Abstract
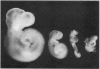
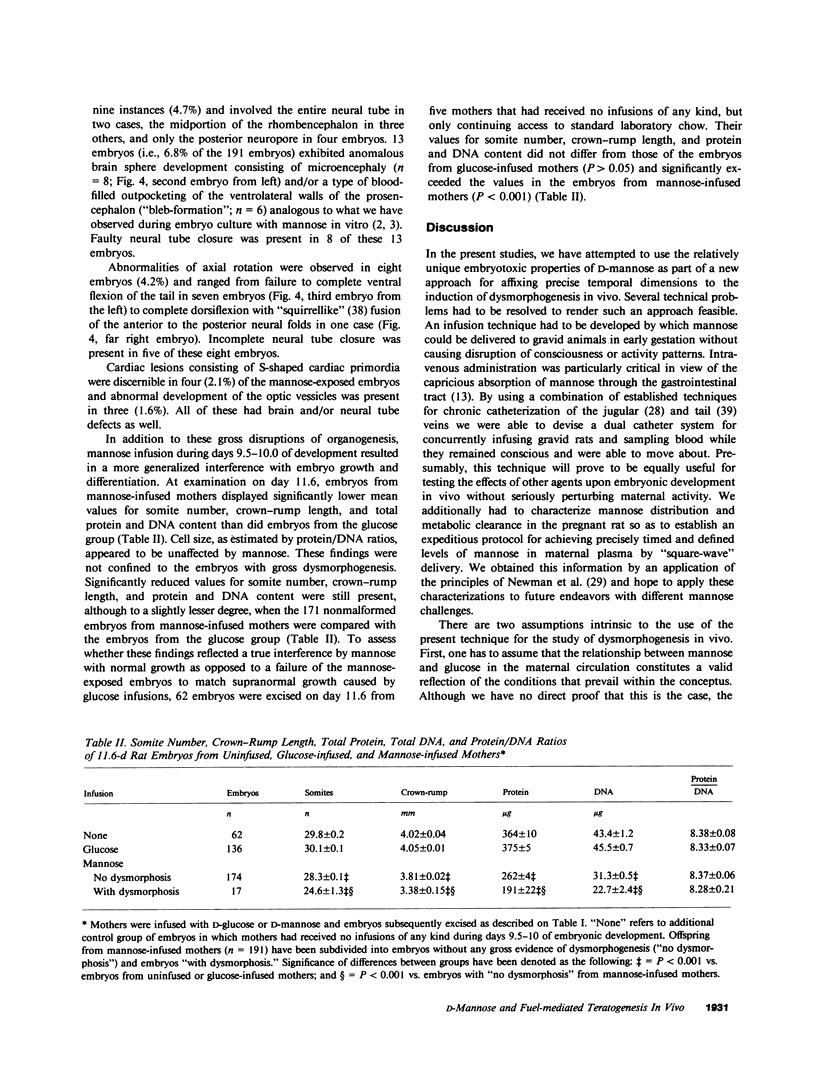
The unique embryotoxic properties of D-mannose have been used as the basis for a new technique to secure precise temporal correlations between metabolic perturbations during organogenesis and subsequent dysmorphogenesis. Conscious, pregnant rats were infused with D-mannose or equimolar amounts of D-glucose by "square wave" delivery during the interval in which the neural plate is established and early fusion of neural folds takes place, that is, days 9.5-10.0 of gestation. Infusions of mannose to maternal plasma levels of 150-200 mg/dl did not elicit any toxicity in the mothers: motor activity, eating behavior, and serum components (electrolytes, osmolality, bilirubin) did not differ in glucose- vis-à-vis mannose-infused dams. Embryos were excised by hysterotomy on day 11.6 for evaluation of development. Examination with a dissecting microscope did not disclose developmental abnormalities in any of the 136 embryos from glucose-infused mothers or in 62 additional embryos from mothers that had not received any infusions. By contrast, dysmorphic changes were seen in 17 of 191 embryos (8.9%) from mannose-infused mothers. 14 of the 17 had abnormal brain or neural tube development with incomplete neural tube closure in 9 instances. Abnormal axial rotation was present in 8 of the 191 embryos (4.2%) and lesions of the heart or optic vesicles were seen in 4 (2.1%) and 3 (1.6%), respectively. Embryos from mannose-infused mothers displayed significant retardations in somite number, crown-rump length, and total protein and DNA content. These stigmata of growth retardation were more marked in the 17 dysmorphic embryos. The experiments indicate that D-mannose may be employed in model systems with rodents for precisely timed interruptions of organogenesis in vivo. Initial applications are consistent with our earlier suggestion that multiple dysmorphic changes may supervene after interference with communally observed metabolic dependencies during organogenesis. The studies do not identify the vulnerable site(s) within the conceptus (e.g., investing membranes, embryos, or both). However, the findings suggest that dysmorphic events are manifest most markedly in a general setting of embryo growth retardation.
Full text
PDF

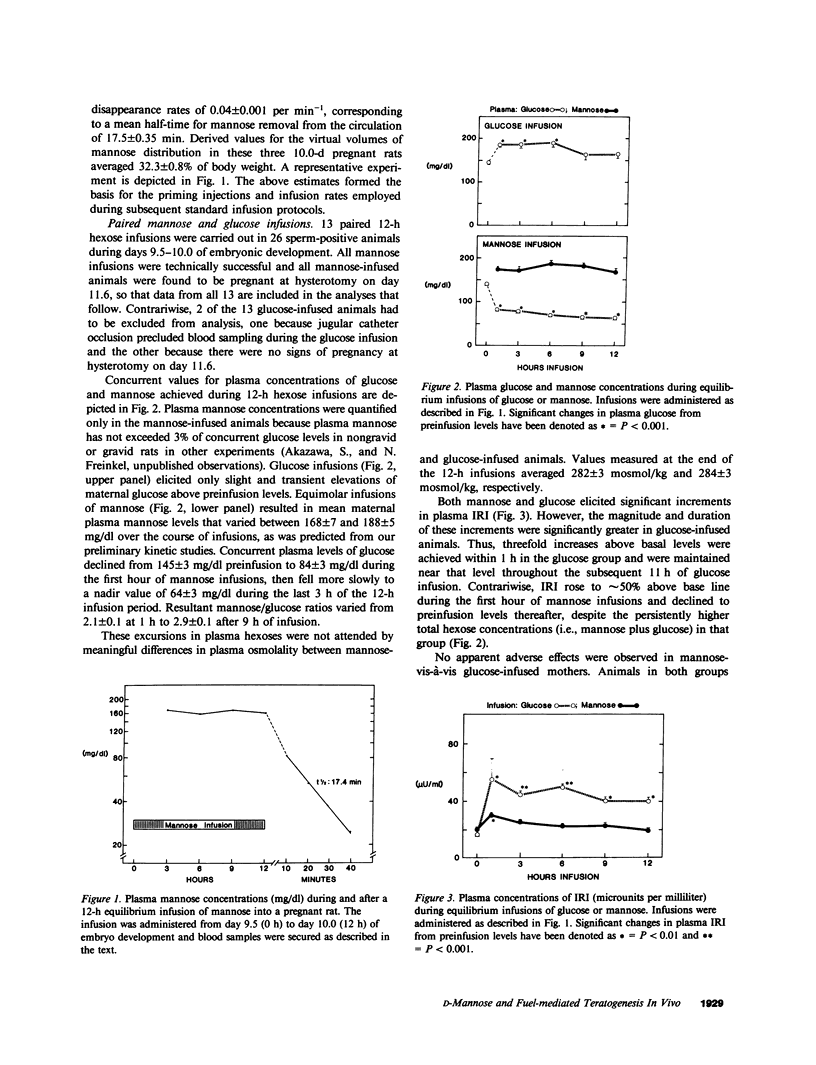
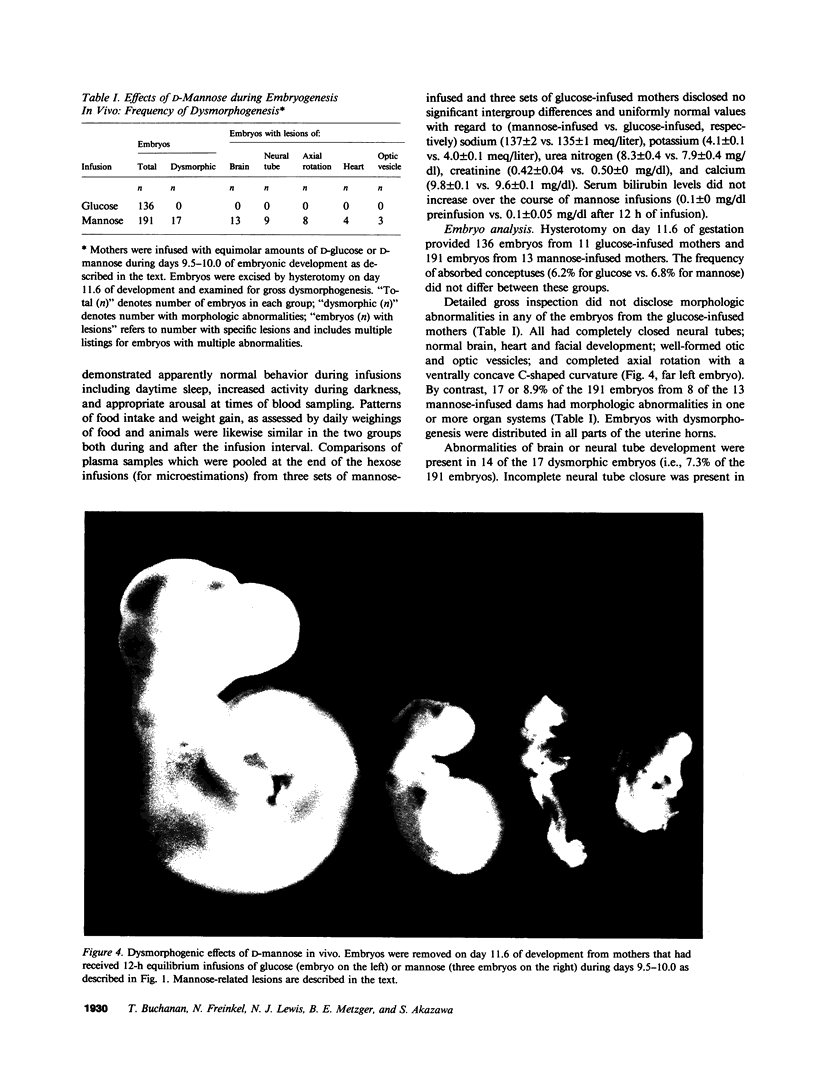



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABRAHAM S., CHAIKOFF I. L. Glycolytic pathways and lipogenesis in mammary glands of lactating and nonlactating normal rats. J Biol Chem. 1959 Sep;234:2246–2253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BALL E. G., COOPER O. Studies on the metabolism of adipose tissue. III. The response to insulin by different types of adipose tissue and in the presence of various metabolites. J Biol Chem. 1960 Mar;235:584–588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker L., Egler J. M., Klein S. H., Goldman A. S. Meticulous control of diabetes during organogenesis prevents congenital lumbosacral defects in rats. Diabetes. 1981 Nov;30(11):955–959. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.11.955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown N. A., Fabro S. Quantitation of rat embryonic development in vitro: a morphological scoring system. Teratology. 1981 Aug;24(1):65–78. doi: 10.1002/tera.1420240108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHRISTIE G. A. DEVELOPMENTAL STAGES IN SOMITE AND POST-SOMITE RAT EMBRYOS, BASED ON EXTERNAL APPEARANCE, AND INCLUDING SOME FEATURES OF THE MACROSCOPIC DEVELOPMENT OF THE ORAL CAVITY. J Morphol. 1964 Mar;114:263–283. doi: 10.1002/jmor.1051140207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chain E. B., Rose S. P., Masi I., Pocchiari F. Metabolism of hexoses in rat cerebral cortex slices. J Neurochem. 1969 Jan;16(1):93–100. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1969.tb10346.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockroft D. L., Coppola P. T. Teratogenic effects of excess glucose on head-fold rat embryos in culture. Teratology. 1977 Oct;16(2):141–146. doi: 10.1002/tera.1420160205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deuchar E. M. Embryonic malformations in rats, resulting from maternal diabetes: preliminary observations. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1977 Oct;41:93–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson U. J., Dahlström E., Hellerström C. Diabetes in pregnancy. Skeletal malformations in the offspring of diabetic rats after intermittent withdrawal of insulin in early gestation. Diabetes. 1983 Dec;32(12):1141–1145. doi: 10.2337/diab.32.12.1141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson U. J., Lewis N. J., Freinkel N. Growth retardation during early organogenesis in embryos of experimentally diabetic rats. Diabetes. 1984 Mar;33(3):281–284. doi: 10.2337/diab.33.3.281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folley S. J., French T. H. The intermediary metabolism of the mammary gland. 1. Respiration of lactating mammary gland slices in presence of carbohydrates. Biochem J. 1949;45(2):117–125. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freinkel N., Lewis N. J., Akazawa S., Gorman L., Potaczek M. The honeybee syndrome: teratogenic effects of mannose during organogenesis in rat embryo culture. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1983;96:44–55. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freinkel N., Lewis N. J., Akazawa S., Roth S. I., Gorman L. The honeybee syndrome - implications of the teratogenicity of mannose in rat-embryo culture. N Engl J Med. 1984 Jan 26;310(4):223–230. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198401263100404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funaki K., Mikamo K. Developmental-stage-dependent teratogenic effects of maternal spontaneous diabetes in the chinese hamster. Diabetes. 1983 Jul;32(7):637–643. doi: 10.2337/diab.32.7.637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh A. K., Mukherji B., Sloviter H. A. Metabolism of isolated rat brain perfused with glucose or mannose as substrate. J Neurochem. 1972 May;19(5):1279–1285. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1972.tb01453.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinegardner R. T. An improved fluorometric assay for DNA. Anal Biochem. 1971 Jan;39(1):197–201. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90476-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honeybee syndrome, glycolysis, and birth defects. N Engl J Med. 1984 Jun 7;310(23):1535–1536. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198406073102319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KISSANE J. M., ROBINS E. The fluorometric measurement of deoxyribonucleic acid in animal tissues with special reference to the central nervous system. J Biol Chem. 1958 Jul;233(1):184–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalter H. How should times during pregnancy be called in teratology? Teratology. 1968 Aug;1(3):231–234. doi: 10.1002/tera.1420010302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalter H., Warkany J. Medical progress. Congenital malformations: etiologic factors and their role in prevention (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1983 Feb 24;308(8):424–431. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198302243080804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacy P. E., Young D. A., Fink C. J. Studies on insulin secretion in vitro from isolated islets of the rat pancreas. Endocrinology. 1968 Dec;83(6):1155–1161. doi: 10.1210/endo-83-6-1155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W., Malaisse-Lagae F., Mahy M. Effets du mannose sur la sécrétion d'insuline. Ann Endocrinol (Paris) 1969 Jul-Aug;30(4):595–597. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merker H. J., Villegas H. Elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchungen zum Problem des Stoffaustausches zwischen Mutter und Keim bei Rattenembryonen des Tages 7-10. Z Anat Entwicklungsgesch. 1970;131(4):325–346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POPOVIC V., POPOVIC P. Permanent cannulation of aorta and vena cava in rats and ground squirrels. J Appl Physiol. 1960 Jul;15:727–728. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1960.15.4.727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen J. F., Molsted-Pedersen L. Early fetal growth delay detected by ultrasound marks increased risk of congenital malformation in diabetic pregnancy. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1981 Jul 25;283(6286):269–271. doi: 10.1136/bmj.283.6286.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes M. L., Patterson C. E. Chronic intravenous infusion in the rat: a nonsurgical approach. Lab Anim Sci. 1979 Feb;29(1):82–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWARTZ I. L. Measurement of extracellular fluid by means of a constant infusion technique without collection of urine. Am J Physiol. 1950 Mar;160(3):526–531. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1950.160.3.526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITHBERG M., RUNNER M. N. TERATOGENIC EFFECTS OF HYPOGLYCEMIC TREATMENTS IN INBRED STRAINS OF MICE. Am J Anat. 1963 Nov;113:479–489. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001130308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schopfer K., Matter L., Tenschert R., Bauer S., Zuppinger K. Anti-glucagon-cell and anti-adrenal-medullary-cell antibodies in islet-cell-autoantibody-positive diabetic children. N Engl J Med. 1984 Jun 7;310(23):1536–1537. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198406073102320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schopfer K., Matter L., Tenschert R., Bauer S., Zuppinger K. Anti-glucagon-cell and anti-adrenal-medullary-cell antibodies in islet-cell-autoantibody-positive diabetic children. N Engl J Med. 1984 Jun 7;310(23):1536–1537. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198406073102320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz I. L., Schachter D., Freinkel N. THE MEASUREMENT OF EXTRACELLULAR FLUID IN MAN BY MEANS OF A CONSTANT INFUSION TECHNIQUE. J Clin Invest. 1949 Sep;28(5 Pt 2):1117–1125. doi: 10.1172/JCI102145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spielmann H., Meyer-Wendecker R., Spielmann F. Influence of 2 deoxy-D-glucose and sodium fluoroacetate on respiratory metabolism of rat embryos during organogenesis. Teratology. 1973 Apr;7(2):127–133. doi: 10.1002/tera.1420070203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiers P. S. Does growth retardation predispose the fetus to congenital malformation? Lancet. 1982 Feb 6;1(8267):312–314. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)91571-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takano K., Nishimura H. Congenital malformations induced by alloxan diabetes in mice and rats. Anat Rec. 1967 Jul;158(3):303–311. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091580310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOOD F. C., Jr, CAHILL G. F., Jr MANNOSE UTILIZATION IN MAN. J Clin Invest. 1963 Aug;42:1300–1312. doi: 10.1172/JCI104814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOOD F. C., Jr, LEBOEUF B., RENOLD A. E., CAHILL G. F., Jr Metabolism of mannose and glucose by adipose tissue and liver slices from normal and alloxan-diabetic rats. J Biol Chem. 1961 Jan;236:18–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOOL I. G. Incorporation of C14 from C14-labeled sugars into CO2, nucleic acids and protein by isolated rat diaphragm. Am J Physiol. 1960 Mar;198:649–651. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1960.198.3.649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WYNGAARDEN J. B., SEGAL S., FOLEY J. B. Physiological disposition and metabolic fate of infused pentoses in man. J Clin Invest. 1957 Oct;36(10):1395–1407. doi: 10.1172/JCI103539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]