SUMMARY
The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) plays pivotal roles in development and is mutated or overexpressed in several cancers. Despite recent advances, the complex allosteric regulation of EGFR remains incompletely understood. In efforts to understand why the negative cooperativity observed for intact EGFR is lost in studies of its isolated extracellular region (ECR), we uncovered unexpected relationships between ligand binding and receptor dimerization. The two processes appear to compete. Surprisingly, dimerization does not enhance ligand binding (although ligand binding promotes dimerization). We further show that simply forcing EGFR ECRs into pre-formed dimers without ligand yields ill-defined, heterogeneous structures. Finally, we demonstrate that extracellular EGFR-activating mutations in glioblastoma enhance ligand-binding affinity without directly promoting EGFR dimerization – suggesting that these oncogenic mutations alter the allosteric linkage between dimerization and ligand binding. Our findings have important implications for understanding how EGFR and its relatives are activated by specific ligands and pathological mutations.
INTRODUCTION
X-ray crystal structures from 2002 and 2003 (Burgess et al., 2003) yielded the scheme for ligand-induced EGFR dimerization shown in Figure 1. Binding of a single ligand to domains I and III within the same extracellular region (ECR) stabilizes an ‘extended’ conformation and exposes a dimerization interface in domain II – promoting self-association with a dissociation constant (KD) in the micromolar range (Burgess et al., 2003; Dawson et al., 2005; Dawson et al., 2007). Although this model satisfyingly explains ligand-induced EGFR dimerization, it fails to capture the complex ligand-binding characteristics seen for cell-surface EGFR – with concave-up Scatchard plots indicating either negative cooperativity (De Meyts, 2008; MacDonald and Pike, 2008) or distinct affinity-classes of EGF-binding site with high-affinity sites responsible for EGFR signaling (Defize et al., 1989). This cooperativity or heterogeneity is lost when the ECR from EGFR is studied in isolation, as also described for the insulin receptor (De Meyts, 2008).
Figure 1. Structural view of ligand-induced dimerization of the hEGFR extracellular region.
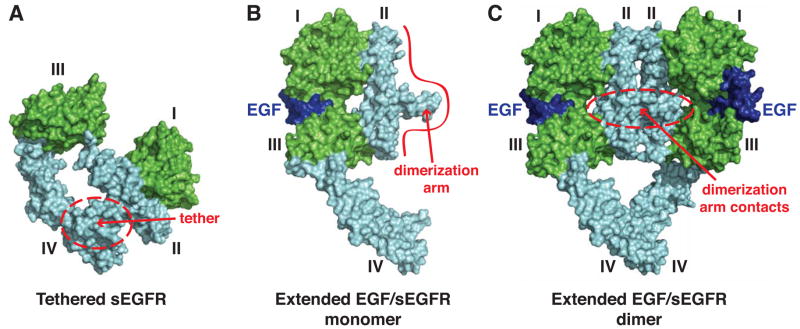
(A) Surface-representation of tethered, unliganded, sEGFR from PDB entry 1NQL (Ferguson et al., 2003). Ligand-binding domains I and III are green, cysteine-rich domains II and IV are cyan. The intramolecular domain II/IV tether is circled in red. (B) Hypothetical model for an extended EGF-bound sEGFR monomer based on SAXS studies of an EGF-bound dimerization-defective sEGFR variant (Dawson et al., 2007), from PDB entry 3NJP (Lu et al., 2012). EGF is blue, and the red boundary represents the primary dimerization interface. (C) 2:2 (EGF/sEGFR) dimer, from PDB entry 3NJP (Lu et al., 2012), colored as in B. Dimerization arm contacts are circled in red.
Insight into structural origins of EGF/EGFR binding complexity was provided by studies of the Drosophila melanogaster EGFR (dEGFR), which – unlike its human counterpart – retains its negative cooperativity when the soluble ECR is isolated (Alvarado et al., 2010). Crystal structures of the ECR from dEGFR revealed a relatively simple ‘half-of-the-sites’ reactivity in which occupying one binding site in an asymmetric dimer restrains and reduces the ligand-binding affinity of the second site (Alvarado et al., 2010). Subsequent detailed comparisons of human and Drosophila receptor ECR dimer structures prompted experiments that suggest a similar half-of-the-sites reactivity for human EGFR (Liu et al., 2012). Moreover, detailed studies of EGF binding to intact hEGFR in cells are consistent with this model (MacDonald and Pike, 2008). The observed (or inferred) negative cooperativity requires formation of a stable singly-liganded receptor dimer, a species that is never seen for the isolated human ECR (Lemmon et al., 1997) but forms readily for its Drosophila counterpart (Alvarado et al., 2010). The ECR of the Drosophila receptor even dimerizes significantly (KD ~ 40 μM) without bound ligand (Alvarado et al., 2009), reminiscent of the ligand-independent (pre-formed) dimers reported for intact, cell-surface, hEGFR in many studies (Lemmon et al., 2014). We therefore reasoned that artificially dimerizing the ECR from the human receptor might restore negative cooperativity and provide avenues for studying details of the complex ligand-binding characteristics of hEGFR. Indeed, engineered dimers of the hEGFR ECR were previously reported to have increased ligand-binding affinity and concave-up Scatchard plots (Adams et al., 2009; Jones et al., 1999). Similarly, concave-up Scatchard plots (suggesting negative cooperativity) were restored to the insulin receptor ECR by fusing it to a dimeric immunoglobulin Fc domain (Bass et al., 1996) or to a dimerizing leucine zipper (Hoyne et al., 2000).
Here, we describe studies of an artificially dimerized ECR from human EGFR that yield useful insight into the heterogeneous nature of pre-formed ECR dimers and into the origins of negative cooperativity. Our data also argue that extracellular structures induced by ligand binding are not ‘optimized’ for dimerization and, conversely, that dimerization does not optimize the ligand-binding sites. We also analyzed the effects of oncogenic mutations found in glioblastoma patients (Lee et al., 2006), revealing that they affect allosteric linkage between ligand binding and dimerization rather than simply promoting EGFR dimerization. These studies have important implications for understanding extracellular activating mutations found in EGFR/ErbB family receptors in glioblastoma and other cancers, and also for understanding specificity of ligand-induced ErbB receptor heterodimerization.
RESULTS and DISCUSSION
Pre-dimerizing the EGFR extracellular region has modest effects on EGF binding
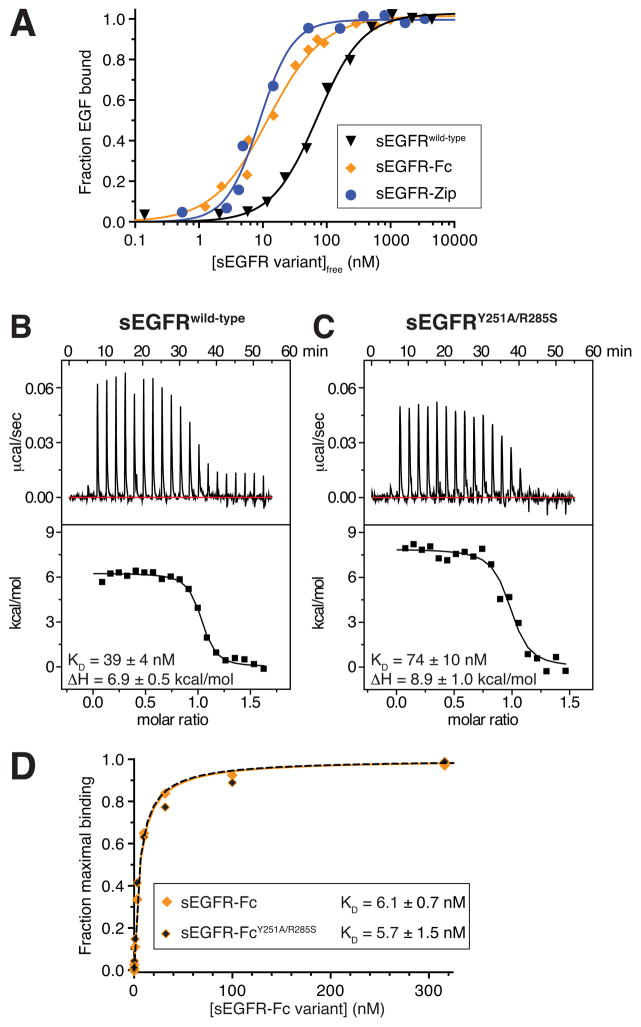
To access pre-formed dimers of the hEGFR extracellular region (sEGFR) experimentally we C-terminally fused (to residue 621 of the mature protein) either a dimerizing Fc domain (creating sEGFR-Fc) or the dimeric leucine zipper from S. cerevisiae GCN4 (creating sEGFR-Zip). Size exclusion chromatography (SEC) and/or sedimentation equilibrium analytical ultracentrifugation (AUC) confirmed that the resulting purified sEGFR fusion proteins are dimeric (Figure S1). To measure KD values for ligand binding to sEGFR-Fc and sEGFR-Zip, we labeled EGF with Alexa-488 and monitored binding in fluorescence anisotropy (FA) assays. As shown in Figure 2A, EGF binds approximately 10-fold more tightly to the dimeric sEGFR-Fc or sEGFR-Zip proteins than to monomeric sEGFR (Table 1). The curves obtained for EGF binding to sEGFR-Fc and sEGFR-Zip showed no signs of negative cooperativity – with sEGFR-Zip actually requiring a Hill coefficient (nH) greater than 1 for a good fit (nH = 1 for both sEGFRwild-type and sEGFR-Fc). Thus, our initial studies argued that simply dimerizing human sEGFR fails to restore the negatively cooperative ligand binding seen for the intact receptor in cells.
Figure 2. Dimerization of the ECR has little effect on affinity for EGF.
(A) Fluorescence anisotropy (FA) data for Alexa-488-labeled EGF (EGF488) binding to monomeric sEGFRwild-type (black triangles), dimeric sEGFR-Fc (orange diamonds) and dimeric sEGFR-Zip (blue circles). Ligand was present at 60 nM for sEGFRwild-type experiments, or 10 nM for sEGFR-Fc and sEGFR-Zip. Both sEGFR-Fc and sEGFR-Zip are dimeric under these conditions (Figure S1), whereas sEGFRwild-type remains monomeric. Data shown are representative of three independent experiments, with means listed in Table 1. (B) Representative ITC analysis of EGF binding to sEGFRwild-type at 25°C, with EGF at 80 μM in the syringe and sEGFRwild-type at 10 μM in the cell. (C) ITC analysis of EGF binding to the non-dimerizing sEGFRY251A/R285S variant, performed as in B. (D) SPR analysis of EGF binding to constitutively-dimeric sEGFR-Fc, with (orange/black diamonds) or without (solid orange diamonds) domain II dimerization-disrupting mutations (Y251A/R285S). All data are representative of three independent experiements, with mean values (± SD) noted. Mean values (± SD) of all thermodynamic parameters are listed in Table 1. See also Figures S1, S2, and S3.
Table 1.
ITC data for EGF binding to sEGFR variants
| sEGFR variant | KD (nM)a | ΔH (kcal/mol)a | ΔG (kcal/mol)b | TΔS (kcal/mol)c |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| sEGFR-Fc | 7.8 ± 3.0d | +10.3 ± 0.5e | −11.1 | 21.4 |
| sEGFR-Zip | 8.9 ± 1.1d | +12.3 ± 0.6e | −11.0 | 23.3 |
| sEGFRwild-type | 78 ± 14d/39 ± 4e | +6.9 ± 0.5e | −9.7d/10.1e | 16.6d/17.0e |
| sEGFRY251A/R285S | 74 ± 10e | +8.9 ± 1.0e | −9.7 | 18.6 |
Values are the mean ± SD of at least three independent experiments.
ΔG values are calculated from the mean KD.
TΔS values are obtained by subtracting ΔG from the mean value for ΔH.
From fluorescence anisotropy-based assay data
From ITC data.
See also Table S1.
One surprise from these data was that forced sEGFR dimerization has only a modest (≤10-fold) effect on EGF-binding affinity. Under the conditions of the FA experiments, isolated sEGFR (without zipper or Fc fusion) remains monomeric; the FA assay contains just 60 nM EGF, so the maximum concentration of EGF-bound sEGFR is also limited to 60 nM – which is over 20-fold lower than the KD for dimerization of the EGF/sEGFR complex (Dawson et al., 2005; Lemmon et al., 1997). This ≤10-fold difference in affinity for dimeric and monomeric sEGFR seems small in light of the strict dependence of sEGFR dimerization on ligand binding (Dawson et al., 2005; Lax et al., 1991; Lemmon et al., 1997). Unliganded sEGFR does not dimerize detectably even at millimolar concentrations, whereas liganded sEGFR dimerizes with KD ~ 1 μM – suggesting that ligand enhances dimerization by at least 104 to 106-fold. Straightforward linkage of dimerization and binding equilibria should stabilize EGF binding to dimeric sEGFR similarly (by 5.5–8 kcal/mol). The modest difference in EGF-binding affinity for dimeric and monomeric sEGFR is also significantly smaller than the 40–100 fold difference typically reported between high-affinity and low-affinity EGF-binding on the cell surface when data are fit to two affinity-classes of binding site (Burgess et al., 2003; Magun et al., 1980).
Mutations that prevent sEGFR dimerization do not significantly reduce ligand-binding affinity
The fact that pre-dimerizing sEGFR only modestly increased ligand-binding affinity led us to question the extent to which domain II-mediated sEGFR dimerization is linked to ligand binding. It is typically assumed that the domain II conformation stabilized upon forming the sEGFR dimer in Figure 1C optimizes the domain I and III positions for EGF binding. To test this hypothesis, we introduced a well-characterized pair of domain II mutations into sEGFR that block dimerization: one at the tip of the dimerization arm (Y251A) and one at its ‘docking site’ on the adjacent molecule in a dimer (R285S). The resulting (Y251A/R285S) mutation abolishes sEGFR dimerization and EGFR signaling (Dawson et al., 2005; Ogiso et al., 2002). Importantly, we chose isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC) for these studies, where all interacting components are free in solution. Previous surface plasmon resonance (SPR) studies have indicated that dimerization-defective sEGFR variants bind immobilized EGF with reduced affinity (Dawson et al., 2005), and we were concerned that this reflects avidity artifacts – where dimeric sEGFR binds more avidly than monomeric sEGFR to sensorchip-immobilized EGF.
Surprisingly, our ITC studies showed that the Y251A/R285S mutation has no significant effect on ligand-binding affinity for sEGFR in solution (Table 1). These experiments employed sEGFR (with no Fc fusion) at 10 μM – ten times higher than KD for dimerization of ligand-saturated wild-type sEGFR (KD ~1 μM). Dimerization of wild-type sEGFR (sEGFRwild-type) should therefore be complete under these conditions, whereas the Y251A/R285S-mutated variant (sEGFRY251A/R285S) does not dimerize at all (Dawson et al., 2005). The KD value for EGF binding to dimeric sEGFRwild-type was essentially the same (within 2-fold) as that for sEGFRY251A/R285S (Figure 2B,C and Table 1), arguing that the favorable Gibbs Free Energy (ΔG) of liganded sEGFR dimerization (−5.5 to −8 kcal/mol) does not contribute significantly (< 0.4 kcal/mol) to enhanced ligand-binding. Affinities of TGFα for sEGFRwild-type and sEGFRY251A/R285S were also indistinguishable at 80 nM and 82 nM respectively (Table S1). These ITC data lead to two important conclusions. First and most importantly, they show that (without SPR avidity effects) domain II-mediated dimerization does not significantly enhance ligand binding to sEGFR – implying that there is no positive linkage between ligand binding and sEGFR dimerization. Second, the results force us to revise the interpretation of EGF/sEGFR ITC studies that we published in 1997 (Lemmon et al., 1997). We previously ascribed the major entropy-driven event (with positive ΔH) to sEGFR dimerization, modeling EGF binding as an enthalpy-driven event based on ITC of EGF binding to isolated domain III (Figure S2). The fact that the entropy-driven event is maintained in the absence of sEGFR dimerization refutes this, and reveals that EGF binding to the intact ECR is entropy driven – consistent with the associated conformational changes (see Figure S2).
Thus, contrary to the expected 104 to 106-fold enhancement expected from straightforward linkage of sEGFR dimerization and EGF binding, our data reveal that blocking sEGFR dimerization has little influence on ligand-binding affinity. Although ΔG for ligand binding is therefore essentially unchanged by the Y251A/R285S mutation, the enthalpy change (ΔH) associated with EGF binding is more favorable (less positive) by 2.0 kcal/mol for sEGFRwild-type than for sEGFRY251A/R285S. Compensating for this, TΔS is less favorable by 1.6 kcal/mol for binding to sEGFRwild-type. Very similar results were obtained for TGFα (Figure S3A/B, Table S1). Moreover, direct comparison of ITC and FA experiments shows that EGF binds sEGFRwild-type with very similar affinities regardless of whether it does (in ITC experiments) or does not (in FA experiments) dimerize (Table 1, Figure 2A,B) – also arguing that ligand binding and dimerization are not linked. Dimerization of EGF-bound sEGFRwild-type is essentially complete in our ITC experiments ([EGF/sEGFR] reaches 10 μM) and is negligible in FA ([EGF/sEGFR] ≤ 60 nM), yet KD for EGF binding remains the same. Moreover, even for covalently-dimerized sEGFR-Fc, dimerization arm mutations do not impair ligand binding, as shown in SPR studies of EGFR binding by Fc-fused wild-type and Y251A/R285S-mutated sEGFR (Figure 2D).
Thermodynamics of EGF binding to sEGFR-Fc
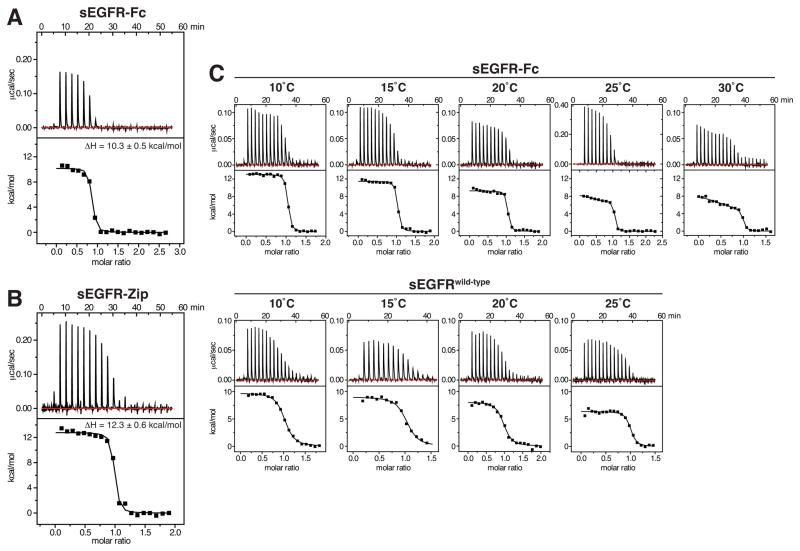
If there is no discernible positive linkage between sEGFR dimerization and EGF binding, why do sEGFR-Fc and sEGFR-Zip bind EGF ~10-fold more strongly than wild-type sEGFR? To investigate this, we used ITC to compare EGF binding to sEGFR-Fc and sEGFR-Zip (Figure 3A and B) with binding to isolated (non-fusion) sEGFRwild-type. As shown in Table 1, the positive (unfavorable) ΔH for EGF binding is further elevated in pre-dimerized sEGFR compared with sEGFRwild-type, suggesting that enforced dimerization may actually impair ligand/receptor interactions such as hydrogen bonds and salt-bridges. The increased ΔH is more than compensated for, however, by a favorable increase in TΔS. This favorable entropic effect may reflect an ‘ordering’ imposed upon unliganded sEGFR when it is pre-dimerized, such that it exhibits fewer degrees of freedom compared to monomeric sEGFR. In particular, since EGF binding does induce sEGFR dimerization it is clear that pre-dimerization will reduce the entropic cost of bringing two sEGFR molecules into a dimer upon ligand binding – possibly underlying this effect.
Figure 3. Evidence for heterogeneity of sites in forced sEGFR dimers.
(A) Representative ITC data for EGF binding to sEGFR-Fc at 25°C, with EGF at 130 μM in the syringe and sEGFR-Fc in the cell at 8.4 μM. (B) ITC data for EGF binding to sEGFR-Zip at 25°C, with EGF in the syringe at 105 μM and sEGFR-Zip in the cell at 11.3 μM. Mean ΔH values from three independent experiments (± SD) are listed. (C) ITC for EGF binding to sEGFR-Fc (upper) and sEGFRwild-type (lower) at the temperatures marked. EGF concentration in the calorimeter syringe was 80 μM, and sEGFR protein was present in the cell at 9 μM. Data for sEGFR-Fc at 25°C employed higher concentrations (25 μM sEGFR-Fc in the cell, 280 μM EGF in the syringe) to improve signal-to-noise in discerning distinct binding events.
Possible heterogeneity of binding sites in sEGFR-Fc
Close inspection of EGF/sEGFR-Fc titrations such as that in Figure 3A suggested some heterogeneity of sites, as evidenced by the slope in the early part of the experiment. To investigate this possibility further, we repeated titrations over a range of temperatures. We reasoned that, if there are two different types of EGF-binding site in an sEGFR-Fc dimer, they might have different values for heat capacity change (ΔCp), with differences that might become more evident at higher (or lower) temperatures. Indeed, ΔCp values correlate with the nonpolar surface area buried upon binding (Livingstone et al., 1991) – and we know that this differs for the two Spitz-binding sites in the asymmetric Drosophila EGFR dimer (Alvarado et al., 2010). As shown in Figure 3C, the heterogeneity was indeed clearer at higher temperatures for sEGFR-Fc – especially at 25°C and 30°C – suggesting the possible presence of distinct classes of binding sites in the sEGFR-Fc dimer. We were not able to fit the two KD values (or ΔH values) uniquely with any precision, because the experiment has insufficient information for unique fitting to a model with 4 variables. Whereas binding to sEGFRwild-type could be fit confidently with a single-site binding model throughout the temperature range, enforced sEGFR dimerization (by Fc fusion) creates apparent heterogeneity in binding sites, which may reflect negative cooperativity of the sort seen with dEGFR. The different binding sites are too close in their KD values to be discerned in ITC or FA studies, and can only be distinguished based on different ΔH values at higher temperature. Nonetheless, these data do suggest that negative cooperativity may be an intrinsic property of the hEGFR extracellular region as suggested (Liu et al., 2012), and as visualized for the Drosophila receptor (Alvarado et al., 2010). Presumably, interactions involving other parts of EGFR are responsible for the greater distinction in KD values seen for the intact receptor in cells (Macdonald-Obermann and Pike, 2009).
Ligand binding is required for well-defined dimerization of the EGFR extracellular region
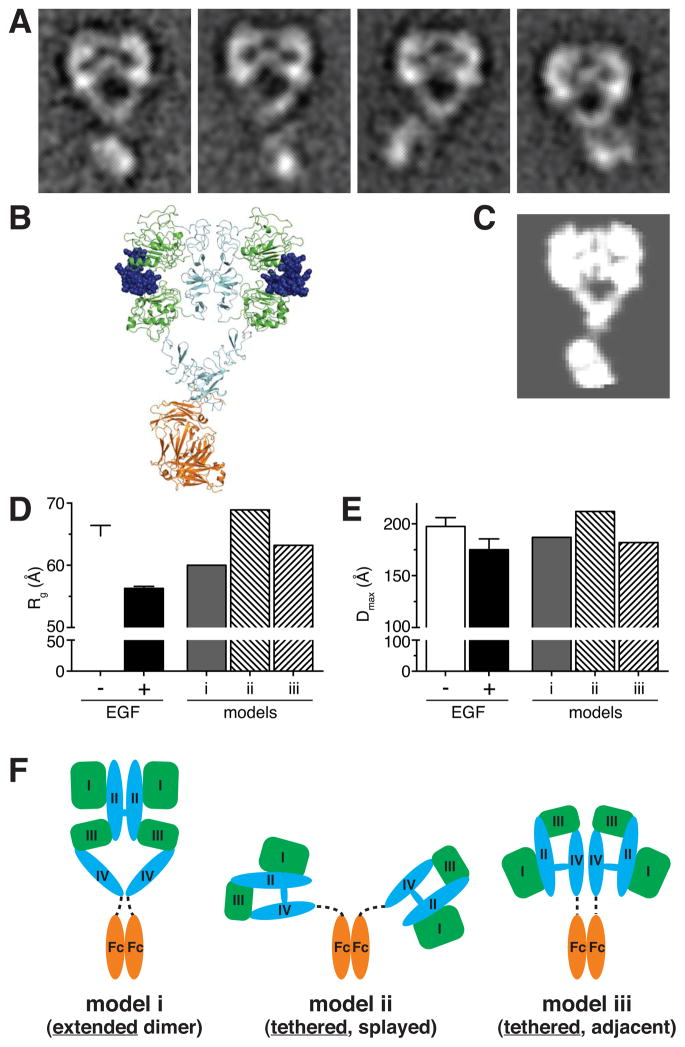
To investigate the structural nature of the pre-formed sEGFR-Fc dimer, we used negative stain electron microscopy (EM). We hypothesized that enforced dimerization might cause the unliganded ECR to form the same type of loose domain II-mediated dimer seen in crystals of unliganded Drosophila sEGFR (Alvarado et al., 2009). When bound to ligand (Figure 4A), the Fc-fused ECR clearly formed the characteristic heart-shape dimer seen by crystallography and EM (Lu et al., 2010; Mi et al., 2011). Figure 4B presents a structural model of an Fc-fused liganded sEGFR dimer, and Figure 4C shows a calculated 12 Å resolution projection of this model. The class averages for sEGFR-Fc plus EGF (Figure 4A) closely resemble this model, yielding clear densities for all 4 receptor domains, arranged as expected for the EGF-induced domain II-mediated ‘back-to-back’ extracellular dimer shown in Figure 1 (Garrett et al., 2002; Lu et al., 2010). In a subset of classes the Fc-domain also appeared well resolved, indicating that these particular arrangements of the Fc domain relative to the ECR represent highly populated states – with the Fc domains occupying similar positions to those of the kinase domain in detergent-solubilized intact receptors (Mi et al., 2011).
Figure 4. Ligand-binding is required for formation of the domain II-mediated ‘back-to-back’ dimer.
(A) Reference-free class averages from single-particle EM images of negatively stained EGF/sEGFR-Fc complexes. (B) Model for an EGF/sEGFR-Fc complex derived by appending an Fc domain to the EGF-bound sEGFR dimer from PDB entry 3NJP (Lu et al., 2012). EGF is blue (space filling), ligand-binding EGFR domains I and III are green, cysteine-rich domains II and IV are cyan, and the Fc domain is orange. (C) Two-dimensional projection from a calculated 12 Å resolution map based on the model in B, generated as described in Supplemental Experimental Procedures. (D) Rg values from Guinier analysis of SAXS data for 10–20 μM sEGFR-Fc with (black bar) or without (open bar) a 1.3-fold molar excess of EGF. Rg values calculated from the three models (i – iii) shown in F are also plotted. (E) SAXS-derived values of maximum interatomic distance (Dmax) for sEGFR-Fc alone (open bar) and the EGF/sEGFR-Fc complex (black bar). Calculated Dmax values for the three models shown in F are also plotted. All SAXS data represent the mean of four independent experiments (± SD). (F) Three distinct structural models (i, ii, and iii) were constructed for unliganded sEGFR-Fc. In model i, sEGFR forms the back-to-back dimer seen in the presence of ligand (or for unliganded Drosophila EGFR). In models ii and iii, sEGFR retains the tethered conformation, but the two sEGFR moieties in the dimer are either maximally splayed apart (model ii) or are adjacent (model iii). Rg and Dmax values calculated for each model are plotted in D and E. See also Figure S4.
Without EGF, by contrast, EM analysis of sEGFR-Fc failed to yield signal-enhanced class averages with interpretable inter-domain relationships (Figure S4) – despite significant effort with the same protein preparations and staining conditions used for Figure 4A. Thus, simply forcing the ECR from hEGFR into a dimer by Fc fusion does not cause it to form well-ordered domain II-mediated back-to-back dimers. Ligand binding is required for this type of dimer to form. Whether the ECRs are tethered or extended (or sample both conformations) in unliganded sEGFR-Fc dimers is not clear. Solution small angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) studies showed that sEGFR-Fc becomes significantly more compact upon EGF binding, with the radius of gyration (Rg) falling from 65.0 Å to 56.4 Å (Figure 4D) and the maximum interatomic distance (Dmax) within the molecule falling from 198 Å to 175 Å (Figure 4E). Values for Rg and Dmax for ligand-bound sEGFR-Fc agree reasonably well (within 8%) with those calculated for a back-to-back dimer model (Figure 4F, model i). The relatively large Rg and Dmax values for sEGFR-Fc in the absence of ligand (Figure 4D and E) are more consistent with a model in which the ECRs are splayed apart, possibly while remaining tethered. Indeed, a model in which two tethered EGFR ECRs are attached to the Fc dimer and splayed maximally (Figure 4F, model ii) yields an Rg of 69 Å (compared with 65 Å for unliganded sEGFR-Fc) and a Dmax value of 212 Å (compared with 198 Å for unliganded sEGFR-Fc). An Fc-fused dimer with the tethered sEGFR moieties adjacent (Figure 4F, model iii) is more compact, suggesting that unliganded sEGFR-Fc lies (on average) between models ii and iii. Thus, our SAXS data also argue that ligand binding is necessary for formation of the well-defined domain II-mediated dimerization interface. Simply forcing the receptor molecules into close proximity is not sufficient – as Springer and colleagues also concluded in related studies (Lu et al., 2012).
Our results, and those of Lu et al. (2012), argue that pre-formed extracellular dimers of hEGFR do not contain a well-defined domain II-mediated interface. Rather, the ECRs in these dimers likely sample a broad range of positions (and possibly conformations). This conclusion argues against recent suggestions that stable unliganded extracellular dimers “disfavor activation in pre-formed dimers by assuming conformations inconsistent with” productive dimerization of the rest of the receptor (Arkhipov et al., 2013). The ligand-free inactive dimeric ECR species modeled by Arkhipov et al., 2013 in their computational studies of the intact receptor do not appear to be stable. The isolated ECR from EGFR has a very low propensity for self-association without ligand, with KD in the millimolar range (or higher). Moreover, sEGFR does not form a defined structure even when forced to dimerize by Fc fusion. It is therefore difficult to envision how it might assume any particular autoinhibitory dimeric conformation in pre-formed dimers. It has also been argued that the unliganded ECR impedes dimerization driven by the intracellular region (Endres et al., 2013). The orientational flexibility of the ECR indicated by our EM and SAXS studies of sEGFR-Fc, and by studies from the Springer laboratory (Lu et al., 2010; Lu et al., 2012; Mi et al., 2011) makes it difficult to imagine how the ECR could sterically constrain dimerization mediated by the other parts of EGFR. Moreover, if ligand binding activates EGFR simply by removing steric constraints imposed by the ECR it is difficult to understand why specific mutations of even single residues in the dimerization interface should block activation (Dawson et al., 2005; Ogiso et al., 2002), and conversely why mutations that destabilize the domain II/IV tether are not activating (Mattoon et al., 2004; Walker et al., 2004).
Structural implications of weak linkage between ligand binding and dimerization
It has typically been assumed that binding of a single ligand molecule between domains I and III of an sEGFR molecule stabilizes a structure that resembles one half of the 2:2 receptor dimer in Figure 1C. Indeed, this is the assumption in the model structure shown in Figure 1B. In addition, the domain II conformation in a ligand-bound sEGFR monomer is thought to be ideally suited (or poised) for dimerization (Dawson et al., 2005; Dawson et al., 2007). These assumptions predict (and presume) that ligand binding and dimerization are strongly positively linked for EGFR and sEGFR. The lack of such linkage in our studies suggests that the domain II conformation stabilized by EGF binding may in fact not be optimal for dimerization. Indeed, the precise conformation of domain II in a liganded sEGFR monomer is not known, even though SAXS studies of a non-dimerizing sEGFR variant showed that it does become extended upon EGF binding, with the dimerization arm exposed (Dawson et al., 2007). Our studies of the Drosophila EGFR (Alvarado et al., 2010) also showed that restraining domain II conformation through interactions at the dimerization interface can significantly impair ligand binding affinity (this is the origin of negative cooperativity). With this precedent in mind, we suggest that domain II-mediated sEGFR dimerization may distort domain II conformation in a way that actually compromises ligand binding to domains I and III. Conversely, we suggest that the domain II conformation stabilized by ligand binding may be suboptimal for dimerization. In this scenario, ligand-binding and dimerization contacts would exert opposing influences on domain II – effectively competing with one another. This competition could effectively nullify the expected positive linkage between ligand binding and dimerization. If this view is correct, the ligand-bound sEGFR dimer visualized by crystallography would reflect a ‘compromise’ in which domain II adopts a structure that is intermediate between the ideal conformation for ligand binding and the ideal conformation for domain II-mediated dimerization.
The precise role played by the extracellular region (ECR) in EGFR activation has been a subject of debate in recent years. The ECR was initially viewed as a module that serves simply to drive ligand-induced receptor dimerization (Burgess et al., 2003). Some more recent data also support this view (Lu et al., 2010; Mi et al., 2011), and this is the simple view that predicts positive linkage between ligand binding and dimerization. Alternatively, the ECR has been argued to function as a steric impediment to ligand-independent receptor dimerization, relieved only when the ECR binds ligand (Chantry, 1995; Endres et al., 2013; Jura et al., 2009) – as mentioned above. In a third possibility it is proposed that the ligand-bound ECR dimer must achieve a particular conformation in order for the receptor to be active (Alvarado et al., 2010; Arkhipov et al., 2013; Lemmon et al., 2014; Liu et al., 2012; Wilson et al., 2009). Although ligand binding certainly promotes ECR dimerization – presumably by exposing the dimerization arm as in Figure 1 – the suggested domain II conformational compromise between optimal ligand binding and optimal dimerization should result in a particular structure, which may be required for productive signaling. Different discrete structures (stabilized by different ligands) may even signal differently (Wilson et al., 2009). A similar compromise between dimerization and ligand binding is also seen in our studies with TGFα (Figure S3 and Table S1), bolstering the view that this domain II conformational ‘competition’ may be functionally important.
Extracellular oncogenic mutations observed in glioblastoma may alter linkage between ligand binding and sEGFR dimerization
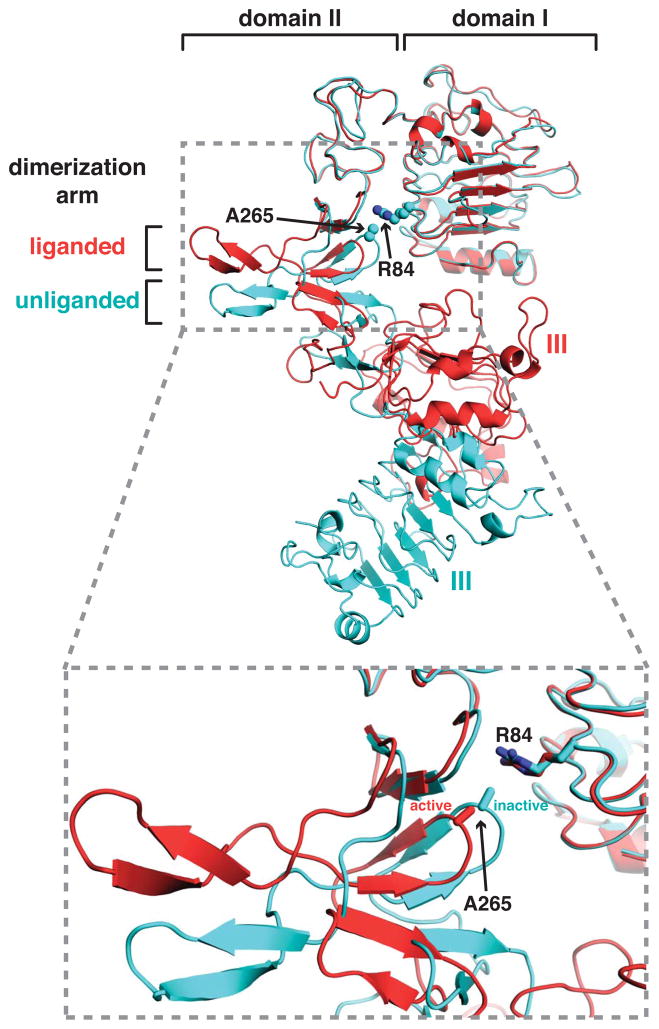
Missense mutations in the hEGFR extracellular region were discovered in several human glioblastoma multiforme samples or cell lines, and occur in 10–15% of glioblastoma cases (Brennan et al., 2013; Lee et al., 2006). Several elevate basal receptor phosphorylation and cause EGFR to transform NIH-3T3 cells in the absence of EGF (Lee et al., 2006). Thus, these are constitutively activating, oncogenic, mutations – although the mutated receptors can be activated further by ligand (Lee et al., 2006; Vivanco et al., 2012). Two of the most commonly mutated sites in glioblastoma, R84 and A265 (R108 and A289 in pro-EGFR) are in domains I and II of the ECR respectively, and contribute directly in inactive sEGFR to intramolecular interactions between these domains that are thought to be autoinhibitory (Figure 5). Domains I and II become separated from one another in this region upon ligand binding to EGFR (Alvarado et al., 2009), as illustrated in the lower part of Figure 5. Interestingly, analogous mutations in the EGFR relative ErbB3 were also found in colon and gastric cancers (Jaiswal et al., 2013).
Figure 5. Location of EGFR domain I/II interface mutations in glioblastoma.
Cartoon representations of sEGFR crystal structures in liganded (red) and unliganded (cyan) states are shown, from PDB entries 1MOX (Garrett et al., 2002) and 1YY9 (Li et al., 2005), aligned using domain I as reference. Side-chains of R84 and A265 are shown, where the majority of mutations have been seen in glioblastoma (Lee et al., 2006; Vivanco et al., 2012) and where the domains I/II separation is increased upon activation (lower panel).
We hypothesized that domain I/II interface mutations might activate EGFR by disrupting autoinhibitory interactions between these two domains – possibly promoting a domain II conformation that drives dimerization even in the absence of ligand. On the contrary, however, sedimentation equilibrium AUC showed that sEGFR variants harboring R84K, A265D or A265V mutations all remained completely monomeric in the absence of ligand (Figure 6A) at a concentration of 10 μM, which is similar to that experienced at the cell surface (Lemmon et al., 1997). As with wild-type sEGFR, however, addition of ligand promoted dimerization of each mutated sEGFR variant – with KD values that were indistinguishable from those of wild-type. Thus, extracellular EGFR mutations seen in glioblastoma do not simply promote ligand-independent ECR dimerization – consistent with our finding that even dimerized sEGFR-Fc requires ligand binding in order to form the characteristic ‘heart-shaped’ dimer.
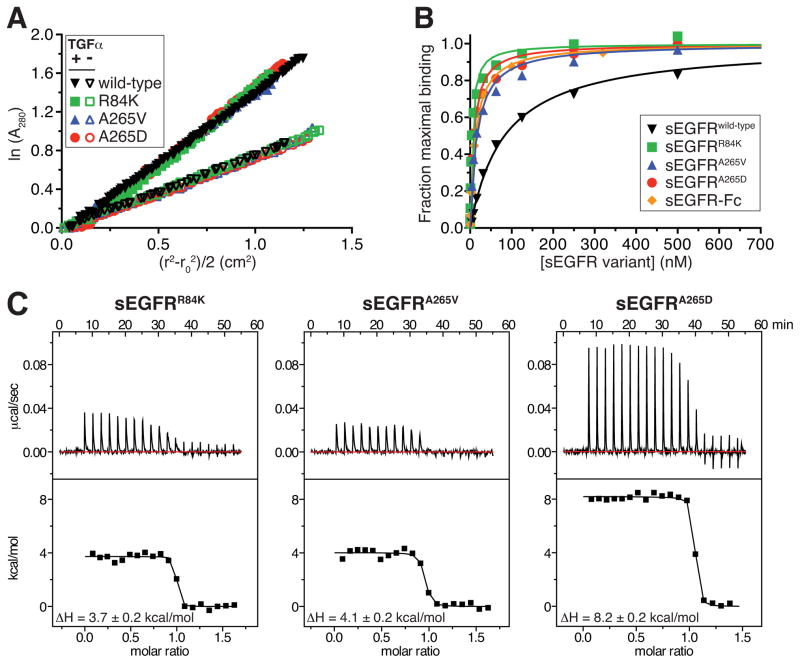
Figure 6. Effects of glioblastoma mutations on sEGFR properties.
(A) Sedimentation equilibrium AUC of sEGFR variants harboring glioblastoma mutations. Data are plotted as the natural logarithm of absorbance at 280 nm (A280, monitoring protein concentration) against (r2−r02)/2, for data obtained at 9000 r.p.m. at room temperature, where r is the radial position in the sample and r0 is the radial position of the meniscus. For ideal species, this representation yields a straight line with slope proportional to molecular mass. Each sEGFR variant was analyzed alone at 10 μM (open symbols) or (at 5 μM) with an added 1.2-fold molar excess of TGFα (closed symbols) – TGFα replacing EGF since it contributes negligibly to A280. Without ligand, best-fit molecular masses were 75 kDa (wild-type); 80 kDa (R84K and A265V); and 89 kDa (A265D). In the presence of TGFα, single-species fits yielded molecular masses of 157 kDa (wild-type); 141 kDa (R84K); 143 kDa (A265V); and 175 kDa (A265D). Estimated KD values (± SD) for sEGFR dimerization in the presence of TGFα, fit as described (Dawson et al., 2005), were 1.5 μM (R84K); 1.0 μM (A265V); and 4.8 μM (A265D) – compared with 1.2 μM for wild-type sEGFR. (B) Ligand binding by each sEGFR variant was analyzed using SPR, flowing protein at a range of concentrations over immobilized EGF. Best fit KD values (± SD) for EGF binding were 83 ± 4.4 nM (wild-type); 4.3 ± 1.5 nM (R84K); 16 ± 4.4 nM (A265V); and 8.6 ± 5.1 nM (A265D). Similar data for TGFα are shown in Figure S5. (C) ITC analysis of EGF binding to sEGFR variant harboring mutations found in glioblastoma patients, performed as in Figure 2B. See also Figures S5 and S6.
Interestingly, the ligand-binding affinity of sEGFR was significantly increased by all of the glioblastoma-derived mutations studied here (Figure 6B). The effects ranged from a 5-fold increase for A265V to an almost 20-fold increase for R84K. Similar affinity increases were also seen for TGFα binding (Figure S5). ITC studies with EGF (Figure 6C) further revealed that the 5–20 fold increase in ligand-binding affinity (a 1–2 kcal/mole reduction in ΔG) for R84K and A265V variants can be accounted for by ΔH values that are more favorable (less positive) by around 3 kcal/mole when compared to the values for wild-type sEGFR (Table 1). The A265D variant differs (with a less favorable ΔH), possibly because it introduces a charged group into a hydrophobic region of the protein. These data are consistent with a model in which the glioblastoma mutations in the domain I/II interface “free up” domains I and II to occupy positions that permit more optimal interactions with bound ligand. For example, replacement of R84 with a lysine – seemingly a rather conservative substitution – may destabilize the domain I/II interface by disrupting its hydrogen bond network.
We suggest that domain I is normally restrained by domain I/II interactions so that its orientation with respect to the ligand is compromised. When the domain I/II interface is weakened with mutations, this effect is mitigated. If this results simply in increased ligand-binding affinity of the monomeric receptor, the biological consequence might be to sensitize cells to lower concentrations of EGF or TGFα (or other agonists). However, cellular studies of EGFR with glioblastoma-derived mutations (Lee et al., 2006; Vivanco et al., 2012) clearly show ligand-independent activation, arguing that this is not the key mechanism. The domain I/II interface mutations may also reduce restraints on domain II so as to permit dimerization of a small proportion of intact receptor, driven by the documented interactions that promote self-association of the transmembrane, juxtamembrane, and intracellular regions or EGFR (Endres et al., 2013; Lemmon et al., 2014; Red Brewer et al., 2009).
One particularly interesting possibility is that the elevated ligand-binding affinity caused by R84K, A265V and A265D mutations does not reflect enhanced ligand binding to monomeric sEGFR, but instead reflects ‘rescue’ of the expected linkage between ligand binding and dimerization – so that that ligand binds significantly more strongly to (mutated) dimers than to (mutated) monomers. To achieve this, the domain I/II interface mutations might reduce communication between the dimerization and ligand-binding sites so that optimal domain II-mediated dimerization has less of a restraining influence on the ligand-binding site. The importance of influences on domain II conformation in EGFR activation by glioblastoma mutations is also supported by studies of tether mutations in EGFR that alter ligand binding in almost exactly the same way, but do not activate the receptor (and do not impact domain II). Mutations that disrupt the intramolecular tether seen in Figure 1A enhance ligand binding to sEGFR to the same degree as the glioblastoma mutations (Elleman et al., 2001; Ferguson et al., 2003). Moreover, four different types of tether-disrupting mutation all have essentially the same effect on ligand-binding thermodynamics (Figure S6) as seen for R84K or A265V (ΔH becomes more favorable by ~4 kcal/mole). None of these tether-disrupting mutations constitutively activates EGFR, however (Mattoon et al., 2004; Walker et al., 2004). The key difference between the (non-activating) tether mutations and the (activating) glioblastoma mutations is that only the latter directly influence domain II conformation, arguing that domain II conformational effects are the key to oncogenicity of R84K and A265V/D mutations.
CONCLUSIONS
Setting out to test the hypothesis that simply dimerizing the EGFR extracellular region is sufficient to recover the negative cooperativity lost when it is removed from the intact receptor, we were led to revisit several central assumptions about this receptor. Our findings suggest three main conclusions. First, we find that enforcing dimerization of the hEGFR extracellular region does not drive formation of a well-defined domain II-mediated dimer that resembles ligand-bound ECRs or the unliganded ECR from Drosophila EGFR. Our EM and SAXS data show that ligand binding is necessary for formation of well-defined ‘heart-shaped’ domain II-mediated dimers. This result argues that the unliganded extracellular dimers modeled by Arkhipov et al. (2013) are not stable, and that it is improbable that stable conformations of pre-formed extracellular dimers disfavor receptor activation by assuming conformations that counter activating dimerization of the rest of the receptor. Recent work from the Springer laboratory employing kinase inhibitors to drive dimerization of hEGFR (Lu et al., 2012) also showed that EGF binding is required to form ‘heart-shaped’ ECR dimers. These findings leave open the question of the nature of the ECR in pre-formed EGFR dimers, but certainly argue that it is unlikely to resemble the crystallographic dimer seen for unliganded Drosophila EGFR (Alvarado et al., 2009) or that suggested by computational studies (Arkhipov et al., 2013).
Second, our results suggest that enforcing dimerization of the hEGFR extracellular region may restore some of the complexity in ligand binding seen for intact hEGFR (but lost for the isolated soluble ECR). Although some heterogeneity in EGF-binding sites was restored in ITC studies of sEGFR-Fc dimers, the difference in KD values was too small to be quantitated with confidence – arguing that simple dimerization fails to recapitulate fully the intact receptor’s negative cooperativity. This finding supports arguments that the transmembrane and/or intracellular regions of the receptor also play an important role in defining negative cooperativity in hEGFR (Adak et al., 2011; Macdonald-Obermann and Pike, 2009), and underlines the need to consider cooperation of interactions mediated by all domains within the intact or nearly-intact receptor (Arkhipov et al., 2013; Bessman and Lemmon, 2012). It is interesting that the relative contributions of intra- and extra-cellular regions to the allosteric properties of the receptor appear to differ greatly between mammals and insects – where negative cooperativity is recapitulated in the isolated ECR (Alvarado et al., 2010). Similar differences can also be seen between human receptors within a family. For example, whereas the characteristic concave-up Scatchard plots seen for the intact insulin receptor can only be recapitulated for the isolated ECR of that receptor by fusion to a dimerization domain (Bass et al., 1996; Hoyne et al., 2000), the related IGF1 receptor ECR retains negative cooperativity without such modifications (Surinya et al., 2008). Differences in the relative contributions of intra- and extra-cellular regions to precise receptor regulation may have important signaling relevance.
Third, our calorimetric studies of hEGFR show that ligand binds to the ECR with the same affinity whether it is capable of dimerizing or not – despite the fact that ligand binding is clearly required for ECR dimerization. This result argues that ligand binding is required to permit dimerization but that domain II-mediated dimerization may compromise, rather than enhance, ligand binding. Assuming flexibility in domain II, we suggest that this domain serves to link dimerization and ligand binding allosterically. Optimal ligand binding may stabilize one conformation of domain II in the scheme shown in Figure 1 that is then distorted upon dimerization of the ECR – in turn reducing the strength of interactions with the ligand. Such a mechanism would give the appearance of a lack of positive linkage between ligand binding and ECR dimerization, and a good test of this model would be to determine the high resolution structure of a liganded sEGFR monomer (which we expect to differ from a half-dimer). This model also suggests a mechanism for selective hetero- over homo- dimerization of certain ErbB receptors. If a ligand-bound EGFR monomer has a domain II conformation that heterodimerizes with ErbB2 in preference to EGFR homodimers, this could explain several important observations. It could explain reports that ErbB2 is a preferred heterodimerization partner of EGFR (Graus-Porta et al., 1997), and might also explain why EGF binds more tightly to EGFR in cells where it can form heterodimers with ErbB2 than in cells lacking ErbB2, where only EGFR homodimers can form (Li et al., 2012). Moreover, if different EGFR agonists stabilize slightly different domain II conformations, this view of a flexible domain II as an allosteric link between ligand binding and dimerization suggests hypotheses for how individual ligands might induce subtly different receptor states or select for specific heterodimer signaling complexes (Wilson et al., 2009). Interestingly – as our data with glioblastoma mutations suggest – alterations in the allosteric communication between domain II and the adjacent ligand-binding domain I can also be oncogenic.
EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES
Reagents and proteins
EGF and TGFα were from Millipore Inc. Wild-type and mutated sEGFR variants were expressed in Sf9 cells employing a baculovirus system as described previously (Ferguson et al., 2000). See Supplemental Experimental Procedures for details.
Binding and dimerization analyses
Binding of ligand to sEGFR proteins and/or sEGFR dimerization was analyzed using isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC); fluorescence anisotropy (FA); surface plasmon resonance (SPR) or sedimentation equilibrium analytical ultracentrifugation (AUC), as summarized below. Full details are provided in Supplemental Experimental Procedures.
ITC
ITC experiments employed a MicroCal ITC200 instrument. Proteins were dialyzed overnight into 20 mM HEPES, pH 8.0, containing 150 mM NaCl, and 3.4 mM EDTA. sEGFR concentration in the calorimeter cell ranged from 8 to 25 μM, and the concentration of ligand in the syringe ranged from 60 to 280 μM. Data were fit to a single-site binding model in ORIGIN. All titrations were performed independently at least three times, and representative titrations are shown. Values for ΔH and other parameters quoted as mean ± standard deviation (SD). KD values were only fit for titrations in which c ([sites]/KD) was less than 250. Titrations where c > 250 were used for ΔH determination only.
FA
EGF was labeled using the Alexa Fluor 488 Protein Labeling Kit from Molecular Probes (Eugene, OR). Labeled EGF (EGF488) at 10 nM (for sEGFR-Fc and sEGFR-Zip) or 60 nM (for sEGFRwild-type) was incubated with varying amounts of sEGFR protein for 30 minutes at room temperature in 20 mM HEPES, pH 8.0, containing 150 mM NaCl. Fluorescence polarization (FP) measurements were taken on a Beacon instrument at 20°C, converted to anisotropy, and analyzed as described in Supplemental Experimental Procedures. Three independent titrations were performed for each receptor variant.
SPR and AUC
SPR and AUC experiments were performed as previously reported (Dawson et al., 2005), with details provided in Supplemental Experimental Procedures.
Electron microscopy (EM)
Receptor samples at a concentration of 2 μg/ml in 25 mM HEPES, pH 8.0, containing 150 mM NaCl were applied to glow-discharged carbon grids and stained with 0.75% uranyl formate. Images were collected on a Tecnai T12 microscope at 67,000x magnification and operating at 120 keV, and were analyzed as described in Supplemental Experimental Procedures.
Small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS)
Protein samples were prepared for SAXS at concentrations of 10–20 μM in 25 mM HEPES, pH 8.0, containing 150 mM NaCl, and 40 minute exposures at 4°C were performed on a Rigaku S-MAX3000 pinhole camera system, with a Rigaku 007HF rotating anode source and a Rigaku 300 mm wire grid ASM DTR 200 detector. Data were processed as described in Supplemental Experimental Procedures.
Supplementary Material
Figure S1, related to Figure 2. Analysis of molecular mass of EGFR-Fc and sEGFR-Zip.
(A) Sedimentation equilibrium AUC data, showing single-species fits for data obtained with sEGFR-Fc alone at 10 μM at a speed of 10000 r.p.m. Data were fit using Sedphat (Schuck, 2003) and yielded an excellent fit – with small random residuals – to a single species of 223 kDa. This compares well with the expected mass of an sEGFR-Fc dimer (190 kDa plus ~20% w/w carbohydrate). (B) An equivalent experiment to that shown in A for sEGFR-Fc, but with the addition of a 1.2-fold molar excess of TGFα. The best-fit molecular mass is unchanged (at 225 kDa), showing that the dimeric sEGFR-Fc is not further oligomerized upon ligand binding. (C) Size exclusion chromatography analysis of sEGFRwild-type (black curve), sEGFR-Zip (blue curve), and sEGFR-Fc (orange curve), injected onto a Superose 6 column at a concentration of 10 μM. The receptor elution volumes reveal that sEGFR-Fc and sEGFR-Zip are both dimers, while sEGFRwild-type is monomeric as expected.
Figure S2, related to Figure 2. ITC of EGF binding to domain III, and EGF/sEGFR dimer dissociation.
(A) EGF was titrated into 10 μM sEGFR domain III purified as described (Lemmon et al., 1997). Fitting to a single binding-site model yielded a KD value of 3.1 ± 2.6 μM, and a ΔH for EGF binding of −4.5 ± 1.0 kcal/mol. (B) To assess the enthalpy associated with dimerization of liganded sEGFR, a dilution experiment was performed in which 17.5 μM sEGFRwild-type to which a 1.3-fold molar excess of EGF had been added was diluted by injection into an ITC cell containing only buffer. 13 injections of 3 μl each were made, allowing measurement of dissociation heats in the ITC cell over an equilibrium concentration range of ~0.2 – 2.4 μM for the EGF/sEGFRwild-type complex. Importantly, EGF dissociation from sEGFRwild-type will be negligible over this concentration range. Because the heat of injection does not change systematically from the first injection to the last, and because the integrated heat of each injection is so low (and can not be distinguished from instrumental noise), we conclude that the ΔH for dimerization of EGF-bound sEGFRwild-type must be ≪|2| kcal/mol.
The titrations in Figures 2B and 2C fit very well to a single entropy-driven (positive ΔH) ligand binding event. In our 1997 studies (Lemmon et al., 1997), which pre-dated structures of sEGFR, we inferred that this entropy-driven event reflects sEGFR dimerization, and that ligand binding has a small negative ΔH (based on studies of EGF binding to isolated domain III, repeated in A). Our new finding that the major entropy-driven event is unaffected by mutations that abolish sEGFR dimerization proves this wrong. Moreover, based on calorimetric dissociation experiments (B) we find that dimerization of ligand-bound sEGFRwild-type has a negligible ΔH. Thus, EGF binding is entropy driven, consistent with another recent report (Alvarenga et al., 2012).
Figure S3, related to Figure 2. TGFα binding to sEGFR and sEGFR-Fc variants.
(A) Representative ITC analysis of TGFα binding to sEGFRwild-type at 25°C. TGFα was present in the syringe at 70 μM, and sEGFRwild-type was present in the calorimeter cell at a concentration of 8 μM. Mean values (± standard deviation) for KD and ΔH for TGFα binding from three independent experiments are listed in the figure. (B) Equivalent experiment to that shown in A for sEGFRY251A/R285S. (C) SPR analysis of TGFα binding to sEGFR-Fc with wild-type domain II or with the Y251A/R285S mutations in the domain II dimerization interface. Note that, whereas these mutations had no effect on EGF binding to sEGFR-Fc, they appear to reduce TGFα binding by ~6-fold, possibly suggesting a slightly different dependence on dimerization for binding of the two ligands – consistent with the observed structural differences in EGF/sEGFR and TGFα/sEGFR complexes (Liu et al., 2012; Wilson et al., 2009). (D) ITC analysis of TGFα binding to sEGFR-Fc. TGFα was present in the syringe at 70 μM, and sEGFR-Fc was present in the calorimeter cell at 9 μM. As with EGF binding, TGFα binding to sEGFR-Fc has a higher (positive or unfavorable) enthalpy than binding to sEGFRwild-type – by 2.8 kcal/mol (compared with 3.4 kcal/mol in the EGF case) – affinity is increased due to entropic effects.
Figure S4, related to Figure 4. Example raw EM images for sEGFR-Fc plus and minus ligand.
Examples of raw image files are shown, from EM studies of negatively stained samples, for sEGFR-Fc plus EGF (left panel) and without ligand (right panel). 150 images such as these were used for single-particle analysis as described in Supplemental Experimental Procedures. Example particles are enclosed in green boxes in each representative image. A 50 nm scale bar is shown.
Figure S5, related to Figure 6. TGFα binding to sEGFR variants harboring glioblastoma mutations.
Binding of each glioblastoma-mutated sEGFR variant to TGFα was analyzed by SPR, using the same approach described for EGF binding in Figure 6B, but with immobilized TGFα instead of EGF. Best fit KD values (± SD) for TGFα binding (from three independent experiments) were 532 ± 39 nM (sEGFRwild-type); 8.6 ± 1.5 nM (sEGFRR84K); 90 ± 10 nM (sEGFRA265V); and 55 ± 7 nM (sEGFRA265D). Glioblastoma mutations in EGFR thus enhance TGFα binding to the isolated ECR by 6–62 fold.
Figure S6, related to Figure 6. ITC studies of EGF binding to sEGFR with tether-disrupting mutations.
(A) EGF was titrated at 25°C into a cell containing 10 μM sEGFR(501), a variant of sEGFR that lacks essentially all of domain IV (Elleman et al., 2001), so cannot make the intramolecular tether. KD for EGF binding to this variant is 7.8 nM (Dawson et al., 2005), and ΔH is 2.2 ± 0.5 kcal/mol. (B) The Δ575–584 mutation deletes a prominent loop from the fifth disulfide-bonded module of domain IV in sEGFR, removing a loop that interacts with the dimerization arm in the tethered sEGFR structure – and thus weakening the tether (Dawson et al., 2005). KD for EGF binding to this variant is 32 nM (Dawson et al., 2005), and ΔH is 2.7 ± 0.3 kcal/mol. (C) The 246–253* mutation was initially described by Garrett et al. (2002), and includes the following 6 mutations, designed to break dimerization arm contacts: Y246E, N247A, T249D, Y251E, Q252A, and M253D. These mutations disrupt the intramolecular tether shown in Figure 1A and the dimerization contacts in Figure 1C. KD for EGF binding to this variant is 260 nM by SPR (Dawson et al., 2005), and ΔH is 3.3 ± 0.3 kcal/mol. (D) The 246–253*/Δ575–584/D563A/H566A/K585A-mutated variant includes all of the changes in the other tether mutations described here, and also includes mutations of D563, H566, and K585 in domain IV to alanine. These residues contribute directly to the domain II/IV tether. Thus, this variant has all tether contacts as well as the dimerization site mutated. ΔH for EGF binding to this variant is 2.5 ± 0.3 kcal/mol. Errors are SDs.
Table S1, related to Table 1. ITC data for TGFα binding to sEGFR variants.
Acknowledgments
We thank Dewight Williams of the Penn Medicine Electron Microscopy Resource Laboratory for guidance with EM, Kushol Gupta and Steve Stayrook for advice with SAXS and AUC, and members of the Lemmon and Ferguson laboratories for discussions. This work was funded in part by National Cancer Institute grants R01-CA079992 (to MAL) and R01-CA112552 (to KMF). NJB and AB were supported in part by a Training Grant in Structural Biology from the National Institutes of Health (T32-GM008275), and NJB received support from a Predoctoral Fellowship from the Great Rivers Affiliate of the American Heart Association (10PRE4140108).
Footnotes
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
NJB, MAL and KMF conceived of the overall study. NJB performed all experimental work except studies of sEGFR variants harboring glioblastoma-derived mutations, which were performed by AB. All authors interpreted results. NJB wrote a first draft of the manuscript, which was rewritten by MAL and NJB, with additional edits from KMF and AB.
Supplementary Information is available at Cell Reports Online
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final citable form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
References
- Adak S, Yang KS, Macdonald-Obermann J, Pike LJ. The membrane-proximal intracellular domain of the epidermal growth factor receptor underlies negative cooperativity in ligand binding. J Biol Chem. 2011;286:45146–45155. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.274175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams TE, Koziolek EJ, Hoyne PH, Bentley JD, Lu L, Lovrecz G, Ward CW, Lee FT, Scott AM, Nash AD, et al. A truncated soluble epidermal growth factor receptor-Fc fusion ligand trap displays anti-tumour activity in vivo. Growth Factors. 2009;27:141–154. doi: 10.1080/08977190902843565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alvarado D, Klein DE, Lemmon MA. ErbB2/HER2/Neu resembles an autoinhibited invertebrate EGF receptor. Nature. 2009;461:287–291. doi: 10.1038/nature08297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alvarado D, Klein DE, Lemmon MA. Structural basis for negative cooperativity in growth factor binding to an EGF receptor. Cell. 2010;142:568–579. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.07.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arkhipov A, Shan Y, Das R, Endres NF, Eastwood MP, Wemmer DE, Kuriyan J, Shaw DE. Architecture and membrane interactions of the EGF receptor. Cell. 2013;152:557–569. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.12.030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bass J, Kurose T, Pashmforoush M, Steiner DF. Fusion of insulin receptor ectodomains to immunoglobulin constant domains reproduces high-affinity insulin binding in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:19367–19375. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.32.19367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bessman NJ, Lemmon MA. Finding the missing links in EGFR. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2012;19:1–3. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan CW, Verhaak RG, McKenna A, Campos B, Noushmehr H, Salama SR, Zheng S, Chakravarty D, Sanborn JZ, Berman SH, et al. The somatic genomic landscape of glioblastoma. Cell. 2013;155:462–477. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.09.034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess AW, Cho HS, Eigenbrot C, Ferguson KM, Garrett TPJ, Leahy DJ, Lemmon MA, Sliwkowski MX, Ward CW, Yokoyama S. An open-and-shut case? Recent insights into the activation of EGF/ErbB receptors. Mol Cell. 2003;12:541–552. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(03)00350-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chantry A. The kinase domain and membrane localization determine intracellular interactions between epidermal growth factor receptors. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:3068–3073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson JP, Berger MB, Lin D, Schlessinger J, Lemmon MA, Ferguson KM. EGF receptor dimerization and activation require ligand-induced conformational changes in the dimer interface. Mol Cell Biol. 2005;25:7734–7742. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.17.7734-7742.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson JP, Bu Z, Lemmon MA. Ligand-induced structural transitions in ErbB receptor extracellular domains. Structure. 2007;15:942–954. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2007.06.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Meyts P. The insulin receptor: a prototype for dimeric, allosteric membrane receptors? Trends Biochem Sci. 2008;33:376–384. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2008.06.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Defize LH, Boonstra J, Meisenhelder J, Kruijer W, Tertoolen LG, Tilly BC, Hunter T, van Bergen en Henegouwen PM, Moolenaar WH, de Laat SW. Signal transduction by epidermal growth factor occurs through the subclass of high affinity receptors. J Cell Biol. 1989;109:2495–2507. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.5.2495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elleman TC, Domagala T, McKern NM, Nerrie M, Lonnqvist B, Adams TE, Lewis J, Lovrecz GO, Hoyne PA, Richards KM, et al. Identification of a determinant of epidermal growth factor receptor ligand-binding specificity using a truncated, high-affinity form of the ectodomain. Biochemistry. 2001;40:8930–8939. doi: 10.1021/bi010037b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endres NF, Das R, Smith AW, Arkhipov A, Kovacs E, Huang Y, Pelton JG, Shan Y, Shaw DE, Wemmer DE, et al. Conformational coupling across the plasma membrane in activation of the EGF receptor. Cell. 2013;152:543–556. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.12.032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson KM, Berger MB, Mendrola JM, Cho HS, Leahy DJ, Lemmon MA. EGF activates its receptor by removing interactions that autoinhibit ectodomain dimerization. Mol Cell. 2003;11:507–517. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(03)00047-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson KM, Darling PJ, Mohan MJ, Macatee TL, Lemmon MA. Extracellular domains drive homo- but not hetero-dimerization of erbB receptors. EMBO J. 2000;19:4632–4643. doi: 10.1093/emboj/19.17.4632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrett TPJ, McKern NM, Lou M, Elleman TC, Adams TE, Lovrecz GO, Zhu HJ, Walker F, Frenkel MJ, Hoyne PA, et al. Crystal structure of a truncated epidermal growth factor receptor domain bound to transforming growth factor alpha. Cell. 2002;110:763–773. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(02)00940-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graus-Porta D, Beerli RR, Daly JM, Hynes NE. ErbB-2, the preferred heterodimerization partner of all ErbB receptors, is a mediator of lateral signaling. EMBO J. 1997;16:1647–1655. doi: 10.1093/emboj/16.7.1647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyne PA, Cosgrove LJ, McKern NM, Bentley JD, Ivancic N, Elleman TC, Ward CW. High affinity insulin binding by soluble insulin receptor extracellular domain fused to a leucine zipper. FEBS Letts. 2000;479:15–18. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(00)01872-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaiswal BS, Kljavin NM, Stawiski EW, Chan E, Parikh C, Durinck S, Chaudhuri S, Pujara K, Guillory J, Edgar KA, et al. Oncogenic ERBB3 mutations in human cancers. Cancer Cell. 2013;23:603–617. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2013.04.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones JT, Akita RW, Sliwkowski MX. Binding specificities and affinities of egf domains for ErbB receptors. FEBS Letters. 1999;447:227–231. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(99)00283-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jura N, Endres NF, Engel K, Deindl S, Das R, Lamers MH, Wemmer DE, Zhang X, Kuriyan J. Mechanism for activation of the EGF receptor catalytic domain by the juxtamembrane segment. Cell. 2009;137:1293–1307. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.04.025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lax I, Mitra AK, Ravera C, Hurwitz DR, Rubinstein M, Ullrich A, Stroud RM, Schlessinger J. Epidermal growth factor (EGF) induces oligomerization of soluble, extracellular, ligand-binding domain of EGF receptor. A low resolution projection structure of the ligand-binding domain. J Biol Chem. 1991;266:13828–13833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee JC, Vivanco I, Beroukhim R, Huang JH, Feng WL, DeBiasi RM, Yoshimoto K, King JC, Nghiemphu P, Yuza Y, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor activation in glioblastoma through novel missense mutations in the extracellular domain. PLoS Med. 2006;3:e485. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0030485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemmon MA, Bu Z, Ladbury JE, Zhou M, Pinchasi D, Lax I, Engelman DM, Schlessinger J. Two EGF molecules contribute additively to stabilization of the EGFR dimer. EMBO J. 1997;16:281–294. doi: 10.1093/emboj/16.2.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemmon MA, Schlessinger J, Ferguson KM. The EGFR family: not so prototypical receptor tyrosine kinases. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2014;6:a020768. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a020768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li S, Schmitz KR, Jeffrey PD, Wiltzius JJ, Kussie P, Ferguson KM. Structural basis for inhibition of the epidermal growth factor receptor by cetuximab. Cancer Cell. 2005;7:301–311. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2005.03.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y, Macdonald-Obermann J, Westfall C, Piwnica-Worms D, Pike LJ. Quantitation of the effect of ErbB2 on epidermal growth factor receptor binding and dimerization. J Biol Chem. 2012;287:31116–31125. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.373647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu P, Cleveland TEt, Bouyain S, Byrne PO, Longo PA, Leahy DJ. A single ligand is sufficient to activate EGFR dimers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2012;109:10861–10866. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1201114109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingstone JR, Spolar RS, Record MT., Jr Contribution to the thermodynamics of protein folding from the reduction in water-accessible nonpolar surface area. Biochemistry. 1991;30:4237–4244. doi: 10.1021/bi00231a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu C, Mi LZ, Grey MJ, Zhu J, Graef E, Yokoyama S, Springer TA. Structural evidence for loose linkage between ligand binding and kinase activation in the epidermal growth factor receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 2010;30:5432–5443. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00742-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu C, Mi LZ, Schurpf T, Walz T, Springer TA. Mechanisms for kinase-mediated dimerization of the epidermal growth factor receptor. J Biol Chem. 2012;287:38244–38253. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.414391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald JL, Pike LJ. Heterogeneity in EGF-binding affinities arises from negative cooperativity in an aggregating system. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105:112–117. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0707080105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald-Obermann JL, Pike LJ. The intracellular juxtamembrane domain of the epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor is responsible for the allosteric regulation of EGF binding. J Biol Chem. 2009;284:13570–13576. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.001487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magun BE, Matrisian LM, Bowden GT. Epidermal growth factor. Ability of tumor promoter to alter its degradation, receptor affinity and receptor number. J Biol Chem. 1980;255:6373–6381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattoon D, Klein P, Lemmon MA, Lax I, Schlessinger J. The tethered configuration of the EGF receptor extracellular domain exerts only a limited control of receptor function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:923–928. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0307286101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mi LZ, Lu C, Li Z, Nishida N, Walz T, Springer TA. Simultaneous visualization of the extracellular and cytoplasmic domains of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2011;18:984–989. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogiso H, Ishitani R, Nureki O, Fukai S, Yamanaka M, Kim JH, Saito K, Sakamoto A, Inoue M, Shirouzu M, et al. Crystal structure of the complex of human epidermal growth factor and receptor extracellular domains. Cell. 2002;110:775–787. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(02)00963-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Red Brewer M, Choi SH, Alvarado D, Moravcevic K, Pozzi A, Lemmon MA, Carpenter G. The juxtamembrane region of the EGF receptor functions as an activation domain. Mol Cell. 2009;34:641–651. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2009.04.034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surinya KH, Forbes BE, Occhiodoro F, Booker GW, Francis GL, Siddle K, Wallace JC, Cosgrove LJ. An investigation of the ligand binding properties and negative cooperativity of soluble insulin-like growth factor receptors. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:5355–5363. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M707054200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vivanco I, Robins HI, Rohle D, Campos C, Grommes C, Nghiemphu PL, Kubek S, Oldrini B, Chheda MG, Yannuzzi N, et al. Differential sensitivity of glioma- versus lung cancer-specific EGFR mutations to EGFR kinase inhibitors. Cancer Disc. 2012;2:458–471. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-11-0284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker F, Orchard SG, Jorissen RN, Hall NE, Zhang HH, Hoyne PA, Adams TE, Johns TG, Ward C, Garrett TPJ, et al. CR1/CR2 interactions modulate the functions of the cell surface epidermal growth factor receptor. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:22387–22398. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M401244200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson KJ, Gilmore JL, Foley J, Lemmon MA, Riese DJ., 2nd Functional selectivity of EGF family peptide growth factors: implications for cancer. Pharmacol Ther. 2009;122:1–8. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2008.11.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Figure S1, related to Figure 2. Analysis of molecular mass of EGFR-Fc and sEGFR-Zip.
(A) Sedimentation equilibrium AUC data, showing single-species fits for data obtained with sEGFR-Fc alone at 10 μM at a speed of 10000 r.p.m. Data were fit using Sedphat (Schuck, 2003) and yielded an excellent fit – with small random residuals – to a single species of 223 kDa. This compares well with the expected mass of an sEGFR-Fc dimer (190 kDa plus ~20% w/w carbohydrate). (B) An equivalent experiment to that shown in A for sEGFR-Fc, but with the addition of a 1.2-fold molar excess of TGFα. The best-fit molecular mass is unchanged (at 225 kDa), showing that the dimeric sEGFR-Fc is not further oligomerized upon ligand binding. (C) Size exclusion chromatography analysis of sEGFRwild-type (black curve), sEGFR-Zip (blue curve), and sEGFR-Fc (orange curve), injected onto a Superose 6 column at a concentration of 10 μM. The receptor elution volumes reveal that sEGFR-Fc and sEGFR-Zip are both dimers, while sEGFRwild-type is monomeric as expected.
Figure S2, related to Figure 2. ITC of EGF binding to domain III, and EGF/sEGFR dimer dissociation.
(A) EGF was titrated into 10 μM sEGFR domain III purified as described (Lemmon et al., 1997). Fitting to a single binding-site model yielded a KD value of 3.1 ± 2.6 μM, and a ΔH for EGF binding of −4.5 ± 1.0 kcal/mol. (B) To assess the enthalpy associated with dimerization of liganded sEGFR, a dilution experiment was performed in which 17.5 μM sEGFRwild-type to which a 1.3-fold molar excess of EGF had been added was diluted by injection into an ITC cell containing only buffer. 13 injections of 3 μl each were made, allowing measurement of dissociation heats in the ITC cell over an equilibrium concentration range of ~0.2 – 2.4 μM for the EGF/sEGFRwild-type complex. Importantly, EGF dissociation from sEGFRwild-type will be negligible over this concentration range. Because the heat of injection does not change systematically from the first injection to the last, and because the integrated heat of each injection is so low (and can not be distinguished from instrumental noise), we conclude that the ΔH for dimerization of EGF-bound sEGFRwild-type must be ≪|2| kcal/mol.
The titrations in Figures 2B and 2C fit very well to a single entropy-driven (positive ΔH) ligand binding event. In our 1997 studies (Lemmon et al., 1997), which pre-dated structures of sEGFR, we inferred that this entropy-driven event reflects sEGFR dimerization, and that ligand binding has a small negative ΔH (based on studies of EGF binding to isolated domain III, repeated in A). Our new finding that the major entropy-driven event is unaffected by mutations that abolish sEGFR dimerization proves this wrong. Moreover, based on calorimetric dissociation experiments (B) we find that dimerization of ligand-bound sEGFRwild-type has a negligible ΔH. Thus, EGF binding is entropy driven, consistent with another recent report (Alvarenga et al., 2012).
Figure S3, related to Figure 2. TGFα binding to sEGFR and sEGFR-Fc variants.
(A) Representative ITC analysis of TGFα binding to sEGFRwild-type at 25°C. TGFα was present in the syringe at 70 μM, and sEGFRwild-type was present in the calorimeter cell at a concentration of 8 μM. Mean values (± standard deviation) for KD and ΔH for TGFα binding from three independent experiments are listed in the figure. (B) Equivalent experiment to that shown in A for sEGFRY251A/R285S. (C) SPR analysis of TGFα binding to sEGFR-Fc with wild-type domain II or with the Y251A/R285S mutations in the domain II dimerization interface. Note that, whereas these mutations had no effect on EGF binding to sEGFR-Fc, they appear to reduce TGFα binding by ~6-fold, possibly suggesting a slightly different dependence on dimerization for binding of the two ligands – consistent with the observed structural differences in EGF/sEGFR and TGFα/sEGFR complexes (Liu et al., 2012; Wilson et al., 2009). (D) ITC analysis of TGFα binding to sEGFR-Fc. TGFα was present in the syringe at 70 μM, and sEGFR-Fc was present in the calorimeter cell at 9 μM. As with EGF binding, TGFα binding to sEGFR-Fc has a higher (positive or unfavorable) enthalpy than binding to sEGFRwild-type – by 2.8 kcal/mol (compared with 3.4 kcal/mol in the EGF case) – affinity is increased due to entropic effects.
Figure S4, related to Figure 4. Example raw EM images for sEGFR-Fc plus and minus ligand.
Examples of raw image files are shown, from EM studies of negatively stained samples, for sEGFR-Fc plus EGF (left panel) and without ligand (right panel). 150 images such as these were used for single-particle analysis as described in Supplemental Experimental Procedures. Example particles are enclosed in green boxes in each representative image. A 50 nm scale bar is shown.
Figure S5, related to Figure 6. TGFα binding to sEGFR variants harboring glioblastoma mutations.
Binding of each glioblastoma-mutated sEGFR variant to TGFα was analyzed by SPR, using the same approach described for EGF binding in Figure 6B, but with immobilized TGFα instead of EGF. Best fit KD values (± SD) for TGFα binding (from three independent experiments) were 532 ± 39 nM (sEGFRwild-type); 8.6 ± 1.5 nM (sEGFRR84K); 90 ± 10 nM (sEGFRA265V); and 55 ± 7 nM (sEGFRA265D). Glioblastoma mutations in EGFR thus enhance TGFα binding to the isolated ECR by 6–62 fold.
Figure S6, related to Figure 6. ITC studies of EGF binding to sEGFR with tether-disrupting mutations.
(A) EGF was titrated at 25°C into a cell containing 10 μM sEGFR(501), a variant of sEGFR that lacks essentially all of domain IV (Elleman et al., 2001), so cannot make the intramolecular tether. KD for EGF binding to this variant is 7.8 nM (Dawson et al., 2005), and ΔH is 2.2 ± 0.5 kcal/mol. (B) The Δ575–584 mutation deletes a prominent loop from the fifth disulfide-bonded module of domain IV in sEGFR, removing a loop that interacts with the dimerization arm in the tethered sEGFR structure – and thus weakening the tether (Dawson et al., 2005). KD for EGF binding to this variant is 32 nM (Dawson et al., 2005), and ΔH is 2.7 ± 0.3 kcal/mol. (C) The 246–253* mutation was initially described by Garrett et al. (2002), and includes the following 6 mutations, designed to break dimerization arm contacts: Y246E, N247A, T249D, Y251E, Q252A, and M253D. These mutations disrupt the intramolecular tether shown in Figure 1A and the dimerization contacts in Figure 1C. KD for EGF binding to this variant is 260 nM by SPR (Dawson et al., 2005), and ΔH is 3.3 ± 0.3 kcal/mol. (D) The 246–253*/Δ575–584/D563A/H566A/K585A-mutated variant includes all of the changes in the other tether mutations described here, and also includes mutations of D563, H566, and K585 in domain IV to alanine. These residues contribute directly to the domain II/IV tether. Thus, this variant has all tether contacts as well as the dimerization site mutated. ΔH for EGF binding to this variant is 2.5 ± 0.3 kcal/mol. Errors are SDs.
Table S1, related to Table 1. ITC data for TGFα binding to sEGFR variants.