Abstract
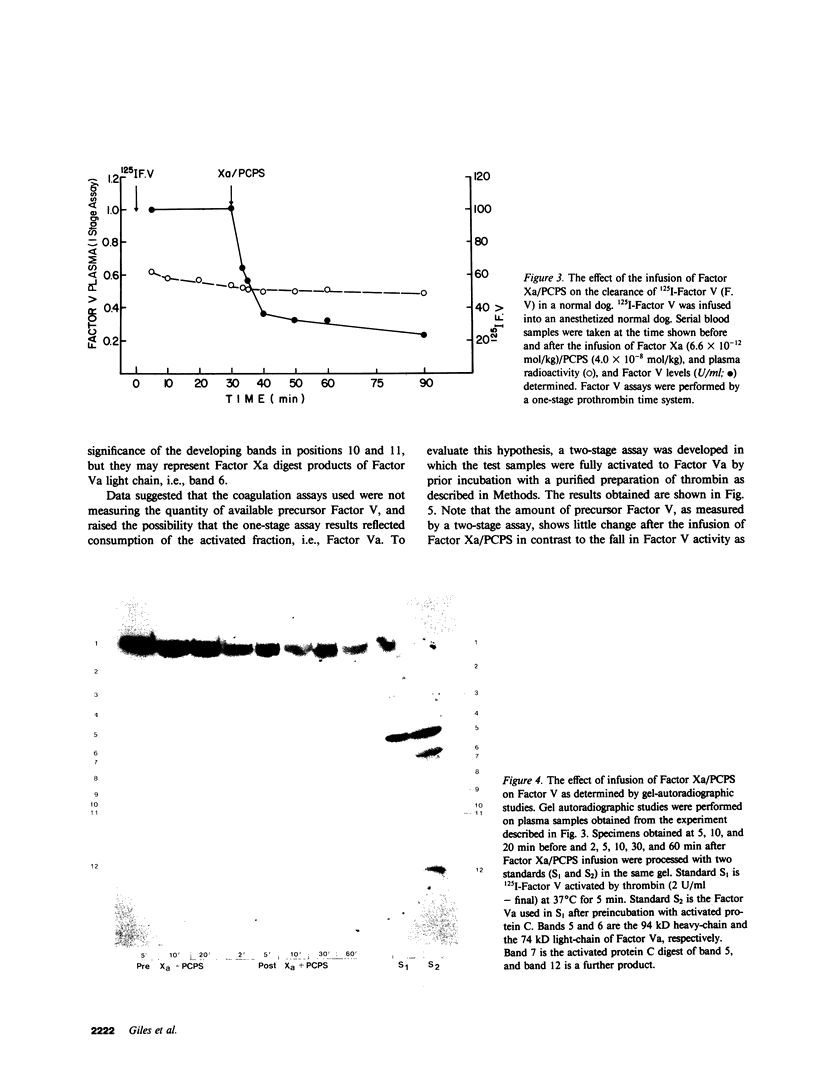
An experimental animal model of disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) induced by the co-infusion of coagulant-active phospholipid and activated Factor X (Factor Xa) is described. The infusion of Factor Xa at a dose of 6.6 X 10(-12) mol/kg with phosphatidylcholine/phosphatidylserine (PCPS) lipid vesicles at a dose of 4.0 X 10(-8) mol/kg was associated with significant falls in the levels of fibrinogen and Factors V and VIII, and a bleeding diathesis developed. Assays of Factors V and VIII were performed by a one-stage prothrombin time and activated partial thrombin time system, respectively. In additional experiments, the effect of the same dose combination of Factor Xa/PCPS on Factor V kinetics was studied by preinfusing 125I-labeled Factor V. After Factor Xa/PCPS infusion, Factors VIII and V were reduced at 2 min by 90 and 50% of the preinfusion levels, respectively, and at 1 h by 80 and 75%, respectively. During the same period, there was little change in the total circulating radioactivity. Autoradiography indicated small but detectable levels of circulating proteolytic products of Factor V that comigrated with peptides obtained by the incubation of Factor V with Factor Xa and activated protein C. The majority of radioactivity remained associated with the intact single-chain precursor Factor V. These observations suggested maintenance of the precursor pool after the onset of DIC. This was confirmed by performing two-stage assays of Factors V and VIII, whereby each was completely converted to the active cofactor, i.e., Va and VIII:Ca, by preincubation of the test sample with thrombin before assaying in a one-stage system as before. The Factor V levels assayed by the two-stage procedure did not change appreciably over 1 h. The Factor VIII levels fell but corrected within 1 h at a time when the level measured by a one-stage assay remained depressed. These results indicate that in the dog, infusion of Factor Xa/PCPS induces changes characteristic of DIC, and this is associated with the appearance of Factor V peptides characteristic of the expression of Factor Xa and activated protein C-like activities. The differences noted between the one-stage and two-stage assays suggest that the one-stage assay is measuring the activated fraction of each cofactor and not the total level of the available precursor for each activated species. The results suggest a close correlation between the activated fraction of both cofactors and the hemostatic abnormality that occurs in DIC.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bajaj S. P., Mann K. G. Simultaneous purification of bovine prothrombin and factor X. Activation of prothrombin by trypsin-activated factor X. J Biol Chem. 1973 Nov 25;248(22):7729–7741. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatt P. M., Lundblad R. L., Kingdon H. S., McLean G., Roberts H. R. Thrombogenic materials in prothrombin complex concentrates. Ann Intern Med. 1974 Dec;81(6):766–770. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-81-6-766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton A. E., Hunter W. M. The labelling of proteins to high specific radioactivities by conjugation to a 125I-containing acylating agent. Biochem J. 1973 Jul;133(3):529–539. doi: 10.1042/bj1330529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLAUSS A. Gerinnungsphysiologische Schnellmethode zur Bestimmung des Fibrinogens. Acta Haematol. 1957 Apr;17(4):237–246. doi: 10.1159/000205234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canfield W. M., Kisiel W. Evidence of normal functional levels of activated protein C inhibitor in combined Factor V/VIII deficiency disease. J Clin Invest. 1982 Dec;70(6):1260–1272. doi: 10.1172/JCI110725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comp P. C., Esmon C. T. Generation of fibrinolytic activity by infusion of activated protein C into dogs. J Clin Invest. 1981 Nov;68(5):1221–1228. doi: 10.1172/JCI110368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comp P. C., Jacocks R. M., Ferrell G. L., Esmon C. T. Activation of protein C in vivo. J Clin Invest. 1982 Jul;70(1):127–134. doi: 10.1172/JCI110584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comp P. C., Jacocks R. M., Rubenstein C., Radcliffe R. A lysine-absorbable plasminogen activator is elevated in conditions associated with increased fibrinolytic activity. J Lab Clin Med. 1981 May;97(5):637–645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deykin D. The clinical challenge of disseminated intravascular coagulation. N Engl J Med. 1970 Sep 17;283(12):636–644. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197009172831207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downing M. R., Butkowski R. J., Clark M. M., Mann K. G. Human prothrombin activation. J Biol Chem. 1975 Dec 10;250(23):8897–8906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giles A. R., Nesheim M. E., Hoogendoorn H., Tracy P. B., Mann K. G. The coagulant-active phospholipid content is a major determinant of in vivo thrombogenicity of prothrombin complex (Factor IX) concentrates in rabbits. Blood. 1982 Feb;59(2):401–407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giles A. R., Tinlin S., Greenwood R. A canine model of hemophilic (factor VIII:C deficiency) bleeding. Blood. 1982 Sep;60(3):727–730. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasper C. K. Thromboembolic complications. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1975 Jun 30;33(3):640–644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kisiel W., Canfield W. M., Ericsson L. H., Davie E. W. Anticoagulant properties of bovine plasma protein C following activation by thrombin. Biochemistry. 1977 Dec 27;16(26):5824–5831. doi: 10.1021/bi00645a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundblad R. L., Uhteg L. C., Vogel C. N., Kingdon H. S., Mann K. G. Preparation and partial characterization of two forms of bovine thrombin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Sep 16;66(2):482–489. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90536-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesheim M. E., Katzmann J. A., Tracy P. B., Mann K. G. Factor V. Methods Enzymol. 1981;80(Pt 100):249–274. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)80023-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesheim M. E., Myrmel K. H., Hibbard L., Mann K. G. Isolation and characterization of single chain bovine factor V. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jan 25;254(2):508–517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesheim M. E., Taswell J. B., Mann K. G. The contribution of bovine Factor V and Factor Va to the activity of prothrombinase. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 10;254(21):10952–10962. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp A. A. Diagnosis and management of disseminated intravascular coagulation. Br Med Bull. 1977 Sep;33(3):265–272. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teien A. N., Lie M. Evaluation of an amidolytic heparin assay method: increased sensitivity by adding purified antithrombin III. Thromb Res. 1977 Mar;10(3):399–410. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(77)90150-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracy P. B., Nesheim M. E., Mann K. G. Proteolytic alterations of factor Va bound to platelets. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):662–669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker F. J., Sexton P. W., Esmon C. T. The inhibition of blood coagulation by activated Protein C through the selective inactivation of activated Factor V. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Dec 7;571(2):333–342. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(79)90103-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White G. C., 2nd, Roberts H. R., Kingdon H. S., Lundblad R. L. Prothrombin complex concentrates: potentially thrombogenic materials and clues to the mechanism of thrombosis in vivo. Blood. 1977 Feb;49(2):159–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



