Abstract
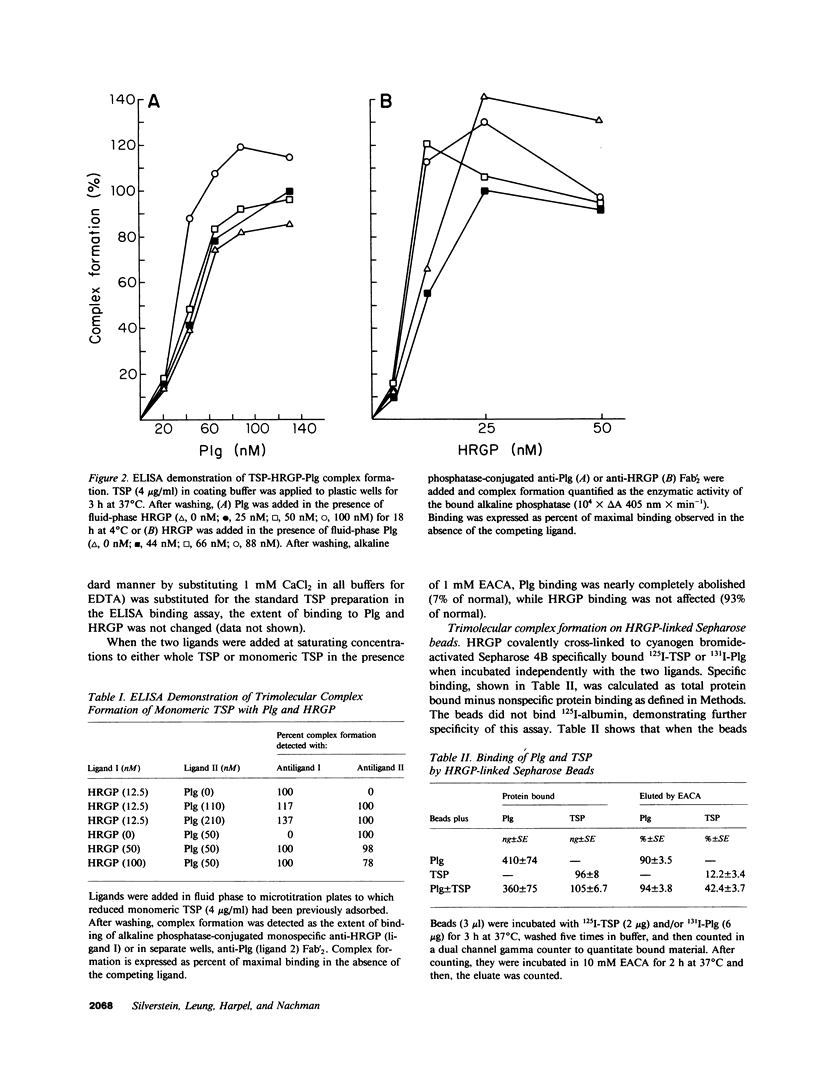
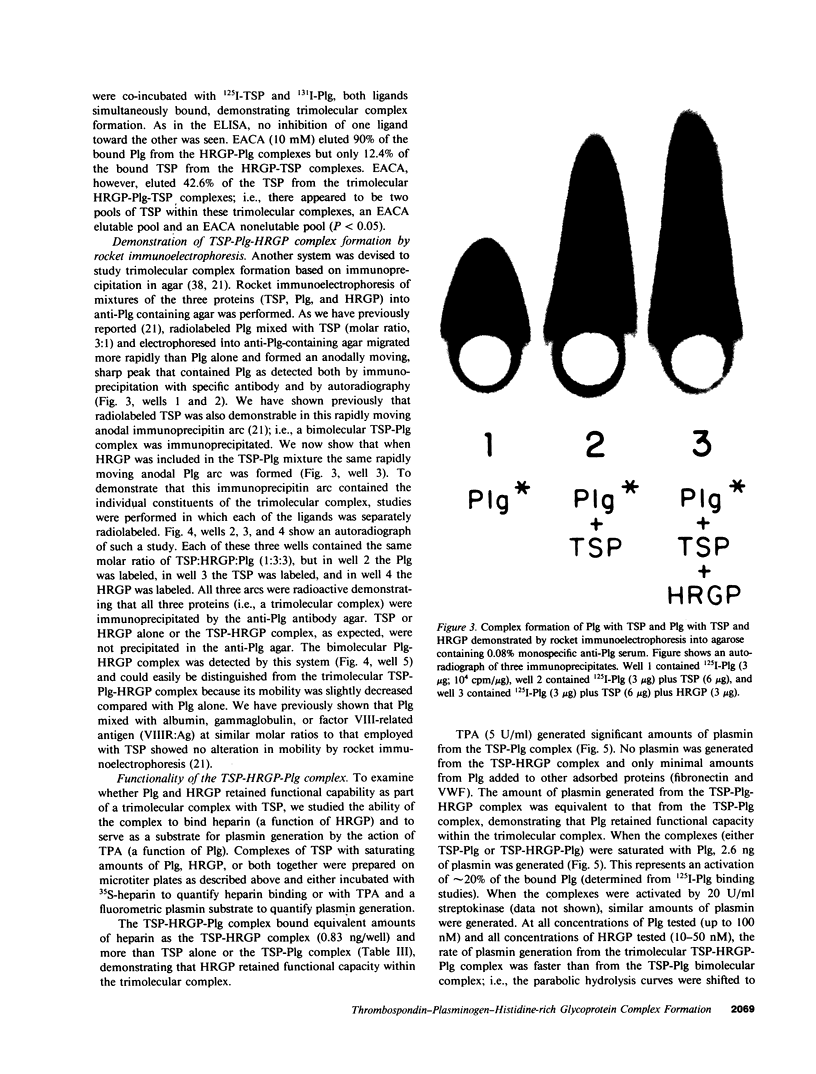
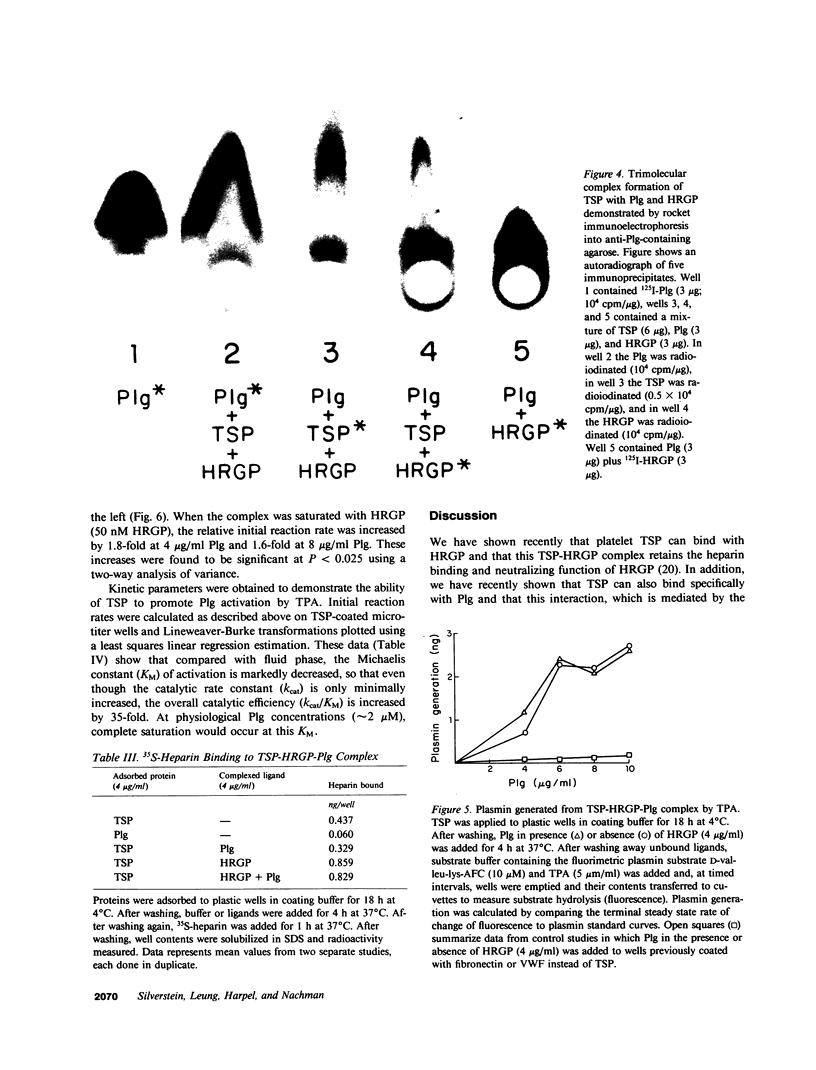
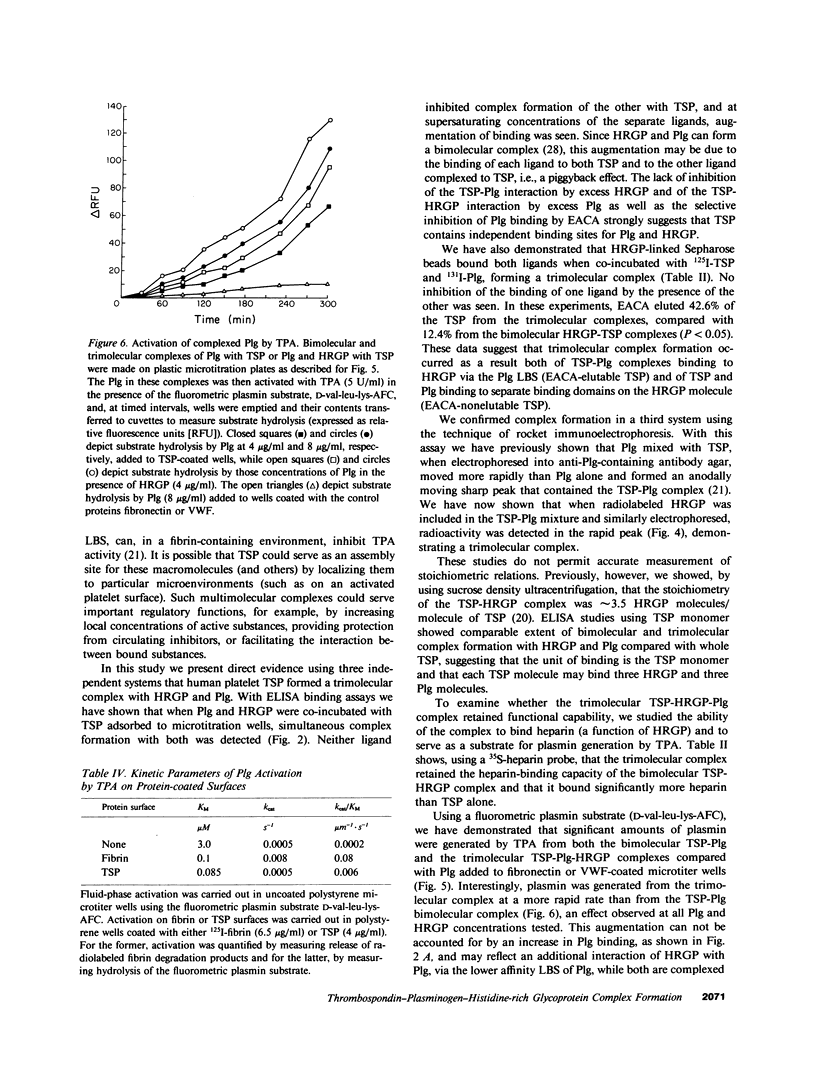
Thrombospondin (TSP), a multifunctional alpha-granule glycoprotein of human platelets binds fibrinogen, fibronectin, heparin, histidine-rich glycoprotein (HRGP), and plasminogen (Plg), and thus, may play an important role in regulating thrombotic influences at vessel surfaces. In this study we have demonstrated that purified human platelet TSP formed a trimolecular complex with human Plg and HRGP. Complex formation was detected by a specific binding enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) which demonstrated simultaneous binding of fluid-phase Plg and HRGP to TSP adsorbed to microtitration wells. While neither ligand inhibited complex formation of the other with TSP, 10 mM epsilon-amino-n-caproic acid selectively blocked incorporation of Plg into the complex, suggesting that TSP contains independent binding sites for Plg and HRGP. Comparable extent of trimolecular complex formation was also detected when TSP monomer was substituted for whole TSP in the ELISA. HRGP covalently cross-linked to Sepharose 4B simultaneously bound both 125I-TSP and 131I-Plg, confirming trimolecular complex formation. Rocket immunoelectrophoresis of mixtures of the purified radiolabeled proteins into anti-Plg containing agarose also confirmed trimolecular complex formation. The TSP-HRGP-Plg complex bound a similar amount of heparin as the TSP-HRGP complex, demonstrating that the HRGP within the trimolecular complex maintained functional capability. Similarly, using a fluorometric plasmin substrate, the trimolecular complex was shown to be an effective substrate for tissue plasminogen activator. Significant amounts of plasmin were generated from the TSP-HRGP-Plg complex (equivalent to that from the TSP-Plg complex), but the rate of plasmin generation from the trimolecular complex was greater than from the bimolecular complex, suggesting an important interaction of HRGP with Plg when both are complexed to TSP. The macromolecular assembly of these three proteins on cellular surfaces, such as the platelet, may serve important regulatory functions, both prothrombotic at sites of active fibrin deposition and proteolytic in nonfibrin-containing microenvironments.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baenziger N. L., Brodie G. N., Majerus P. W. A thrombin-sensitive protein of human platelet membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jan;68(1):240–243. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.1.240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bányai L., Patthy L. Importance of intramolecular interactions in the control of the fibrin affinity and activation of human plasminogen. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 25;259(10):6466–6471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
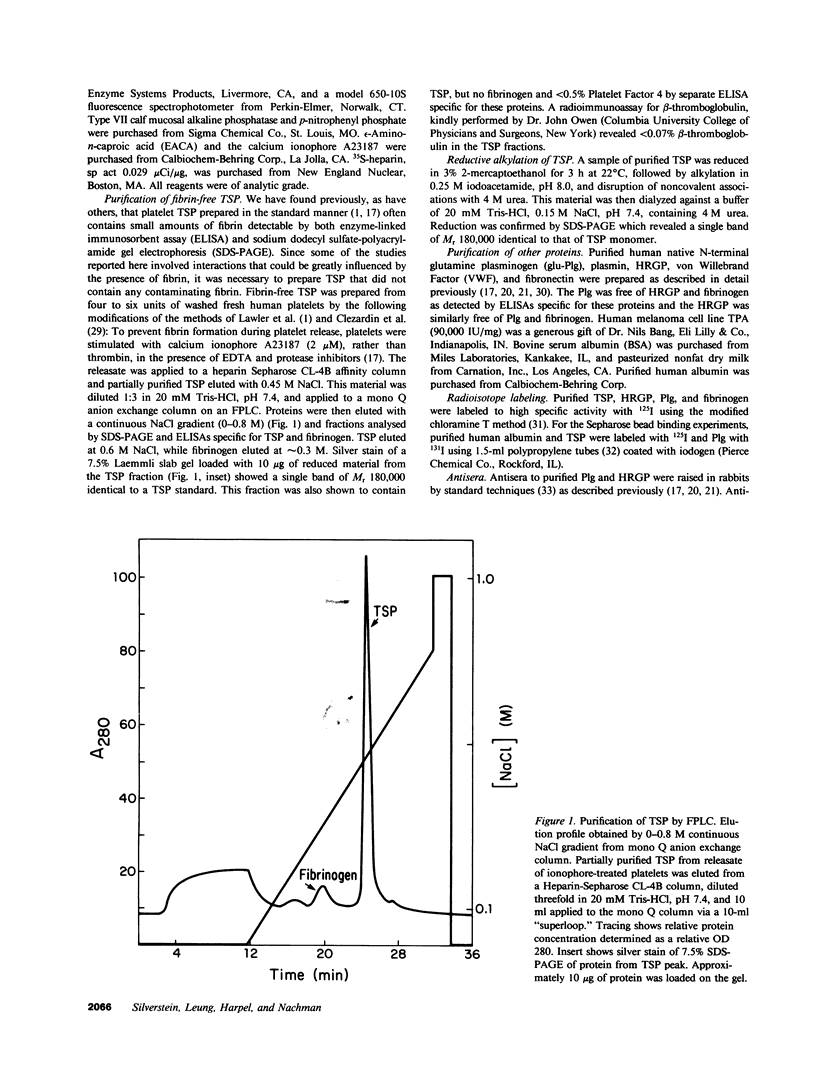
- Clezardin P., McGregor J. L., Manach M., Robert F., Dechavanne M., Clemetson K. J. Isolation of thrombospondin released from thrombin-stimulated human platelets by fast protein liquid chromatography on an anion-exchange Mono-Q column. J Chromatogr. 1984 Jul 27;296:249–256. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)96418-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch D. G., Mertz E. T. Plasminogen: purification from human plasma by affinity chromatography. Science. 1970 Dec 4;170(3962):1095–1096. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3962.1095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixit V. M., Grant G. A., Frazier W. A., Santoro S. A. Isolation of the fibrinogen-binding region of platelet thrombospondin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Mar 30;119(3):1075–1081. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90884-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixit V. M., Grant G. A., Santoro S. A., Frazier W. A. Isolation and characterization of a heparin-binding domain from the amino terminus of platelet thrombospondin. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 25;259(16):10100–10105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker P. J., Speck J. C., Jr Protein and cell membrane iodinations with a sparingly soluble chloroamide, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3a,6a-diphrenylglycoluril. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 28;80(4):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerrard J. M., Phillips D. R., Rao G. H., Plow E. F., Walz D. A., Ross R., Harker L. A., White J. G. Biochemical studies of two patients with the gray platelet syndrome. Selective deficiency of platelet alpha granules. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jul;66(1):102–109. doi: 10.1172/JCI109823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagen I. Effects of thrombin on washed, human platelets: changes in the subcellular fractions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jun 12;392(2):242–254. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(75)90006-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haupt H., Heimburger N. Humanserumproteine mit hoher Affinität zu Carboxymethylcellulose. I. Isolierung von Lysozym, C1q und bisher unbekannten -Globulinen. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1972 Jul;353(7):1125–1132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoylaerts M., Rijken D. C., Lijnen H. R., Collen D. Kinetics of the activation of plasminogen by human tissue plasminogen activator. Role of fibrin. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):2912–2919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O., Yamada K. M. Fibronectins: multifunctional modular glycoproteins. J Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;95(2 Pt 1):369–377. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.2.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A., Leung L. L., Nachman R. L., Levin R. I., Mosher D. F. Thrombospondin is the endogenous lectin of human platelets. Nature. 1982 Jan 21;295(5846):246–248. doi: 10.1038/295246a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A., Ruggiero J. T., Falcone D. J. Monocytes and macrophages synthesize and secrete thrombospondin. Blood. 1985 Jan;65(1):79–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A., Ruggiero J. T., Leung L. K., Doyle M. J., McKeown-Longo P. J., Mosher D. F. Cultured human fibroblasts synthesize and secrete thrombospondin and incorporate it into extracellular matrix. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(4):998–1002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.4.998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb W. P., Kolb L. M. Antithrombin III binding to SC5b-9 attack complexes of human complement: dissociation of a modified antithrombin III derivative subsequent to complex formation. Biochemistry. 1983 Jan 18;22(2):496–504. doi: 10.1021/bi00271a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosow D. P., Furie B., Forastieri H. Activation of factor X: kinetic properties of the reaction. Thromb Res. 1974 Feb;4(2):219–227. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(74)90087-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lahav J., Schwartz M. A., Hynes R. O. Analysis of platelet adhesion with a radioactive chemical crosslinking reagent: interaction of thrombospondin with fibronectin and collagen. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):253–262. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90425-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawler J. W., Slayter H. S., Coligan J. E. Isolation and characterization of a high molecular weight glycoprotein from human blood platelets. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 10;253(23):8609–8616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawler J. W., Slayter H. S. The release of heparin binding peptides from platelet thrombospondin by proteolytic action of thrombin, plasmin and trypsin. Thromb Res. 1981 May 1;22(3):267–279. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(81)90119-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung L. L., Harpel P. C., Nachman R. L., Rabellino E. M. Histidine-rich glycoprotein is present in human platelets and is released following thrombin stimulation. Blood. 1983 Nov;62(5):1016–1021. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung L. L., Nachman R. L. Complex formation of platelet thrombospondin with fibrinogen. J Clin Invest. 1982 Sep;70(3):542–549. doi: 10.1172/JCI110646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung L. L., Nachman R. L., Harpel P. C. Complex formation of platelet thrombospondin with histidine-rich glycoprotein. J Clin Invest. 1984 Jan;73(1):5–12. doi: 10.1172/JCI111206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung L. L. Role of thrombospondin in platelet aggregation. J Clin Invest. 1984 Nov;74(5):1764–1772. doi: 10.1172/JCI111595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lijnen H. R., Hoylaerts M., Collen D. Heparin binding properties of human histidine-rich glycoprotein. Mechanism and role in the neutralization of heparin in plasma. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 25;258(6):3803–3808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lijnen H. R., Hoylaerts M., Collen D. Isolation and characterization of a human plasma protein with affinity for the lysine binding sites in plasminogen. Role in the regulation of fibrinolysis and identification as histidine-rich glycoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 10;255(21):10214–10222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lijnen H. R., Rylatt D. B., Collen D. Physicochemical, immunochemical and functional comparison of human histidine-rich glycoprotein and autorosette inhibition factor. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jan 12;742(1):109–115. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(83)90365-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lijnen H. R., Van Hoef B., Collen D. Histidine-rich glycoprotein modulates the anticoagulant activity of heparin in human plasma. Thromb Haemost. 1984 Apr 30;51(2):266–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. A method of trace iodination of proteins for immunologic studies. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;29(2):185–189. doi: 10.1159/000229699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson J., Sage H., Bornstein P. Isolation and characterization of a glycoprotein secreted by aortic endothelial cells in culture. Apparent identity with platelet thrombospondin. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):11330–11336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan W. T. Interactions of the histidine-rich glycoprotein of serum with metals. Biochemistry. 1981 Mar 3;20(5):1054–1061. doi: 10.1021/bi00508a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosher D. F., Doyle M. J., Jaffe E. A. Synthesis and secretion of thrombospondin by cultured human endothelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1982 May;93(2):343–348. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.2.343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mumby S. M., Raugi G. J., Bornstein P. Interactions of thrombospondin with extracellular matrix proteins: selective binding to type V collagen. J Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;98(2):646–652. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.2.646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips D. R., Jennings L. K., Prasanna H. R. Ca2+-mediated association of glycoprotein G (thrombinsensitive protein, thrombospondin) with human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11629–11632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raugi G. J., Mumby S. M., Abbott-Brown D., Bornstein P. Thrombospondin: synthesis and secretion by cells in culture. J Cell Biol. 1982 Oct;95(1):351–354. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.1.351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein R. L., Leung L. L., Harpel P. C., Nachman R. L. Complex formation of platelet thrombospondin with plasminogen. Modulation of activation by tissue activator. J Clin Invest. 1984 Nov;74(5):1625–1633. doi: 10.1172/JCI111578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland S., Reich E., Sherman M. I. Plasminogen activator in early embryogenesis: enzyme production by trophoblast and parietal endoderm. Cell. 1976 Oct;9(2):231–240. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90114-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unkeless J. C., Gordon S., Reich E. Secretion of plasminogen activator by stimulated macrophages. J Exp Med. 1974 Apr 1;139(4):834–850. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.4.834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILKINSON G. N. Statistical estimations in enzyme kinetics. Biochem J. 1961 Aug;80:324–332. doi: 10.1042/bj0800324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson E. L., Dowdle E. Secretion of plasminogen activator by normal, reactive and neoplastic human tissues cultured in vitro. Int J Cancer. 1978 Oct 15;22(4):390–399. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910220405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]