Abstract
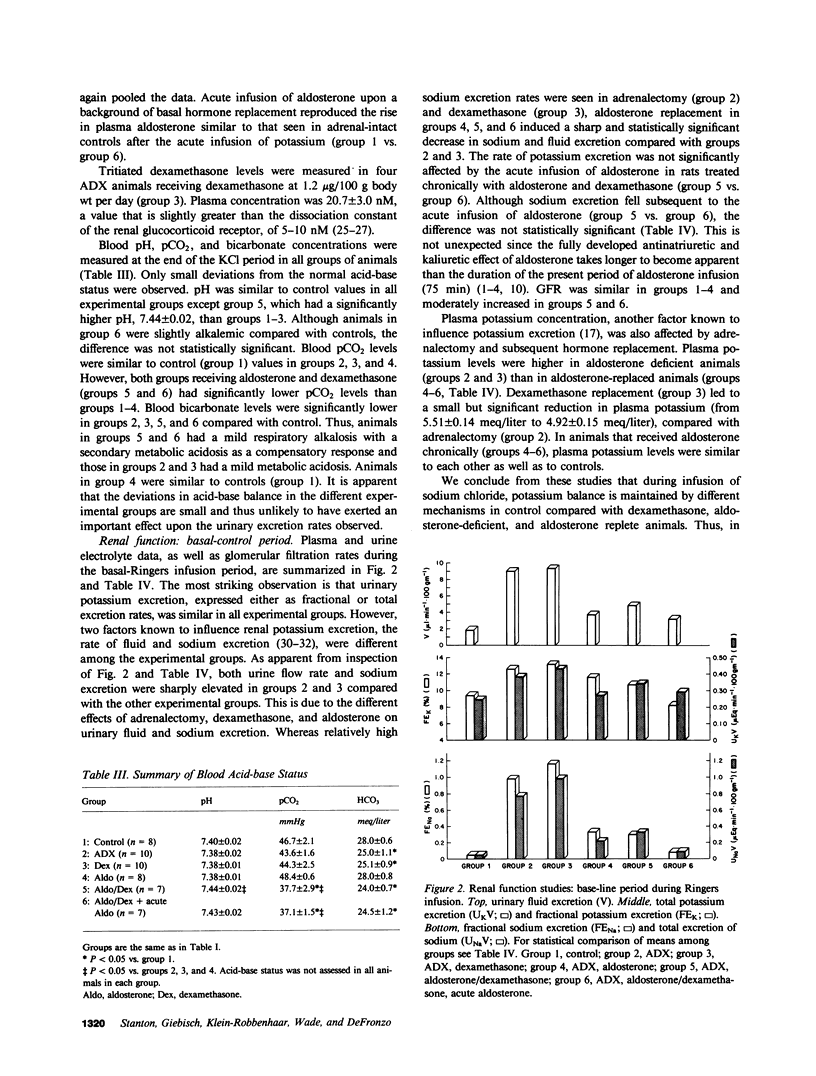
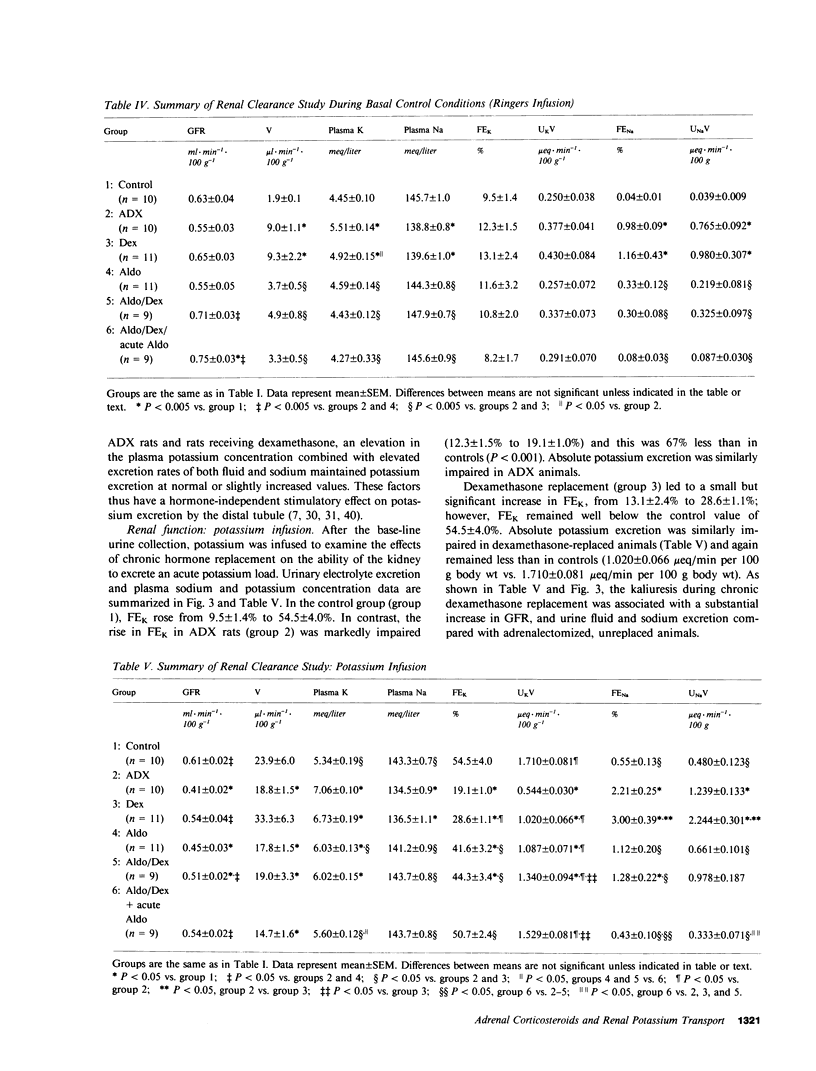
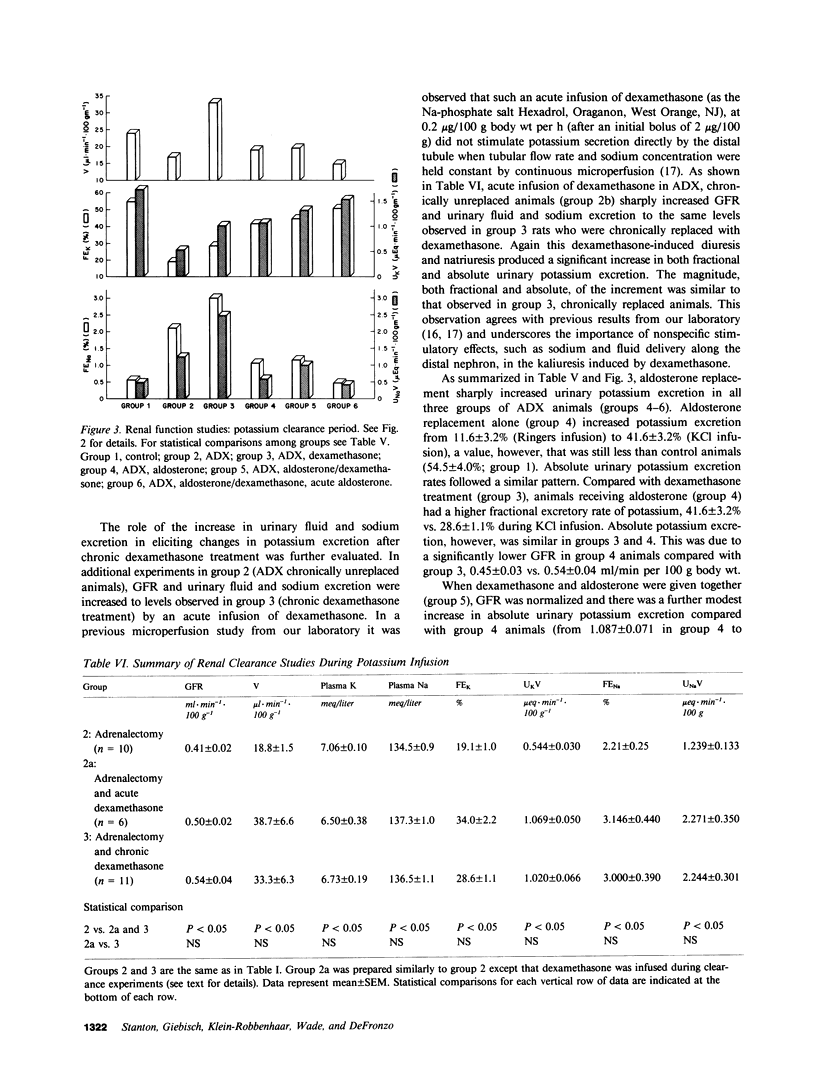
Clearance experiments were carried out in pair-fed rats to examine the long-term effects of adrenalectomy and selective adrenal corticosteroid replacement in physiological amounts on renal potassium transport. To this end, clearance studies were conducted in rats that were sham operated, or adrenalectomized (ADX). ADX animals were given either vehicle, aldosterone (0.5 microgram/100 g body wt per day), dexamethasone (1.2 micrograms/100 g body wt per day), or aldosterone and dexamethasone, by osmotic minipump for 7-9 d whereupon clearance experiments were conducted. After chronic hormone treatment, during basal conditions when only Ringers solution was infused, all groups excreted similar amounts of potassium. However, in all ADX animals without mineralocorticoid replacement, the maintenance of urinary potassium excretion at control levels was associated with hyperkalemia, increased urine flow, and natriuresis; all are factors known to stimulate urinary potassium excretion. During acute potassium infusion, the increase in urinary potassium excretion was less in ADX rats than in controls. This functional deficiency in potassium excretion was partially corrected by dexamethasone and was uniformly associated with a significant increase in urine flow. Aldosterone replacement or aldosterone and dexamethasone given together chronically, sharply increased potassium excretion but did not restore excretion to control levels. Only acute aldosterone infusion (0.2 microgram/100 g body wt bolus plus 0.2 microgram/100 g body wt per hour), superimposed upon chronic aldosterone and dexamethasone treatment, fully restored potassium excretion to control levels. This aldosterone induced enhancement of potassium excretion, both chronic and acute, was not associated with hyperkalemia, and increased urine flow or natriuresis. Thus, physiological levels of both classes of adrenal corticosteroids stimulate renal potassium excretion albeit by different mechanisms. Mineralocorticoids stimulate tubular potassium excretion directly, whereas glucocorticoids augment excretion indirectly by increasing fluid and sodium delivery along the distal nephron.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adam W. R., Goland G. J., Wellard R. M. Renal potassium adaptation in the rat: role of glucocorticoids and aldosterone. Am J Physiol. 1984 Mar;246(3 Pt 2):F300–F308. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1984.246.3.F300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTTER F. C., FOURMAN P. The different effects of aldosterone-like steroids and hydrocortisone-like steroids on urinary excretion of potassium and acid. Metabolism. 1962 Jan;11:6–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylis C., Brenner B. M. Mechanism of the glucocorticoid-induced increase in glomerular filtration rate. Am J Physiol. 1978 Feb;234(2):F166–F170. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1978.234.2.F166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bengele H. H., Evan A., McNamara E. R., Alexander E. A. Tubular sites of potassium regulation in the normal and uninephrectomized rat. Am J Physiol. 1978 Feb;234(2):F146–F153. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1978.234.2.F146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bia J. M., Tyler K., DeFronzo R. A. The effect of dexamethasone on renal electrolyte excretion in the adrenalectomized rat. Endocrinology. 1982 Sep;111(3):882–888. doi: 10.1210/endo-111-3-882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campen T. J., Vaughn D. A., Fanestil D. D. Mineralo- and glucocorticoid effects on renal excretion of electrolytes. Pflugers Arch. 1983 Oct;399(2):93–101. doi: 10.1007/BF00663903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cortney M. A. Renal tubular transfer of water and electrolytes in adrenalectomized rats. Am J Physiol. 1969 Mar;216(3):589–598. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.216.3.589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman I. S. Receptors and effectors in hormone action on the kidney. Am J Physiol. 1981 Oct;241(4):F333–F339. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.241.4.F333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field M. J., Stanton B. A., Giebisch G. H. Differential acute effects of aldosterone, dexamethasone, and hyperkalemia on distal tubular potassium secretion in the rat kidney. J Clin Invest. 1984 Nov;74(5):1792–1802. doi: 10.1172/JCI111598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fimognari G. M., Fanestil D. D., Edelman I. S. Induction of RNA and protein synthesis in the action of aldosterone in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1967 Oct;213(4):954–962. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1967.213.4.954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funder J. W., Feldman D., Edelman I. S. The roles of plasma binding and receptor specificity in the mineralocorticoid action of aldosterone. Endocrinology. 1973 Apr;92(4):994–1004. doi: 10.1210/endo-92-4-994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARROD O., DAVIES S. A., CAHILL G., Jr The action of cortisone and desoxycorticosterone acetate on glomerular filtration rate and sodium and water exchange in the adrenalectomized dog. J Clin Invest. 1955 Jun;34(6):761–776. doi: 10.1172/JCI103131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Good D. W., Wright F. S. Luminal influences on potassium secretion: sodium concentration and fluid flow rate. Am J Physiol. 1979 Feb;236(2):F192–F205. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1979.236.2.F192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiatt N., Chapman L. W., Davidson M. B., Sheinkopf J. A. Adrenal hormones and the regulation of serum potassium in potassium-loaded adrenalectomized dogs. Endocrinology. 1979 Jul;105(1):215–219. doi: 10.1210/endo-105-1-215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holbrook M. M., Dale S. L., Melby J. C. Peripheral plasma steroid concentrations in rats sacrificed by anoxia. J Steroid Biochem. 1980 Nov;13(11):1355–1358. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(80)90097-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horisberger J. D., Diezi J. Effects of mineralocorticoids on Na+ and K+ excretion in the adrenalectomized rat. Am J Physiol. 1983 Jul;245(1):F89–F99. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1983.245.1.F89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulter H. N., Licht J. H., Bonner E. L., Jr, Glynn R. D., Sebastian A. Effects of glucocorticoid steroids on renal and systemic acid-base metabolism. Am J Physiol. 1980 Jul;239(1):F30–F43. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1980.239.1.F30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khuri R. N., Strieder W. N., Giebisch G. Effects of flow rate and potassium intake on distal tubular potassium transfer. Am J Physiol. 1975 Apr;228(4):1249–1261. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.228.4.1249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lan N. C., Graham B., Bartter F. C., Baxter J. D. Binding of steroids to mineralocorticoid receptors: implications for in vivo occupancy by glucocorticoids. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 Feb;54(2):332–342. doi: 10.1210/jcem-54-2-332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLS J. N., THOMAS S., WILLIAMSON K. S. The acute effect of hydrocortisone, deoxycorticosterone and aldosterone upon the excretion of sodium, potassium and acid by the human kidney. J Physiol. 1960 May;151:312–331. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. S., Jones W. J., Hayslett J. P. Animal model to study the effect of adrenal hormones on epithelial function. Kidney Int. 1983 Sep;24(3):386–391. doi: 10.1038/ki.1983.171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marver D., Kokko J. P. Renal target sites and the mechanism of action of aldosterone. Miner Electrolyte Metab. 1983 Jan-Feb;9(1):1–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neil R. G., Helman S. I. Transport characteristics of renal collecting tubules: influences of DOCA and diet. Am J Physiol. 1977 Dec;233(6):F544–F558. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1977.233.6.F544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peart W. S., Pessina A. C. The mechanism of acute renal ischaemia caused by adrenalectomy in the rat. J Physiol. 1975 Aug;250(1):23–37. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson L. N., Wright F. S. Effect of sodium intake on renal potassium excretion. Am J Physiol. 1977 Sep;233(3):F225–F234. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1977.233.3.F225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez H. J., Sinha S. K., Starling J., Klahr S. Regulation of renal Na+-K+-ATPase in the rat by adrenal steroids. Am J Physiol. 1981 Aug;241(2):F186–F195. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.241.2.F186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosselin G., Assan R., Yalow R. S., Berson S. A. Separation of antibody-bound and unbound peptide hormones labelled with iodine-131 by talcum powder and precipitated silica. Nature. 1966 Oct 22;212(5060):355–357. doi: 10.1038/212355a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz G. J., Burg M. B. Mineralocorticoid effects on cation transport by cortical collecting tubules in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1978 Dec;235(6):F576–F585. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1978.235.6.F576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanton B. A., Biemesderfer D., Wade J. B., Giebisch G. Structural and functional study of the rat distal nephron: effects of potassium adaptation and depletion. Kidney Int. 1981 Jan;19(1):36–48. doi: 10.1038/ki.1981.5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanton B. A., Giebisch G. H. Potassium transport by the renal distal tubule: effects of potassium loading. Am J Physiol. 1982 Nov;243(5):F487–F493. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1982.243.5.F487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanton B. A., Giebisch G. Effects of pH on potassium transport by renal distal tubule. Am J Physiol. 1982 May;242(5):F544–F551. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1982.242.5.F544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanton B., Janzen A., Klein-Robbenhaar G., DeFronzo R., Giebisch G., Wade J. Ultrastructure of rat initial collecting tubule. Effect of adrenal corticosteroid treatment. J Clin Invest. 1985 Apr;75(4):1327–1334. doi: 10.1172/JCI111833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes J. B., Ingram M. J., Williams A. D., Ingram D. Heterogeneity of the rabbit collecting tubule: localization of mineralocorticoid hormone action to the cortical portion. Kidney Int. 1981 Sep;20(3):340–347. doi: 10.1038/ki.1981.144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes J. B. Potassium secretion by cortical collecting tubule: relation to sodium absorption, luminal sodium concentration, and transepithelial voltage. Am J Physiol. 1981 Oct;241(4):F395–F402. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.241.4.F395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiederholt M., Behn C., Schoormans W., Hansen L. Effect of aldosterone on sodium and potassium transport in the kidney. J Steroid Biochem. 1972 Feb;3(2):151–159. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(72)90045-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiederholt M., Schoormans W., Hansen L., Behn C. Sodium conductance changes by aldosterone in the rat kidney. Pflugers Arch. 1974 Apr 11;348(2):155–165. doi: 10.1007/BF00586477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiederholt M., Wiederholt B. Der Einfluss von Dexamethason auf die Wasser- und Elektrolytausscheidung adrenalektomierter Ratten. Pflugers Arch. 1968;302(1):57–78. doi: 10.1007/BF00586782. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox C. S., Cemerikic D. A., Giebisch G. Differential effects of acute mineralo- and glucocorticosteroid administration on renal acid elimination. Kidney Int. 1982 Apr;21(4):546–556. doi: 10.1038/ki.1982.61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wingo C. S., Seldin D. W., Kokko J. P., Jacobson H. R. Dietary modulation of active potassium secretion in the cortical collecting tubule of adrenalectomized rabbits. J Clin Invest. 1982 Sep;70(3):579–586. doi: 10.1172/JCI110650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodhall P. B., Tisher C. C. Response of the distal tubule and cortical collecting duct to vasopressin in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1973 Dec;52(12):3095–3108. doi: 10.1172/JCI107509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young D. B., Jackson T. E. Effects of aldosterone on potassium distribution. Am J Physiol. 1982 Nov;243(5):R526–R530. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1982.243.5.R526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young D. B., Jackson T. E., Tipayamontri U., Scott R. C. Effects of sodium intake on steady-state potassium excretion. Am J Physiol. 1984 Jun;246(6 Pt 2):F772–F778. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1984.246.6.F772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young D. B., McCaa R. E., Pan U. J., Guyton A. C. Effectiveness of the aldosterone-sodium and -potassium feedback control system. Am J Physiol. 1976 Sep;231(3):945–953. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.231.3.945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young D. B. Relationship between plasma potassium concentration and renal potassium excretion. Am J Physiol. 1982 Jun;242(6):F599–F603. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1982.242.6.F599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



