In Figure 2, the symbols above the 3rd and 4th bars are incorrect. Please see the corrected Figure 2 here.
Figure 2. Pre-treatment of EPO increases cell viability in H/R induced H9C2 cells.
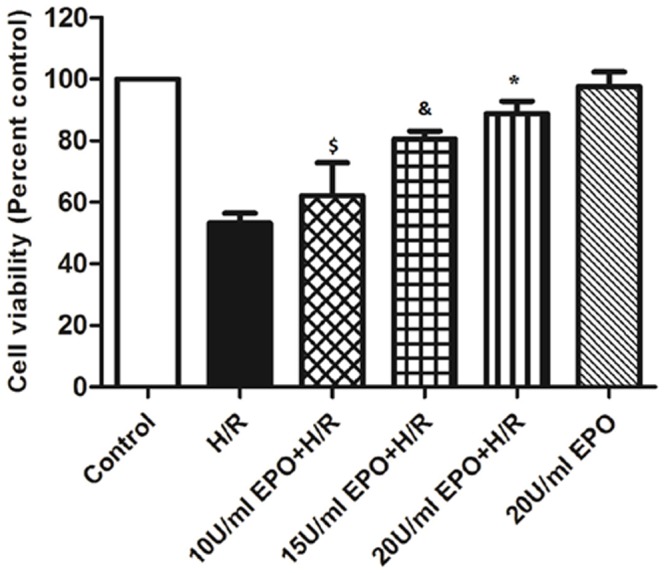
The effect of EPO on cell viability was determined using MTT assay. H9C2 cells were subjected to H/R with or without pre-treatment with (10 U/ml, 15 U/ml and 20 U/ml) EPO for 24 hrs. 20 U/ml EPO significantly increases cell viability after H/R. Data are presented as means ± SEM of the ratios from five independent experiments. $denotes p<0.05, & denotes p<0.01, * denotes p<0.001 for analyses compared to H/R.
Reference
- 1. Parvin A A, A RP, U S, Devendran A, Baker JE, et al. (2014) Erythropoietin Protects Cardiomyocytes from Cell Death during Hypoxia/Reperfusion Injury through Activation of Survival Signaling Pathways. PLoS ONE 9(9): e107453 doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0107453 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


