Abstract
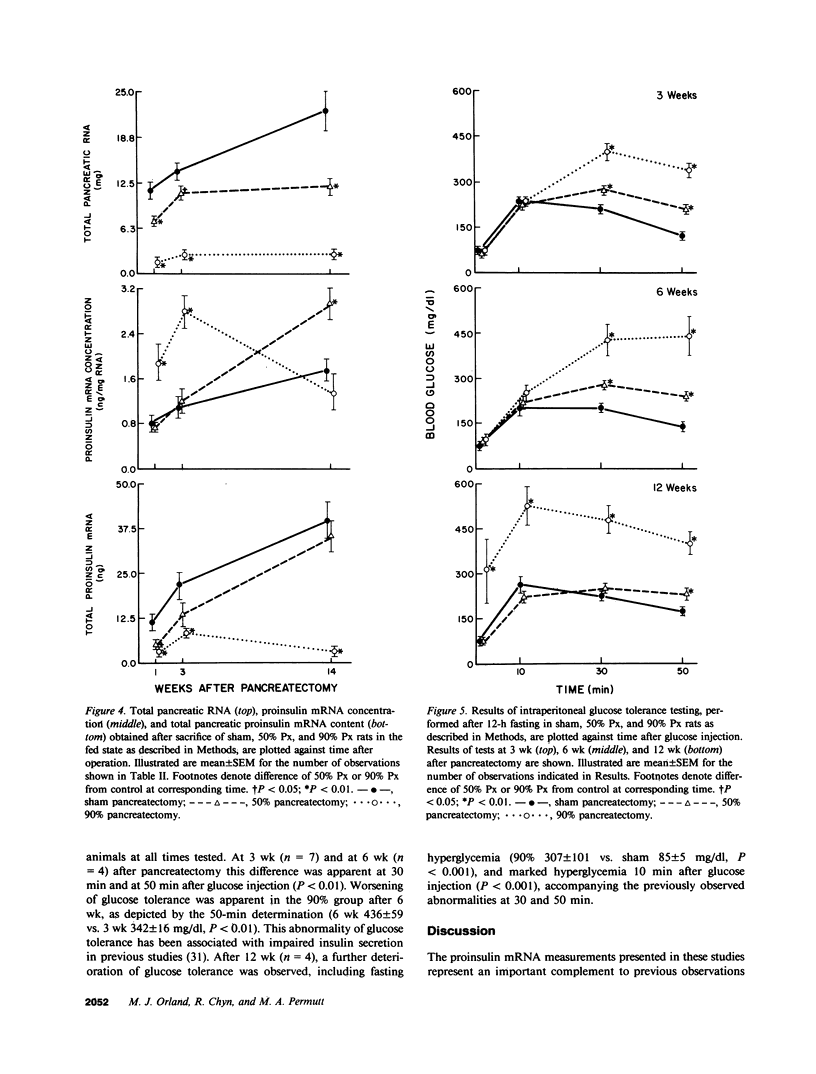
These studies of partial pancreatectomy assess pancreatic proinsulin messenger RNA (mRNA) levels as an index of in vivo insulin biosynthesis, and show relationships to glucose homeostasis. Rats were subjected to sham operation, 50% pancreatectomy (Px), or 90% Px, and were examined after 1, 3, or 14 wk. Proinsulin mRNA was measured by dot hybridization to complementary DNA. After 50% Px there was a nearly complete adaptation of proinsulin mRNA. After 90% Px a marked increase of proinsulin mRNA occurred, but it was insufficient and it was not maintained with time. The deficit in insulin production is related to development of hyperglycemia. Sham-operated controls showed no worsening of fasting or fed blood glucose or of intraperitoneal glucose tolerance within the period of observation. Total proinsulin mRNA and pancreatic insulin content rose in proportion to body weight. 50% Px produced no change from controls in body weight or blood glucose. The concentration of proinsulin mRNA in the 50% pancreatic remnant paralleled that of controls after 1 and 3 wk, but then increased after 14 wk, such that total proinsulin mRNA approached control levels. This adaptive response was reflected by changes in serum insulin, but not by pancreatic insulin content, which was only 30% of control after 14 wk. Intraperitoneal glucose tolerance was impaired mildly, and did not worsen with time after pancreatectomy. 90% Px led to elevated fed blood glucose and reduced serum insulin after 3 wk, and fasting hyperglycemia was seen after 14 wk. Proinsulin mRNA concentration in the 10% pancreatic remnant showed an adaptive increase after 1 and 3 wk, such that total proinsulin mRNA reached 40% of control. After 14 wk, however, remnant proinsulin mRNA concentration was no longer increased; total proinsulin mRNA and pancreatic insulin content were severely reduced. Intraperitoneal glucose tolerance was impaired more dramatically than with the 50% Px animals, and worsened with time after operation. These observations indicate ability to increase proinsulin mRNA levels as an adaptation to pancreatectomy. Insufficiency of this adaptation is associated with the development of hyperglycemia, and the loss of this adaptation correlates with a worsening of glucose tolerance.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrén-Sandberg A., Ihse I. Factors influencing survival after total pancreatectomy in patients with pancreatic cancer. Ann Surg. 1983 Nov;198(5):605–610. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198311000-00008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Autio V., Juusela E., Lauslahti K., Markkula H., Pessi T. Resection of the pancreas for acute hemorrhagic and necrotizing pancreatitis. World J Surg. 1979 Sep 20;3(5):631–639. doi: 10.1007/BF01654774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner-Weir S., Trent D. F., Weir G. C. Partial pancreatectomy in the rat and subsequent defect in glucose-induced insulin release. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jun;71(6):1544–1553. doi: 10.1172/JCI110910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunstedt J., Chan S. J. Direct effect of glucose on the preproinsulin mRNA level in isolated pancreatic islets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jun 30;106(4):1383–1389. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91267-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman D. L. Obese and diabetes: two mutant genes causing diabetes-obesity syndromes in mice. Diabetologia. 1978 Mar;14(3):141–148. doi: 10.1007/BF00429772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordell B., Bell G., Tischer E., DeNoto F. M., Ullrich A., Pictet R., Rutter W. J., Goodman H. M. Isolation and characterization of a cloned rat insulin gene. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):533–543. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90070-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohan F. C., Lukens F. D. Lesions of the Pancreatic Islets Produced in Cats by Administration of Glucose. Science. 1947 Feb 14;105(2720):183–183. doi: 10.1126/science.105.2720.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganda O. P., Srikanta S., Brink S. J., Morris M. A., Gleason R. E., Soeldner J. S., Eisenbarth G. S. Differential sensitivity to beta-cell secretagogues in "early," type I diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1984 Jun;33(6):516–521. doi: 10.2337/diab.33.6.516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gepts W., Lecompte P. M. The pancreatic islets in diabetes. Am J Med. 1981 Jan;70(1):105–115. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(81)90417-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giddings S. J., Chirgwin J., Permutt M. A. Effects of glucose on proinsulin messenger RNA in rats in vivo. Diabetes. 1982 Jul;31(7):624–629. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.7.624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giddings S. J., Chirgwin J., Permutt M. A. The effects of fasting and feeding on preproinsulin messenger RNA in rats. J Clin Invest. 1981 Apr;67(4):952–960. doi: 10.1172/JCI110145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giddings S. J., Orland M. J., Weir G. C., Bonner-Weir S., Permutt M. A. Impaired insulin biosynthetic capacity in a rat model for non-insulin-dependent diabetes. Studies with dexamethasone. Diabetes. 1985 Mar;34(3):235–240. doi: 10.2337/diab.34.3.235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giorgi D., Bernard J. P., Lapointe R., Dagorn J. C. Regulation of amylase messenger RNA concentration in rat pancreas by food content. EMBO J. 1984 Jul;3(7):1521–1524. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02005.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh N., Sei T., Nose K., Okamoto H. Glucose stimulation of the proinsulin synthesis in isolated pancreatic islets without increasing amount of proinsulin mRNA. FEBS Lett. 1978 Sep 15;93(2):343–347. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)81136-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakita K., Giddings S. J., Rotwein P. S., Permutt M. A. Insulin gene expression in the developing rat pancreas. Diabetes. 1983 Aug;32(8):691–696. doi: 10.2337/diab.32.8.691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACLEAN N., OGILVIE R. F. Quantitative estimation of the pancreatic islet tissue in diabetic subjects. Diabetes. 1955 Sep-Oct;4(5):367–376. doi: 10.2337/diab.4.5.367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN J. M., GREGOR W. H., LACY P. E., EVENS R. G. THE EFFECT OF HYPERGLYCEMIA UPON ISLET REGENERATION IN RATS. Diabetes. 1963 Nov-Dec;12:538–544. doi: 10.2337/diab.12.6.538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madsbad S. Prevalence of residual B cell function and its metabolic consequences in Type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes. Diabetologia. 1983 Mar;24(3):141–147. doi: 10.1007/BF00250151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Carmichael G. G. Analysis of single- and double-stranded nucleic acids on polyacrylamide and agarose gels by using glyoxal and acridine orange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4835–4838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris G. E., Korner A. The effect of glucose on insulin biosynthesis by isolated islets of Langerhans of the rat. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Jun;208(3):404–413. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(70)90213-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peavy D. E., Taylor J. M., Jefferson L. S. Correlation of albumin production rates and albumin mRNA levels in livers of normal, diabetic, and insulin-treated diabetic rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):5879–5883. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.5879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahier J., Goebbels R. M., Henquin J. C. Cellular composition of the human diabetic pancreas. Diabetologia. 1983 May;24(5):366–371. doi: 10.1007/BF00251826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rall L. B., Pictet R. L., Rutter W. J. Synthesis and accumulation of proinsulin and insulin during development of the embryonic rat pancreas. Endocrinology. 1979 Sep;105(3):835–841. doi: 10.1210/endo-105-3-835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rastogi G. K., Sinha M. K., Dash R. J. Insulin and proinsulin content of pancreases from diabetic and nondiabetic subjects. Diabetes. 1973 Nov;22(11):804–807. doi: 10.2337/diab.22.11.804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaven E. P., Gold G., Reaven G. M. Effect of age on glucose-stimulated insulin release by the beta-cell of the rat. J Clin Invest. 1979 Aug;64(2):591–599. doi: 10.1172/JCI109498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe D. W., Moen R. C., Davidson J. M., Byers P. H., Bornstein P., Palmiter R. D. Correlation of procollagen mRNA levels in normal and transformed chick embryo fibroblasts with different rates of procollagen synthesis. Biochemistry. 1978 May 2;17(9):1581–1590. doi: 10.1021/bi00602a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito K., Yaginuma N., Takahashi T. Differential volumetry of A, B and D cells in the pancreatic islets of diabetic and nondiabetic subjects. Tohoku J Exp Med. 1979 Nov;129(3):273–283. doi: 10.1620/tjem.129.273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefan Y., Orci L., Malaisse-Lagae F., Perrelet A., Patel Y., Unger R. H. Quantitation of endocrine cell content in the pancreas of nondiabetic and diabetic humans. Diabetes. 1982 Aug;31(8 Pt 1):694–700. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.8.694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland D. E., Goetz F. C., Najarian J. S. Living-related donor segmental pancreatectomy for transplantation. Transplant Proc. 1980 Dec;12(4 Suppl 2):19–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA transferred or dotted nitrocellulose paper. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:255–266. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00060-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trimble E. R., Halban P. A., Wollheim C. B., Renold A. E. Functional differences between rat islets of ventral and dorsal pancreatic origin. J Clin Invest. 1982 Feb;69(2):405–413. doi: 10.1172/JCI110464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WRENSHALL G. A., BOGOCH A., RITCHIE R. C. Extractable insulin of pancreas; correlation with pathological and clinical findings in diabetic and nondiabetic cases. Diabetes. 1952 Mar-Apr;1(2):87–107. doi: 10.2337/diab.1.2.87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir G. C., Clore E. T., Zmachinski C. J., Bonner-Weir S. Islet secretion in a new experimental model for non-insulin-dependent diabetes. Diabetes. 1981 Jul;30(7):590–595. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.7.590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir G. C. Non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: interplay between B-cell inadequacy and insulin resistance. Am J Med. 1982 Oct;73(4):461–464. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(82)90321-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]