Abstract
Hemorrhagic complications have been reported in up to 30% of critically ill patients with AKI undergoing RRT with systemic anticoagulation. Because bleeding is associated with significantly increased mortality risk, strategies aimed at reducing hemorrhagic complications while maintaining extracorporeal circulation should be implemented. Among the alternatives to systemic anticoagulation, regional citrate anticoagulation has been shown to prolong circuit life while reducing the incidence of hemorrhagic complications and lowering transfusion needs. For these reasons, the recently published Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes Clinical Practice Guidelines for Acute Kidney Injury have recommended regional citrate anticoagulation as the preferred anticoagulation modality for continuous RRT in critically ill patients in whom it is not contraindicated. However, the use of regional citrate anticoagulation is still limited because of concerns related to the risk of metabolic complications, the complexity of the proposed protocols, and the need for customized solutions. The introduction of simplified anticoagulation protocols based on citrate and the development of dialysis monitors with integrated infusion systems and dedicated software could lead to the wider use of regional citrate anticoagulation in upcoming years.
Keywords: AKI, citrate, CRRT, regional anticoagulation, SLED
Introduction
Although AKI is a well recognized high–bleeding risk condition (1), the patency of the extracorporeal circuit for RRT is usually maintained by the use of systemic anticoagulation with unfractionated heparin (2,3). However, a high incidence of hemorrhagic complications has been documented in patients undergoing RRT in the intensive care unit (ICU), with wide variability (5%–30%) related to differences in patient populations and anticoagulation protocols (4–7). Thus, the choice of the anticoagulant strategy, possibly limited to the extracorporeal circuit (i.e., regional anticoagulation), represents a key issue for safe and effective RRT in AKI. Although RRT can be performed without anticoagulation (8–11), this approach increases the risk of delivering low RRT doses in up to 30% of patients (12) because of shorter circuit life, increased downtime, and reduced filter performance (12–14).
A number of recent clinical studies has shown advantages of regional citrate anticoagulation (RCA) compared with heparin in terms of prolonged circuit life, reduced incidence of hemorrhagic complications, and lower transfusion needs (14–19). On the basis of these data, the 2012 Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Clinical Practice Guidelines for Acute Kidney Injury recommend use of RCA as the preferred anticoagulation modality for continuous RRT (CRRT) in patients without contra-indications for citrate, even in the absence of an increased bleeding risk or deranged coagulation (20). In addition, the same guidelines also recommend using RCA rather than no anticoagulation in patients with a high risk of bleeding (20). These KDIGO guidelines were also endorsed by the Canadian Society of Nephrology (21). However, issues remain regarding the use of citrate for RRT in AKI, including a clear definition of potential contraindications to its use, heterogeneity of RCA protocols, optimal bedside monitoring, and cost.
This review provides a critical overview of the use of RCA in patients undergoing RRT for AKI. The metabolism and kinetics of citrate will be discussed along with the advantages and potential drawbacks of RCA in the clinical setting of AKI in the ICU. Moreover, the practical application of RCA for various RRT modalities will be discussed in depth, including future perspectives for simplification of RCA protocols.
RCA: Basic Principles and Citrate Metabolism
Citrate, the anionic salt of citric acid, is available at various concentrations of the trisodium salt. Citrate anticoagulates the extracorporeal circuit by chelating ionized calcium (10,11,22), the key cofactor of many steps of the clotting cascade (23). Additional antihemostatic and anti-inflammatory activities of citrate may indirectly derive from its effects on blood cell components, including reduced activation of white blood cells and platelets (24–29), and protective effects against endothelial-cell inflammation and dysfunction (30). Furthermore, citrate may be directly involved as a signal molecule in several cellular processes related to inflammation and balance of oxidative species (31). On this basis, citrate may behave as a true anti-inflammatory agent (10,18).
Citrate is infused in the most proximal portion of the RRT circuit at rates proportional to blood flow. The infusion rates also vary with the concentration of the citrate solution used and the target blood citrate concentration (Figure 1) (11,22). The citrate infusion rate is titrated to maintain low ionized calcium levels in the extracorporeal circuit that are sufficient to achieve full blood anticoagulation (i.e., 0.3–0.4 mmol/L) (11,22); this target is generally attained with a citrate level in the extracorporeal circuit of approximately 3 mmol/L (Figure 1) (32). Because both citrate anion and trisodium citrate complexes have low molecular weight (198 and 258, respectively), high sieving coefficients (0.85–1), and high diffusive/convective clearances, a significant quantity of the citrate anions and calcium-citrate complexes is lost in the effluent fluid (33,34). As a result, calcium infusion is usually needed to replace calcium losses and maintain systemic ionized calcium levels within the normal range (Figure 1). Although some reports suggest possible differences in the rapidity of calcium release from calcium chloride (CaCl2) compared with calcium gluconate (35), chemically equivalent doses of these formulations produce equally rapid increases in systemic ionized calcium during the anhepatic stage of liver transplantation (36). Thus, simple dissociation rather than hepatic metabolism is probably the main mechanism for the release of ionized calcium from both preparations (36). In practice, 10% CaCl2 and 10% calcium gluconate solutions provide 0.68 and 0.226 mmol/ml elemental calcium, respectively.
Figure 1.
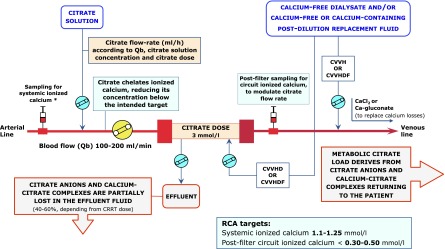
RCA in continuous RRT: basic principles. *Sampling for systemic ionized calcium is from the circuit arterial line or the patient’s arterial line (to avoid the effects of vascular access recirculation). Systemic total calcium can be measured from a central venous line. CVVH, continuous venovenous hemofiltration; CVVHD, continuous venovenous hemodialysis; CVVHDF, continuous venovenous hemodiafiltration; Qb, blood flow rate; RCA, regional citrate anticoagulation.
Specific clinical situations, such as severe rhabdomyolysis, can potentially complicate the management of serum ionized calcium concentrations during RCA (22,37). Although hypocalcemia is a common complication in the early phase of rhabdomyolysis, full correction of calcium levels is not recommended because of potentially harmful effects of excessive calcium supplementation (e.g., tissue calcium deposition and episodes of late hypercalcemia) (38). Thus, a lower than usual systemic ionized calcium level (0.9–1 mmol/L) should be considered a reasonable target while performing RCA CRRT in this clinical scenario (22,37).
Because ionized magnesium is also chelated by citrate, this cation is also removed by RRT. However, magnesium is partially replaced with dialysate and/or replacement fluid; therefore, the need for supplementation is related to exchanged volumes and the magnesium concentration in CRRT solutions (22,39).
The metabolic load of citrate is the difference between the citrate infused into the extracorporeal circuit and the amount of citrate lost in the effluent. This citrate load is rapidly metabolized through the aerobic pathways of the Krebs cycle (tricarboxylic acid cycle) in the liver and to a lesser extent, the skeletal muscle and the kidney (11,22). Thus, the final whole-body citrate balance, which is the main determinant of systemic citrate levels, results from the difference between the citrate load and metabolic disposal. Although the metabolic clearance of citrate is reduced and the half-life is prolonged in patients with liver disease (40), no major differences in citrate kinetics have been documented in patients with AKI compared with subjects with normal renal function (41).
The ensuing bicarbonate production from citrate metabolism along with bicarbonate in replacement/dialysis fluids provides the buffer supply to the patient. Indeed, for each 1 mmol citrate metabolized in the Krebs cycle, 3 mmol hydrogen ions are consumed, and 3 mmol bicarbonate is generated (11,22). In citrate solutions containing citric acid, 3 mmol hydrogen ions are generated from each 1 mmol citric acid, counterbalancing the ensuing 3 mmol bicarbonate. Therefore, although the citric acid contained in some citrate solutions contributes to attaining the target blood citrate concentration and extracorporeal circuit anticoagulation, it should not be considered as a buffer source.
Finally, citrate also represents a source of carbohydrate-like energy, providing 0.59 kcal/mmol (10,42). Thus, with the more commonly reported citrate protocols, which provide a citrate load of 11–20 mmol/h, the energy derived from citrate is approximately 150–280 kcal/24 h. Moreover, when anticoagulant citrate dextrose solution A (ACD-A) is used, which contains 2.5% dextrose, an additional caloric load is derived from dextrose metabolism (0.73 kcal/mmol), therefore providing 350–600 kcal/24 h. Lastly, in RCA protocols using lactate-buffered CRRT solutions, an additional supply of energy (500–600 kcal/24 h) may be derived from lactate (0.33 kcal/mmol). Therefore, the energy delivered from RRT fluid components (both anticoagulation and replacement fluid) should be taken into account when calculating the nutritional needs of critically ill patients undergoing RRT (10,42,43).
Citrate Accumulation Risk and RCA Monitoring
Citrate accumulation represents the most common complication of RCA, with a reported incidence of 0%–12% of patients depending on the RCA protocol used and the patient case mix (14,16,18,19,44–51). Because hepatic clearance represents the main metabolic fate of endogenous and exogenous citrate, citrate metabolism may be significantly slowed in clinical conditions where liver function is impaired, with a higher risk of citrate accumulation and consequent acid-base and electrolyte complications. In clinical conditions such as severe liver failure or septic/cardiogenic shock, impaired citrate metabolism may prevent bicarbonate generation from citrate, leading to negative buffer balance and metabolic acidosis during RCA RRT. Moreover, inadequate citrate metabolism may be associated with a fall in ionized serum calcium levels as the result of impaired calcium release from the calcium-citrate complexes. As a consequence, progressively higher calcium infusion rates may be required to maintain the ionized calcium concentration within physiologic limits, and there may be a disproportionate rise in both the total systemic calcium concentration and the total-to-ionized calcium ratio (the calcium ratio) (11,22,44,52). In clinical practice, because the calcium ratio is related to the blood citrate concentration, it is commonly accepted as an indirect index of citrate accumulation during RCA (45,48,53–55). A calcium ratio>2.5 is considered the critical threshold for increased risk of metabolic complications caused by impaired citrate metabolism (54). However, it has been reported that a lower cutoff of 2.1 seems to accurately predict citrate overdose (systemic citrate concentration>1 mmol/L) with high sensitivity and specificity (89% and 100%, respectively) (55). It should be recognized that the suggested cutoff values for the calcium ratio were obtained without any adjustment of total systemic calcium for serum albumin.
The suitability of the calcium ratio as a surrogate for blood citrate accumulation has only been partially confirmed (34,40). However, the measurement of blood or plasma citrate concentration is not widely available and generally cannot be obtained in a timely manner for rapid bedside clinical decision making. Thus, assessment of the calcium ratio along with accurate monitoring of acid-base status, systemic ionized calcium levels, and changes in calcium substitution requirements is the most reasonable approach for early detection of citrate accumulation. Close attention to the early signs of citrate accumulation is mandatory in high-risk patients (21); in particular, because the main risk of citrate accumulation is a rapid fall in the systemic ionized calcium level, potentially resulting in serious complications, such as hypotension and arrhythmias (10,52), the usual calcium monitoring intervals (4–6 hours) as well as the timing of the calcium ratio assessment should be shortened in patients who may have impaired citrate metabolism (e.g., those with severe liver failure and tissue hypoperfusion). Despite these concerns, there is increasing evidence of the safety of RCA in patients with severe liver failure/liver transplant with or without molecular adsorbent recirculating system support (53,56–58) or severe septic shock with liver hypoperfusion (47). In these clinical settings, strategies for the prevention of citrate accumulation should be targeted to reduce the citrate load by decreasing citrate administration (lower blood flow rates and higher ionized calcium targets) and/or increasing citrate clearance (higher convective and/or diffusive dialysis dose) (59). Moreover, because liberal administration of citrate-containing blood products (i.e., blood transfusions and fresh frozen plasma) may significantly increase the citrate metabolic load, this potential source of additional exogenous citrate should be taken into account in any strategy aimed at preventing citrate accumulation (59).
Finally, because the value of conventional liver function tests is poor at predicting metabolic clearance in critically ill patients with decompensated liver cirrhosis or acute liver failure, it may be difficult to identify subjects at increased risk for citrate accumulation (53). Instead, a prothrombin time≤26%, roughly corresponding to ≥33 seconds, and elevation of the serum lactate to ≥3.4 mmol/L seem to be the best predictors of RCA-related metabolic complications (53), serving as surrogates of the liver’s capacity for citrate metabolism.
Solutions and Protocols for RCA
RCA was first described for intermittent hemodialysis in the 1960s (60), and it was later applied to CRRT (61). Using commercially available or pharmacy-made citrate solutions, which generally were not specifically intended for RRT use (i.e., ACD solutions), multiple RCA protocols were developed for different RRT modalities (14–19,46,47,49,50,61–67) (Table 1). The wide array of citrate solutions and dialysate/replacement fluids as well as the widely changing operational parameters are associated with exposure of patients to different electrolyte and buffer combinations, significantly affecting acid-base status and electrolyte balance during RCA (46,62,65,66).
Table 1.
Characteristics of the main regional citrate anticoagulation protocols
| Citrate Solution/RRT Modality | Blood Flow and Citrate Infusion Rates | Citrate Solution | Dialysate | Replacement Fluid | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| High concentration (hypertonic in sodium) | |||||
| Postdilution CVVH | Qb=150–300 ml/min; citrate=38–77 ml/h (38–77 mmol/h) | TSC=1000 mmol/L; Na+=3000 mmol/L | N/A | Low sodium (120 mmol/L); buffer-free; calcium-free | Monchi et al. (15) |
| Predilution CVVHDF | Qb=150 ml/min; citrate 150 ml/h (16.9 mmol/h) | ACD-A: citrate=112.9 mmol/L (TSC=2.2%/citric acid=0.8%); Na+=224 mmol/L | Low sodium (132 mmol/L); lactate=40 mmol/L; calcium containing (1.25 mmol/L) | Isotonic saline (Na+=154 mmol/L) | Gupta et al. (103) |
| Postdilution CVVHDF | Qb=125 ml/min; citrate=190 ml/h (25.3 mmol/h) | TSC=133 mmol/L; Na+=399 mmol/L | Low sodium (117 mmol/L); buffer-free; calcium-free | Low sodium (117 mmol/L); variable bicarbonate (33–50 mmol/L according to A-B status); calcium-free | Kutsogiannis et al. (16) |
| Postdilution CVVH | Qb=220 ml/min; citrate flow rate not reported (target citratemia=3 mmol/L) | TSC/citric acid=500 mmol/L; Na+=1352 mmol/L | N/A | Low sodium (109.5 mmol/L); buffer-free combined with a bicarbonate-buffered solution according to A-B status; Ca2+=1.81 mmol/L | Oudemans-van Straaten et al. (18) |
| CVVHD | Qb=80–120 ml/min; citrate=140–205 ml/h (19–27.9 mmol/h) | TSC=136 mmol/L; Na+=408 mmol/L | Low sodium (133 mmol/L); low bicarbonate (20 mmol/L); calcium-free | N/A | Morgera et al. (46) |
| CVVHD | Qb=150–200 ml/min; citrate flow rate not reported (target citratemia=4 mmol/L) | TSC=136 mmol/L; Na+=408 mmol/L | Low sodium (133 mmol/L); low bicarbonate (20 mmol/L); calcium-free | N/A | Kalb et al. (49) |
| Predilution CVVHDF | Qb=120 ml/min; citrate=700 ml/h (19.75 mmol/h) | ACD-A–based diluted citrate solution=28.22 mmol/L; Na+=163.3 mmol/L; bicarbonate=30 mmol/L | Low sodium (133 mmol/L); low bicarbonate (20 mmol/L); calcium-free | N/A | Mariano et al. (47) |
| CVVHD | Qb=75–100 ml/min; citrate=35–45 ml/h (39.3–50.6 mmol/h) | TSC/citric acid=743/381 mmol/L; Na+=2229 mmol/L | Low to standard sodium (129–140 mmol/L); variable bicarbonate (13.2–34.3 mmol/L according to A-B status); calcium containing (1.75 mmol/L) | N/A | Saner et al. (57) |
| SLED | Qb 200 ml/min; citrate 180 ml/h (24.5 mmol/h) | TSC=136 mmol/L; Na+=408 mmol/L | Standard dialysate (Genius system; 180–200 ml/min); calcium containing (1.0 mmol/L) | N/A | Morgera et al. (105) |
| SLED | Qb=250 ml/min; citrate=231–261 ml/h (31.4–35.5 mmol/h) | TSC=136 mmol/L; Na+=408 mmol/L | Standard sodium and bicarbonate dialysate (300 ml/min); calcium-free | N/A | Clark et al. (86) |
| SLED-HDF | Qb=130 ml/min; citrate=1350 ml/h (38.1 mmol/h) | ACD-A–based diluted citrate solution=28.22 mmol/L; Na+=163.3 mmol/L; bicarbonate=30 mmol/L | Low sodium (133 mmol/L); low bicarbonate (20 mmol/L); calcium-free | N/A | Mariano et al. (47) |
| SLED | Qb=200 ml/min; citrate=200–400 ml/h (22.6–45.2 mmol/h) | ACD-A: citrate=112.9 mmol/L (TSC=2.2%/citric acid=0.8%); Na+=224 mmol/L | Cocurrent flow standard dialysate (300 ml/min); calcium containing (1.25 mmol/L) | N/A | Fiaccadori et al. (51) |
| Low concentration (isotonic in sodium) | |||||
| Predilution CVVHDF | Qb=100–150 ml/min; citrate=1000–2000 ml/h (18–46 mmol/h) | TSC=18 or 23 mmol/L obtained by diluting a TSC 4% citrate solution; Na+=140 mmol/L | Standard sodium (140 mmol/L); low bicarbonate (25 mmol/L); calcium-free | N/A | Tolwani et al. (62) |
| Predilution CVVH | Qb=100–200 ml/min; citrate=2000–4000 ml/h (26–52 mmol/h) | TSC=13 mmol/L; Na+=140 mmol/L | N/A | N/A | Hetzel et al. (19) |
| Pre- and postdilution CVVH | Qb=130–150 ml/min; citrate=1560–1800 ml/h (18.7–21.6 mmol/h) | TSC/citric acid=10/2 mmol/L; Na+=136 mmol/L | N/A | Standard sodium (140 mmol/L); standard bicarbonate (32 mmol/L); calcium containing (1.75 mmol/L) | Morabito et al. (14) |
| Predilution CVVH | Qb=150 ml/min; citrate=2500 ml/h (30 mmol/h) | TSC/citric acid=10/2 mmol/L; Na+=136 mmol/L | N/A | N/A | Shum et al. (64) |
| Predilution CVVH | Qb=180 ml/min; citrate=2400 ml/h (31.9 mmol/h) | TSC=13.3 mmol/L; Na+=140 mmol/L | N/A | N/A | Nurmohamed et al. (50) |
| Pre- and postdilution CVVHDF | Qb=140 ml/min; citrate=1000 ml/h (18 mmol/h) | TSC=18 mmol/L; Na+=140 mmol/L | Standard sodium (140 mmol/L); standard bicarbonate (30 mmol/L); calcium containing (1.25 mmol/L); phosphate containing (HPO42+=1.2 mmol/L) | Standard sodium (140 mmol/L); standard bicarbonate (30 mmol/L); calcium containing (1.25 mmol/L); phosphate containing (HPO42−=1.2 mmol/L) | Morabito et al. (66) |
The definitions SLED and SLED-HDF have been maintained as in the original articles; both treatment modalities may be included under the term prolonged intermittent RRT (PIRRT). CVVH, continuous venovenous hemofiltration; CVVHDF, continuous venovenous hemodiafiltration; CVVHD, continuous venovenous hemodialysis; SLED, sustained low-efficiency dialysis; SLED-HDF, sustained low-efficiency hemodiafiltration; Qb, blood flow rate; TSC, trisodium citrate; ACD-A, anticoagulant citrate dextrose solution A; N/A, not applicable.
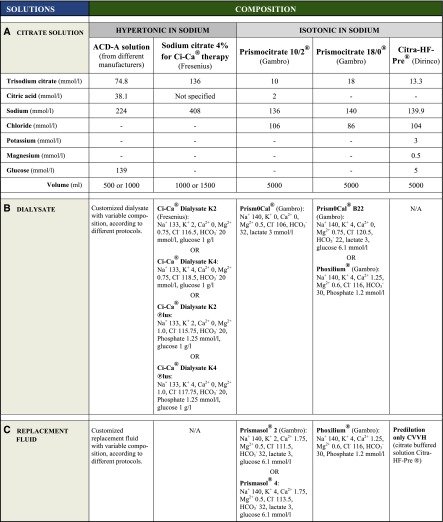
For the sake of simplicity, RCA solutions may be classified on the basis of citrate concentration as high- and low-concentration solutions, with high citrate concentrations corresponding to hypertonicity with regard to sodium.
High-Concentration Citrate Solutions (Hypertonic in Sodium)
High-concentration citrate solutions are also known as hypertonic citrate solutions because of their high sodium content as trisodium citrate. Although the use of standard sodium concentration CRRT solutions has also been reported in RCA protocols adopting hypertonic citrate formulations (68,69), these solutions are usually combined with customized low-sodium dialysis/replacement fluids to prevent hypernatremia. As long as a well designed protocol is implemented, hypertonic citrate solutions can be used to perform RCA with all modalities of CRRT (Figure 2, Table 1) (15,16,18,46,47,49). RCA protocols based on hypertonic citrate solutions use citrate as the primary buffer, regardless of CRRT modality. In the case of continuous venovenous hemodialysis (CVVHD), a custom-made or commercially available low-bicarbonate concentration dialysate is commonly used to obtain a negative bicarbonate mass balance to compensate for the indirect bicarbonate load derived from citrate (46). Therefore, in these protocols, the optimization of acid-base status and prevention/treatment of metabolic alkalosis can be achieved by enhancing the diffusive removal of citrate and bicarbonate through increased flow rates of a low-bicarbonate dialysate. Conversely, as in the case of metabolic acidosis, an increase in the buffer supply to the patient can be achieved by increasing the citrate load throughout a parallel rise of blood and citrate flow rates (46). This approach permits flexibility in the management of acid-base status, but it may result in the development of metabolic acidosis if a high dialysis dose is required (high diffusive removal of buffers related to the increase of low-bicarbonate dialysate flow rate) (46,49). A different approach, using pharmacy-made solutions, was adopted to perform RCA in continuous venovenous hemofiltration (CVVH). This approach used a very high-concentration citrate solution (500 mmol/L) along with a variable bicarbonate concentration in the replacement fluid (18). Specifically, a buffer-free replacement solution was mixed in various proportions with bicarbonate-buffered fluids to modulate the postdilution buffer supply on the basis of clinical needs (18). A similar approach was described for continuous venovenous hemodiafiltration (CVVHDF), combining a hypertonic citrate solution with buffer-free dialysate and postdilution replacement fluid with variable bicarbonate concentrations (33.3–50 mmol/L) (16).
Figure 2.
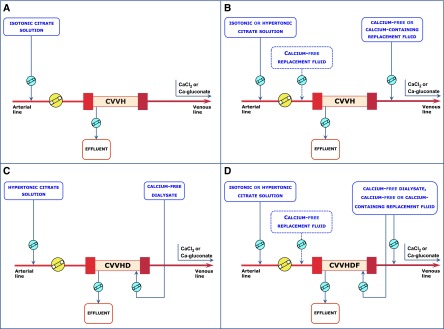
Schematic representation of RCA for the different continuous RRT modalities. In protocols adopting high-concentration citrate solutions, the use of a low-sodium dialysate and/or replacement fluid is generally required to prevent hypernatremia. In protocols adopting low-concentration citrate solutions, citrate acts as both an anticoagulant and a predilution replacement fluid, thus contributing to the total continuous RRT dose. Sections A and C display RCA circuits in predilution-only CVVH and CVVHD modalities, respectively. The dotted boxes in B and D indicate the possibility of using a calcium-free predilution replacement fluid along with a separate hypertonic citrate solution to obtain predilution and postdilution CVVH or CVVHDF.
In an alternative approach, hypertonic ACD-A has been used to prepare a custom-made replacement solution: ACD-A was diluted with a commercially available CRRT solution, making a hypertonic citrate-containing predilution replacement fluid (28.22 mmol/L citrate, 163.3 mmol/L Na, 77.2 mmol/L chloride, and 30 mmol/L NaHCO3−), which was combined with a low-bicarbonate dialysate (20 mmol/L) to perform RCA in CVVHDF (47).
Low-Concentration Citrate Solutions (Isotonic in Sodium)
In protocols using low-concentration citrate solutions, a higher citrate flow rate is required to achieve the target citrate levels in the extracorporeal circuit. As a consequence, citrate acts as both an anticoagulant and a predilution replacement fluid (citrate-buffered replacement solutions), thus contributing significantly to the total dialysis dose (Figure 2). The physiologic sodium content of isotonic solutions allows RCA CVVH or RCA CVVHDF without the need of a low-sodium replacement fluid and/or dialysate (Table 1). In protocols using citrate-buffered replacement solutions, the buffer supply derives from citrate (predilution CVVH) or citrate and bicarbonate in various proportions (predilution and postdilution CVVH and CVVHDF) in relation to the composition and the combination of the solutions that are used (14,19,50,62,64–67). A simplification on the basis of the use of solutions with an appropriately low citrate concentration allows RCA CRRT as CVVH in the predilution-only modality (19,50). This approach has the advantage of allowing RCA despite the use of CRRT equipment without a dedicated citrate infusion pump, but the downside is that the CRRT dose is intimately linked to the citrate dose (50). The buffer supply to the patient is exclusively derived from citrate, making handling of acid-base status more difficult and potentially increasing the risk of citrate accumulation when a high dialysis dose is used or in other specific clinical settings (50). The use of standard sodium and bicarbonate replacement fluids in addition to the citrate-buffered solution provides a simplified method for RCA CVVH when predilution and postdilution replacement fluids are used without requiring customized CRRT solutions (14,67); a standard (66) or lower than usual bicarbonate (62) dialysate can be used to design an RCA CVVHDF protocol with the advantage of operating at lower filtration fractions (Table 1).
Safety and Efficacy of RCA
Several studies comparing citrate-based protocols with heparin-based protocols have reported better filter survival and/or fewer bleeding events during RCA (14–19). Two separate meta-analyses, including six randomized trials comparing RCA with systemic anticoagulation with heparin, confirmed a significant decrease of bleeding events in the citrate arm (70,71); however, they provided slightly different results about filter survival. In particular, Zhang and Hongying (70) showed a significantly prolonged filter life (mean difference>20 hours) and a highly significant reduction of bleeding risk with RCA (0.28 risk ratio compared with heparin). The meta-analysis of Wu et al. (71), which excluded one of six randomized controlled trials from the analysis of filter life, confirmed the lower risk of bleeding with RCA without showing significant advantages in terms of circuit survival. Transfusion needs were also reduced with the use of RCA (14,15,17). Compared with unfractioned heparin, RCA was associated with a marked reduction in transfusion requirements in 20 patients treated with CVVH (0.2 versus 1.0 blood units/d, P<0.001) (15). More recently, in patients with high-bleeding risk cardiac surgery switched to citrate from heparin or no anticoagulation at all, no bleeding complications were observed with RCA, and the transfusion rate was significantly lower compared with the other anticoagulation modalities (P<0.02) (14). In addition, RCA was associated with an increase in platelet count and antithrombin-III activity, thus avoiding platelet concentrate administration and antithrombin-III supplementation (14). At the same time, RCA safely prolonged filter life in the absence of CRRT interruption for filter clotting, minimizing CRRT downtime (mean delivered dose around 95%) (14).
No robust demonstration is currently available concerning the possible positive effects of RCA on patient survival. In a large single-center randomized trial including 200 critically ill patients on CRRT using nadroparin or citrate anticoagulation, RCA was associated with an unexpected 15% absolute increase in 3-month survival, which was not completely explained by the lower incidence of bleeding (18). Post hoc analysis showed that RCA might be particularly beneficial in specific clinical conditions (e.g., surgery, sepsis, severe multiple organ dysfunction syndrome, and younger age). To explain the survival benefit of RCA, the previously discussed interference of citrate with the activation of the inflammatory cascade was suggested (18). However, although RCA was associated with prolonged circuit patency and a marked reduction in bleeding complications, no survival benefit of citrate was shown in a subsequent multicenter randomized trial comparing unfractioned heparin with RCA in 170 patients undergoing CVVH (19).
RCA in Prolonged Intermittent RRT
Sustained low-efficiency dialysis, also known as extended daily dialysis, is a prolonged intermittent RRT (PIRRT) usually lasting 8–12 hours that is increasingly used in patients with AKI in the ICU (12,72–76). PIRRT is considered a hybrid RRT modality; it combines the main advantages of conventional intermittent forms of RRT (e.g., standard hemodialysis equipment, online-produced dialysate, flexible scheduling, and lower costs) with those of CRRT (e.g., better hemodynamic tolerance, excellent metabolic control, and gentle osmotic fluctuation and fluid removal capacity) (74,77–81).
Despite shorter treatment duration, even with PIRRT, anticoagulation of the extracorporeal circuit is often required. The optimal strategy for anticoagulation during PIRRT is still a matter of debate (13,82). Saline flushes without a antihemostatic agent (81,83,84), unfractioned heparin (79,81,83,85), or prostacyclin (80) are among the different options proposed thus far for the maintenance of the extracorporeal PIRRT circuit. Treatment interruption because of circuit clotting is found in 26%–46% of cases with saline flushes and 17%–26% of cases with standard heparin (500–1000 IU/h) (81,83,84). A 10% incidence of circuit interruption (one half for circuit coagulation) has been reported when relatively low doses of epoprostenol, a synthetic analog of the antiaggregant and vasodilatory prostacyclin PGI2, are used (80). In parallel to the expanding use of citrate as a regional anticoagulation method in CRRT, increasing interest has been devoted to the application of this anticoagulant strategy to PIRRT. Protocols for RCA have been proposed for PIRRT on the basis of the use of different citrate solutions and the use of either CRRT or standard dialysis machines (86,87) (Table 1). In one of these studies, in 30 patients undergoing 117 PIRRT sessions with citrate, treatment interruption caused by circuit clotting never occurred, with an average treatment duration of 6.7–7.3 h (86). However, the protocol required calcium-free dialysis fluid and CaCl2 supplementation, with a stepwise titration protocol for both citrate and calcium administration (86). Recently, a simple RCA protocol for PIRRT was proposed and validated in a single-institution observational study of 116 patients in the ICU with AKI who underwent 807 PIRRT sessions (51). The protocol used ACD-A solution and standard dialysis equipment with maintenance of blood calcium levels provided by calcium back-transport from calcium-containing dialysis fluid (1.25 mmol/L) (Figure 3). Interruptions of PIRRT caused by impending/irreversible clotting were recorded in 19 sessions (2.4%); blood restitution was complete in 98% of the cases. Major bleeding was observed in six patients (5.2% or 0.4 episodes per 100 person-days on PIRRT), with a hemorrhagic complication rate similar or even lower to that reported in previous studies (4,5,70,71,88–91). No citrate accumulation was observed, even in patients with severe liver dysfunction (51). Intravenous calcium for systemic hypocalcemia (ionized calcium levels<0.90 mmol/L) was needed during 28 treatment sessions (3.4%); however, in eight of 28 sessions, low ionized calcium was already present before starting PIRRT. Systemic coagulation of patients remained unchanged, and metabolic/fluid control was easily achieved. These results suggest that simplified protocols with commercially available citrate solutions allow safe and effective RCA for PIRRT with limited laboratory monitoring and without the need for systemic calcium infusion in most patients.
Figure 3.
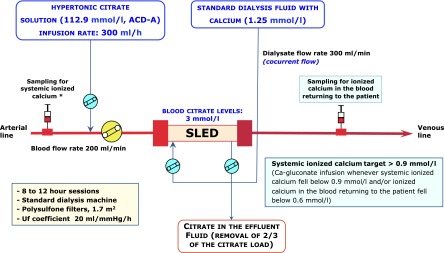
Schematic representation of a simplified regional citrate anticoagulation protocol for SLED using a calcium-containing dialysate. Detailed protocol is shown as supplemental material in ref. 51. *Sampling for systemic ionized calcium is from the circuit arterial line or the patient’s arterial line (to avoid the effects of vascular access recirculation). Systemic total calcium can be measured from a central venous line. ACD-A, anticoagulant citrate dextrose solution A; SLED, sustained low-efficiency dialysis; Uf, ultrafiltration.
RCA: Electrolyte Balance, Acid-Base Status, and Effects on Bone Metabolism
Despite its recognized advantages, concerns about the risk of electrolyte and acid-base disorders are probably among the main factors still precluding the more widespread use of RCA in critically ill patients undergoing RRT. Although reported issues with citrate include hypernatremia or hyponatremia, hypercalcemia or hypocalcemia, hypermagnesemia or hypomagnesemia, and metabolic acidosis or alkalosis (Table 2), these complications are quite uncommon when strict adherence to the RCA protocol and accurate monitoring of the procedure by an adequately trained staff are ensured (Table 3) (22,92).
Table 2.
Potential acid-base and electrolyte complications during regional citrate anticoagulation and preventive measures
| Complication | Mechanism | Preventive Measures |
|---|---|---|
| Metabolic alkalosis | Excessive buffer load related to high citrate delivery to the patient (imbalance between citrate infusion rate and citrate removal with the effluent) and/or inadequate matching of RCA solutions (citrate concentration, bicarbonate concentration in dialysate/replacement fluid) in the case of CRRT | Decrease citrate infusion rate by reducing blood flow and/or reducing target citrate dose (with a corresponding higher circuit ionized calcium) |
| Increase citrate and bicarbonate losses by increasing dialysate/replacement fluid flow rate | ||
| Reduce bicarbonate concentration in the dialysate/replacement fluid | ||
| Remove or limit exogenous buffer sources (acetate in total parenteral nutrition solutions and citrate-containing blood products) | ||
| Metabolic acidosis | Inadequate buffer supply (imbalance between citrate/bicarbonate delivered to the patient and citrate/bicarbonate removed with the effluent) | After excluding inadequate citrate metabolism, increase citrate delivery to the patients by increasing citrate infusion rate and/or increasing target citrate dose, reduce citrate and bicarbonate losses by reducing dialysate/replacement fluid flow rate, or increase bicarbonate concentration in the dialysate/replacement fluid or start bicarbonate supplementation by systemic infusion |
| Inadequate citrate metabolism (i.e., severe liver failure and septic or cardiogenic shock with tissue hypoperfusion) preventing bicarbonate production | In the presence of signs of citrate accumulation, reduce or stop citrate infusion and/or increase citrate loss by increasing dialysate/replacement fluid flow rate or switch to a standard bicarbonate dialysate/replacement fluid and/or start bicarbonate supplementation by systemic infusion | |
| Systemic ionized hypercalcemia | Excessive calcium replacement | Reduce calcium infusion rate |
| Systemic ionized hypocalcemia | Inadequate calcium replacement | After excluding inadequate citrate metabolism, increase calcium infusion rate (check infusion pump to exclude technical issues) |
| Inadequate citrate metabolism preventing calcium release from calcium-citrate complexes | In the presence of signs of citrate accumulation, increase calcium infusion rate and consider the measures suggested for citrate accumulation | |
| Hypernatremia | Use of high-concentration trisodium citrate solutions without adequate lowering of sodium concentration in the dialysate/replacement fluid | Use a low-sodium dialysate/replacement fluid in protocols based on hypertonic citrate solutions |
| Hyponatremia | Accidental omission of hypertonic citrate solution in protocols adopting hypotonic dialysate/replacement fluid (rarely observed) | Verify the correct matching of RCA solutions |
| Hypomagnesemia | Inadequate magnesium replacement | Increase magnesium replacement (check infusion pump to exclude technical issues) |
RCA, regional citrate anticoagulation; CRRT, continuous RRT.
Table 3.
Monitoring of regional citrate anticoagulation for continuous RRT
| Parameter | Monitoring Intervals | Aim |
|---|---|---|
| Circuit ionized calcium (postfilter) | Within 1 h from the start of the treatment and then at least every 6–8 h | To evaluate the maintenance of circuit ionized calcium within the intended target and modify citrate dose accordingly |
| Systemic ionized calcium | Baseline (before starting RRT) | To check baseline levels and set initial calcium infusion rate |
| Within 1 h from the start of the treatment and then at least every 4–6 h | To evaluate the maintenance of systemic ionized calcium within the physiologic range and modulate calcium infusion rate accordingly | |
| Systemic total calcium | At least every 12–24 h (simultaneous to systemic ionized calcium) | To calculate calcium ratio (total-to-ionized systemic calcium) as an indirect index of citrate accumulation (≥2.5) |
| Acid-base parameters (pH and bicarbonate)a | Baseline (before starting RRT) | To exclude acid-base imbalances (metabolic acidosis or alkalosis) and modify RCA and RRT parameters setting if needed |
| Within 1 h from the start of the treatment and then at least every 4–6 h | ||
| Magnesium | At least every 24 h | To modulate the amount of magnesium supplementation if needed |
| Serum sodium | Once daily | To exclude hypernatremia or hyponatremia (rarely observed with a correct matching of RCA solutions) |
| Citratemia (if available) | Not routinely used for clinical purposes | To confirm hypercitratemia in the presence of indirect signs of citrate accumulation |
| Serum lactate | Baseline (before starting RRT) | To identify patients at higher risk for citrate accumulation and monitor lactate levels during RCA |
| At least every 6–12 h or according to clinical needs |
Sample drawn from an arterial line.
Hypernatremia represents a potential but rarely observed complication related to the use of hypertonic solutions without low-sodium concentration dialysate and/or replacement fluids (22,92). Calcium and magnesium imbalances are usually caused by effluent losses of both electrolytes, mainly in the form of citrate complexes, not adequately counterbalanced by systemic supplementation (22,92). As previously discussed, alterations of ionized calcium levels may also occur as a consequence of accumulation of calcium-citrate complexes in patients with impaired citrate metabolism. In this situation, increasing levels of total serum calcium coexist with low systemic ionized calcium levels, leading to high–calcium ratio values (10,54). Metabolic acidosis may develop when impaired citrate metabolism prevents bicarbonate generation or, alternatively, from an insufficient buffer supply. The latter may be related to the suboptimal setting of RCA CRRT parameters and/or an inadequate combination of CRRT fluids resulting in an imbalance between the amount of buffers (citrate/bicarbonate) delivered to the patients and the amount removed with the effluent fluid (Table 2). Conversely, metabolic alkalosis may develop when buffer overload is caused by inappropriate setting of RCA parameters and/or inadequate matching of RCA CRRT solutions (Table 2) (10,22). In patients receiving significant amounts of citrate-containing blood products, the exogenous citrate load may increase the risk of buffer overload and metabolic alkalosis and must be taken into account in the RCA protocol (10).
The development of well designed RCA protocols, characterized by a balanced combination of citrate and CRRT solutions, facilitates the modulation of the buffer supply according to clinical needs, minimizing the risk of acid-base imbalances. For example, the combination of a highly concentrated trisodium citrate solution (136 mmol/L) with a customized low-bicarbonate dialysate (20 mmol/L) has been successfully used for CVVHD (46). Acid-base and electrolyte control was excellent in the majority of patients, and any occurrence of metabolic imbalances was rapidly corrected by modifying either the dialysate or the blood flow rate (46). An appropriate matching of citrate and CRRT solutions is also required with the use of isotonic solutions. In a comparison between two different low-concentration citrate solutions in RCA CVVHDF, the use of a citrate concentration of 23 mmol/L was frequently associated with metabolic alkalosis, whereas a lower citrate concentration (18 mmol/L) provided more appropriate acid-base balance (62). In both cases, the target CRRT dose was 35 ml/kg per hour, and a lower than usual dialysate bicarbonate concentration (25 mmol/L) was adopted to optimize the buffer supply to the patient (62). Aside from fluid composition, citrate and dialysis dose may significantly affect acid-base status. Indeed, by adopting a lower target blood citrate concentration (2.5–3 mmol/L) along with a CRRT dose of 30 ml/kg per hour, the above-mentioned 18-mmol/L citrate solution was successfully combined with a phosphate-containing dialysate/replacement fluid with a standard bicarbonate concentration (30 mmol/L). This combination afforded adequate acid-base control without the occurrence of metabolic alkalosis. At the same time, it minimized CRRT-related phosphate depletion (66,67). The use of a lower-concentration isotonic citrate solution (12 or 13 mmol/L) alone (predilution CVVH) (19,64) or combined with postdilution conventional replacement fluid (predilution and postdilution CVVH) (14) may be associated with a suboptimal buffer supply, which is not easily balanced through the optimization of RCA settings and frequently requires additional bicarbonate supplementation directly to the patient.
Abnormalities of parathyroid hormone (PTH) release during RCA have been reported (93,94) and seem to be mainly related to calcium balance during RRT. In particular, negative calcium balance during RCA CRRT seems to stimulate PTH release (93,95). Although the significance of PTH secretion in this setting is still unclear, concerns about the potential harmful effects on bone metabolism have been expressed (10). Indeed, recruitment of body calcium stores as compensation for negative calcium balance could lead to severe bone reabsorption during prolonged RCA CRRT, which was reported after discontinuation of calcium supplementation in patients with immobilization-related hypercalcemia, possibly masked by calcium chelation during RCA (96). Although additional investigations are required to establish the most appropriate calcium substitution strategies, adequate calcium replacement aimed at avoiding episodes of hypocalcemia should help prevent bone loss during prolonged RCA (10,93). Strict maintenance of systemic ionized calcium within physiologic values has been shown to prevent a short-term increase in PTH levels in acutely ill patients on maintenance hemodialysis undergoing RCA (93). In addition to the potential effects of RCA on PTH levels, other factors (i.e., immobilization, vitamin D deficiency, and cytokine effects) may negatively affect bone turnover rates in critically ill patients (10,93).
RCA Protocols Simplification: Future Perspectives
Despite positive reports about the safety and efficacy of RCA, use of this alternative method of anticoagulation is still relatively limited. The Beginning and Ending Supportive Therapy for the Kidney study, an international survey of RRT in critically ill patients involving 54 ICUs, reported the use of RCA in only about 10% of CRRT treatments (97). More recently, in the multicenter randomized Veterans Affairs/National Institutes of Health Acute Renal Failure Trial Network study, RCA was used in only 20% of CVVHDF treatments (12). It is likely that many reasons limit the widespread use of RCA: complexity of published protocols, concerns about the risk of metabolic complications, and lack of commercially available CRRT-specific citrate solutions and/or custom-designed dialysis equipment (98). However, the growing availability of dedicated commercial solutions (Figure 4), along with the introduction of technologically advanced CRRT equipment with integrated infusion systems and RCA-dedicated software, could help to simplify RCA delivery, improving the safety of RCA and facilitating a more expanded use of citrate (46,99). In this regard, the use of mathematical models and the application of target-oriented algorithms specifically developed for different RRT modalities (87,95,100–102) could provide an estimation of calcium balance during RCA, allowing modulation of calcium infusion rates on the basis of variations in treatment- and patient-related parameters (i.e., blood flow rate, citrate dose, hematocrit, albumin, and serum calcium). The latest generation of CRRT equipment partially fulfills the characteristics required for near-automated RCA by keeping the citrate dose stable even when blood flow changes and adjusting calcium replacement according to the estimated RCA CRRT calcium balance (46,99). In particular, the initial calcium infusion rate as well as subsequent adjustments could be calculated according to RCA CRRT operational parameters, taking into account the estimated calcium losses with the effluent and the calcium supply possibly deriving from the optional use of calcium-containing CRRT solutions.
Figure 4.
Composition of commercially available citrate and CRRT solutions for RCA. To design the appropriate RCA protocol (CVVHD, CVVH, CVVHDF), each citrate solution should be combined with the correctly matched dialysate and/or replacement fluid. Availability and trade name of each solution may vary according to different countries. The list of commercially available citrate and CRRT solutions derives from the more recently reported RCA protocols and could be partial. N/A, not applicable or not available.
Finally, additional refinements of the composition of RCA CRRT solutions could help minimize the need for supplementation of calcium, magnesium, potassium, and phosphate, with the aim of simplifying RRT management. For example, the adoption of RCA protocols in which predilution citrate is combined with a calcium-containing dialysate and/or replacement fluid may reduce the calcium infusion requirements and minimize the risks of errors related to the handling of calcium-free solutions (14,51,66,67,103). These protocols seem to be able to provide prolonged filter survival without any increase in venous drip chamber clotting rates or the need to increase the initial citrate dose (14,66,67). However, in any protocol, variations in operational parameters and calcium concentration in the CRRT solutions could significantly affect the need for citrate dose adjustments.
Costs of RCA
Concerns related to cost issues could represent another potential drawback for a wider use of RCA. Currently, comparative data on the cost-effectiveness ratio of different anticoagulation methods for RRT in AKI are lacking (21). RCA could be more costly than heparin-based anticoagulation because of the higher cost of citrate solutions (especially commercial solutions developed specifically for CRRT) and the need for more intensive monitoring of metabolic parameters (85). However, it is likely that savings related to both the lower incidence of bleeding complications and the lower frequency of circuit replacement could shift the balance toward RCA (104). Finally, in the cost-benefit evaluation of RCA, indirect costs should be taken into account, such as platelet and red cell transfusions, as well as the need for antithrombin-III supplementation (14).
Conclusions
In conclusion, several studies on RCA use have documented prolonged filter survival associated with lower bleeding risk and transfusion needs in critically ill patients with AKI on RRT. On the basis of these results, the 2012 KDIGO Clinical Practice Guidelines for Acute Kidney Injury recommended RCA as the preferred anticoagulation modality in patients without contraindications for citrate (20). Recently, the Canadian Society of Nephrology commentary on these KDIGO guidelines endorsed this statement, suggesting the possibility of cautiously extending RCA use in patients with relative contraindications for citrate (21). In this regard, the adoption of well designed RCA protocols, characterized by reduced citrate load and careful monitoring, could permit safe delivery of RCA in patients with severely impaired liver function and/or shock with tissue hypoperfusion (47,53,56–58). Moreover, although the incidence of metabolic and/or electrolyte disorders with RCA is low, operational parameters and combinations of different CRRT solutions with either isotonic or hypertonic citrate formulations may significantly affect electrolyte and buffer balance during RCA.
Finally, the introduction of simplified protocols and the development of RRT equipment with RCA-dedicated software could minimize the risk of errors in RCA handling, thus improving the safety of citrate use and facilitating a more expanded use of this highly effective anticoagulation modality for RRT.
Disclosures
None.
Footnotes
Published online ahead of print. Publication date available at www.cjasn.org.
References
- 1.Fiaccadori E, Maggiore U, Clima B, Melfa L, Rotelli C, Borghetti A: Incidence, risk factors, and prognosis of gastrointestinal hemorrhage complicating acute renal failure. Kidney Int 59: 1510–1519, 2001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Mehta RL: Anticoagulation during continuous renal replacement therapy. ASAIO J 40: 931–935, 1994 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.van de Wetering J, Westendorp RG, van der Hoeven JG, Stolk B, Feuth JD, Chang PC: Heparin use in continuous renal replacement procedures: The struggle between filter coagulation and patient hemorrhage. J Am Soc Nephrol 7: 145–150, 1996 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ward DM, Mehta RL: Extracorporeal management of acute renal failure patients at high risk of bleeding. Kidney Int Suppl 41: S237–S244, 1993 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Brophy PD, Somers MJ, Baum MA, Symons JM, McAfee N, Fortenberry JD, Rogers K, Barnett J, Blowey D, Baker C, Bunchman TE, Goldstein SL: Multi-centre evaluation of anticoagulation in patients receiving continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT). Nephrol Dial Transplant 20: 1416–1421, 2005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Oudemans-van Straaten HM, Wester JP, de Pont AC, Schetz MR: Anticoagulation strategies in continuous renal replacement therapy: Can the choice be evidence based? Intensive Care Med 32: 188–202, 2006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Tolwani AJ, Wille KM: Anticoagulation for continuous renal replacement therapy. Semin Dial 22: 141–145, 2009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Tan HK, Baldwin I, Bellomo R: Continuous veno-venous hemofiltration without anticoagulation in high-risk patients. Intensive Care Med 26: 1652–1657, 2000 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Morabito S, Guzzo I, Solazzo A, Muzi L, Luciani R, Pierucci A: Continuous renal replacement therapies: Anticoagulation in the critically ill at high risk of bleeding. J Nephrol 16: 566–571, 2003 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Oudemans-van Straaten HM, Ostermann M: Bench-to-bedside review: Citrate for continuous renal replacement therapy, from science to practice. Crit Care 16: 249, 2012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Tolwani A, Wille KM: Advances in continuous renal replacement therapy: Citrate anticoagulation update. Blood Purif 34: 88–93, 2012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Palevsky PM, Zhang JH, O’Connor TZ, Chertow GM, Crowley ST, Choudhury D, Finkel K, Kellum JA, Paganini E, Schein RM, Smith MW, Swanson KM, Thompson BT, Vijayan A, Watnick S, Star RA, Peduzzi P, VA/NIH Acute Renal Failure Trial Network : Intensity of renal support in critically ill patients with acute kidney injury. N Engl J Med 359: 7–20, 2008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Joannidis M, Oudemans-van Straaten HM: Clinical review: Patency of the circuit in continuous renal replacement therapy. Crit Care 11: 218, 2007 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Morabito S, Pistolesi V, Tritapepe L, Zeppilli L, Polistena F, Strampelli E, Pierucci A: Regional citrate anticoagulation in cardiac surgery patients at high risk of bleeding: A continuous veno-venous hemofiltration protocol with a low concentration citrate solution. Crit Care 16: R111, 2012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Monchi M, Berghmans D, Ledoux D, Canivet JL, Dubois B, Damas P: Citrate vs. heparin for anticoagulation in continuous venovenous hemofiltration: A prospective randomized study. Intensive Care Med 30: 260–265, 2004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Kutsogiannis DJ, Gibney RT, Stollery D, Gao J: Regional citrate versus systemic heparin anticoagulation for continuous renal replacement in critically ill patients. Kidney Int 67: 2361–2367, 2005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Betjes MG, van Oosterom D, van Agteren M, van de Wetering J: Regional citrate versus heparin anticoagulation during venovenous hemofiltration in patients at low risk for bleeding: Similar hemofilter survival but significantly less bleeding. J Nephrol 20: 602–608, 2007 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Oudemans-van Straaten HM, Bosman RJ, Koopmans M, van der Voort PH, Wester JP, van der Spoel JI, Dijksman LM, Zandstra DF: Citrate anticoagulation for continuous venovenous hemofiltration. Crit Care Med 37: 545–552, 2009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Hetzel GR, Schmitz M, Wissing H, Ries W, Schott G, Heering PJ, Isgro F, Kribben A, Himmele R, Grabensee B, Rump LC: Regional citrate versus systemic heparin for anticoagulation in critically ill patients on continuous venovenous haemofiltration: A prospective randomized multicentre trial. Nephrol Dial Transplant 26: 232–239, 2011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Acute Kidney Injury Work Group : KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline for Acute Kidney Injury. Kidney Int [Suppl 2]: 1–138, 2012 [Google Scholar]
- 21.James M, Bouchard J, Ho J, Klarenbach S, LaFrance JP, Rigatto C, Wald R, Zappitelli M, Pannu N: Canadian Society of Nephrology commentary on the 2012 KDIGO clinical practice guideline for acute kidney injury. Am J Kidney Dis 61: 673–685, 2013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Davenport A, Tolwani A: Citrate anticoagulation for continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT) in patients with acute kidney injury admitted to the intensive care unit. NDT Plus 2: 439–447, 2009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Abramson S, Niles JL: Anticoagulation in continuous renal replacement therapy. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 8: 701–707, 1999 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Böhler J, Schollmeyer P, Dressel B, Dobos G, Hörl WH: Reduction of granulocyte activation during hemodialysis with regional citrate anticoagulation: Dissociation of complement activation and neutropenia from neutrophil degranulation. J Am Soc Nephrol 7: 234–241, 1996 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Bos JC, Grooteman MP, van Houte AJ, Schoorl M, van Limbeek J, Nubé MJ: Low polymorphonuclear cell degranulation during citrate anticoagulation: A comparison between citrate and heparin dialysis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 12: 1387–1393, 1997 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Dhondt A, Vanholder R, Tielemans C, Glorieux G, Waterloos MA, De Smet R, Lameire N: Effect of regional citrate anticoagulation on leukopenia, complement activation, and expression of leukocyte surface molecules during hemodialysis with unmodified cellulose membranes. Nephron 85: 334–342, 2000 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Gabutti L, Ferrari N, Mombelli G, Keller F, Marone C: The favorable effect of regional citrate anticoagulation on interleukin-1beta release is dissociated from both coagulation and complement activation. J Nephrol 17: 819–825, 2004 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Gritters M, Grooteman MP, Schoorl M, Schoorl M, Bartels PC, Scheffer PG, Teerlink T, Schalkwijk CG, Spreeuwenberg M, Nubé MJ: Citrate anticoagulation abolishes degranulation of polymorphonuclear cells and platelets and reduces oxidative stress during haemodialysis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 21: 153–159, 2006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Schilder L, Nurmohamed SA, ter Wee PM, Paauw NJ, Girbes AR, Beishuizen A, Beelen RH, Groeneveld AB: Citrate confers less filter-induced complement activation and neutrophil degranulation than heparin when used for anticoagulation during continuous venovenous haemofiltration in critically ill patients. BMC Nephrol 15: 19, 2014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Bryland A, Wieslander A, Carlsson O, Hellmark T, Godaly G: Citrate treatment reduces endothelial death and inflammation under hyperglycaemic conditions. Diab Vasc Dis Res 9: 42–51, 2012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Iacobazzi V, Infantino V: Citrate - new functions for an old metabolite. Biol Chem 395: 387–399, 2014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Oudemans-van Straaten HM, Kellum JA, Bellomo R: Clinical review: Anticoagulation for continuous renal replacement therapy—heparin or citrate? Crit Care 15: 202, 2011 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Swartz R, Pasko D, O’Toole J, Starmann B: Improving the delivery of continuous renal replacement therapy using regional citrate anticoagulation. Clin Nephrol 61: 134–143, 2004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Mariano F, Morselli M, Bergamo D, Hollo Z, Scella S, Maio M, Tetta C, Dellavalle A, Stella M, Triolo G: Blood and ultrafiltrate dosage of citrate as a useful and routine tool during continuous venovenous haemodiafiltration in septic shock patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant 26: 3882–3888, 2011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.White RD, Goldsmith RS, Rodriguez R, Moffitt EA, Pluth JR: Plasma ionic calcium levels following injection of chloride, gluconate, and gluceptate salts of calcium. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 71: 609–613, 1976 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Martin TJ, Kang Y, Robertson KM, Virji MA, Marquez JM: Ionization and hemodynamic effects of calcium chloride and calcium gluconate in the absence of hepatic function. Anesthesiology 73: 62–65, 1990 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Morgan DJ, Ho KM: Profound hypocalcaemia in a patient being anticoagulated with citrate for continuous renal replacement therapy. Anaesthesia 64: 1363–1366, 2009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Vanholder R, Sever MS, Erek E, Lameire N: Rhabdomyolysis. J Am Soc Nephrol 11: 1553–1561, 2000 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Brain M, Anderson M, Parkes S, Fowler P: Magnesium flux during continuous venovenous haemodiafiltration with heparin and citrate anticoagulation. Crit Care Resusc 14: 274–282, 2012 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Kramer L, Bauer E, Joukhadar C, Strobl W, Gendo A, Madl C, Gangl A: Citrate pharmacokinetics and metabolism in cirrhotic and noncirrhotic critically ill patients. Crit Care Med 31: 2450–2455, 2003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Zheng Y, Xu Z, Zhu Q, Liu J, Qian J, You H, Gu Y, Hao C, Jiao Z, Ding F: Citrate pharmacokinetics in critically ill patients with acute kidney injury. PLoS ONE 8: e65992, 2013 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Balik M, Zakharchenko M, Leden P, Otahal M, Hruby J, Polak F, Rusinova K, Stach Z, Tokarik M, Vavrova J, Jabor A, Oudemans-van Straaten HM: Bioenergetic gain of citrate anticoagulated continuous hemodiafiltration—a comparison between 2 citrate modalities and unfractionated heparin. J Crit Care 28: 87–95, 2013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Fiaccadori E, Regolisti G, Maggiore U: Specialized nutritional support interventions in critically ill patients on renal replacement therapy. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 16: 217–224, 2013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Meier-Kriesche HU, Gitomer J, Finkel K, DuBose T: Increased total to ionized calcium ratio during continuous venovenous hemodialysis with regional citrate anticoagulation. Crit Care Med 29: 748–752, 2001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Khadzhynov D, Schelter C, Lieker I, Mika A, Staeck O, Neumayer HH, Peters H, Slowinski T: Incidence and outcome of metabolic disarrangements consistent with citrate accumulation in critically ill patients undergoing continuous venovenous hemodialysis with regional citrate anticoagulation. J Crit Care 29: 265–271, 2014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Morgera S, Schneider M, Slowinski T, Vargas-Hein O, Zuckermann-Becker H, Peters H, Kindgen-Milles D, Neumayer HH: A safe citrate anticoagulation protocol with variable treatment efficacy and excellent control of the acid-base status. Crit Care Med 37: 2018–2024, 2009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Mariano F, Tedeschi L, Morselli M, Stella M, Triolo G: Normal citratemia and metabolic tolerance of citrate anticoagulation for hemodiafiltration in severe septic shock burn patients. Intensive Care Med 36: 1735–1743, 2010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Link A, Klingele M, Speer T, Rbah R, Pöss J, Lerner-Gräber A, Fliser D, Böhm M: Total-to-ionized calcium ratio predicts mortality in continuous renal replacement therapy with citrate anticoagulation in critically ill patients. Crit Care 16: R97, 2012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Kalb R, Kram R, Morgera S, Slowinski T, Kindgen-Milles D: Regional citrate anticoagulation for high volume continuous venovenous hemodialysis in surgical patients with high bleeding risk. Ther Apher Dial 17: 202–212, 2013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Nurmohamed SA, Jallah BP, Vervloet MG, Yldirim G, ter Wee PM, Groeneveld AB: Continuous venovenous haemofiltration with citrate-buffered replacement solution is safe and efficacious in patients with a bleeding tendency: A prospective observational study. BMC Nephrol 14: 89, 2013 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Fiaccadori E, Regolisti G, Cademartiri C, Cabassi A, Picetti E, Barbagallo M, Gherli T, Castellano G, Morabito S, Maggiore U: Efficacy and safety of a citrate-based protocol for sustained low-efficiency dialysis in AKI using standard dialysis equipment. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 8: 1670–1678, 2013 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Meier-Kriesche HU, Finkel KW, Gitomer JJ, DuBose TD, Jr.: Unexpected severe hypocalcemia during continuous venovenous hemodialysis with regional citrate anticoagulation. Am J Kidney Dis 33: e8, 1999 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Schultheiß C, Saugel B, Phillip V, Thies P, Noe S, Mayr U, Haller B, Einwächter H, Schmid RM, Huber W: Continuous venovenous hemodialysis with regional citrate anticoagulation in patients with liver failure: A prospective observational study. Crit Care 16: R162, 2012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Hetzel GR, Taskaya G, Sucker C, Hennersdorf M, Grabensee B, Schmitz M: Citrate plasma levels in patients under regional anticoagulation in continuous venovenous hemofiltration. Am J Kidney Dis 48: 806–811, 2006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Bakker AJ, Boerma EC, Keidel H, Kingma P, van der Voort PH: Detection of citrate overdose in critically ill patients on citrate-anticoagulated venovenous haemofiltration: Use of ionised and total/ionised calcium. Clin Chem Lab Med 44: 962–966, 2006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Faybik P, Hetz H, Mitterer G, Krenn CG, Schiefer J, Funk GC, Bacher A: Regional citrate anticoagulation in patients with liver failure supported by a molecular adsorbent recirculating system. Crit Care Med 39: 273–279, 2011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Saner FH, Treckmann JW, Geis A, Lösch C, Witzke O, Canbay A, Herget-Rosenthal S, Kribben A, Paul A, Feldkamp T: Efficacy and safety of regional citrate anticoagulation in liver transplant patients requiring post-operative renal replacement therapy. Nephrol Dial Transplant 27: 1651–1657, 2012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Meijers B, Laleman W, Vermeersch P, Nevens F, Wilmer A, Evenepoel P: A prospective randomized open-label crossover trial of regional citrate anticoagulation vs. anticoagulation free liver dialysis by the Molecular Adsorbents Recirculating System. Crit Care 16: R20, 2012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Bouchard J, Madore F: Role of citrate and other methods of anticoagulation in patients with severe liver failure requiring continuous renal replacement therapy. NDT Plus 2: 11–19, 2009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Morita Y, Johnson RW, Dorn RE, Hall DS: Regional anticoagulation during hemodialysis using citrate. Am J Med Sci 242: 32–43, 1961 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Mehta RL, McDonald BR, Aguilar MM, Ward DM: Regional citrate anticoagulation for continuous arteriovenous hemodialysis in critically ill patients. Kidney Int 38: 976–981, 1990 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Tolwani AJ, Prendergast MB, Speer RR, Stofan BS, Wille KM: A practical citrate anticoagulation continuous venovenous hemodiafiltration protocol for metabolic control and high solute clearance. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 1: 79–87, 2006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Cubattoli L, Teruzzi M, Cormio M, Lampati L, Pesenti A: Citrate anticoagulation during CVVH in high risk bleeding patients. Int J Artif Organs 30: 244–252, 2007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Shum HP, Chan KC, Yan WW: Regional citrate anticoagulation in predilution continuous venovenous hemofiltration using prismocitrate 10/2 solution. Ther Apher Dial 16: 81–86, 2012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Morabito S, Pistolesi V, Tritapepe L, Zeppilli L, Polistena F, Fiaccadori E, Pierucci A: Regional citrate anticoagulation in CVVH: A new protocol combining citrate solution with a phosphate-containing replacement fluid. Hemodial Int 17: 313–320, 2013 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Morabito S, Pistolesi V, Tritapepe L, Vitaliano E, Zeppilli L, Polistena F, Fiaccadori E, Pierucci A: Continuous venovenous hemodiafiltration with a low citrate dose regional anticoagulation protocol and a phosphate-containing solution: Effects on acid-base status and phosphate supplementation needs. BMC Nephrol 14: 232, 2013 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Morabito S, Pistolesi V, Tritapepe L, Vitaliano E, Zeppilli L, Polistena F, Fiaccadori E, Pierucci A: Continuous veno-venous hemofiltration using a phosphate-containing replacement fluid in the setting of regional citrate anticoagulation. Int J Artif Organs 36: 845–852, 2013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Tobe SW, Aujla P, Walele AA, Oliver MJ, Naimark DM, Perkins NJ, Beardsall M: A novel regional citrate anticoagulation protocol for CRRT using only commercially available solutions. J Crit Care 18: 121–129, 2003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Munjal S, Ejaz AA: Regional citrate anticoagulation in continuous venovenous haemofiltration using commercial preparations. Nephrology (Carlton) 11: 405–409, 2006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Zhang Z, Hongying N: Efficacy and safety of regional citrate anticoagulation in critically ill patients undergoing continuous renal replacement therapy. Intensive Care Med 38: 20–28, 2012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Wu MY, Hsu YH, Bai CH, Lin YF, Wu CH, Tam KW: Regional citrate versus heparin anticoagulation for continuous renal replacement therapy: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am J Kidney Dis 59: 810–818, 2012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Fliser D, Kielstein JT: Technology insight: Treatment of renal failure in the intensive care unit with extended dialysis. Nat Clin Pract Nephrol 2: 32–39, 2006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Mariano F, Pozzato M, Canepari G, Vitale C, Bermond F, Sacco C, Amore A, Manes M, Navino C, Piedmont and Aosta Valley Section of Italian Society of Nephrology : Renal replacement therapy in intensive care units: A survey of nephrological practice in northwest Italy. J Nephrol 24: 165–176, 2011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Marshall MR, Golper TA: Low-efficiency acute renal replacement therapy: Role in acute kidney injury. Semin Dial 24: 142–148, 2011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Marshall MR, Creamer JM, Foster M, Ma TM, Mann SL, Fiaccadori E, Maggiore U, Richards B, Wilson VL, Williams AB, Rankin AP: Mortality rate comparison after switching from continuous to prolonged intermittent renal replacement for acute kidney injury in three intensive care units from different countries. Nephrol Dial Transplant 26: 2169–2175, 2011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Schwenger V, Weigand MA, Hoffmann O, Dikow R, Kihm LP, Seckinger J, Miftari N, Schaier M, Hofer S, Haar C, Nawroth PP, Zeier M, Martin E, Morath C: Sustained low efficiency dialysis using a single-pass batch system in acute kidney injury - a randomized interventional trial: The REnal Replacement Therapy Study in Intensive Care Unit PatiEnts. Crit Care 16: R140, 2012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Fieghen HE, Friedrich JO, Burns KE, Nisenbaum R, Adhikari NK, Hladunewich MA, Lapinsky SE, Richardson RM, Wald R, University of Toronto Acute Kidney Injury Research Group : The hemodynamic tolerability and feasibility of sustained low efficiency dialysis in the management of critically ill patients with acute kidney injury. BMC Nephrol 11: 32, 2010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Kron J, Kron S, Wenkel R, Schuhmacher HU, Thieme U, Leimbach T, Kern H, Neumayer HH, Slowinski T: Extended daily on-line high-volume haemodiafiltration in septic multiple organ failure: A well-tolerated and feasible procedure. Nephrol Dial Transplant 27: 146–152, 2012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Kielstein JT, Kretschmer U, Ernst T, Hafer C, Bahr MJ, Haller H, Fliser D: Efficacy and cardiovascular tolerability of extended dialysis in critically ill patients: A randomized controlled study. Am J Kidney Dis 43: 342–349, 2004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Fiaccadori E, Maggiore U, Parenti E, Giacosa R, Picetti E, Rotelli C, Tagliavini D, Cabassi A: Sustained low-efficiency dialysis (SLED) with prostacyclin in critically ill patients with acute renal failure. Nephrol Dial Transplant 22: 529–537, 2007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Marshall MR, Golper TA, Shaver MJ, Alam MG, Chatoth DK: Sustained low-efficiency dialysis for critically ill patients requiring renal replacement therapy. Kidney Int 60: 777–785, 2001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Oudemans-Van Straaten HM: Review and guidelines for regional anticoagulation with citrate in continuous hemofiltration. Neth J Crit Care 8: 146–156, 2004 [Google Scholar]
- 83.Kumar VA, Craig M, Depner TA, Yeun JY: Extended daily dialysis: A new approach to renal replacement for acute renal failure in the intensive care unit. Am J Kidney Dis 36: 294–300, 2000 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Marshall MR, Ma T, Galler D, Rankin AP, Williams AB: Sustained low-efficiency daily diafiltration (SLEDD-f) for critically ill patients requiring renal replacement therapy: Towards an adequate therapy. Nephrol Dial Transplant 19: 877–884, 2004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Berbece AN, Richardson RM: Sustained low-efficiency dialysis in the ICU: Cost, anticoagulation, and solute removal. Kidney Int 70: 963–968, 2006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Clark JA, Schulman G, Golper TA: Safety and efficacy of regional citrate anticoagulation during 8-hour sustained low-efficiency dialysis. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 3: 736–742, 2008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Szamosfalvi B, Frinak S, Yee J: Automated regional citrate anticoagulation: Technological barriers and possible solutions. Blood Purif 29: 204–209, 2010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Fiaccadori E, Lombardi M, Leonardi S, Rotelli CF, Tortorella G, Borghetti A: Prevalence and clinical outcome associated with preexisting malnutrition in acute renal failure: A prospective cohort study. J Am Soc Nephrol 10: 581–593, 1999 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Ronco C, Bellomo R, Homel P, Brendolan A, Dan M, Piccinni P, La Greca G: Effects of different doses in continuous veno-venous haemofiltration on outcomes of acute renal failure: A prospective randomised trial. Lancet 356: 26–30, 2000 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Schiffl H, Lang SM, Fischer R: Daily hemodialysis and the outcome of acute renal failure. N Engl J Med 346: 305–310, 2002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Bouman CS, Oudemans-Van Straaten HM, Tijssen JG, Zandstra DF, Kesecioglu J: Effects of early high-volume continuous venovenous hemofiltration on survival and recovery of renal function in intensive care patients with acute renal failure: A prospective, randomized trial. Crit Care Med 30: 2205–2211, 2002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Fall P, Szerlip HM: Continuous renal replacement therapy: Cause and treatment of electrolyte complications. Semin Dial 23: 581–585, 2010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Apsner R, Gruber D, Hörl WH, Sunder-Plassmann G: Parathyroid hormone secretion during citrate anticoagulated hemodialysis in acutely ill maintenance hemodialysis patients. Anesth Analg 99: 1199–1204, 2004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.van der Voort PH, Postma SR, Kingma WP, Boerma EC, de Heide LJ, Bakker AJ: An observational study on the effects of nadroparin-based and citrate-based continuous venovenous hemofiltration on calcium metabolism. Blood Purif 25: 267–273, 2007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Brain M, Parkes S, Fowler P, Robertson I, Brown A: Calcium flux in continuous venovenous haemodiafiltration with heparin and citrate anticoagulation. Crit Care Resusc 13: 72–81, 2011 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Wang PL, Meyer MM, Orloff SL, Anderson S: Bone resorption and “relative” immobilization hypercalcemia with prolonged continuous renal replacement therapy and citrate anticoagulation. Am J Kidney Dis 44: 1110–1114, 2004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Uchino S, Bellomo R, Morimatsu H, Morgera S, Schetz M, Tan I, Bouman C, Macedo E, Gibney N, Tolwani A, Oudemans-van Straaten H, Ronco C, Kellum JA: Continuous renal replacement therapy: A worldwide practice survey. The beginning and ending supportive therapy for the kidney (B.E.S.T. kidney) investigators. Intensive Care Med 33: 1563–1570, 2007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Morabito S, Pistolesi V, Pierucci A: Regional citrate anticoagulation: Towards a first-choice treatment. G Ital Nefrol 29: 14–19, 2012 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Liet JM, Allain-Launay E, Gaillard-Leroux B, Barrière F, Chenouard A, Dejode JM, Joram N: Regional citrate anticoagulation for pediatric CRRT using integrated citrate software and physiological sodium concentration solutions [published online ahead of print February 15, 2014]. Pediatr Nephrol 10.1007/s00467-014-2770-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Thijssen S, Kruse A, Raimann J, Bhalani V, Levin NW, Kotanko P: A mathematical model of regional citrate anticoagulation in hemodialysis. Blood Purif 29: 197–203, 2010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Brandl M, Strobl K, Hartmann J, Kellner K, Posnicek T, Falkenhagen D: A target-orientated algorithm for regional citrate-calcium anticoagulation in extracorporeal therapies. Blood Purif 33: 7–20, 2012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Strobl K, Hartmann J, Wallner M, Brandl M, Falkenhagen D: A target-oriented algorithm for citrate-calcium anticoagulation in clinical practice. Blood Purif 36: 136–145, 2013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Gupta M, Wadhwa NK, Bukovsky R: Regional citrate anticoagulation for continuous venovenous hemodiafiltration using calcium-containing dialysate. Am J Kidney Dis 43: 67–73, 2004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Park JS, Kim GH, Kang CM, Lee CH: Regional anticoagulation with citrate is superior to systemic anticoagulation with heparin in critically ill patients undergoing continuous venovenous hemodiafiltration. Korean J Intern Med 26: 68–75, 2011 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Morgera S, Scholle C, Melzer C, Slowinski T, Liefeld L, Baumann G, Peters H, Neumayer HH: A simple, safe and effective citrate anticoagulation protocol for the genius dialysis system in acute renal failure. Nephron Clin Pract 98: c35–c40, 2004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]