Abstract
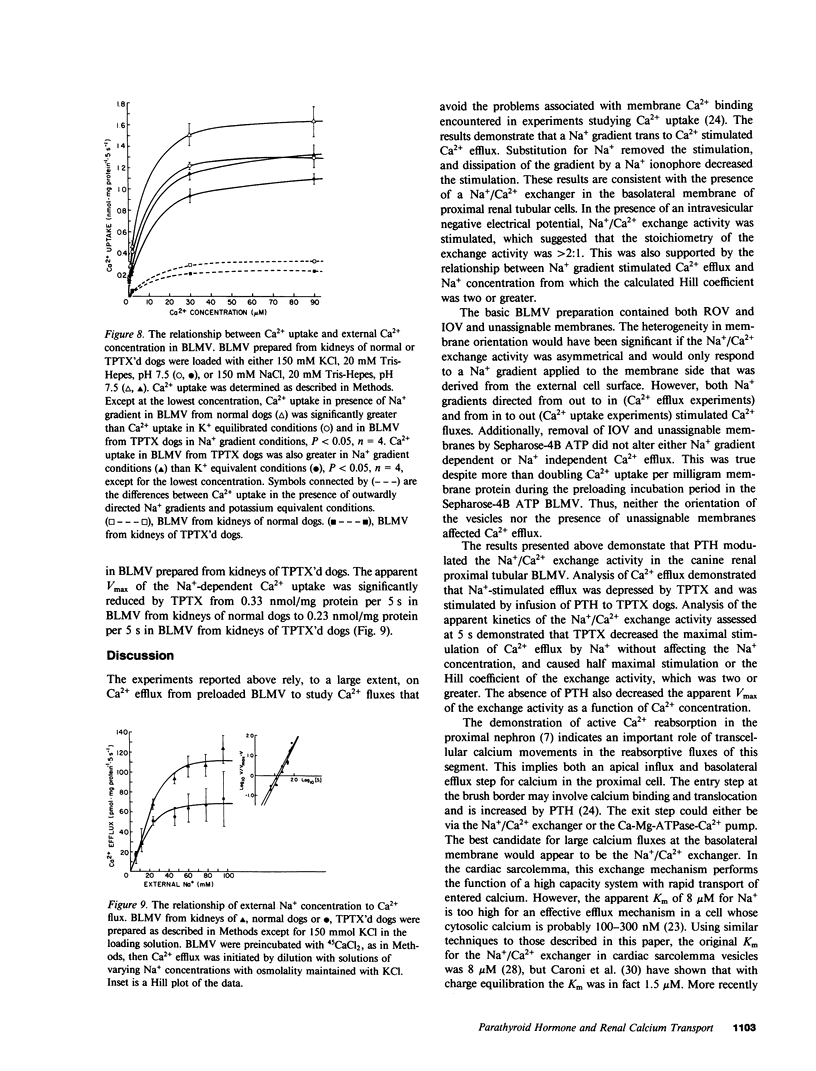
The effects of parathyroid hormone were studied on Ca2+ fluxes in canine renal proximal tubular basolateral membrane vesicles (BLMV). Efflux of Ca2+ from preloaded BLMV was found to be stimulated by an external Na+ gradient, and this was inhibited by the Na+ ionophore, monensin, and enhanced by intravesicular negative electrical potentials, which indicated electrogenic Na+/Ca2+ exchange activity. There was a Na+ gradient independent Ca2+ flux, but membrane binding of Ca2+ was excluded from contributing to the Na+ gradient-dependent efflux. The Na+ gradient-dependent flux of Ca2+ was very rapid, and even 2- and 5-s points may not fully represent absolute initial rates. It was saturable with respect to the interaction of Ca2+ and Na+ with an apparent (5 s) Km for Na+-dependent Ca2+ uptake of 10 microM, and an apparent (5 s) Vmax of 0.33 nmol/mg protein per 5 s. The Na+ concentration that yielded half maximal Ca2+ efflux (2 s) was 11 mM, and the Hill coefficient was two or greater. Both Na+ gradient dependent and independent Ca2+ efflux were decreased in BLMV prepared from kidneys of thyroparathyroidectomized (TPTX) dogs, and both were stimulated by parathyroid hormone (PTH) infusion to TPTX dogs. BLMV from TPTX dogs exhibited significantly reduced maximal stimulation of Na+ gradient-dependent Ca2+ uptake with an apparent (5 s) Vmax of 0.23 nmol/mg protein per 5 s, but the apparent Km was 8 microM, which was unchanged from normal. The Na+ gradient independent Ca2+ uptake was also reduced in BLMV from TPTX dogs compared with normal. Thus, PTH stimulated both Na+/Ca2+ exchange activity and Na+ independent Ca2+ flux. In vivo, the latter could result in an elevation of cytosolic Ca2+ by PTH, and this might contribute to the observed decrease in solute transport in the proximal tubule.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agus Z. S., Gardner L. B., Beck L. H., Goldberg M. Effects of parathyroid hormone on renal tubular reabsorption of calcium, sodium, and phosphate. Am J Physiol. 1973 May;224(5):1143–1148. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.224.5.1143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell N. H., Avery S., Sinha T., Clark C. M., Jr, Allen D. O., Johnston C., Jr Effects of dibutyryl cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate and parathyroid extract on calcium and phosphorus metabolism in hypoparathyroidism and pseudohypoparathyroidism. J Clin Invest. 1972 Apr;51(4):816–823. doi: 10.1172/JCI106876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger S. J., Sacktor B. Isolation and biochemical characterization of brush borders from rabbit kidney. J Cell Biol. 1970 Dec;47(3):637–645. doi: 10.1083/jcb.47.3.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bers D. M. A simple method for the accurate determination of free [Ca] in Ca-EGTA solutions. Am J Physiol. 1982 May;242(5):C404–C408. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1982.242.5.C404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bomsztyk K., George J. P., Wright F. S. Effects of luminal fluid anions on calcium transport by proximal tubule. Am J Physiol. 1984 May;246(5 Pt 2):F600–F608. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1984.246.5.F600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnatowska M. A., Harris C. A., Sutton R. A., Dirks J. H. Effects of PTH and cAMP on renal handling of calcium, magnesium, and phosphate in the hamster. Am J Physiol. 1977 Dec;233(6):F514–F518. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1977.233.6.F514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caroni P., Carafoli E. The regulation of the Na+ -Ca2+ exchanger of heart sarcolemma. Eur J Biochem. 1983 May 16;132(3):451–460. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07383.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caroni P., Reinlib L., Carafoli E. Charge movements during the Na+-Ca2+ exchange in heart sarcolemmal vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6354–6358. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chase H. S., Jr, Al-Awqati Q. Calcium reduces the sodium permeability of luminal membrane vesicles from toad bladder. Studies using a fast-reaction apparatus. J Gen Physiol. 1983 May;81(5):643–665. doi: 10.1085/jgp.81.5.643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chase H. S., Jr, Al-Awqati Q. Regulation of the sodium permeability of the luminal border of toad bladder by intracellular sodium and calcium: role of sodium-calcium exchange in the basolateral membrane. J Gen Physiol. 1981 Jun;77(6):693–712. doi: 10.1085/jgp.77.6.693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis V. W., Bello-Reuss E., Robinson R. R. Response of phosphate transport to parathyroid hormone in segments of rabbit nephron. Am J Physiol. 1977 Jul;233(1):F29–F38. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1977.233.1.F29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duarte C. G., Watson J. F. Calcium reabsorption in proximal tubule of the dog nephron. Am J Physiol. 1967 Jun;212(6):1355–1360. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1967.212.6.1355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frick A., Rumrich G., Ullrich K. J., Lassiter W. E. Microperfusion study of calcium transport in the proximal tubule of the rat kidney. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1965 Oct 12;286(2):109–117. doi: 10.1007/BF00363855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gmaj P., Murer H., Kinne R. Calcium ion transport across plasma membranes isolated from rat kidney cortex. Biochem J. 1979 Mar 15;178(3):549–557. doi: 10.1042/bj1780549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUEBSCHER G., WEST G. R. SPECIFIC ASSAYS OF SOME PHOSPHATASES IN SUBCELLULAR FRACTIONS OF SMALL INTESTINAL MUCOSA. Nature. 1965 Feb 20;205:799–800. doi: 10.1038/205799a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammerman M. R., Karl I. E., Hruska K. A. Regulation of canine renal vesicle Pi transport by growth hormone and parathyroid hormone. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Dec 12;603(2):322–335. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90378-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris C. A., Burnatowska M. A., Seely J. F., Sutton R. A., Quamme G. A., Dirks J. H. Effects of parathyroid hormone on electrolyte transport in the hamster nephron. Am J Physiol. 1979 Apr;236(4):F342–F348. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1979.236.4.F342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaczorowski G. J., Costello L., Dethmers J., Trumble M. J., Vandlen R. L. Mechanisms of Ca2+ transport in plasma membrane vesicles prepared from cultured pituitary cells. I. Characterization of Na+/Ca2+ exchange activity. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 10;259(15):9395–9403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khalifa S., Mills S., Hruska K. A. Stimulation of calcium uptake by parathyroid hormone in renal brush-border membrane vesicles. Relationship to membrane phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14400–14406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuntziger H., Amiel C., Roinel N., Morel F. Effects of parathyroidectomy and cyclic AMP on renal transport of phosphate, calcium, and magnesium. Am J Physiol. 1974 Oct;227(4):905–911. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1974.227.4.905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorentz W. B. Effect of parathyroid hormone on renal tubular permeability. Am J Physiol. 1976 Nov;231(5 Pt 1):1401–1407. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.231.5.1401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. J., Smith G. L. EGTA purity and the buffering of calcium ions in physiological solutions. Am J Physiol. 1984 Jan;246(1 Pt 1):C160–C166. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1984.246.1.C160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morel F. Sites of hormone action in the mammalian nephron. Am J Physiol. 1981 Mar;240(3):F159–F164. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.240.3.F159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murayama Y., Morel F., Le Grimellec C. Phosphate, calcium and magnesium transfers in proximal tubules and loops of Henle, as measured by single nephron microperfusion experiments in the rat. Pflugers Arch. 1972;333(1):1–16. doi: 10.1007/BF00586037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitts B. J. Stoichiometry of sodium-calcium exchange in cardiac sarcolemmal vesicles. Coupling to the sodium pump. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 25;254(14):6232–6235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quigley J. P., Gotterer G. S. Distribution of (Na+-K+)-stimulated ATPase activity in rat intestinal mucosa. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Apr;173(3):456–468. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(69)90010-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves J. P., Sutko J. L. Sodium-calcium exchange activity generates a current in cardiac membrane vesicles. Science. 1980 Jun 27;208(4451):1461–1464. doi: 10.1126/science.7384788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacktor B., Rosenbloom I. L., Liang C. T., Cheng L. Sodium gradient- and sodium plus potassium gradient-dependent L-glutamate uptake in renal basolateral membrane vesicles. J Membr Biol. 1981 May 15;60(1):63–71. doi: 10.1007/BF01870833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scalera V., Huang Y. K., Hildmann B., Murer H. A simple isolation method for basal-lateral plasma membranes from rat kidney cortex. Membr Biochem. 1981;4(1):49–61. doi: 10.3109/09687688109065422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schafer J. A. Robert F. Pitts Memorial Lecture. Mechanisms coupling the absorption of solutes and water in the proximal nephron. Kidney Int. 1984 Apr;25(4):708–716. doi: 10.1038/ki.1984.78. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab S. J., Klahr S., Hammerman M. R. Na+ gradient-dependent Pi uptake in basolateral membrane vesicles from dog kidney. Am J Physiol. 1984 May;246(5 Pt 2):F663–F669. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1984.246.5.F663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiler S., Fleischer S. Isolation of plasma membrane vesicles from rabbit skeletal muscle and their use in ion transport studies. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13862–13871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sottocasa G. L., Kuylenstierna B., Ernster L., Bergstrand A. An electron-transport system associated with the outer membrane of liver mitochondria. A biochemical and morphological study. J Cell Biol. 1967 Feb;32(2):415–438. doi: 10.1083/jcb.32.2.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton R. A., Wong N. L., Dirks J. H. Effects of parathyroid hormone on sodium and calcium transport in the dog nephron. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1976 Oct;51(4):345–351. doi: 10.1042/cs0510345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor A., Windhager E. E. Possible role of cytosolic calcium and Na-Ca exchange in regulation of transepithelial sodium transport. Am J Physiol. 1979 Jun;236(6):F505–F512. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1979.236.6.F505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich K. J., Rumrich G., Klöss S. Active Ca2+ reabsorption in the proximal tubule of the rat kidney. Dependence on sodium- and buffer transport. Pflugers Arch. 1976 Aug 24;364(3):223–228. doi: 10.1007/BF00581759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIDROW S. H., LEVINSKY N. G. The effect of parathyroid extract on renal tubular calcium reabsorption in the dog. J Clin Invest. 1962 Dec;41:2151–2159. doi: 10.1172/JCI104673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winaver J., Fragola J., Chen T. C., Sylk D. B., Robertson J. S., Puschett J. B. Potentiation by calcium of the proximal tubular transport effects of parathyroid hormone. Miner Electrolyte Metab. 1982 Nov;8(5):275–288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windus D. W., Cohn D. E., Klahr S., Hammerman M. R. Glutamine transport in renal basolateral vesicles from dogs with metabolic acidosis. Am J Physiol. 1984 Jan;246(1 Pt 2):F78–F86. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1984.246.1.F78. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Heeswijk M. P., Geertsen J. A., van Os C. H. Kinetic properties of the ATP-dependent Ca2+ pump and the Na+/Ca2+ exchange system in basolateral membranes from rat kidney cortex. J Membr Biol. 1984;79(1):19–31. doi: 10.1007/BF01868523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




