Abstract
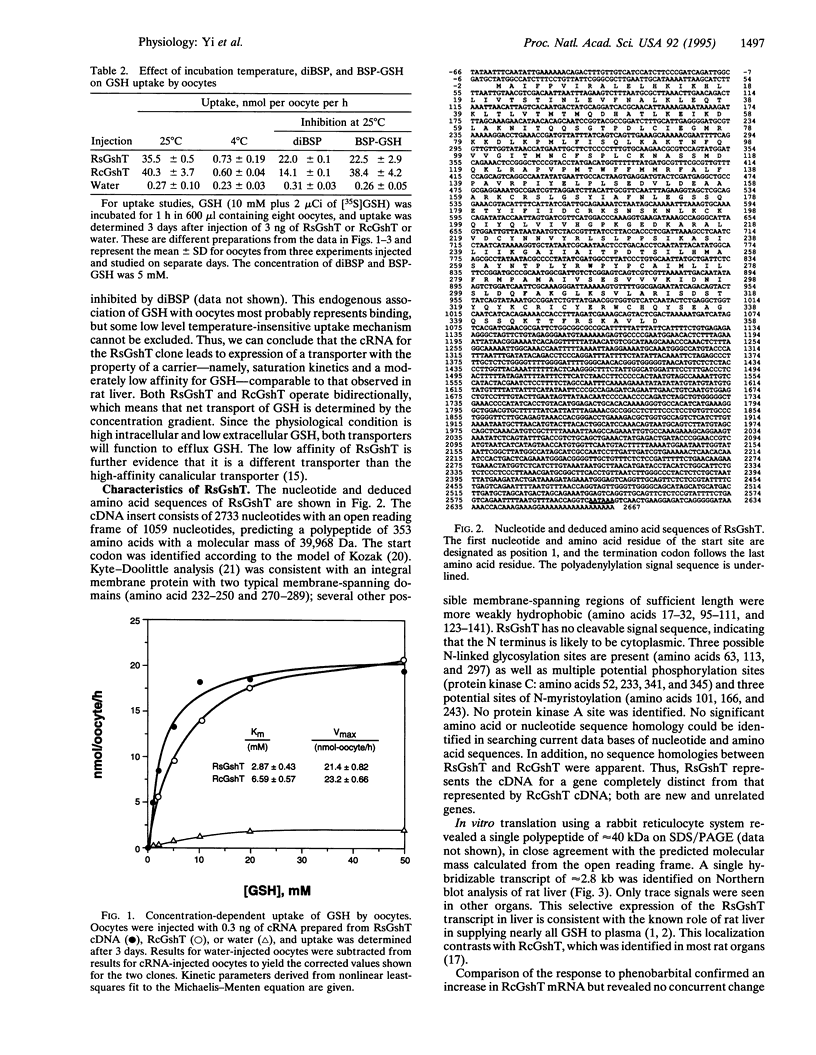
Using the Xenopus oocyte expression system, we previously identified an approximately 4-kb fraction of mRNA from rat liver that expresses sulfobromophthalein reduced glutathione S-conjugate (BSP-GSH)-insensitive and an approximately 2.5-kb fraction expressing BSP-GSH-sensitive reduced glutathione (GSH) transport. From the former, a 4.05-kb cDNA was cloned and characterized as the putative rat canalicular GSH transporter. Starting with a cDNA library constructed from the approximately 2.5-kb fraction, we have now isolated a single clone that leads to expression of a BSP-GSH- and cystathionine-inhibitable GSH transporter activity with Km approximately 3 mM characteristic of the sinusoidal GSH transporter. The cDNA for the rat sinusoidal GSH transporter-associated polypeptide (RsGshT) is 2733 bases with an open reading frame of 1059 nucleotides encoding a polypeptide of 353 amino acids (39,968 Da) with two putative membrane-spanning domains. No identifiable homologies were found in searching various data bases. An approximately 40-kDa protein is generated in in vitro translation of cRNA for RsGshT. Northern blot analysis revealed a single approximately 2.8-kb transcript in rat and human liver with negligible hybridization signal in other organs. The abundance of mRNA for RsGshT did not increase with phenobarbital treatment. Cis-inhibition by BSP-GSH and trans-inhibition by cystathionine and lack of induction by phenobarbital are characteristic of sinusoidal GSH secretion and thus indicate that RsGshT either encodes the sinusoidal GSH transporter itself or a regulatory subunit of the transporter that determines its liver-specific activity.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aw T. Y., Ookhtens M., Kaplowitz N. Inhibition of glutathione efflux from isolated rat hepatocytes by methionine. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 10;259(15):9355–9358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aw T. Y., Ookhtens M., Kaplowitz N. Mechanism of inhibition of glutathione efflux by methionine from isolated rat hepatocytes. Am J Physiol. 1986 Sep;251(3 Pt 1):G354–G361. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1986.251.3.G354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballatori N., Dutczak W. J. Identification and characterization of high and low affinity transport systems for reduced glutathione in liver cell canalicular membranes. J Biol Chem. 1994 Aug 5;269(31):19731–19737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertran J., Werner A., Moore M. L., Stange G., Markovich D., Biber J., Testar X., Zorzano A., Palacin M., Murer H. Expression cloning of a cDNA from rabbit kidney cortex that induces a single transport system for cystine and dibasic and neutral amino acids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5601–5605. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgunder J. M., Lauterburg B. H. Decreased production of glutathione in patients with cirrhosis. Eur J Clin Invest. 1987 Oct;17(5):408–414. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1987.tb01135.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canessa C. M., Horisberger J. D., Rossier B. C. Epithelial sodium channel related to proteins involved in neurodegeneration. Nature. 1993 Feb 4;361(6411):467–470. doi: 10.1038/361467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dröge W., Eck H. P., Näher H., Pekar U., Daniel V. Abnormal amino-acid concentrations in the blood of patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) may contribute to the immunological defect. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1988 Mar;369(3):143–148. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1988.369.1.143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutczak W. J., Ballatori N. Transport of the glutathione-methylmercury complex across liver canalicular membranes on reduced glutathione carriers. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 1;269(13):9746–9751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Checa J. C., Maddatu T., Ookhtens M., Kaplowitz N. Inhibition of GSH efflux from rat liver by methionine: effects of GSH synthesis in cells and perfused organ. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jun;258(6 Pt 1):G967–G973. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1990.258.6.G967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Checa J. C., Ookhtens M., Kaplowitz N. Selective induction by phenobarbital of the electrogenic transport of glutathione and organic anions in rat liver canalicular membrane vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 25;268(15):10836–10841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Checa J. C., Takikawa H., Horie T., Ookhtens M., Kaplowitz N. Canalicular transport of reduced glutathione in normal and mutant Eisai hyperbilirubinemic rats. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 25;267(3):1667–1673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Checa J. C., Yi J. R., Garcia-Ruiz C., Knezic Z., Tahara S. M., Kaplowitz N. Expression of rat liver reduced glutathione transport in Xenopus laevis oocytes. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 5;268(4):2324–2328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García-Ruiz C., Fernández-Checa J. C., Kaplowitz N. Bidirectional mechanism of plasma membrane transport of reduced glutathione in intact rat hepatocytes and membrane vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 5;267(31):22256–22264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho K., Nichols C. G., Lederer W. J., Lytton J., Vassilev P. M., Kanazirska M. V., Hebert S. C. Cloning and expression of an inwardly rectifying ATP-regulated potassium channel. Nature. 1993 Mar 4;362(6415):31–38. doi: 10.1038/362031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaeschke H. Enhanced sinusoidal glutathione efflux during endotoxin-induced oxidant stress in vivo. Am J Physiol. 1992 Jul;263(1 Pt 1):G60–G68. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1992.263.1.G60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplowitz N., Aw T. Y., Ookhtens M. The regulation of hepatic glutathione. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1985;25:715–744. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.25.040185.003435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplowitz N., Eberle D. E., Petrini J., Touloukian J., Corvasce M. C., Kuhlenkamp J. Factors influencing the efflux of hepatic glutathione into bile in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Jan;224(1):141–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of 5'-noncoding sequences from 699 vertebrate messenger RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8125–8148. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubo Y., Baldwin T. J., Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y. Primary structure and functional expression of a mouse inward rectifier potassium channel. Nature. 1993 Mar 11;362(6416):127–133. doi: 10.1038/362127a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meister A., Anderson M. E. Glutathione. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:711–760. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.003431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosckovitz R., Udenfriend S., Felix A., Heimer E., Tate S. S. Membrane topology of the rat kidney neutral and basic amino acid transporter. FASEB J. 1994 Oct;8(13):1069–1074. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.8.13.7926373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ookhtens M., Hobdy K., Corvasce M. C., Aw T. Y., Kaplowitz N. Sinusoidal efflux of glutathione in the perfused rat liver. Evidence for a carrier-mediated process. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jan;75(1):258–265. doi: 10.1172/JCI111682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ookhtens M., Lyon I., Fernandez-Checa J., Kaplowitz N. Inhibition of glutathione efflux in the perfused rat liver and isolated hepatocytes by organic anions and bilirubin. Kinetics, sidedness, and molecular forms. J Clin Invest. 1988 Aug;82(2):608–616. doi: 10.1172/JCI113639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ookhtens M., Mittur A. V. Developmental changes in plasma thiol-disulfide turnover in rats: a multicompartmental approach. Am J Physiol. 1994 Aug;267(2 Pt 2):R415–R425. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1994.267.2.R415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ookhtens M., Mittur A. V., Erhart N. A. Changes in plasma glutathione concentrations, turnover, and disposal in developing rats. Am J Physiol. 1994 Mar;266(3 Pt 2):R979–R988. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1994.266.3.R979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sippel C. J., Suchy F. J., Ananthanarayanan M., Perlmutter D. H. The rat liver ecto-ATPase is also a canalicular bile acid transport protein. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 25;268(3):2083–2091. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder P. M., McDonald F. J., Stokes J. B., Welsh M. J. Membrane topology of the amiloride-sensitive epithelial sodium channel. J Biol Chem. 1994 Sep 30;269(39):24379–24383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staal F. J., Ela S. W., Roederer M., Anderson M. T., Herzenberg L. A., Herzenberg L. A. Glutathione deficiency and human immunodeficiency virus infection. Lancet. 1992 Apr 11;339(8798):909–912. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)90939-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells R. G., Hediger M. A. Cloning of a rat kidney cDNA that stimulates dibasic and neutral amino acid transport and has sequence similarity to glucosidases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5596–5600. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yi J. R., Lu S., Fernandez-Checa J., Kaplowitz N. Expression cloning of a rat hepatic reduced glutathione transporter with canalicular characteristics. J Clin Invest. 1994 Apr;93(4):1841–1845. doi: 10.1172/JCI117170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]