Abstract
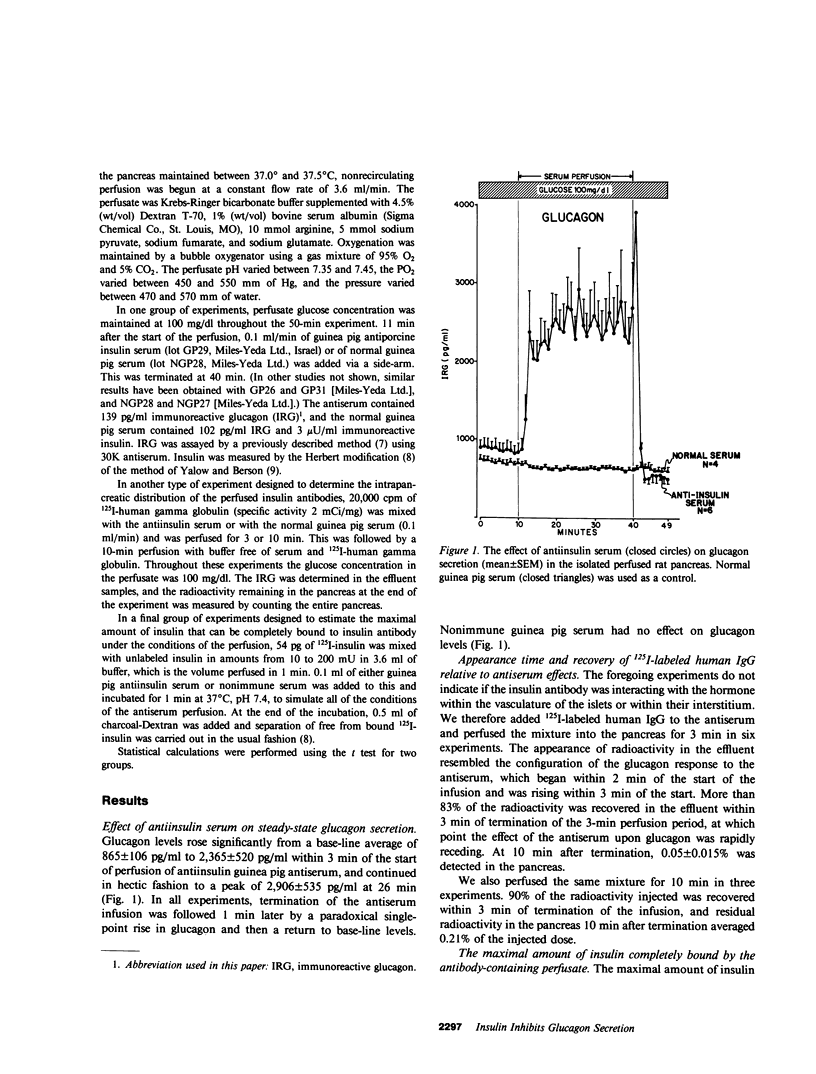
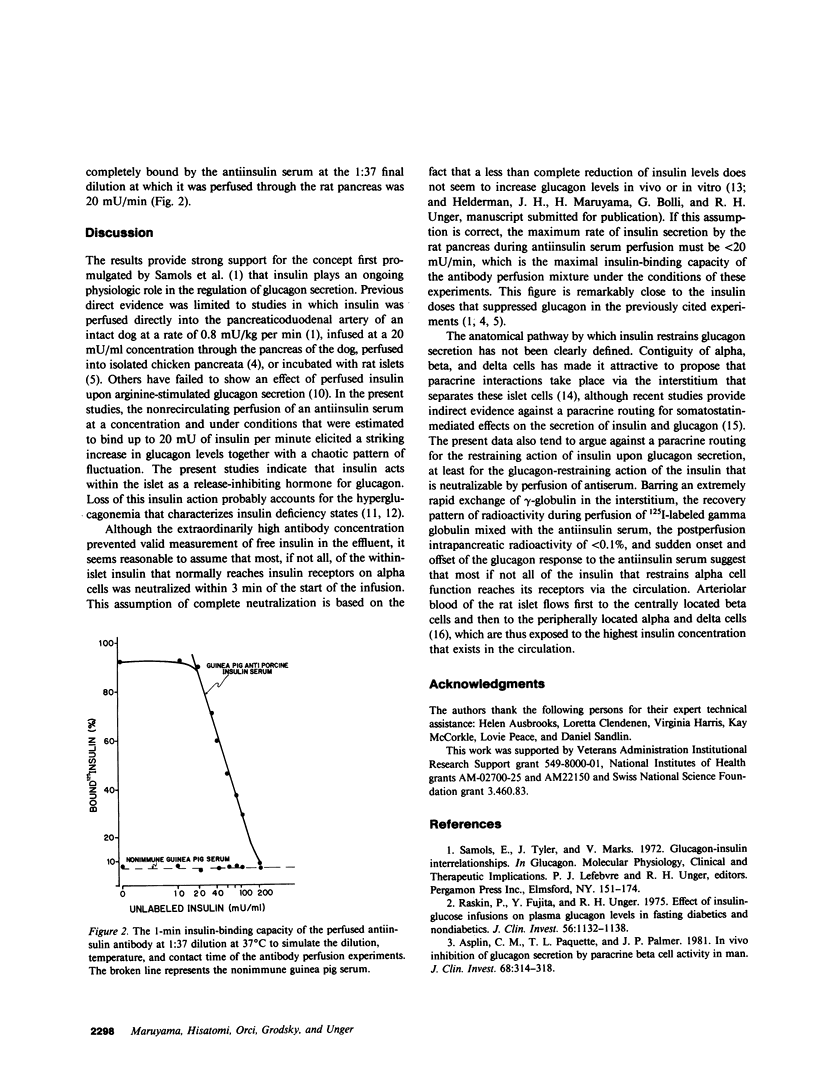
To determine if glucagon secretion is under physiological control of intra-islet insulin, pancreata from normal rats were perfused at a 100 mg/dl glucose concentration with either guinea pig antiinsulin serum or normal guinea pig serum in a nonrecirculating system. Perfusion of antiserum was followed within 3 min by a significant rise in glucagon that reached peak levels three times the base-line values and assumed a hectic pattern that returned rapidly to base-line levels upon termination of the antiserum perfusion. Nonimmune guinea pig serum had no effect. To gain insight into the probable site of insulin neutralization, 125I-labeled human gamma-globulin was added to antiserum or nonimmune serum and perfused for 3 min. More than 83% of the radioactivity was recovered in the effluent within 3 min after termination of the infusion, and only 0.05 +/- 0.015% of the radioactivity injected was present in the pancreas 10 min after the perfusion. The maximal amount of insulin that could be completely bound to insulin antibody at a dilution and under conditions simulating those of the perfusion experiments was 20 mU/min. It is concluded that insulin maintains an ongoing restraint upon alpha cell secretion and in its absence causes hectic hypersecretion of glucagon. This restraint probably occurs largely in the intravascular compartment. Loss of this release-inhibiting action of insulin may account for initiation of hyperglucagonemia in insulin-deficient states.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asplin C. M., Paquette T. L., Palmer J. P. In vivo inhibition of glucagon secretion by paracrine beta cell activity in man. J Clin Invest. 1981 Jul;68(1):314–318. doi: 10.1172/JCI110251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolli G., De Feo P., Perriello G., De Cosmo S., Compagnucci P., Santeusanio F., Brunetti P., Unger R. H. Mechanisms of glucagon secretion during insulin-induced hypoglycemia in man. Role of the beta cell and arterial hyperinsulinemia. J Clin Invest. 1984 Apr;73(4):917–922. doi: 10.1172/JCI111315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner-Weir S., Orci L. New perspectives on the microvasculature of the islets of Langerhans in the rat. Diabetes. 1982 Oct;31(10):883–889. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.10.883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan K. D., Mawhinney W. A. Insulin control of glucagon release from insulin-deficient rat islets. Diabetes. 1973 Nov;22(11):801–803. doi: 10.2337/diab.22.11.801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grodsky G. M., Epstein G. H., Fanska R., Karam J. H. Pancreatic action of the sulfonylureas. Fed Proc. 1977 Dec;36(13):2714–2719. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grodsky G. M., Fanska R. E. The in vitro perfused pancreas. Methods Enzymol. 1975;39:364–372. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(75)39033-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert V., Lau K. S., Gottlieb C. W., Bleicher S. J. Coated charcoal immunoassay of insulin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1965 Oct;25(10):1375–1384. doi: 10.1210/jcem-25-10-1375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honey R. N., Fallon M. B., Weir G. C. Effects of exogenous insulin, glucagon, and somatostatin on islet hormone secretion in the perfused chicken pancreas. Metabolism. 1980 Dec;29(12):1242–1246. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(80)90152-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai K., Ipp E., Orci L., Perrelet A., Unger R. H. Circulating somatostatin acts on the islets of Langerhans by way of a somatostatin-poor compartment. Science. 1982 Oct 29;218(4571):477–478. doi: 10.1126/science.6126931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller W. A., Faloona G. R., Unger R. H. The effect of experimental insulin deficiency on glucagon secretion. J Clin Invest. 1971 Sep;50(9):1992–1999. doi: 10.1172/JCI106691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raskin P., Fujita Y., Unger R. H. Effect of insulin-glucose infusions on plasma glucagon levels in fasting diabetics and nondiabetics. J Clin Invest. 1975 Nov;56(5):1132–1138. doi: 10.1172/JCI108188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger R. H., Aguilar-Parada E., Müller W. A., Eisentraut A. M. Studies of pancreatic alpha cell function in normal and diabetic subjects. J Clin Invest. 1970 Apr;49(4):837–848. doi: 10.1172/JCI106297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger R. H., Orci L. Possible roles of the pancreatic D-cell in the normal and diabetic states. Diabetes. 1977 Mar;26(3):241–244. doi: 10.2337/diab.26.3.241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YALOW R. S., BERSON S. A. Immunoassay of endogenous plasma insulin in man. J Clin Invest. 1960 Jul;39:1157–1175. doi: 10.1172/JCI104130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


