Summary
Abnormal nuclear size and shape are hallmarks of aging and cancer [1, 2]. However, the mechanisms regulating nuclear morphology and nuclear envelope (NE) expansion are poorly understood. In metazoans, the NE disassembles prior to chromosome segregation and reassembles at the end of mitosis [3]. In budding yeast, the NE remains intact. The nucleus elongates as chromosomes segregate and then divides at the end of mitosis to form two daughter nuclei without NE disassembly. The budding yeast nucleus also undergoes remodeling during a mitotic arrest; the NE continues to expand despite the pause in chromosome segregation, forming a nuclear extension, or “flare”, that encompasses the nucleolus [4]. The distinct nucleolar localization of the mitotic flare indicates that the NE is compartmentalized and that there is a mechanism by which NE expansion is confined to the region adjacent to the nucleolus. Here we show that mitotic flare formation is dependent on the yeast polo kinase, Cdc5. This function of Cdc5 is independent of its known mitotic roles, including rDNA condensation. High-resolution imaging revealed that following Cdc5 inactivation, nuclei expand isometrically rather than forming a flare, indicating that Cdc5 is needed for NE compartmentalization. Even in an uninterrupted cell cycle, a small NE expansion occurs adjacent to the nucleolus prior to anaphase in a Cdc5-dependent manner. Our data provides the first evidence that polo kinase, a key regulator of mitosis [5], plays a role in regulating nuclear morphology and NE expansion.
Results and Discussion
Cdc5 affects nuclear morphology during a mitotic arrest
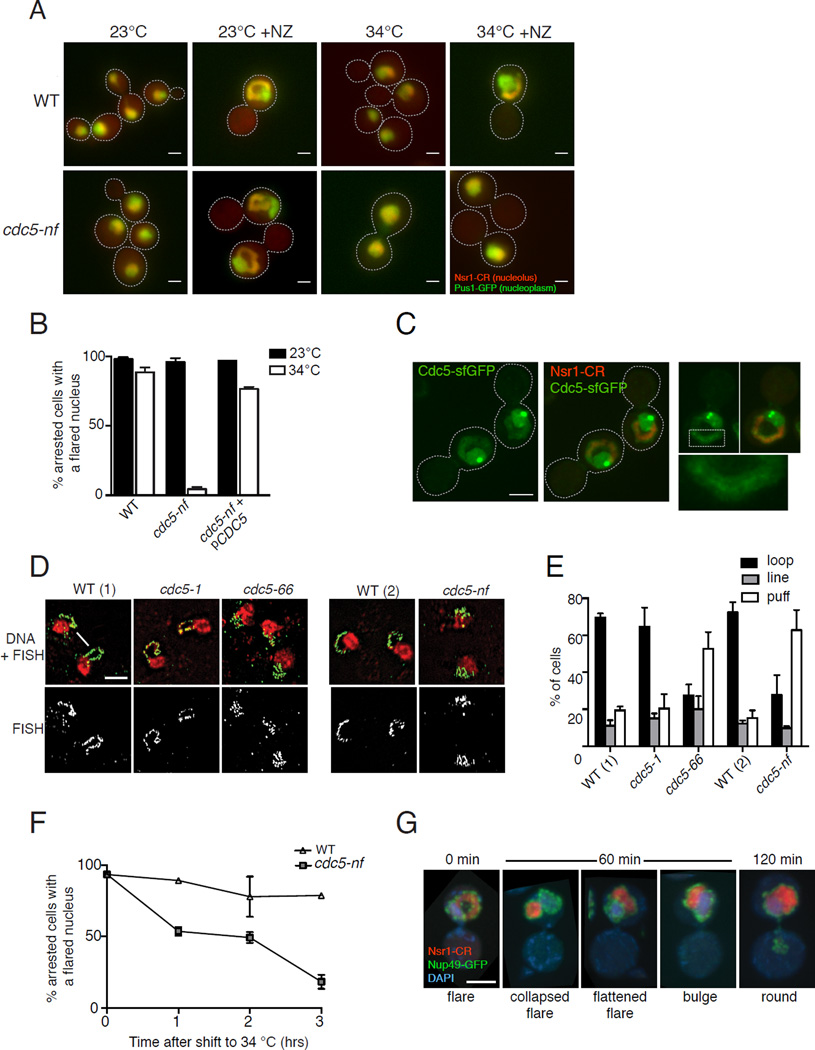
During interphase, nuclei of budding yeast are typically round, with the nucleolus forming a crescent-shaped mass at the nuclear periphery (Fig. 1A). During a mitotic delay the NE continues to expand, forming an extension, or flare, that encompasses the nucleolus (Fig. 1A) [4]. While in interphase the interface between the nucleolus and the rest of the nucleoplasm is extensive (Fig. 1A image 1, arrow), in the flare the nucleolus has only a very narrow interface with the rest of the nucleoplasm (Fig. 1A, image 2, arrow). To understand this spatially restricted NE expansion we screened for mutants that maintain a round nucleus when arrested in mitosis. Because flare formation may occur through the same process that normally drives NE expansion, genes involved in flare formation may be essential. Therefore, we generated a collection of 1500 conditional mutants that were viable at the 23°C but not at 34°C and screened them for mutants that arrested in mitosis at 34°C with a round nucleus (Fig. 1A). We found “no-flare” (nf) mutants in the yeast polo kinase gene, CDC5, and in the lipid synthesis genes, FAS1, FAS2 and ACC1. The cdc5-nf mutant is the focus of this study.
Figure 1. Cdc5 affects nuclear morphology during a mitotic arrest.
A) Merged fluorescence images of fixed mitotic-arrested WT (top row) and cdc5-nf (bottom row) cells. The nucleoplasm is marked with Pus1-GFP (green) and nucleolus with Nsr1-mCherry (red). A nuclear flare containing the nucleolus forms in WT cells during a mitotic arrest induced by nocodazole (NZ) at both 23°C and 34°C (panels 2, 4) and in cdc5-nf cells at 23°C (panel 6). Nuclei of cdc5-nf cells are round at 34°C in the presence of NZ (panel 8). In the absence of NZ, cdc5-nf cells arrest in late telophase at 34°C (panel 7, Fig. S2E). White arrows indicate the interface between the nucleolus and nucleoplasm (panels 1 and 2). Scale bar, 2 µm. B) Quantification of phenotypes of NZ-treated cells shown in panel A (for each condition n=100 in at least 2 biological replicates). C) Cdc5 nuclear localization during a mitotic arrest. WT cells expressing Cdc5-sfGFP and Nsr1-mCherry (nucleolar marker) were arrested in NZ at 30°C and imaged using fluorescence confocal microscopy. Bright green spots are at the spindle pole bodies. Area contained in the white dashed box (right panels) is expanded in the bottom right panel to show a thin line of Cdc5-sfGFP within the nucleolar flare. Scale bar, 3 µm. D) Images from fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) using a probe for rDNA in WT and cdc5 mutants. Cells were arrested in NZ at 34°C for 150 min. WT(1) is isogenic to strains cdc5-1 and cdc5-66 while WT(2) is isogenic to strain cdc5-nf. WT cells arrested in mitosis typically exhibit an rDNA “loop” (arrow), while mutants defective in rDNA condensation exhibit amorphous structures referred to as “puff” (arrowhead) [31]. Scale bar, 5 µm. E) Quantification of rDNA phenotypes of cdc5 mutants from FISH described in D. F) Cdc5 is required for the maintenance of a nuclear flare. cdc5-nf and WT cells were arrested in mitosis at 23°C to allow flare formation and then shifted to 34°C. Samples were taken at the indicated time points. For each time point n=100 in at least 3 biological replicates. See also Fig. S2F. G) Images of cdc5-nf cells from the experiment in Fig. S2F showing examples of the collapse and eventual loss of nuclear flares upon the inactivation of Cdc5. NZ-arrested WT and cdc5-nf cells were shifted from 23°C to 34°C. Cells were fixed every 30 min and were imaged by confocal fluorescence microscopy. The images shown are from 60 and 120 min. The NE is marked with Nup49-GFP (green), the nucleolus with Nsr1-mCherry (red) and DNA with DAPI (blue). Scale bar, 3 µm. Error bars in all panels indicate SD.
The cdc5-nf allele carries a mutation, E178K, in a highly conserved residue within the kinase domain (Fig. S1A). Less than 10% of mitotically arrested cdc5-nf cells possessed a nuclear flare, compared to around 90% of wild type (WT) cells (Fig. 1A, 1B). Expression of WT CDC5 from a CEN plasmid restores the flared nuclear phenotype (Fig. 1B). A similar result was observed when a mitotic arrest was induced by inactivating an Anaphase Promoting Complex subunit, Cdc16 [6] (Fig. S1B, S1C). As with previously isolated cdc5 mutant alleles [7–9], the terminal phenotype of cdc5-nf at 34°C was a telophase arrest (Fig. 1A, S2D) due to a requirement for Cdc5 in mitotic exit. In mitotically arrested cells, Cdc5 accumulated in the nucleoplasm (Fig. 1C and S1D), spindle pole bodies [10] and was occasionally visible as a fine thread through the nucleolus, possibly due to its association with the ribosomal DNA array (rDNA) [11]. As expected, cdc5-nf did not affect nuclear remodeling following exposure to alpha-factor mating pheromone, (Fig. S1E and F) since Cdc5 is not expressed during G1 [12].
The no-flare phenotype was not specific to cdc5-nf, as other cdc5 alleles that were inviable at 34°C, cdc5-1 and cdc5-66 [13] (Fig. S1A, S2A), also exhibited a mitotic flare formation defect (Fig. S2B). The severity of the no-flare phenotype was inversely proportional to the Cdc5 activity at 34°C as measured by the degree of rDNA condensation (Fig. 1D, 1E). Depletion of Cdc5 using an auxin-induced Cdc5-degron allele [14] (Fig. S2C, S2D) also resulted in a mitotic no-flare phenotype (Fig. S2E). These data suggest that the no-flare nuclear phenotype seen in the cdc5-nf strain is due to reduced Cdc5 activity.
Cdc5 is required for maintenance of the nuclear flare
When mitotically arrested cdc5-nf cells were allowed to form flares at 23°C and then shifted to 34°C, the number of cells with flared nuclei dropped precipitously (Fig. 1F). The flares that did persist in cdc5-nf cells tended to be collapsed (a smaller loop than in time 0) or flattened onto the DAPI mass (Fig. 1G, S2F). Based on their rate of appearance "bulged" nuclei, where the nucleolus only slightly protruded away from the DAPI mass, may be an intermediate step between a flared and round nucleus (Fig. 1G, S2F). Thus, Cdc5 is required for flare maintenance during a mitotic arrest.
The effect of Cdc5 on nuclear morphology is not imposed through FEAR, MEN or rDNA condensation
Cdc5 has been implicated in multiple mitotic processes, including FEAR (Cdc Fourteen Early Anaphase Release), MEN (Mitotic Exit Network) [15, 16] and rDNA condensation [17]. All mitotically arrested FEAR and MEN mutants tested displayed a flared nuclear phenotype indistinguishable from WT (Fig. S2G, S2H), indicating that flare formation is independent of FEAR and MEN.
Given the inverse correlation between Cdc5 activity and the severity of the no-flare phenotype noted above (Fig. 1D, 1E, and S2B), it was possible that flare formation was dependent on rDNA condensation. If that were the case, then disruption of rDNA condensation by other means, such as condensin inactivation [18], should also result in a no-flare phenotype. However, condensin mutants (brn1-9 [19] and ycs4-1 [20]) that exhibit rDNA condensation defects at 34°C (Fig. 2A, 2B) still form flares when arrested in mitosis at 34°C (Fig. 2C, 2D and S3), demonstrating that rDNA condensation is not required for flare formation. Condensin mutants, however, displayed wider and less extended flares than those seen in WT cells (Fig. 2C and S3). Thus, while flares are present in mutants defective in rDNA condensation, the shape of the flare may be affected by the structure of the rDNA/nucleolus.
Figure 2. Cdc5 is not affecting nuclear morphology through rDNA condensation or attachment to the NE.
A) Images from FISH using a probe for rDNA in condensin mutants. Cells were arrested in NZ at 34°C for 150 min. rDNA is shown in green, DNA in red. Scale bar, 5 µm. B) Quantification of rDNA phenotypes of condensin mutants from FISH described in A. C) Merged fluorescence images of WT and condensin mutant cells arrested in NZ at 34°C. The nucleoplasm is marked with Pus1-GFP (green) and nucleolus with Nsr1-mCherry (red). D) Quantification of nuclear phenotypes for NZ-arrested condensin mutants experiment shown in C. WT(1) is isogenic to strain cdc5-nf while WT(2) is isogenic to strains brn1-9 and ycs4-1. E) Merged fluorescence images of asynchronous and NZ-arrested cells in a strain where the chromosomal rDNA was replaced by a single plasmid-borne copy of the rDNA. White arrows indicate nuclear flares. The nuclear pore subunit Nup49-GFP marks the NE (green), Nsr1-mCherry the "dot" nucleolus (red spot) and DAPI-stained DNA is shown in blue. F) Quantification of nuclear phenotypes of NZ-arrested rDNA-NE detachment mutants alone and in combination with the cdc5-nf allele. For panels B, D and F for each condition n=100 in each of at least 2 biological replicates. Error bars in all panels indicate SD.
Further evidence that rDNA condensation is not required for flare formation came from a strain in which the rDNA was deleted and replaced by a plasmid carrying a single rDNA repeat [21]. As a result, the nucleolus forms a "dot" rather than the typical crescent shape (Fig. 2E). This strain grew poorly and exhibited jagged edged nuclei (Fig. 2E). However, flared nuclei were observed in 70 ± 7% of mitotically arrested cells compared to only 21 ± 1% of interphase cells (Fig. 2E). The presence of NE extensions during interphase may be due to the poor growth of this strain. Nonetheless, mitotic flares can form independently of rDNA.
Finally, we examined whether Cdc5 affects nuclear morphology through the attachment of rDNA to the NE [22]. If this anchoring allowed flare formation, then mutations that lead to the detachment of the rDNA from the NE should produce a no-flare phenotype. However, such mutants, including heh1Δ, csm1Δ, lrs4Δ and nur1Δ [22], exhibited flared nuclei when arrested in mitosis (Fig. 2F). Conversely, if the rDNA had to detach from the NE for a flare to form, and Cdc5 were required for this detachment, then combining cdc5-nf and rDNA detachment mutants should give rise to flared nuclei, as the rDNA is constitutively detached from the NE. However, deletion of rDNA attachment genes in a cdc5-nf background did not restore flare formation (Fig. 2F). Therefore, Cdc5 is not affecting nuclear morphology via rDNA condensation or its NE attachment.
Cdc5 confines NE expansion to the nucleolar region during a mitotic arrest
Since flare formation involves NE expansion [4], we imagine that in the mitotically arrested cdc5-nf mutant either the NE does not expand, or the NE does expand, but the added nuclear membrane is distributed uniformly throughout the NE, resulting in isometric expansion. To distinguish between these two possibilities, NE expansion during a mitotic arrest was measured using soft X-ray tomography (SXT). WT and cdc5-nf cells were staged in G1, released into media containing NZ at 34°C and NE expansion was followed as cells progressed towards a mitotic arrest (Fig. 3A), using cell volume as a proxy for cell cycle progression.
Figure 3. Nuclei of cdc5-nf cells expand isometrically during a mitotic arrest.
A) Outline of the experiment. WT and cdc5-nf cells were arrested in G1 with alpha factor and then released into NZ at 34°C. Samples were taken every 20 min and processed for soft X-ray imaging. B) Surface rendered views of the cell (pink) and nucleus (pale green) after segmentation of three dimensional reconstructions of WT and cdc5-nf cells from the experiment described in panel A. Scale bar, 1 µm. C) Quantification of nuclear surface areas as a function of cell size of WT and cdc5-nf cells (n=74 and 86, respectively). Nuclear flares begin to appear in cells of approximately 140 μm3 (black triangle). Linear regressions were calculated using Prism (R2 WT=0.633, R2 cdc5-nf=0.774). There is no significant difference between the slope of the line describing the increase in nuclear surface areas in WT and cdc5-nf (p=0.44, ANCOVA). Nuclei of WT cells have a slightly greater surface area than nuclei of cdc5-nf across all cell sizes (p=0.0006, ANCOVA). D) Quantification of nuclear volumes as a function of cell size of the same cells as panel C. There is no significant difference between nuclear volumes in WT (R2=0.677) and cdc5-nf (R2=0.762) across all cell sizes (p=0.48, ANCOVA).
Tomographic reconstructions (Fig. 3B) revealed that, as seen previously by fluorescence, very few nuclei (9%) in large budded cdc5-nf cells (cell volume > 140 μm3) were flared, whereas 95% of large budded WT cells contained flared nuclei. However, the nuclear surface areas in both WT and cdc5-nf cells increased at the same rate (i.e. amount of surface area added as a function of cell volume) (Fig. 3C), demonstrating that cdc5-nf nuclei are expanding isometrically. This suggests that Cdc5 is required to designate the nucleolus as the site NE expansion during a mitotic arrest. Interestingly, mutant cells had the same nuclear:cell volume ratio as WT cells despite their different morphologies (Fig. 3D). Nuclear:cell volume ratio was shown previously to be constant [23, 24], although the underlying mechanism and the functional importance of this ratio are not known. We speculate that flare formation allows the cell to expand its nuclear surface area without altering its nuclear volume, thus maintaining a constant nuclear:cell volume ratio and limiting the disruption to the space in which the bulk of the DNA resides. The isometric expansion of the cdc5-nf nucleus likely increases the space occupied by the chromosomes, the consequences of which are currently unknown.
Cdc5 allows transient NE expansion at the nucleolus during uninterrupted mitosis
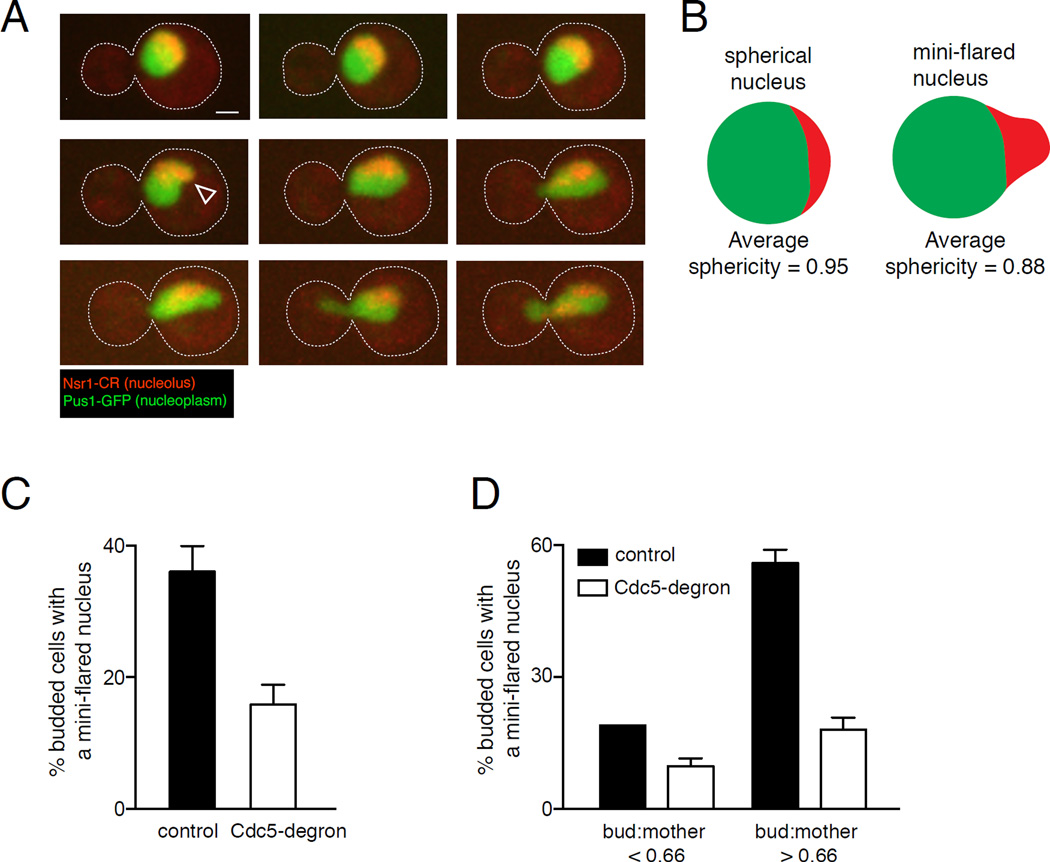
To characterize NE dynamics in cycling cells, WT cells were imaged every 5 minutes until they completed anaphase. Small-budded cells (Fig. 4A, 0 min) had a spherical nucleus, but in 10 out of 16 time courses a small expansion of the nucleus in the nucleolar region was visible prior to anaphase (Fig. 4A, 15 min, white arrowhead, and Fig S4B). This expansion, or “mini-flare”, was defined as an expansion of an interphase nucleus that disrupts the continuity of the normal round nuclear shape (Fig. 4B). It always occurred at the nucleolar region and was more prevalent in cells with a larger bud:mother size ratio, shortly before entering anaphase (Fig. 4C, 4D).
Figure 4. Cdc5 allows NE expansion at the nucleolar region during an uninterrupted mitosis.
A) Time course of images of a WT cell progressing from a small budded stage into anaphase. The nucleoplasm is marked with Pus1-GFP (green) and the nucleolus with Nsr1-mCherry (red). Images shown are maximum projections of merged fluorescence confocal images. A mini-flare (white arrowhead) is visible at 15 min. Scale bar, 1 µm. B) A mini-flare disrupts the spherical surface of the nucleus (green), specifically at the site of the nucleolus (red). Sphericity data are from Fig. S4A. C) Mini-flares are Cdc5-dependent. Quantification of the frequency of mini-flares in a control strain and Cdc5-degron cells. Fixed log-phase cells were imaged by fluorescence confocal microscopy and nuclear phenotypes of all budded cells were scored. The frequency of mini-flares in budded cells was lower in the Cdc5-degron strain (p<0.0001, Fisher’s exact test). D) Data from panel C divided into categories by bud:mother cell size ratio. For bud:mother <0.66, n=79 and 66 for WT and Cdc5-degron, respectively. For bud:mother >0.66, n= 69 and 134 for WT and Cdc5-degron, respectively. The frequency of mini-flares in cells with larger buds is significantly lower in the Cdc5-degron strain (p<0.0001, Fisher’s exact test). The difference in frequency of mini-flares in cells with small buds is not statistically significant (p=0.1665, Fisher’s exact test). Error bars in all panels represent SD.
As a more objective measure of the formation of a mini-flare, the sphericity of interphase nuclei was determined. The sphericity of a given object is the ratio between the surface area of a sphere with the same volume as that object and the surface area of the object itself [25]. Thus, the sphericity of a sphere=1, and perturbations to the shape of a sphere, which would increase its surface area, would result in sphericity values that are less than 1. For example, the sphericity of the elongated nuclei in alpha factor arrested cells (Fig. S1E) is around 0.8. We found that nuclei that did not have a mini-flare had an average sphericity value of 0.95 while the average sphericity of nuclei that were designated as having a mini-flare was 0.88 [Fig. S4A, S4B].
We next determined whether these mini-flares were dependent on Cdc5 using the auxin-inducible Cdc5-degron strain. Both the Cdc5-degron and control strains were grown at 23°C to mid-log phase and exposed to auxin. Interphase cells were analyzed after 2 hrs in the presence of auxin, when ~50% of the Cdc5-degron cells had arrested in telophase and Cdc5 levels were significantly reduced (Fig. S2C). Mini-flares were visible in 36% of budded control cells, but only in 18% of budded Cdc5-depleted cells (Fig. 4C) and this difference was even more pronounced in cells with larger buds (bud:mother size ratio > 0.66) (Fig. 4D). Moreover, the sphericity of nuclei in the absence of Cdc5 was significantly greater than the sphericity of the control cells (Fig. S4A). Thus, Cdc5 plays a role in regulating NE expansion not only during a mitotic delay but also in unperturbed cycling cells.
Our studies uncovered a new role for Cdc5 in the compartmentalization of the yeast NE. Cdc5 regulates nuclear morphology by designating the NE adjacent to the nucleolus as the site of NE expansion in both mitotically-arrested and cycling cells. By coupling Cdc5, which is active in later stages of the cell cycle, to NE expansion, the cell can expand its nucleus isometrically during G1 and S phase, and confine NE expansion to the nucleolar region early in mitosis and during a mitotic delay. It is likely that when mitosis is delayed and lipid synthesis continues unabated [4], the mini-flare develops into a full-sized flare. How might Cdc5 affect NE distribution? While the precise mechanism is not known, it is independent of Cdc5's roles in the FEAR pathway, the MEN and rDNA condensation. The confinement of the flare or mini-flare to the NE adjacent to the nucleolus may prevent disruption to the rest of the nucleus, where the majority of the chromosomes reside. Once released from a mitotic arrest, the non-flared nuclei of cdc5-nf are able to complete anaphase without rupturing, but their recovery from the arrest is delayed compared to WT, as judged by their initial rate of spindle elongation (data not shown). Whether this is due to the altered nuclear shape or to another Cdc5-related function awaits the identification of the relevant Cdc5 target(s) involved in flare formation.
The regulation of NE expansion is of great significance to the study of aging and cancer, where nuclear size and shape are often disrupted. While the role of Cdc5 in flare formation may be specific to closed mitosis, the relevant target(s) of this conserved kinase may play a role in membrane dynamics in higher eukaryotes. The mammalian polo kinase (Plk1) has known functions in membrane restructuring during mitosis, playing a role in Golgi breakdown [26] and in coordinating abcission with other mitotic events during cytokinesis [27]. Plk1 has also been proposed to affect NE breakdown [28, 29]. In mammalian cells, depletion of Plk1 leads to altered nuclear morphology [30], a phenotype that has been attributed to chromosome mis-segregation in the absence of Plk1. Our findings linking yeast polo kinase to NE expansion indicate that Plk1 may have a more direct role in regulating nuclear shape.
Supplementary Material
Highlights.
Yeast polo kinase Cdc5 regulates compartmentalization of the nuclear envelope (NE)
Cdc5 confines NE expansion to the nucleolar region during a mitotic delay
Cdc5 also affects NE expansion during an uninterrupted cell cycle
Cdc5 affects NE expansion independently of FEAR, MEN and rDNA condensation
Acknowledgments
We thank D. Reynolds, A. Hoyt, T. Eng, D. Koshland, A. Amon, S. Lacefield and J. Diffley for yeast strains and plasmids and M. Lichten, W. Prinz, F. Chang and members of the Cohen-Fix lab for discussions on the manuscript. A.D.W., C.K.M., E.S.D. and O.C.F. are funded by an intramural NIDDK Diseases grant. C.A.L., B.P.C. and E.A.S. are funded by the National Institute of General Medical Science of the National Institutes of Health (P41GM103445) and the US Department of Energy, Office of Biological and Environmental Research (DE-AC02-05CH11231). Research in D.D.'s laboratory is supported by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (MOP 82912 and MOP 136788). D.D. is a recipient of a TierII Canada Research Chair in Cell Cycle Regulation and Genomic Integrity.
Footnotes
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final citable form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
References
- 1.Chow K-H, Factor RE, Ullman KS. The nuclear envelope environment and its cancer connections. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2012;12:196–209. doi: 10.1038/nrc3219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Scaffidi P, Misteli T. Lamin A-dependent nuclear defects in human aging. Science. 2006;312:1059–1063. doi: 10.1126/science.1127168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kutay U, Hetzer MW. Reorganization of the nuclear envelope during open mitosis. Current Opinion in Cell Biology. 2008;20:669–677. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2008.09.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Witkin KL, Chong Y, Shao S, Webster MT, Lahiri S, Walters AD, Lee B, Koh JLY, Prinz WA, Andrews BJ, et al. The budding yeast nuclear envelope adjacent to the nucleolus serves as a membrane sink during mitotic delay. Curr. Biol. 2012;22:1128–1133. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2012.04.022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Archambault V, Glover DM. Polo-like kinases: conservation and divergence in their functions and regulation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2009;10:265–275. doi: 10.1038/nrm2653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Irniger S, Piatti S, Michaelis C, Nasmyth K. Genes involved in sister chromatid separation are needed for B-type cyclin proteolysis in budding yeast. Cell. 1995;81:269–278. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90337-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Jaspersen SL, Charles JF, Tinker-Kulberg RL, Morgan DO. A late mitotic regulatory network controlling cyclin destruction in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol. Biol. Cell. 1998;9:2803–2817. doi: 10.1091/mbc.9.10.2803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Lee SE, Frenz LM, Wells NJ, Johnson AL, Johnston LH. Order of function of the budding-yeast mitotic exit-network proteins Tem1, Cdc15, Mob1, Dbf2, and Cdc5. Curr. Biol. 2001;11:784–788. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(01)00228-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Visintin R, Craig K, Hwang ES, Prinz S, Tyers M, Amon A. The phosphatase Cdc14 triggers mitotic exit by reversal of Cdk-dependent phosphorylation. Molecular Cell. 1998;2:709–718. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(00)80286-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Song S, Grenfell TZ, Garfield S, Erikson RL, Lee KS. Essential function of the polo box of Cdc5 in subcellular localization and induction of cytokinetic structures. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000;20:286–298. doi: 10.1128/mcb.20.1.286-298.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Rossio V, Galati E, Ferrari M, Pellicioli A, Sutani T, Shirahige K, Lucchini G, Piatti S. The RSC chromatin-remodeling complex influences mitotic exit and adaptation to the spindle assembly checkpoint by controlling the Cdc14 phosphatase. The Journal of Cell Biology. 2010;191:981–997. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201007025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Shirayama M, Zachariae W, Ciosk R, Nasmyth K. The Polo-like kinase Cdc5p and the WD-repeat protein Cdc20p/fizzy are regulators and substrates of the anaphase promoting complex in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J. 1998;17:1336–1349. doi: 10.1093/emboj/17.5.1336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Ratsima H, Ladouceur A-M, Pascariu M, Sauvé V, Salloum Z, Maddox PS, D'Amours D. Independent modulation of the kinase and polo-box activities of Cdc5 protein unravels unique roles in the maintenance of genome stability. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2011;108:E914–E923. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1106448108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Nishimura K, Fukagawa T, Takisawa H, Kakimoto T, Kanemaki M. An auxin-based degron system for the rapid depletion of proteins in nonplant cells. Nat. Methods. 2009;6:917–922. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Rock JM, Amon A. The FEAR network. Curr. Biol. 2009;19:R1063–R1068. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2009.10.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Segal M. Mitotic exit control: a space and time odyssey. Curr. Biol. 2011;21:R857–R859. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2011.09.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.St-Pierre J, Douziech M, Bazile F, Pascariu M, Bonneil E, Sauvé V, Ratsima H, Amours DD. Polo Kinase Regulates Mitotic Chromosome Condensation by Hyperactivation of Condensin DNA Supercoiling Activity. Molecular Cell. 2009;34:416–426. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2009.04.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Freeman L, Aragon-Alcaide L, Strunnikov A. The condensin complex governs chromosome condensation and mitotic transmission of rDNA. J. Cell Biol. 2000;149:811–824. doi: 10.1083/jcb.149.4.811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Lavoie BD, Tuffo KM, Oh S, Koshland D, Holm C. Mitotic chromosome condensation requires Brn1p, the yeast homologue of Barren. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2000;11:1293–1304. doi: 10.1091/mbc.11.4.1293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Biggins S, Bhalla N, Chang A, Smith DL, Murray AW. Genes involved in sister chromatid separation and segregation in the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 2001;159:453–470. doi: 10.1093/genetics/159.2.453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Wai HH, Vu L, Oakes M, Nomura M. Complete deletion of yeast chromosomal rDNA repeats and integration of a new rDNA repeat: use of rDNA deletion strains for functional analysis of rDNA promoter elements in vivo. Nucleic Acids Research. 2000;28:3524–3534. doi: 10.1093/nar/28.18.3524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Mekhail K, Seebacher J, Gygi SP, Moazed D. Role for perinuclear chromosome tethering in maintenance of genome stability. Nature. 2008;456:667–670. doi: 10.1038/nature07460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Jorgensen P, Edgington NP, Schneider BL, Rupes I, Tyers M, Futcher B. The size of the nucleus increases as yeast cells grow. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2007;18:3523–3532. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E06-10-0973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Neumann FR, Nurse P. Nuclear size control in fission yeast. The Journal of Cell Biology. 2007;179:593–600. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200708054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Wadell H. Volume, Shape and Roundness of Quartz Particles. Journal of Geology. 1935;43:250–280. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Lin CY, Madsen ML, Yarm FR, Jang YJ, Liu X, Erikson RL. Peripheral Golgi protein GRASP65 is a target of mitotic polo-like kinase (Plk) and Cdc2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2000;97:12589–12594. doi: 10.1073/pnas.220423497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Chen C-T, Hehnly H, Doxsey SJ. Orchestrating vesicle transport, ESCRTs and kinase surveillance during abscission. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012;13:483–488. doi: 10.1038/nrm3395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Li H, Liu XS, Yang X, Song B, Wang Y, Liu X. Polo-like kinase 1 phosphorylation of p150Glued facilitates nuclear envelope breakdown during prophase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2010;107:14633–14638. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1006615107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Laurell E, Beck K, Krupina K, Theerthagiri G, Bodenmiller B, Horvath P, Aebersold R, Antonin W, Kutay U. Phosphorylation of Nup98 by multiple kinases is crucial for NPC disassembly during mitotic entry. Cell. 2011;144:539–550. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.01.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Lera RF, Burkard ME. High Mitotic Activity of Polo-like Kinase 1 Is Required for Chromosome Segregation and Genomic Integrity in Human Epithelial Cells. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2012;287:42812–42825. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.412544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Lavoie BD, Hogan E, Koshland D. In vivo requirements for rDNA chromosome condensation reveal two cell-cycle-regulated pathways for mitotic chromosome folding. Genes Dev. 2004;18:76–87. doi: 10.1101/gad.1150404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.