Abstract
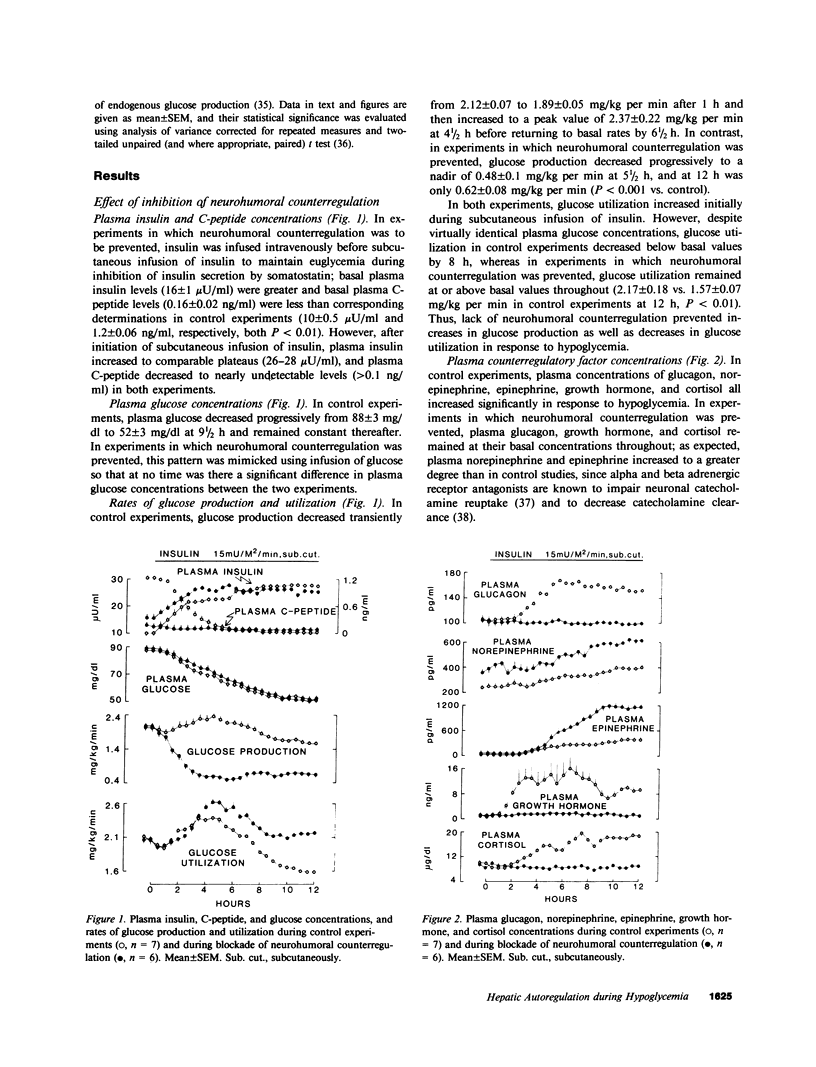
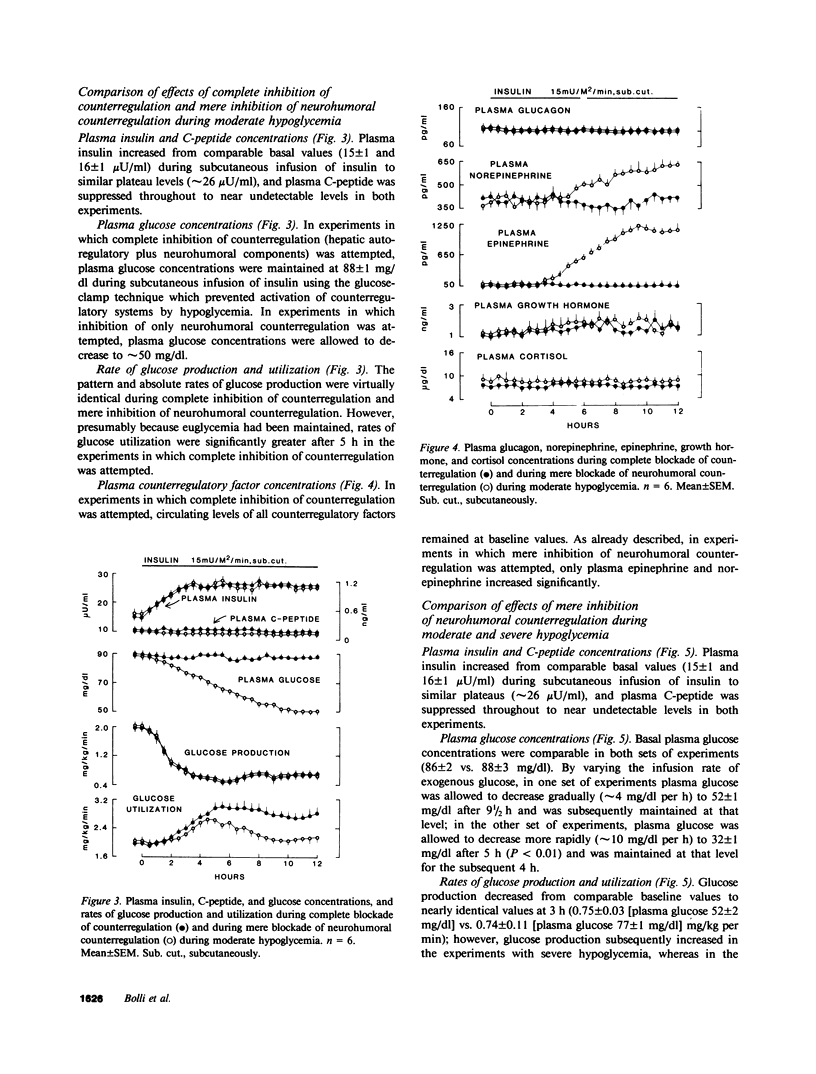
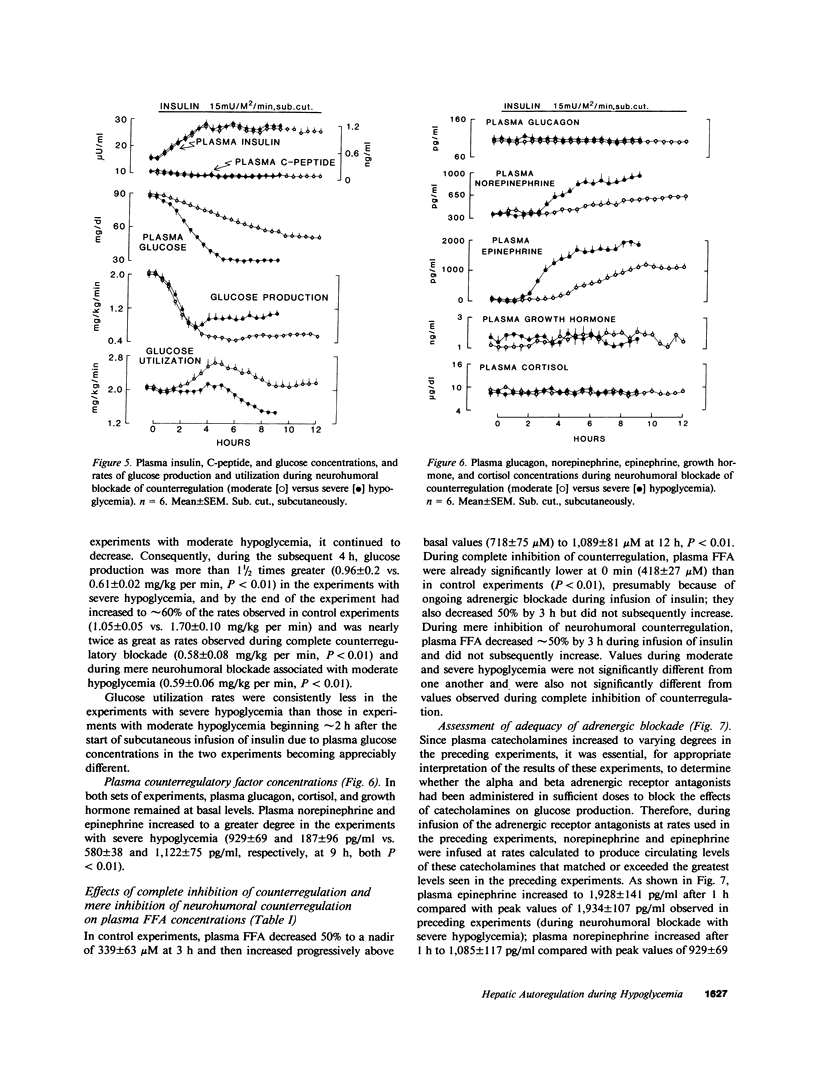
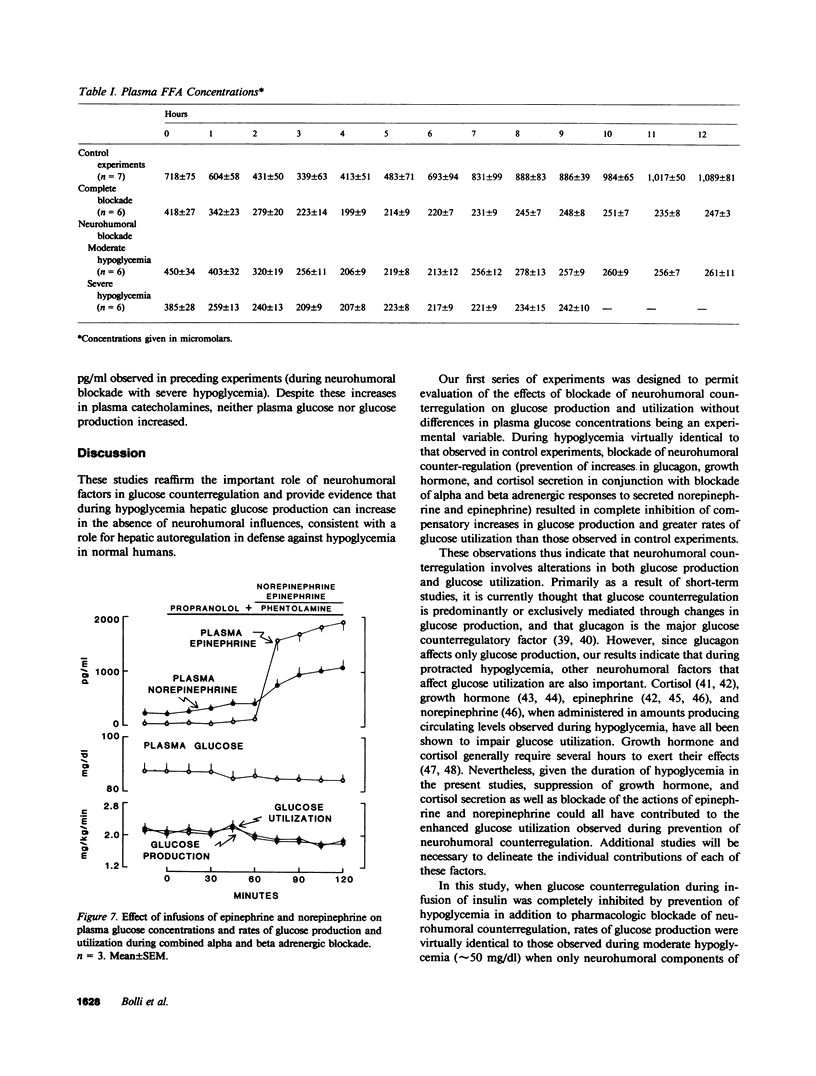
To assess the role of hepatic autoregulation in defense against hypoglycemia, we compared the effects of complete blockade of glucose counterregulation with those of blockade of only neurohumoral counterregulation during moderate (approximately 50 mg/dl) and severe (approximately 30 mg/dl) hypoglycemia induced by physiologic hyperinsulinemia during subcutaneous infusion of insulin in normal volunteers. Compared with observations in control experiments, neurohumoral counterregulatory blockade (somatostatin, propranolol, phentolamine, and metyrapone), during which identical moderate hypoglycemia was achieved using the glucose clamp technique, resulted in suppressed glucose production (0.62 +/- 0.08 vs. 1.56 +/- 0.07 mg/kg per min at 12 h, P less than 0.01) and augmented glucose utilization (2.17 +/- 0.18 vs. 1.57 +/- 0.07 mg/kg per min at 12 h, P less than 0.01). Complete blockade of counterregulation (neurohumoral blockade plus prevention of hypoglycemia) did not further enhance the suppressive effects of insulin on glucose production. However, when severe hypoglycemia was induced during neurohumoral counterregulatory blockade, glucose production was nearly two times greater (1.05 +/- 0.05 mg/kg per min at 9 h) than that observed during complete counterregulatory blockade (0.58 +/- 0.08 mg/kg per min at 9 h, P less than 0.01) and that observed during mere neurohumoral blockade with moderate hypoglycemia (0.59 +/- 0.06 mg/kg per min at 9 h, P less than 0.01). These results demonstrate that glucose counterregulation involves both neurohumoral and hepatic autoregulatory components: neurohumoral factors, which require only moderate hypoglycemia for their activation, augment glucose production and reduce glucose utilization; hepatic autoregulation requires severe hypoglycemia for its activation and may thus serve as an emergency system to protect the brain when other counterregulatory factors fail to prevent threatening hypoglycemia.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auer R. N., Olsson Y., Siesjö B. K. Hypoglycemic brain injury in the rat. Correlation of density of brain damage with the EEG isoelectric time: a quantitative study. Diabetes. 1984 Nov;33(11):1090–1098. doi: 10.2337/diab.33.11.1090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter J. D., Forsham P. H. Tissue effects of glucocorticoids. Am J Med. 1972 Nov;53(5):573–589. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(72)90154-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boden G., Reichard G. A., Jr, Hoeldtke R. D., Rezvani I., Owen O. E. Severe insulin-induced hypoglycemia associated with deficiencies in the release of counterregulatory hormones. N Engl J Med. 1981 Nov 12;305(20):1200–1205. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198111123052007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolli G. B., De Feo P., De Cosmo S., Perriello G., Ventura M. M., Benedetti M. M., Santeusanio F., Gerich J. E., Brunetti P. A reliable and reproducible test for adequate glucose counterregulation in type I diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1984 Aug;33(8):732–737. doi: 10.2337/diab.33.8.732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolli G. B., Dimitriadis G. D., Pehling G. B., Baker B. A., Haymond M. W., Cryer P. E., Gerich J. E. Abnormal glucose counterregulation after subcutaneous insulin in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1984 Jun 28;310(26):1706–1711. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198406283102605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bratusch-Marrain P. R., Smith D., DeFronzo R. A. The effect of growth hormone on glucose metabolism and insulin secretion in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 Nov;55(5):973–982. doi: 10.1210/jcem-55-5-973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucolo R. J., Bergman R. N., Marsh D. J., Yates F. E. Dynamics of glucose autoregulation in the isolated, blood-perfused canine liver. Am J Physiol. 1974 Jul;227(1):209–217. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1974.227.1.209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clutter W. E., Bier D. M., Shah S. D., Cryer P. E. Epinephrine plasma metabolic clearance rates and physiologic thresholds for metabolic and hemodynamic actions in man. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jul;66(1):94–101. doi: 10.1172/JCI109840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryer P. E., Gerich J. E. Relevance of glucose counterregulatory systems to patients with diabetes: critical roles of glucagon and epinephrine. Diabetes Care. 1983 Jan-Feb;6(1):95–99. doi: 10.2337/diacare.6.1.95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryer P. E. Hypoglycemic glucose counterregulation in patients with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Lab Clin Med. 1982 Apr;99(4):451–456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryer P. E., Rizza R. A., Haymond M. W., Gerich J. E. Epinephrine and norepinephrine are cleared through beta-adrenergic, but not alpha-adrenergic, mechanisms in man. Metabolism. 1980 Nov;29(11 Suppl 1):1114–1118. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(80)90019-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEBODO R. C., STEELE R., ALTSZULER N., DUNN A., BISHOP J. S. ON THE HORMONAL REGULATION OF CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM; STUDIES WITH C14 GLUCOSE. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1963;19:445–488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOLE V. P., MEINERTZ H. Microdetermination of long-chain fatty acids in plasma and tissues. J Biol Chem. 1960 Sep;235:2595–2599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson M. B. Autoregulation by glucose of hepatic glucose balance: permissive effect of insulin. Metabolism. 1981 Mar;30(3):279–284. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(81)90152-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faber O. K., Binder C., Markussen J., Heding L. G., Naithani V. K., Kuzuya H., Blix P., Horwitz D. L., Rubenstein A. H. Characterization of seven C-peptide antisera. Diabetes. 1978;27 (Suppl 1):170–177. doi: 10.2337/diab.27.1.s170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerich J., Cryer P., Rizza R. Hormonal mechanisms in acute glucose counterregulation: the relative roles of glucagon, epinephrine, norepinephrine, growth hormone, and cortisol. Metabolism. 1980 Nov;29(11 Suppl 1):1164–1175. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(80)90026-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glinsmann W. H., Hern E. P., Lynch A. Intrinsic regulation of glucose output by rat liver. Am J Physiol. 1969 Apr;216(4):698–703. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.216.4.698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert V., Lau K. S., Gottlieb C. W., Bleicher S. J. Coated charcoal immunoassay of insulin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1965 Oct;25(10):1375–1384. doi: 10.1210/jcem-25-10-1375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hers H. G., Van Schaftingen E. Fructose 2,6-bisphosphate 2 years after its discovery. Biochem J. 1982 Jul 15;206(1):1–12. doi: 10.1042/bj2060001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang S. C., Phelps M. E., Hoffman E. J., Sideris K., Selin C. J., Kuhl D. E. Noninvasive determination of local cerebral metabolic rate of glucose in man. Am J Physiol. 1980 Jan;238(1):E69–E82. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1980.238.1.E69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Järhult J., Falck B., Ingemansson S., Nobin A. The functional importance of sympathetic nerves to the liver and endocrine pancreas. Ann Surg. 1979 Jan;189(1):96–100. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197901000-00018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinbaum J., Shamoon H. Impaired counterregulation of hypoglycemia in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1983 Jun;32(6):493–498. doi: 10.2337/diab.32.6.493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koerker D. J., Halter J. B. Glucoregulation during insulin and glucagon deficiency: role of catecholamines. Am J Physiol. 1982 Sep;243(3):E225–E233. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1982.243.3.E225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreisberg R. A. Glucose-lactate inter-relations in man. N Engl J Med. 1972 Jul 20;287(3):132–137. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197207202870307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljenquist J. E., Mueller G. L., Cherrington A. D., Perry J. M., Rabinowitz D. Hyperglycemia per se (insulin and glucagon withdrawn) can inhibit hepatic glucose production in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1979 Jan;48(1):171–175. doi: 10.1210/jcem-48-1-171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATTINGLY D. A simple fluorimetric method for the estimation of free 11-hydroxycorticoids in human plasma. J Clin Pathol. 1962 Jul;15:374–379. doi: 10.1136/jcp.15.4.374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGorman L. R., Rizza R. A., Gerich J. E. Physiological concentrations of growth hormone exert insulin-like and insulin antagonistic effects on both hepatic and extrahepatic tissues in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1981 Sep;53(3):556–559. doi: 10.1210/jcem-53-3-556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCraw E. F., Peterson M. J., Ashmore J. Autoregulation of glucose metabolism in the isolated perfused rat liver. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Oct;126(1):232–236. doi: 10.3181/00379727-126-32410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCraw E. F., Peterson M. J., Ashmore J. Autoregulation of glucose metabolism in the isolated perfused rat liver. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Oct;126(1):232–236. doi: 10.3181/00379727-126-32410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newgard C. B., Foster D. W., McGarry J. D. Evidence for suppression of hepatic glucose-6-phosphatase with carbohydrate feeding. Diabetes. 1984 Feb;33(2):192–195. doi: 10.2337/diab.33.2.192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polonsky K., Bergenstal R., Pons G., Schneider M., Jaspan J., Rubenstein A. Relation of counterregulatory responses to hypoglycemia in type I diabetics. N Engl J Med. 1982 Oct 28;307(18):1106–1112. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198210283071802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popp D. A., Shah S. D., Cryer P. E. Role of epinephrine-mediated beta-adrenergic mechanisms in hypoglycemic glucose counterregulation and posthypoglycemic hyperglycemia in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1982 Feb;69(2):315–326. doi: 10.1172/JCI110455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pozefsky T., Felig P., Tobin J. D., Soeldner J. S., Cahill G. F., Jr Amino acid balance across tissues of the forearm in postabsorptive man. Effects of insulin at two dose levels. J Clin Invest. 1969 Dec;48(12):2273–2282. doi: 10.1172/JCI106193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renzini V., Brunori C. A., Valori C. A sensitive and specific fluorimetric method for the determination of noradrenalin and adrenalin in human plasma. Clin Chim Acta. 1970 Dec;30(3):587–594. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(70)90249-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizza R. A., Cryer P. E., Gerich J. E. Role of glucagon, catecholamines, and growth hormone in human glucose counterregulation. Effects of somatostatin and combined alpha- and beta-adrenergic blockade on plasma glucose recovery and glucose flux rates after insulin-induced hypoglycemia. J Clin Invest. 1979 Jul;64(1):62–71. doi: 10.1172/JCI109464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizza R. A., Cryer P. E., Haymond M. W., Gerich J. E. Adrenergic mechanisms for the effects of epinephrine on glucose production and clearance in man. J Clin Invest. 1980 Mar;65(3):682–689. doi: 10.1172/JCI109714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizza R. A., Mandarino L. J., Gerich J. E. Cortisol-induced insulin resistance in man: impaired suppression of glucose production and stimulation of glucose utilization due to a postreceptor detect of insulin action. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 Jan;54(1):131–138. doi: 10.1210/jcem-54-1-131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizza R. A., Mandarino L. J., Gerich J. E. Dose-response characteristics for effects of insulin on production and utilization of glucose in man. Am J Physiol. 1981 Jun;240(6):E630–E639. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1981.240.6.E630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizza R. A., Mandarino L. J., Gerich J. E. Effects of growth hormone on insulin action in man. Mechanisms of insulin resistance, impaired suppression of glucose production, and impaired stimulation of glucose utilization. Diabetes. 1982 Aug;31(8 Pt 1):663–669. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.8.663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruderman N. B., Herrera M. G. Glucose regulation of hepatic gluconeogenesis. Am J Physiol. 1968 Jun;214(6):1346–1351. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.214.6.1346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacca L., Hendler R., Sherwin R. S. Hyperglycemia inhibits glucose production in man independent of changes in glucoregulatory hormones. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1978 Nov;47(5):1160–1163. doi: 10.1210/jcem-47-5-1160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saccà L., Morrone G., Cicala M., Corso G., Ungaro B. Influence of epinephrine, norepinephrine, and isoproterenol on glucose homeostasis in normal man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1980 Apr;50(4):680–684. doi: 10.1210/jcem-50-4-680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saccà L., Sherwin R., Hendler R., Felig P. Influence of continuous physiologic hyperinsulinemia on glucose kinetics and counterregulatory hormones in normal and diabetic humans. J Clin Invest. 1979 May;63(5):849–857. doi: 10.1172/JCI109384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shamoon H., Hendler R., Sherwin R. S. Synergistic interactions among antiinsulin hormones in the pathogenesis of stress hyperglycemia in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1981 Jun;52(6):1235–1241. doi: 10.1210/jcem-52-6-1235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shulman G. I., Liljenquist J. E., Williams P. E., Lacy W. W., Cherrington A. D. Glucose disposal during insulinopenia in somatostatin-treated dogs. The roles of glucose and glucagon. J Clin Invest. 1978 Aug;62(2):487–491. doi: 10.1172/JCI109150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalmans W. The role of the liver in the homeostasis of blood glucose. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1976;11:51–97. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152811-9.50009-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verdonk C. A., Rizza R. A., Nelson R. L., Go V. L., Gerich J. E., Service F. J. Interaction of fat-stimulated gastric inhibitory polypeptide on pancreatic alpha and beta cell function. J Clin Invest. 1980 May;65(5):1119–1125. doi: 10.1172/JCI109765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White N. H., Skor D. A., Cryer P. E., Levandoski L. A., Bier D. M., Santiago J. V. Identification of type I diabetic patients at increased risk for hypoglycemia during intensive therapy. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 3;308(9):485–491. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303033080903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson J. R., Kreisberg R. A., Felts P. W. Mechanism for the stimulation of gluconeogenesis by fatty acids in perfused rat liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jul;56(1):247–254. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.1.247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



