Full text
PDF

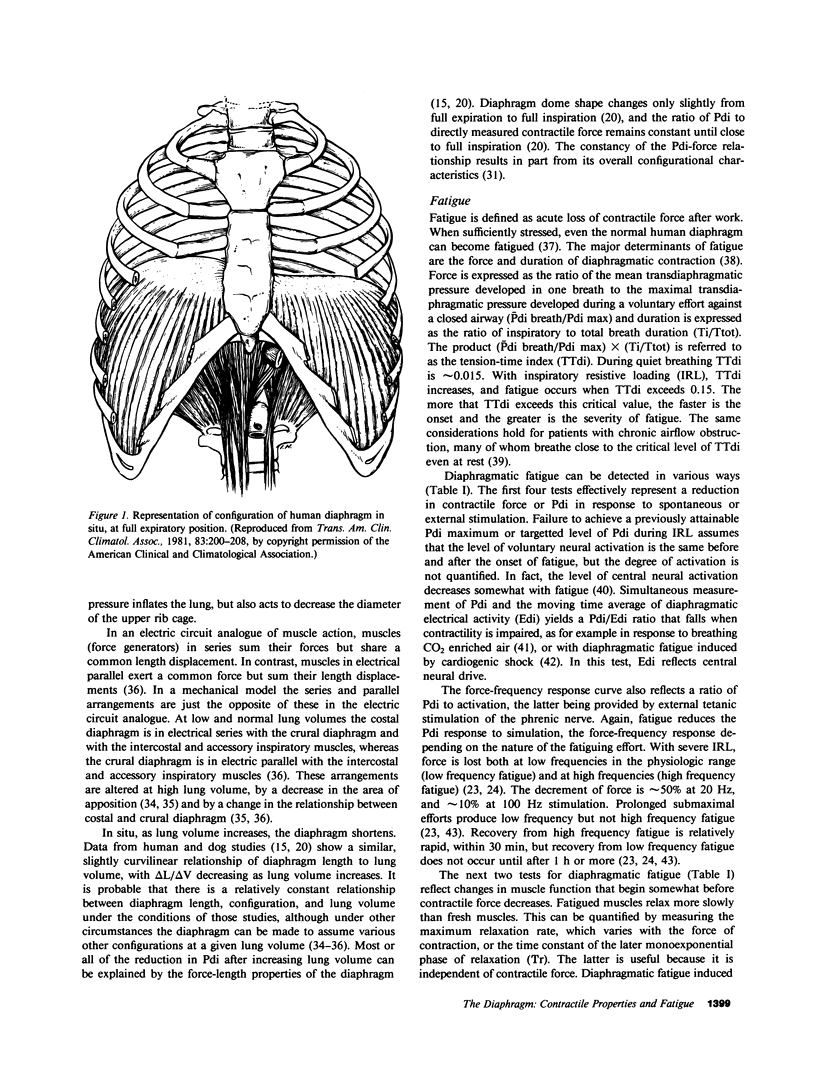



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aldrich T. K., Adams J. M., Arora N. S., Rochester D. F. Power spectral analysis of the diaphragm electromyogram. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1983 Jun;54(6):1579–1584. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1983.54.6.1579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arora N. S., Rochester D. F. Effect of body weight and muscularity on human diaphragm muscle mass, thickness, and area. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1982 Jan;52(1):64–70. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1982.52.1.64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arora N. S., Rochester D. F. Respiratory muscle strength and maximal voluntary ventilation in undernourished patients. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1982 Jul;126(1):5–8. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1982.126.1.5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aubier M., De Troyer A., Sampson M., Macklem P. T., Roussos C. Aminophylline improves diaphragmatic contractility. N Engl J Med. 1981 Jul 30;305(5):249–252. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198107303050503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aubier M., Farkas G., De Troyer A., Mozes R., Roussos C. Detection of diaphragmatic fatigue in man by phrenic stimulation. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1981 Mar;50(3):538–544. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1981.50.3.538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aubier M., Murciano D., Viires N., Lecocguic Y., Pariente R. Diaphragmatic contractility enhanced by aminophylline: role of extracellular calcium. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1983 Feb;54(2):460–464. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1983.54.2.460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aubier M., Trippenbach T., Roussos C. Respiratory muscle fatigue during cardiogenic shock. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1981 Aug;51(2):499–508. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1981.51.2.499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aubier M., Viires N., Murciano D., Medrano G., Lecocguic Y., Pariente R. Effects and mechanism of action of terbutaline on diaphragmatic contractility and fatigue. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1984 Apr;56(4):922–929. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1984.56.4.922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellemare F., Bigland-Ritchie B. Assessment of human diaphragm strength and activation using phrenic nerve stimulation. Respir Physiol. 1984 Dec;58(3):263–277. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(84)90003-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellemare F., Grassino A. Effect of pressure and timing of contraction on human diaphragm fatigue. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1982 Nov;53(5):1190–1195. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1982.53.5.1190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellemare F., Grassino A. Evaluation of human diaphragm fatigue. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1982 Nov;53(5):1196–1206. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1982.53.5.1196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellemare F., Grassino A. Force reserve of the diaphragm in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1983 Jul;55(1 Pt 1):8–15. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1983.55.1.8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellemare F., Woods J. J., Johansson R., Bigland-Ritchie B. Motor-unit discharge rates in maximal voluntary contractions of three human muscles. J Neurophysiol. 1983 Dec;50(6):1380–1392. doi: 10.1152/jn.1983.50.6.1380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun N. M., Arora N. S., Rochester D. F. Force-length relationship of the normal human diaphragm. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1982 Aug;53(2):405–412. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1982.53.2.405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun N. M., Arora N. S., Rochester D. F. Respiratory muscle and pulmonary function in polymyositis and other proximal myopathies. Thorax. 1983 Aug;38(8):616–623. doi: 10.1136/thx.38.8.616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchthal F., Schmalbruch H. Motor unit of mammalian muscle. Physiol Rev. 1980 Jan;60(1):90–142. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1980.60.1.90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CORDA M., VONEULER C., LENNERSTRAND G. PROPRIOCEPTIVE INNERVATION OF THE DIAPHRAGM. J Physiol. 1965 May;178:161–177. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen C. A., Zagelbaum G., Gross D., Roussos C., Macklem P. T. Clinical manifestations of inspiratory muscle fatigue. Am J Med. 1982 Sep;73(3):308–316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson M. J., Gadian D. G., Wilkie D. R. Mechanical relaxation rate and metabolism studied in fatiguing muscle by phosphorus nuclear magnetic resonance. J Physiol. 1980 Feb;299:465–484. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Troyer A., Sampson M., Sigrist S., Macklem P. T. Action of costal and crural parts of the diaphragm on the rib cage in dog. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1982 Jul;53(1):30–39. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1982.53.1.30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Troyer A., Sampson M., Sigrist S., Macklem P. T. The diaphragm: two muscles. Science. 1981 Jul 10;213(4504):237–238. doi: 10.1126/science.7244632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decramer M., De Troyer A., Kelly S., Macklem P. T. Mechanical arrangement of costal and crural diaphragms in dogs. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1984 Jun;56(6):1484–1490. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1984.56.6.1484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards R. H. The diaphragm as a muscle. Mechanisms underlying fatigue. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1979 Feb;119(2 Pt 2):81–84. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1979.119.2P2.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esau S. A., Bellemare F., Grassino A., Permutt S., Roussos C., Pardy R. L. Changes in relaxation rate with diaphragmatic fatigue in humans. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1983 May;54(5):1353–1360. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1983.54.5.1353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farkas G. A., Roussos C. Acute diaphragmatic shortening: in vitro mechanics and fatigue. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Sep;130(3):434–438. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1984.130.3.434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farkas G. A., Roussos C. Adaptability of the hamster diaphragm to exercise and/or emphysema. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1982 Nov;53(5):1263–1272. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1982.53.5.1263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farkas G. A., Roussos C. Diaphragm in emphysematous hamsters: sarcomere adaptability. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1983 Jun;54(6):1635–1640. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1983.54.6.1635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farkas G. A., Roussos C. Histochemical and biochemical correlates of ventilatory muscle fatigue in emphysematous hamsters. J Clin Invest. 1984 Oct;74(4):1214–1220. doi: 10.1172/JCI111530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faulkner J. A., Maxwell L. C., Ruff G. L., White T. P. The diaphragm as a muscle. Contractile properties. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1979 Feb;119(2 Pt 2):89–92. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1979.119.2P2.89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gal T. J., Arora N. S. Respiratory mechanics in supine subjects during progressive partial curarization. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1982 Jan;52(1):57–63. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1982.52.1.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross D., Grassino A., Ross W. R., Macklem P. T. Electromyogram pattern of diaphragmatic fatigue. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1979 Jan;46(1):1–7. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1979.46.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell S., Roussos C. Isoproterenol and aminophylline improve contractility of fatigued canine diaphragm. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Jan;129(1):118–124. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1984.129.1.118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iscoe S., Dankoff J., Migicovsky R., Polosa C. Recruitment and discharge frequency of phrenic motoneurones during inspiration. Respir Physiol. 1976 Feb;26(1):113–128. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(76)90056-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jardim J., Farkas G., Prefaut C., Thomas D., Macklem P. T., Roussos C. The failing inspiratory muscles under normoxic and hypoxic conditions. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1981 Sep;124(3):274–279. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1981.124.3.274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juan G., Calverley P., Talamo C., Schnader J., Roussos C. Effect of carbon dioxide on diaphragmatic function in human beings. N Engl J Med. 1984 Apr 5;310(14):874–879. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198404053101402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRNJEVIC K., MILEDI R. Motor units in the rat diaphragm. J Physiol. 1958 Mar 11;140(3):427–439. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim M. J., Druz W. S., Danon J., Machnach W., Sharp J. T. Mechanics of the canine diaphragm. J Appl Physiol. 1976 Sep;41(3):369–382. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1976.41.3.369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kranz H., Williams A. M., Cassell J., Caddy D. J., Silberstein R. B. Factors determining the frequency content of the electromyogram. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1983 Aug;55(2):392–399. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1983.55.2.392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreitzer S. M., Feldman N. T., Saunders N. A., Ingram R. H., Jr Bilateral diaphragmatic paralysis with hypercapnic respiratory failure. A physiologic assessment. Am J Med. 1978 Jul;65(1):89–95. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(78)90697-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loring S. H., Mead J. Action of the diaphragm on the rib cage inferred from a force-balance analysis. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1982 Sep;53(3):756–760. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1982.53.3.756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILIC-EMILI J., ORZALESI M. M., COOK C. D., TURNER J. M. RESPIRATORY THORACO-ABDOMINAL MECHANICS IN MAN. J Appl Physiol. 1964 Mar;19:217–223. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1964.19.2.217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macklem P. T., Macklem D. M., De Troyer A. A model of inspiratory muscle mechanics. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1983 Aug;55(2):547–557. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1983.55.2.547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCully K. K., Faulkner J. A. Length-tension relationship of mammalian diaphragm muscles. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1983 Jun;54(6):1681–1686. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1983.54.6.1681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mead J., Loring S. H. Analysis of volume displacement and length changes of the diaphragm during breathing. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1982 Sep;53(3):750–755. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1982.53.3.750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moxham J., Edwards R. H., Aubier M., De Troyer A., Farkas G., Macklem P. T., Roussos C. Changes in EMG power spectrum (high-to-low ratio) with force fatigue in humans. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1982 Nov;53(5):1094–1099. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1982.53.5.1094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moxham J., Morris A. J., Spiro S. G., Edwards R. H., Green M. Contractile properties and fatigue of the diaphragm in man. Thorax. 1981 Mar;36(3):164–168. doi: 10.1136/thx.36.3.164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murciano D., Aubier M., Lecocguic Y., Pariente R. Effects of theophylline on diaphragmatic strength and fatigue in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. N Engl J Med. 1984 Aug 9;311(6):349–353. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198408093110601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman S., Road J., Bellemare F., Clozel J. P., Lavigne C. M., Grassino A. Respiratory muscle length measured by sonomicrometry. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1984 Mar;56(3):753–764. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1984.56.3.753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid M. B., Johnson R. L., Jr Efficiency, maximal blood flow, and aerobic work capacity of canine diaphragm. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1983 Mar;54(3):763–772. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1983.54.3.763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rochester D. F., Arora N. S., Braun N. M. Maximum contractile force of human diaphragm muscle, determined in vivo. Trans Am Clin Climatol Assoc. 1982;93:200–208. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rochester D. F., Braun N. M., Arora N. S. Respiratory muscle strength in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1979 Feb;119(2 Pt 2):151–154. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1979.119.2P2.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roussos C. S., Macklem P. T. Diaphragmatic fatigue in man. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1977 Aug;43(2):189–197. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1977.43.2.189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruff R. L., Secrist D. Inhibitors of prostaglandin synthesis or cathepsin B prevent muscle wasting due to sepsis in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1984 May;73(5):1483–1486. doi: 10.1172/JCI111352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANT'AMBROGIO G., FRAZIER D. T., WILSON M. F., AGOSTONI E. Motor innervation and pattern of activity of cat diaphragm. J Appl Physiol. 1963 Jan;18:43–46. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1963.18.1.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweitzer T. W., Fitzgerald J. W., Bowden J. A., Lynne-Davies P. Spectral analysis of human inspiratory diaphragmatic electromyograms. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1979 Jan;46(1):152–165. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1979.46.1.152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigrist S., Thomas D., Howell S., Roussos C. The effect of aminophylline on inspiratory muscle contractility. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1982 Jul;126(1):46–50. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1982.126.1.46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperelakis N. Changes in conductances of frog sartorius fibers produced by CO2, ReO4-, and temperature. Am J Physiol. 1969 Oct;217(4):1069–1075. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.217.4.1069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Supinski G. S., Deal E. C., Jr, Kelsen S. G. The effects of caffeine and theophylline on diaphragm contractility. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Sep;130(3):429–433. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1984.130.3.429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Supinski G. S., Kelsen S. G. Effect of elastase-induced emphysema on the force-generating ability of the diaphragm. J Clin Invest. 1982 Nov;70(5):978–988. doi: 10.1172/JCI110709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitelaw W. A., Hajdo L. E., Wallace J. A. Relationships among pressure, tension, and shape of the diaphragm. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1983 Dec;55(6):1899–1905. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1983.55.6.1899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiles C. M., Moxham J., Newham D., Edwards R. H. Aminophylline and fatigue of adductor pollicis in man. Clin Sci (Lond) 1983 May;64(5):547–550. doi: 10.1042/cs0640547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



