin Chem. 1962 Apr;8:130–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUGDALE A. E., EDKINS E. URINARY UREA/CREATININE RATIO IN HEALTHY AND MALNOURISHED CHILDREN. Lancet. 1964 May 16;1(7342):1062–1064. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)91266-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAKAGAWA I., TAKAHASHI T., SUZUKI T., KOBAYASHI K. Amino acid requirements of children: minimal needs of tryptophan, arginine and histidine based on nitrogen balance method. J Nutr. 1963 Jul;80:305–310. doi: 10.1093/jn/80.3.305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shigesada K., Aoyagi K., Tatibana M. Role of acetylglutamate in ureotelism. Variations in acetylglutamate level and its possible significance in control of urea synthesis in mammalian liver. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Apr 17;85(2):385–391. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12250.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



