Abstract
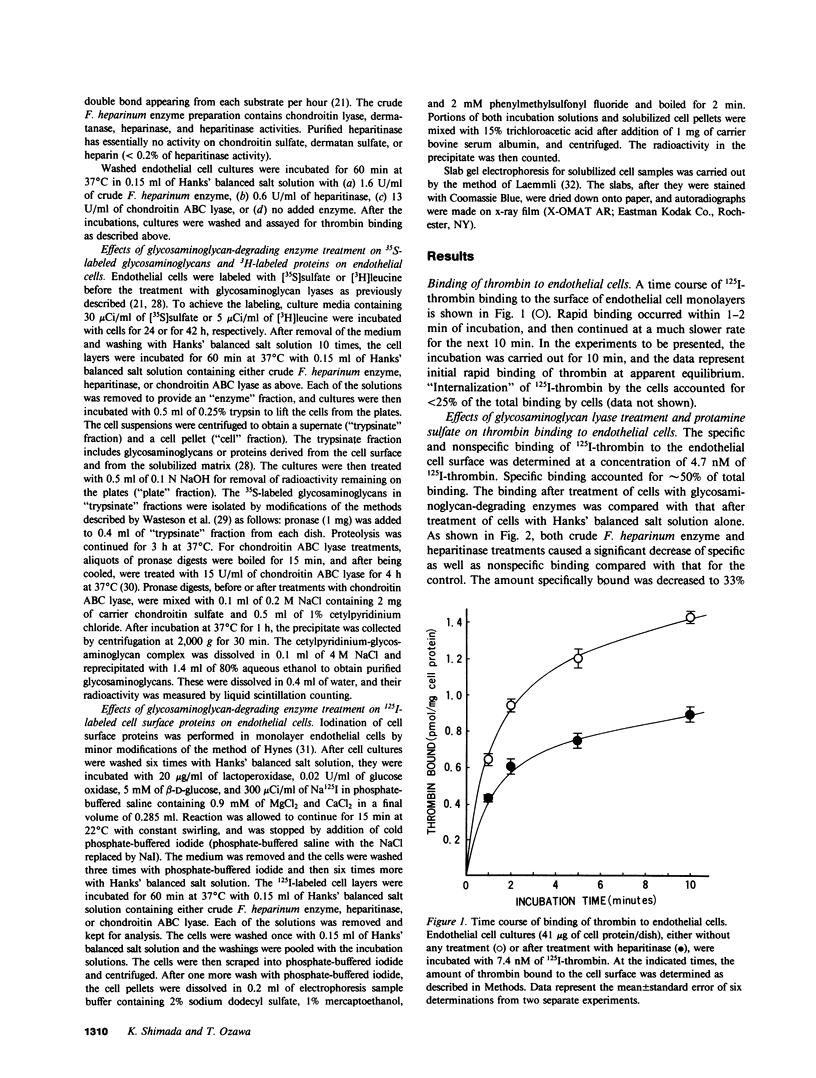
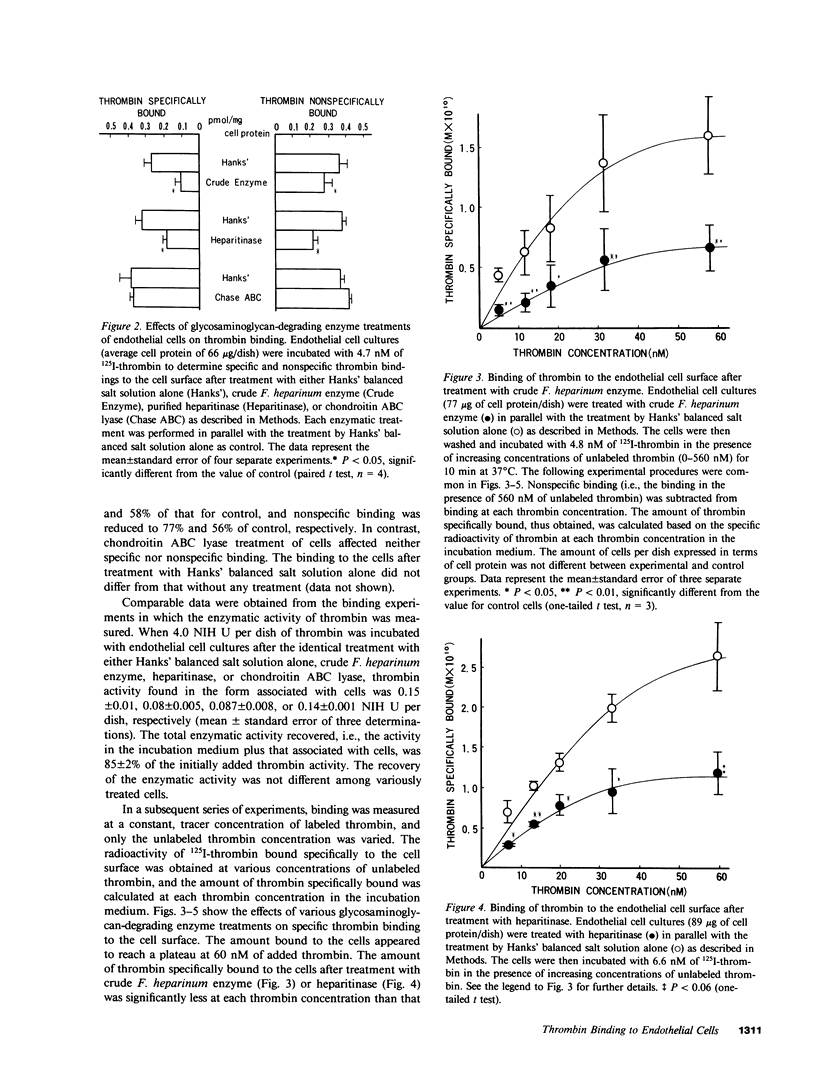
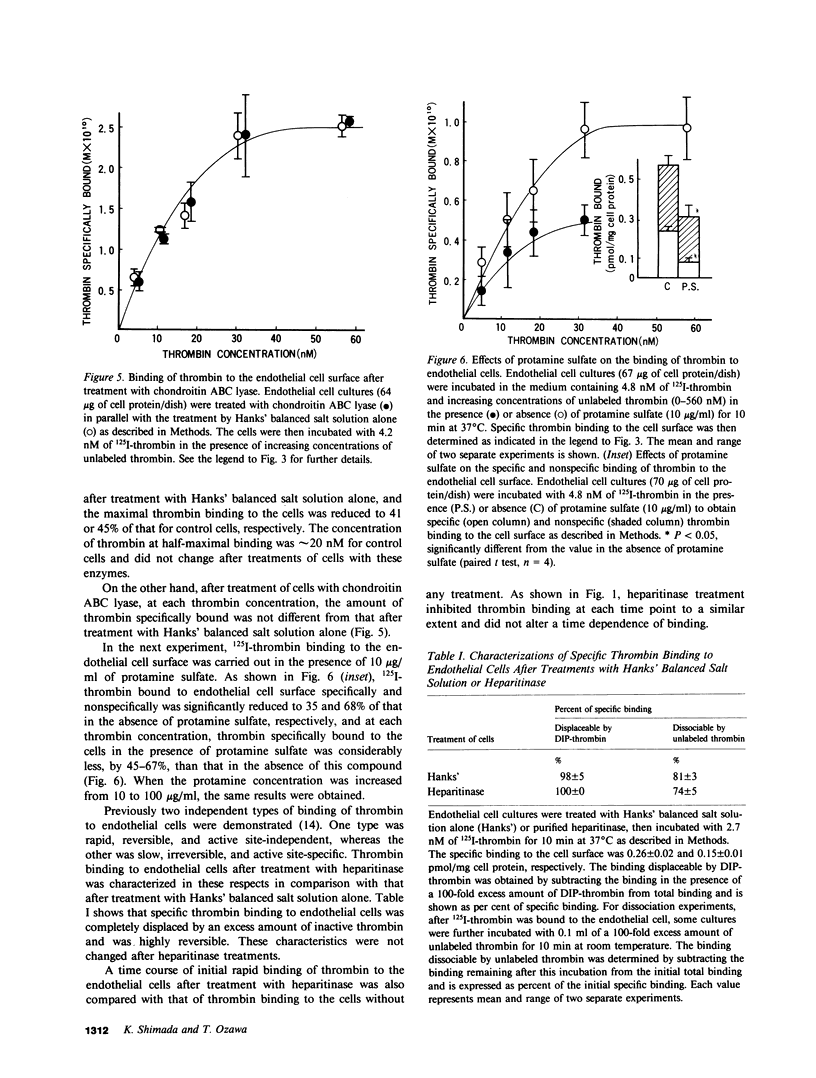
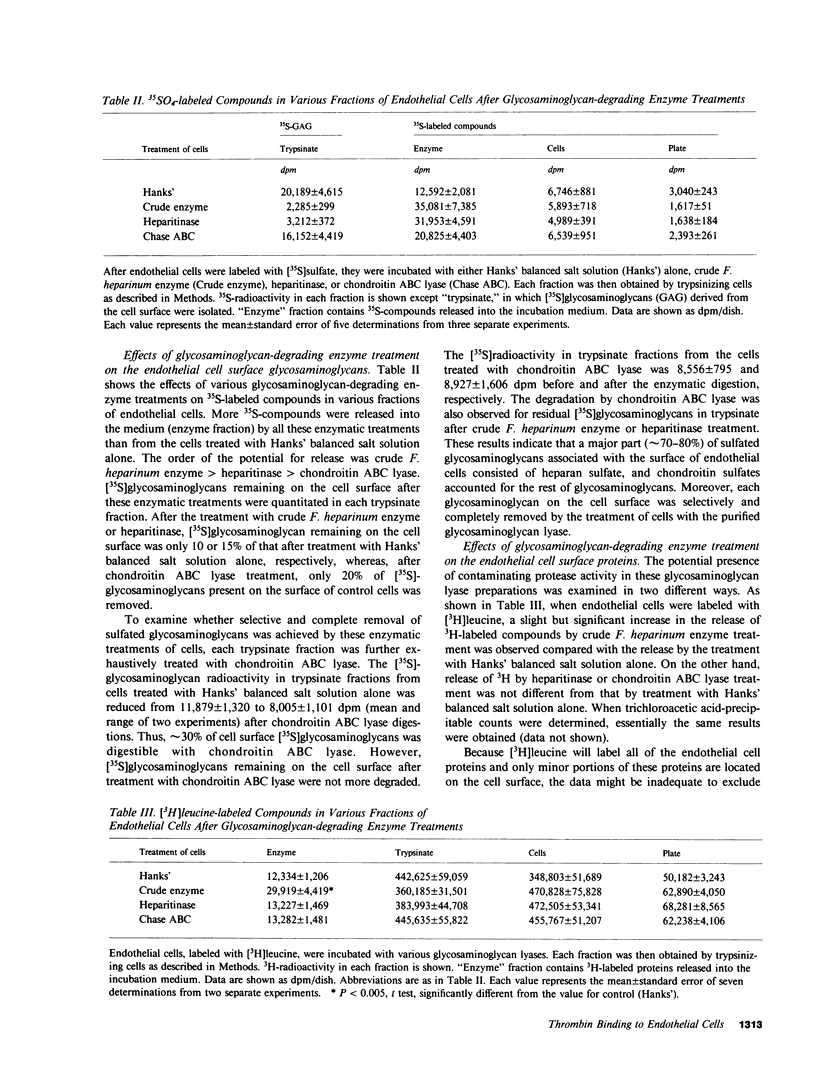
It has been postulated that thrombin binds to endothelial cells through, at least in part, cell surface glycosaminoglycans such as heparan sulfate, which could serve as antithrombin cofactor on the endothelium. In the present study, we have directly evaluated the binding of 125I-labeled bovine thrombin to cultured porcine aortic endothelial cells. The thrombin binding to the cell surface was rapid, reversible, and displaced by enzymatically inactive diisopropylphosphoryl-thrombin. The concentration of thrombin at half-maximal binding was approximately 20 nM. Both specific and nonspecific binding of 125I-thrombin to the endothelial cell surface was partially inhibited in the presence of protamine sulfate, after the removal of cell surface heparan sulfate by the treatment of cells with crude Flavobacterium heparinum enzyme or purified heparitinase. The binding as a function of the concentration of thrombin revealed that the maximal amount of specific binding was reduced by approximately 50% with little alteration in binding affinity by these enzymatic treatments. The reversibility and active-site independence as well as the rate of the binding did not change after heparitinase treatment. Whereas removal of chondroitin sulfates by chondroitin ABC lyase treatment of cells did not affect the binding, identical enzymatic treatments of [35S]sulfate-labeled cells showed that either heparan sulfate or chondroitin sulfate was selectively and completely removed from the cell surface by heparitinase or chondroitin ABC lyase treatment, respectively. Furthermore, proteolysis of cell surface proteins by the purified glycosaminoglycan lyases was excluded by the identical enzymatic treatments of [3H]leucine-labeled or cell surface radioiodinated cells. Our results provide the first direct evidence that heparan sulfate on the cell surface is involved in the high-affinity, active site-independent thrombin binding by endothelial cells, and also suggest the presence of thrombin-binding sites that are not directly related to heparan sulfate.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Awbrey B. J., Hoak J. C., Owen W. G. Binding of human thrombin to cultured human endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 25;254(10):4092–4095. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer P. T., Machovich R., Arányi P., Büki K. G., Csonka E., Horváth I. Mechanism of thrombin binding to endothelial cells. Blood. 1983 Feb;61(2):368–372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buonassisi V., Colburn P. Antibodies to the heparan sulfate proteoglycans synthesized by endothelial cell cultures. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Oct 4;760(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(83)90118-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buonassisi V., Root M. Enzymatic degradation of heparin-related mucopolysaccharides from the surface of endothelial cell cultures. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 14;385(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(75)90067-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busch C., Owen W. G. Identification in vitro of an endothelial cell surface cofactor for antithrombin III. Parallel studies with isolated perfused rat hearts and microcarrier cultures of bovine endothelium. J Clin Invest. 1982 Mar;69(3):726–729. doi: 10.1172/JCI110502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colburn P., Buonassisi V. Anti-clotting activity of endothelial cell cultures and heparan sulfate proteoglycans. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jan 15;104(1):220–227. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91962-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damus P. S., Hicks M., Rosenberg R. D. Anticoagulant action of heparin. Nature. 1973 Dec 7;246(5432):355–357. doi: 10.1038/246355a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dryjski M., Larsson R., Olsson P., Swedenborg J. Effect of glycosaminoglycans and antithrombin III on uptake and inhibition of thrombin by the vascular wall. Thromb Res. 1983 Nov 15;32(4):355–363. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(83)90088-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dryjski M., Olsson P., Swedenborg J. The vascular endothelium as an inhibitor of thrombin. Thromb Res Suppl. 1983;5:67–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dryjski M., Olsson P., Swedenborg J. Uptake and inhibition of thrombin by the vascular wall. Thromb Res. 1982 Aug 15;27(4):467–475. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(82)90064-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill P. J., Adler J., Silbert C. K., Silbert J. E. Removal of glycosaminoglycans from cultures of human skin fibroblasts. Biochem J. 1981 Jan 15;194(1):299–307. doi: 10.1042/bj1940299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Alteration of cell-surface proteins by viral transformation and by proteolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Nov;70(11):3170–3174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.11.3170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacs J., Savion N., Gospodarowicz D., Shuman M. A. Effect of cell density on thrombin binding to a specific site on bovine vascular endothelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1981 Sep;90(3):670–674. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.3.670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasahara Y., Ashihara Y. Colorimetry of angiotensin-I converting enzyme activity in serum. Clin Chem. 1981 Nov;27(11):1922–1925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lijnen H. R., Hoylaerts M., Collen D. Heparin binding properties of human histidine-rich glycoprotein. Mechanism and role in the neutralization of heparin in plasma. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 25;258(6):3803–3808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lollar P., Hoak J. C., Owen W. G. Binding of thrombin to cultured human endothelial cells. Nonequilibrium aspects. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 10;255(21):10279–10283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lollar P., MacIntosh S. C., Owen W. G. Reaction of antithrombin III with thrombin bound to the vascular endothelium. Analysis in a recirculating perfused rabbit heart preparation. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 10;259(7):4335–4338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lollar P., Owen W. G. Clearance of thrombin from circulation in rabbits by high-affinity binding sites on endothelium. Possible role in the inactivation of thrombin by antithrombin III. J Clin Invest. 1980 Dec;66(6):1222–1230. doi: 10.1172/JCI109973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcum J. A., Fritze L., Galli S. J., Karp G., Rosenberg R. D. Microvascular heparin-like species with anticoagulant activity. Am J Physiol. 1983 Nov;245(5 Pt 1):H725–H733. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1983.245.5.H725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcum J. A., McKenney J. B., Rosenberg R. D. Acceleration of thrombin-antithrombin complex formation in rat hindquarters via heparinlike molecules bound to the endothelium. J Clin Invest. 1984 Aug;74(2):341–350. doi: 10.1172/JCI111429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita T., Nishibe H., Iwanaga S., Suzuki T. Studies on the activation of bovine prothrombin. Isolation and characterization of the fragments released from the prothrombin by activated factor X. J Biochem. 1974 Nov;76(5):1031–1048. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen W. G., Esmon C. T. Functional properties of an endothelial cell cofactor for thrombin-catalyzed activation of protein C. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 10;256(11):5532–5535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen W. G. The control of hemostasis. Role of endothelium in the regulation of inhibitory and catabolic pathways. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1982 May;106(5):209–213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savion N., Isaacs J. D., Gospodarowicz D., Shuman M. A. Internalization and degradation of thrombin and up regulation of thrombin-binding sites in corneal endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 10;256(9):4514–4519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shifman M. A., Pizzo S. V. In vivo metabolism of reversibly inhibited alpha-thrombin. Biochem Pharmacol. 1983 Feb 15;32(4):739–741. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(83)90507-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shifman M. A., Pizzo S. V. The in vivo metabolism of antithrombin III and antithrombin III complexes. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3243–3248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada K., Gill P. J., Silbert J. E., Douglas W. H., Fanburg B. L. Involvement of cell surface heparin sulfate in the binding of lipoprotein lipase to cultured bovine endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1981 Oct;68(4):995–1002. doi: 10.1172/JCI110354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simionescu M., Simionescu N., Silbert J. E., Palade G. E. Differentiated microdomains on the luminal surface of the capillary endothelium. II. Partial characterization of their anionic sites. J Cell Biol. 1981 Sep;90(3):614–621. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.3.614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall R. T., Harker L. A. The endothelium and thrombosis. Annu Rev Med. 1980;31:361–371. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.31.020180.002045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasteson A., Uthne K., Westermark B. A novel assay for the biosynthesis of sulphated polysaccharide and its application to studies on the effects of somatomedin on cultured cells. Biochem J. 1973 Dec;136(4):1069–1074. doi: 10.1042/bj1361069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamagata T., Saito H., Habuchi O., Suzuki S. Purification and properties of bacterial chondroitinases and chondrosulfatases. J Biol Chem. 1968 Apr 10;243(7):1523–1535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]