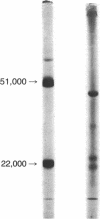
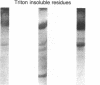
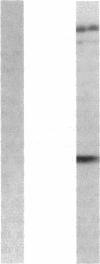
Abstract
Erythrocyte skeletal proteins are known to play an important role in determining membrane deformability. In order to see whether transmembrane proteins also influence deformability and, if so, whether this influence is mediated by an interaction with the membrane skeleton, we examined the effect on deformability of ligands specific for transmembrane proteins. We found membrane deformability markedly reduced in erythrocytes that were pretreated with glycophorin A-specific ligands. In contrast, ligands specific for band 3 and A and B blood group antigens had no effect. The increase in membrane rigidity appeared to depend upon a transmembrane event and not upon a rigidity-inducing lattice on the outside surface of the cell in that a monovalent Fab of antiglycophorin IgG caused decreased deformability. We therefore looked for a ligand-induced association of glycophorin and the skeletal proteins and found, in Triton X-100-insoluble residues, a partitioning of glycophorin with the skeletal proteins only after preincubation with a ligand specific for glycophorin. We then studied cells and resealed membranes with skeletal protein abnormalities. In spectrin-deficient and protein 4.1-deficient erythrocytes and in 2,3-diphosphoglycerate-treated resealed membranes, the antiglycophorin IgG was only one-third as effective in decreasing deformability as it was in normal cells. Thus, normal skeletal proteins appear to be essential for liganded glycophorin to affect membrane deformability maximally. Taken together, these observations indicate that there is a ligand-induced interaction between glycophorin A and skeletal proteins and that this interaction can directly influence membrane deformability.
Full text
PDF


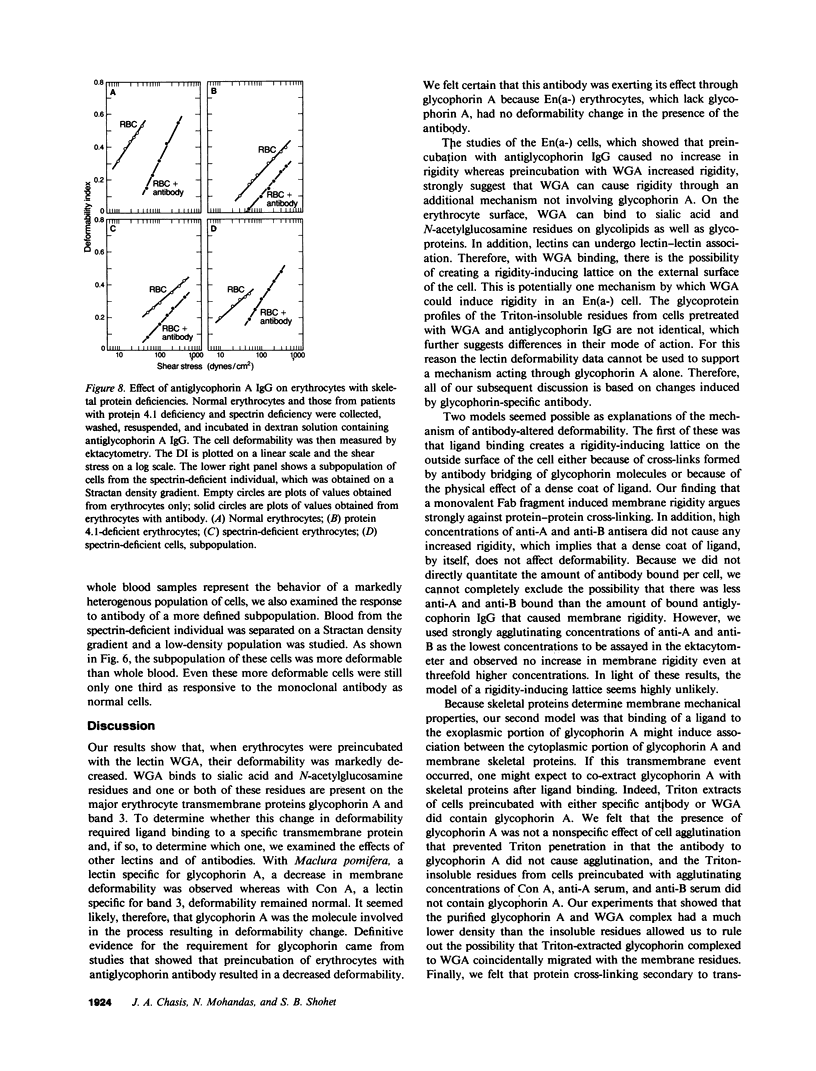


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson R. A., Lovrien R. E. Erythrocyte membrane sidedness in lectin control of the Ca2+-A23187-mediated diskocyte goes to and comes from echinocyte conversion. Nature. 1981 Jul 9;292(5819):158–161. doi: 10.1038/292158a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson R. A., Lovrien R. E. Glycophorin is linked by band 4.1 protein to the human erythrocyte membrane skeleton. Nature. 1984 Feb 16;307(5952):655–658. doi: 10.1038/307655a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anstee D. J., Edwards P. A. Monoclonal antibodies to human erythrocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1982 Mar;12(3):228–232. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830120311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhavanandan V. P., Katlic A. W. The interaction of wheat germ agglutinin with sialoglycoproteins. The role of sialic acid. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 25;254(10):4000–4008. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen C. M. The molecular organization of the red cell membrane skeleton. Semin Hematol. 1983 Jul;20(3):141–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahr W., Uhlenbruck G., Leikola J., Wagstaff W., Landfried K. Studies on the membrane glycoprotein defect of En(a-) erythrocytes. I. Biochemical aspects. J Immunogenet. 1976 Oct;3(5):329–346. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-313x.1976.tb00592.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Economidou J., Hughes-Jones N. C., Gardner B. Quantitative measurements concerning A and B antigen sites. Vox Sang. 1967 May;12(5):321–328. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1967.tb03362.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards P. A. Monoclonal antibodies that bind to the human erythrocyte-membrane glycoproteins glycophorin A and Band 3 [proceedings]. Biochem Soc Trans. 1980 Jun;8(3):334–335. doi: 10.1042/bst0080334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elgsaeter A., Branton D. Intramembrane particle aggregation in erythrocyte ghosts. I. The effects of protein removal. J Cell Biol. 1974 Dec;63(3):1018–1036. doi: 10.1083/jcb.63.3.1018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans E. A., Hochmuth R. M. A solid-liquid composite model of the red cell membrane. J Membr Biol. 1977 Jan 28;30(4):351–362. doi: 10.1007/BF01869676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans E. A., Skalak R. Mechanics and thermodynamics of biomembranes: part 2. CRC Crit Rev Bioeng. 1979 Nov;3(4):331–418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feix J. B., Green L. L., Butterfield D. A. Effects of phytohaemagglutinin, wheat-germ agglutinin, and concanavalin-A on the physical state of sialic acid and membrane proteins in human erythrocyte ghosts: a spin label study. Life Sci. 1982 Sep 6;31(10):1001–1009. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90172-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findlay J. B. The receptor proteins for concanavalin A and Lens culinaris phytohemagglutinin in the membrane of the human erythrocyte. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 25;249(14):4398–4403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furthmayr H. Structural analysis of a membrane glycoprotein: glycophorin A. J Supramol Struct. 1977;7(1):121–134. doi: 10.1002/jss.400070111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furthmayr H. Structural comparison of glycophorins and immunochemical analysis of genetic variants. Nature. 1978 Feb 9;271(5645):519–524. doi: 10.1038/271519a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENBURY C. L., MOORE D. H., NUNN L. A. REACTION OF 7S AND 19S COMPONENTS OF IMMUNE RABBIT ANTISERA WITH HUMAN GROUP A AND AB RED CELLS. Immunology. 1963 Sep;6:421–433. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gahmberg C. G., Myllyla G., Leikola J., Pirkola A., Nordling S. Absence of the major sialoglycoprotein in the membrane of human En(a--) erythrocytes and increased glycosylation of band 3. J Biol Chem. 1976 Oct 10;251(19):6108–6116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haest C. W., Fischer T. M., Plasa G., Deuticke B. Stabilization of erythrocyte shape by a chemical increase in membrane shear stiffness. Blood Cells. 1980;6(3):539–553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovrien R. E., Anderson R. A. Stoichiometry of wheat germ agglutinin as a morphology controlling agent and as a morphology controlling agent and as a morphology protective agent for the human erythrocyte. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jun;85(3):534–548. doi: 10.1083/jcb.85.3.534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchesi V. T. The red cell membrane skeleton: recent progress. Blood. 1983 Jan;61(1):1–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchesi V. T., Tillack T. W., Jackson R. L., Segrest J. P., Scott R. E. Chemical characterization and surface orientation of the major glycoprotein of the human erythrocyte membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1445–1449. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohandas N., Chasis J. A., Shohet S. B. The influence of membrane skeleton on red cell deformability, membrane material properties, and shape. Semin Hematol. 1983 Jul;20(3):225–242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohandas N., Clark M. R., Jacobs M. S., Shohet S. B. Analysis of factors regulating erythrocyte deformability. J Clin Invest. 1980 Sep;66(3):563–573. doi: 10.1172/JCI109888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson G. L., Painter R. G. Anionic sites of human erythrocyte membranes. II. Antispectrin-induced transmembrane aggregation of the binding sites for positively charged colloidal particles. J Cell Biol. 1973 Nov;59(2 Pt 1):395–406. doi: 10.1083/jcb.59.2.395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigg E. A., Bron C., Girardet M., Cherry R. J. Band 3-glycophorin A association in erythrocyte membrane demonstrated by combining protein diffusion measurements with antibody-induced cross-linking. Biochemistry. 1980 Apr 29;19(9):1887–1893. doi: 10.1021/bi00550a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Painter R. G., Ginsberg M. Concanavalin A induces interactions between surface glycoproteins and the platelet cytoskeleton. J Cell Biol. 1982 Feb;92(2):565–573. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.2.565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees D. A., Lloyd C. W., Thom D. Control of grip and stick in cell adhesion through lateral relationships of membrane glycoproteins. Nature. 1977 May 12;267(5607):124–128. doi: 10.1038/267124a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross A. H., Radhakrishnan R., Robson R. J., Khorana H. G. The transmembrane domain of glycophorin A as studied by cross-linking using photoactivatable phospholipids. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4152–4161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar M., Wu A. M., Kabat E. A. Immunochemical studies on the carbohydrate specificity of Maclura pomifera lectin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Jun;209(1):204–218. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90273-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekiguchi K., Asano A. Participation of spectrin in Sendai virus-induced fusion of human erythrocyte ghosts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1740–1744. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheetz M. P., Casaly J. 2,3-Diphosphoglycerate and ATP dissociate erythrocyte membrane skeletons. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 25;255(20):9955–9960. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheetz M. P. Integral membrane protein interaction with Triton cytoskeletons of erythrocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Oct 19;557(1):122–134. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90095-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheterline P., Hopkins C. R. Transmembrane linkage between surface glycoproteins and components of the cytoplasm in neutrophil leukocytes. J Cell Biol. 1981 Sep;90(3):743–754. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.3.743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva P. P., Nicolson G. L. Freeze-etch localization of concanavalin A receptors to the membrane intercalated particles of human erythrocyte ghost membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Sep 23;363(3):311–319. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90071-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith L., Hochmuth R. M. Effect of wheat germ agglutinin on the viscoelastic properties of erythrocyte membrane. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jul;94(1):7–11. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.1.7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanner M. J., Anstee D. J. The membrane change in En(a-) human erythrocytes. Absence of the major erythrocyte sialoglycoprotein. Biochem J. 1976 Feb 1;153(2):271–277. doi: 10.1042/bj1530271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tillack T. W., Scott R. E., Marchesi V. T. The structure of erythrocyte membranes studied by freeze-etching. II. Localization of receptors for phytohemagglutinin and influenza virus to the intramembranous particles. J Exp Med. 1972 Jun 1;135(6):1209–1227. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.6.1209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomita M., Furthmayr H., Marchesi V. T. Primary structure of human erythrocyte glycophorin A. Isolation and characterization of peptides and complete amino acid sequence. Biochemistry. 1978 Oct 31;17(22):4756–4770. doi: 10.1021/bi00615a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Petris S., Raff M. C. Distribution of immunoglobulin on the surface of mouse lymphoid cells as determined by immunoferritin electron microscopy. Antibody-induced, temperature-dependent redistribution and its implications for membrane structure. Eur J Immunol. 1972 Dec;2(6):523–535. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830020611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]