Abstract
Angiosarcoma is a rare and aggressive type of sarcoma, and primary angiosarcoma of the ovary is extremely rare. We report the case of a 29-year-old woman who was diagnosed with ovarian angiosarcoma and possible bone metastases. We treated this patient with a gemcitabine-based regimen as postoperative adjuvant chemotherapy, after which she achieved at least 7 years of progression-free survival, an extremely long duration given the aggressive features of this tumour. We retrospectively performed immunohistochemical analyses and fluorescence in situ hybridization to make a pathology diagnosis and to investigate the tumour features. MYC amplification and c-Myc protein overexpression were positively detected. It might be possible to correlate the effectiveness of the gemcitabine-based chemotherapeutic regimen with MYC gene amplification and c-Myc protein overexpression.
Keywords: Angiosarcoma, mucinous cystadenoma, surgical resection, chemotherapy, gemcitabine, MYC
1. INTRODUCTION
Angiosarcoma, an aggressive soft-tissue neoplastic disease, is rare, having an annual incidence of less than 1 per million population1. Angiosarcomas arise at various sites; in elderly people, these tumours commonly arise in the scalp and face2. Primary angiosarcoma of the ovary is extremely rare3, with only 35 cases being reported to date (Table i). The median overall survival of patients with metastatic angiosarcoma is generally less than 11 months30, and the median overall survival of patients with angiosarcoma of the ovary is 6–7 months17. Systemic chemotherapy for patients presenting with unresectable disease is therefore generally considered palliative.
TABLE I.
Primary angiosarcoma of the ovary reported in the literature
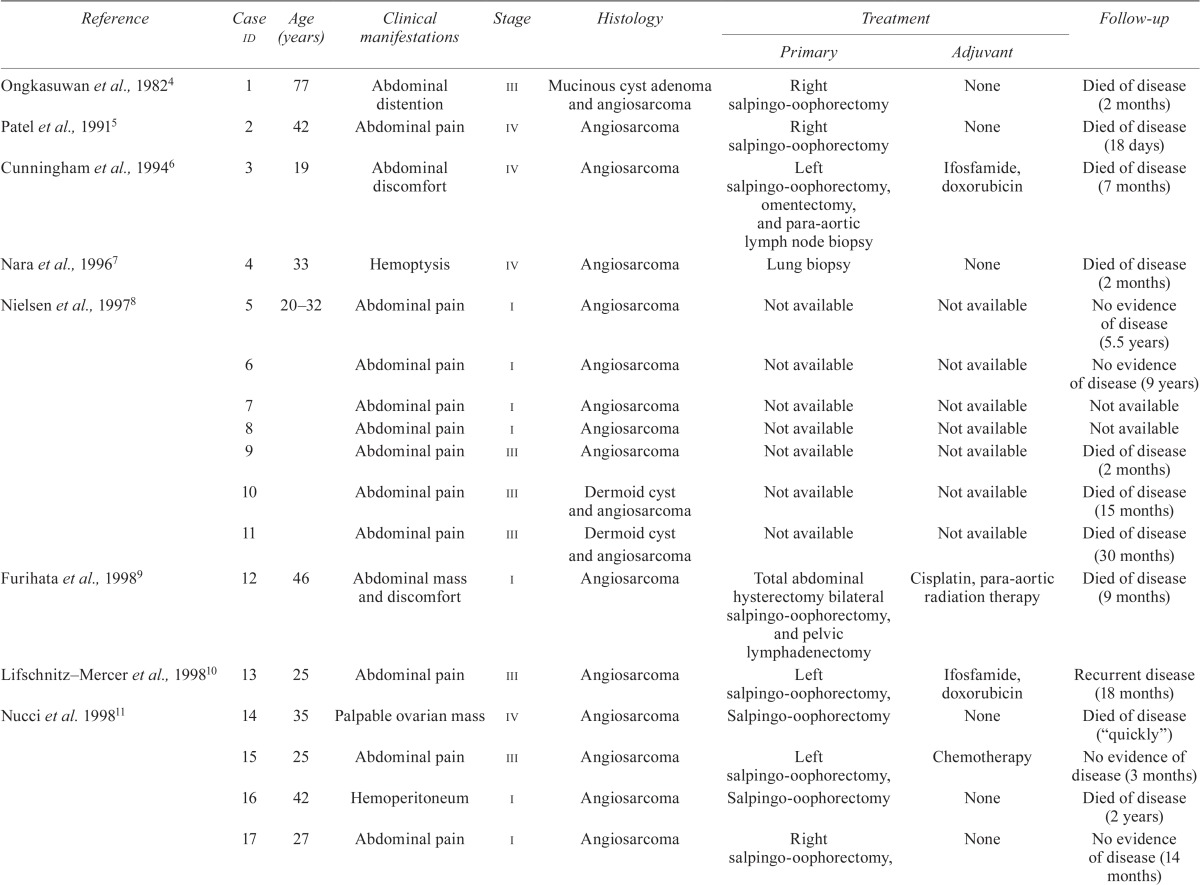
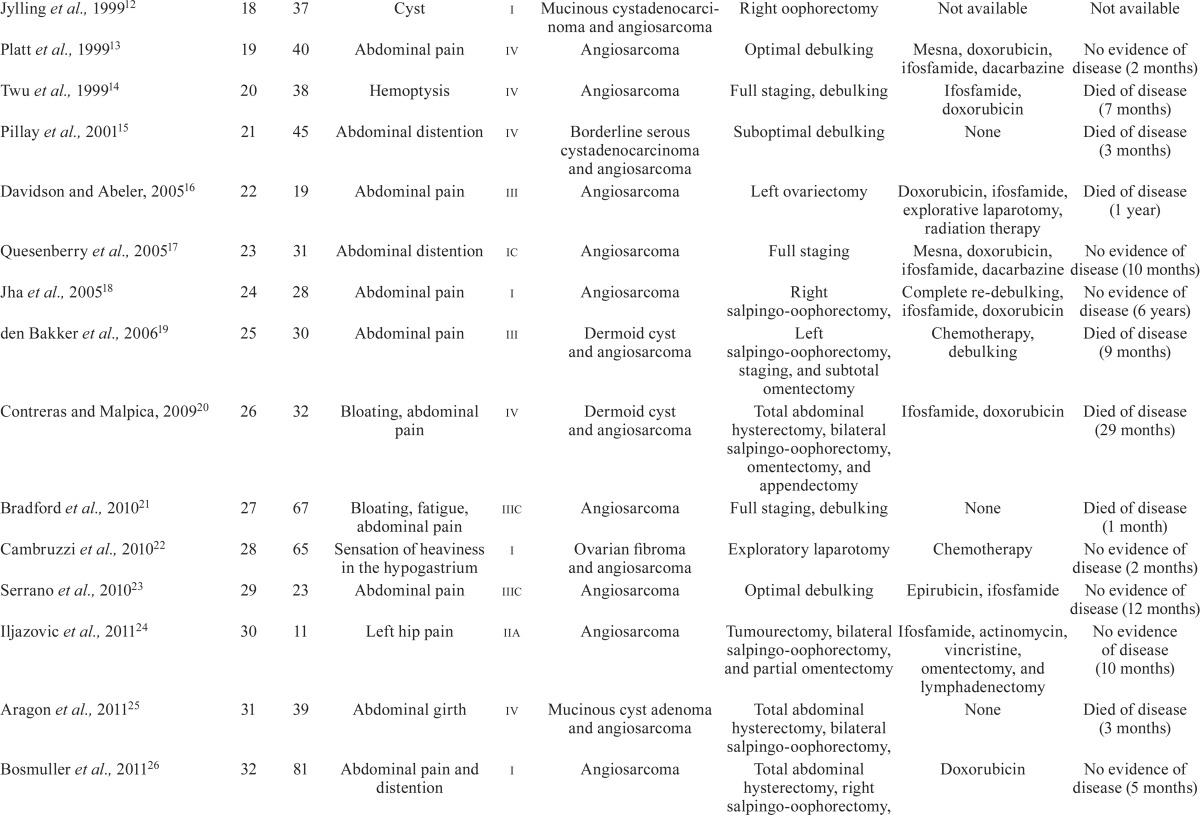
| Reference | Case id | Age (years) | Clinical manifestations | Stage | Histology | Treatment | Follow-up | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| ||||||||
| Primary | Adjuvant | |||||||
| Ongkasuwan et al., 19824 | 1 | 77 | Abdominal distention | iii | Mucinous cyst adenoma and angiosarcoma | Right salpingo-oophorectomy | None | Died of disease (2 months) |
| Patel et al., 19915 | 2 | 42 | Abdominal pain | iv | Angiosarcoma | Right salpingo-oophorectomy | None | Died of disease (18 days) |
| Cunningham et al., 19946 | 3 | 19 | Abdominal discomfort | iv | Angiosarcoma | Left salpingo-oophorectomy, omentectomy, and para-aortic lymph node biopsy | Ifosfamide, doxorubicin | Died of disease (7 months) |
| Nara et al., 19967 | 4 | 33 | Hemoptysis | iv | Angiosarcoma | Lung biopsy | None | Died of disease (2 months) |
| Nielsen et al., 19978 | 5 | 20–32 | Abdominal pain | i | Angiosarcoma | Not available | Not available | No evidence of disease (5.5 years) |
| 6 | Abdominal pain | i | Angiosarcoma | Not available | Not available | No evidence of disease (9 years) | ||
| 7 | Abdominal pain | i | Angiosarcoma | Not available | Not available | Not available | ||
| 8 | Abdominal pain | i | Angiosarcoma | Not available | Not available | Not available | ||
| 9 | Abdominal pain | iii | Angiosarcoma | Not available | Not available | Died of disease (2 months) | ||
| 10 | Abdominal pain | iii | Dermoid cyst and angiosarcoma | Not available | Not available | Died of disease (15 months) | ||
| 11 | Abdominal pain | iii | Dermoid cyst and angiosarcoma | Not available | Not available | Died of disease (30 months) | ||
| Furihata et al., 19989 | 12 | 46 | Abdominal mass and discomfort | i | Angiosarcoma | Total abdominal hysterectomy bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy, and pelvic lymphadenectomy | Cisplatin, para-aortic radiation therapy | Died of disease (9 months) |
| Lifschnitz–Mercer et al., 199810 | 13 | 25 | Abdominal pain | iii | Angiosarcoma | Left salpingo-oophorectomy, | Ifosfamide, doxorubicin | Recurrent disease (18 months) |
| Nucci et al. 199811 | 14 | 35 | Palpable ovarian mass | iv | Angiosarcoma | Salpingo-oophorectomy | None | Died of disease (“quickly”) |
| 15 | 25 | Abdominal pain | iii | Angiosarcoma | Left salpingo-oophorectomy, | Chemotherapy | No evidence of disease (3 months) | |
| 16 | 42 | Hemoperitoneum | i | Angiosarcoma | Salpingo-oophorectomy | None | Died of disease (2 years) | |
| 17 | 27 | Abdominal pain | i | Angiosarcoma | Right salpingo-oophorectomy, | None | No evidence of disease (14 months) | |
| Jylling et al., 199912 | 18 | 37 | Cyst | i | Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma and angiosarcoma | Right oophorectomy | Not available | Not available |
| Platt et al., 199913 | 19 | 40 | Abdominal pain | iv | Angiosarcoma | Optimal debulking | Mesna, doxorubicin, ifosfamide, dacarbazine | No evidence of disease (2 months) |
| Twu et al., 199914 | 20 | 38 | Hemoptysis | iv | Angiosarcoma | Full staging, debulking | Ifosfamide, doxorubicin | Died of disease (7 months) |
| Pillay et al., 200115 | 21 | 45 | Abdominal distention | iv | Borderline serous cystadenocarcinoma and angiosarcoma | Suboptimal debulking | None | Died of disease (3 months) |
| Davidson and Abeler, 200516 | 22 | 19 | Abdominal pain | iii | Angiosarcoma | Left ovariectomy | Doxorubicin, ifosfamide, explorative laparotomy, radiation therapy | Died of disease (1 year) |
| Quesenberry et al., 200517 | 23 | 31 | Abdominal distention | ic | Angiosarcoma | Full staging | Mesna, doxorubicin, ifosfamide, dacarbazine | No evidence of disease (10 months) |
| Jha et al., 200518 | 24 | 28 | Abdominal pain | i | Angiosarcoma | Right salpingo-oophorectomy, | Complete re-debulking, ifosfamide, doxorubicin | No evidence of disease (6 years) |
| den Bakker et al., 200619 | 25 | 30 | Abdominal pain | iii | Dermoid cyst and angiosarcoma | Left salpingo-oophorectomy, staging, and subtotal omentectomy | Chemotherapy, debulking | Died of disease (9 months) |
| Contreras and Malpica, 200920 | 26 | 32 | Bloating, abdominal pain | iv | Dermoid cyst and angiosarcoma | Total abdominal hysterectomy, bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy, omentectomy, and appendectomy | Ifosfamide, doxorubicin | Died of disease (29 months) |
| Bradford et al., 201021 | 27 | 67 | Bloating, fatigue, abdominal pain | iiic | Angiosarcoma | Full staging, debulking | None | Died of disease (1 month) |
| Cambruzzi et al., 201022 | 28 | 65 | Sensation of heaviness in the hypogastrium | i | Ovarian fibroma and angiosarcoma | Exploratory laparotomy | Chemotherapy | No evidence of disease (2 months) |
| Serrano et al., 201023 | 29 | 23 | Abdominal pain | iiic | Angiosarcoma | Optimal debulking | Epirubicin, ifosfamide | No evidence of disease (12 months) |
| Iljazovic et al., 201124 | 30 | 11 | Left hip pain | iia | Angiosarcoma | Tumourectomy, bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy, and partial omentectomy | Ifosfamide, actinomycin, vincristine, omentectomy, and lymphadenectomy | No evidence of disease (10 months) |
| Aragon et al., 201125 | 31 | 39 | Abdominal girth | iv | Mucinous cyst adenoma and angiosarcoma | Total abdominal hysterectomy, bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy, | None | Died of disease (3 months) |
| Bosmuller et al., 201126 | 32 | 81 | Abdominal pain and distention | i | Angiosarcoma | Total abdominal hysterectomy, right salpingo-oophorectomy, | Doxorubicin | No evidence of disease (5 months) |
| Takahashi et al., 201227 | 33 | 59 | Acute abdominopelvic pain | Not avail-able | Clear cell carcinoma, dermoid cyst, and angiosarcoma | Total abdominal hysterectomy, bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy, infracolic omentectomy | Paclitaxel, platinum | Not available |
| Guseh et al., 201328 | 34 | 40 | Fatigue and nausea | iiic | Angiosarcoma | Total abdominal hysterectomy, bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy, | Ifosfamide, doxorubicin | Recurrent disease |
| Yaqoob et al., 201429 | 35 | 41 | Abdominal pain and vaginal bleeding | ia | Angiosarcoma | Left salpingo-oophorectomy, incisional biopsy of right ovary | None | Not available |
Our patient presented with advanced ovarian angiosarcoma and bone metastases and still achieved 7 years of progression-free survival after treatment with a gemcitabine-based regimen. Recently, MYC amplification was proposed to occur in a proportion of primary31 and radiation-induced angiosarcomas32. Enhanced expression of c-Myc is an important mediator leading to disease development33. We therefore report our case and the results of retrospective MYC gene amplification and c-Myc protein expression analyses, discuss the relevance of those factors in terms of therapy and prognosis, and review the related literature.
2. CASE DESCRIPTION
A 29-year-old woman was admitted to the emergency room with abdominal pain and fever. Abdominal palpation revealed rebound tenderness. Transvaginal ultrasonography revealed a cystic mass of approximately 9 cm in the right pelvis, within which several solid masses existed. The masses were recognized as blood clots or other artefacts unrelated to the tumour component. A small amount of ascites in the Douglas pouch was also observed.
Laboratory data revealed a white blood cell count of 9320×103/μL, with 85.6% neutrophils, and 2.30 mg/dL serum C-reactive protein. On the following day, serum C-reactive protein increased to 11.22 mg/dL, indicating a level of inflammation.
Clinically, a rupture or torsion of the right ovarian tumour with acute peritonitis was suspected. Intravenous administration of ceftriaxone sodium hydrate 2 g daily was initiated and continued for 3 days.
Magnetic resonance imaging revealed a cystic right ovarian tumour whose cystic portion contained a fluid or blood component [Figure 1(A,B)]. Computed tomography revealed low-density areas in several bones, suggestive of osteolytic bone metastases [Figure 2(A)]. We also examined the tumour markers cancer antigen 125, carbohydrate antigen 19-9, and carcinoembryonic antigen, whose values were 40.3 IU/mL (reference range: 0–35 IU/mL), 1349.0 IU/mL (reference range: 0–37 IU/mL), and 48.6 ng/mL (reference range: 0–5 ng/mL) respectively. In other words, all values exceeded their reference range. We considered that the right ovarian tumour was malignant in nature.
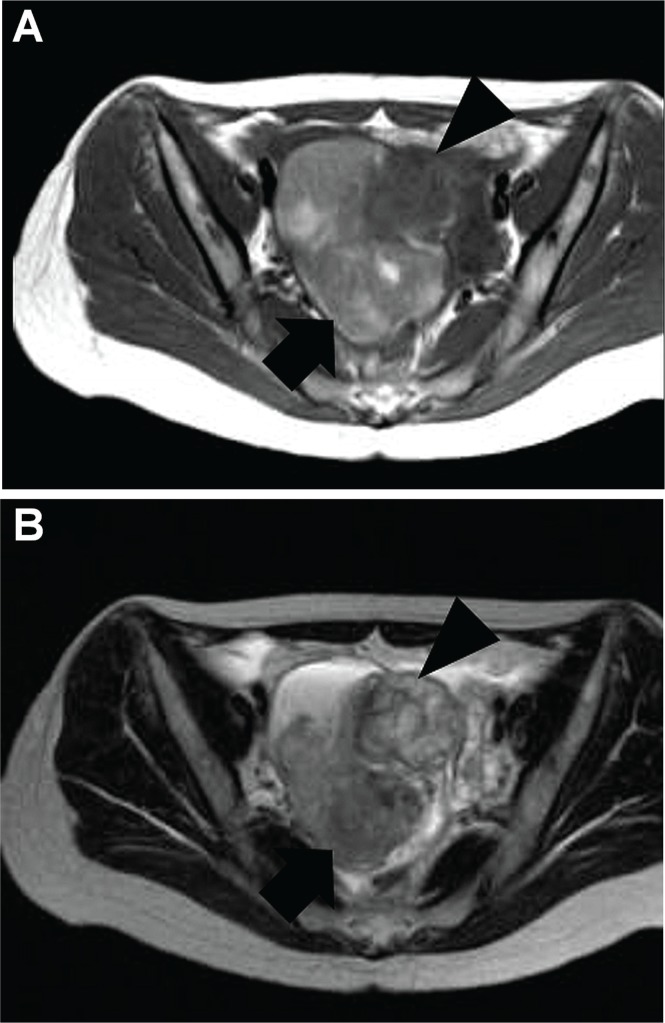
FIGURE 1.
Magnetic resonance image of patient’s pelvis at admission. A right adnexal cystic mass, 9.8×9.1×6.0 cm, containing fluid or bloody components (arrow) and a solid tumour (arrow head), 4.5×3.5×3 cm, in the cyst is suggestive of malignancy (A) T1-weighted image. (B) T2-weighted image.
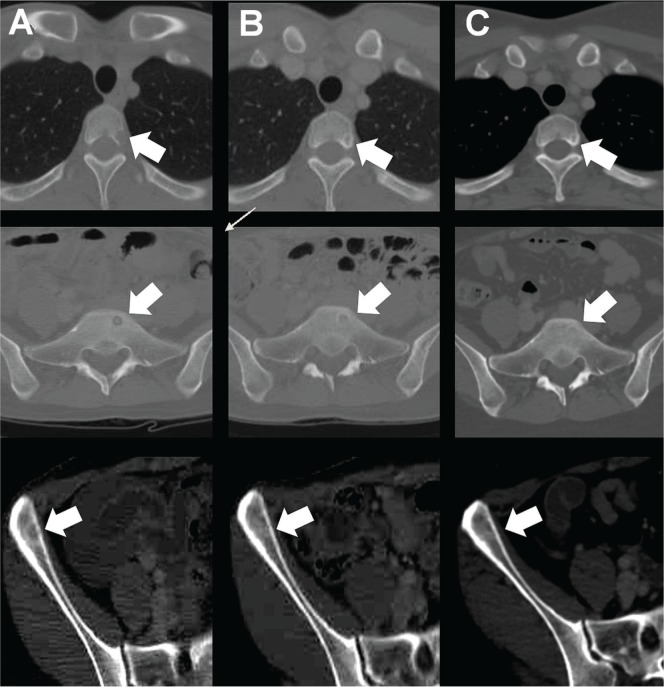
FIGURE 2.
Systemic computed tomography showing the long-term response of bone metastases in T3, sacral bone, and right ilium. (A) Initial admission (baseline). (B) Immediately after 6 courses of chemotherapy. (C) After 7 years of chemotherapy. Low-density areas were ossified from peripheral areas at time B and remained ossified at time C, suggesting that the regimen was effective in treating the metastatic angiosarcoma; the patient experienced 7 years of progression-free survival.
Given the patient’s wish to preserve fertility, a right salpingo-oophorectomy was performed. Bloody ascites was observed, and the right ovarian tumour was found to ooze from a minute surface rupture. We re-examined the tumour markers at 13 days post-surgery and found normalized levels (cancer antigen 125, 26.5 IU/mL; carbohydrate antigen 19–9, 14.0 IU/mL; carcinoembryonic antigen, 1.2 ng/mL). We continued to evaluate those markers for 7 years post-surgery, and the values never rose above their reference range.
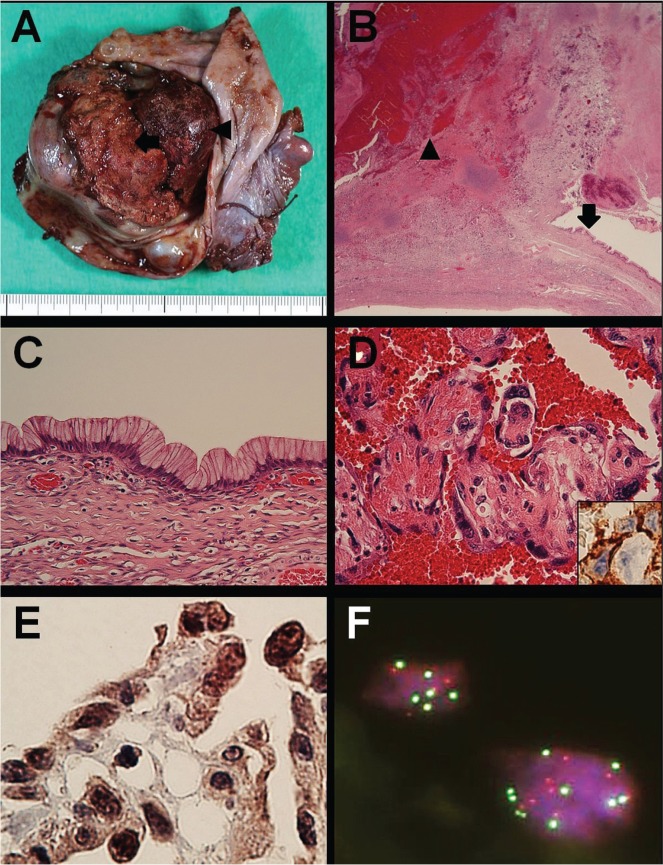
The resected specimen revealed a cystic tumour with a maximum diameter of approximately 9 cm and a solid portion measuring 4.5×3.5×3 cm. The cystic portion contained mucinous material and large blood clots [Figure 3(A)]. Histologic examination of the tumour revealed that the solid portion had originated from the cyst wall [Figure 3(B)]. The cystic portion consisted of a mucinous epithelium overlying a cyst wall that was almost flat and showed no nuclear pseudostratification, weak nuclear irregularity, and non-prominent nucleoli. Those findings were consistent with mucinous cystadenoma [Figure 3(C)]. However, the solid portion exhibited an anastomosing vascular structure with atypical endothelial cells consistent with angiosarcoma [Figure 3(D)]. By immunohistochemistry, the atypical endothelial cells were found to be positive for CD31 [Figure 3(D), inset], CD34, and factor VIII–related antigen. A diagnosis of ovarian angiosarcoma arising from a mucinous cystadenoma was made.
FIGURE 3.
Pathology observations. (A) The cystic tumour has a hemorrhagic mural nodule (arrow) containing mucinous material and a large blood clot (arrowhead). (B) A low-power view shows the cyst wall, comprising mucinous epithelium (arrow) and an abrupt transition to the hemorrhagic nodule (arrowhead). Hematoxylin and eosin (he) stain; 12.5× original magnification. (C) In a high-power view of the mucinous epithelium, no significant atypia is seen. he stain; 400× original magnification. (D) In a high-power view of the hemorrhagic nodule, vascular channels are seen to be covered with highly atypical endothelial cells. he stain; 400× original magnification. Inset, shows atypical endothelial cells positive for CD31. Immunostain; 400× original magnification. (E) Highly atypical endothelial cells are strongly reactive for c-Myc. Immunostain; 400× original magnification. (F) Fluorescence in situ hybridization reveals MYC amplification, as indicated by red (MYC probe) and green (chromosome 8 centromere probe) signals, which were almost equal in number and often exceeded 5 in number. 1000× original magnification.
Retrospective immunohistochemistry and fluorescence in situ hybridization performed 7 years after the initial diagnosis revealed diffuse c-Myc–positive angiosarcoma cells [Figure 3(E)] and nuclear MYC (8q24) amplification [Figure 3(F)] respectively. Using fluorescence in situ hybridization, red (MYC probe) and green signals (chromosome 8 centromere) were counted in 50 cells. Of those cells, 18 (36%) had copy numbers of 3 or 4, 31 (62%) had copy numbers of 5 or more, and 1 (2%) had a copy number of more than 15 for both probes, thus confirming MYC amplification.
A diagnosis of primary angiosarcoma of the ovary with bone metastases (stage iv, T1cN0M1) was clinically appropriate. Although no evidence-based chemotherapeutic regimen was available at the time, gemcitabine-based chemotherapy had been reported to be efficacious in a few angiosarcoma cases34,35. We therefore administered gemcitabine-based therapy in combination with cisplatin, which is frequently used for ovarian cancers. The patient received intravenous gemcitabine 1000 mg/m2 on days 1 and 8 and intravenous cisplatin 70 mg/m2 on day 1 every 28 days for 6 cycles. No significant adverse events were observed during chemotherapy; however, grade 1 neutropenia and grade 2 nausea were identified according to the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (version 3.0).
The patient’s status was repeatedly monitored using tumour markers and computed tomography, without suggestion of tumour recurrence. Notably, immediately after the 6 chemotherapy courses, computed tomography revealed low-density areas of ossification in several bones [Figure 2(B)]. Those areas remained ossified for 7 years after chemotherapy initiation [Figure 2(C)], reflecting progression-free survival of at least 7 years’ duration.
During the follow-up period, to the time of writing, the patient had not achieved pregnancy—not for organic reasons, but likely because of side effects from the chemotherapeutic agents.
3. DISCUSSION
Table i summarizes the 35 previously reported primary angiosarcomas. As mentioned earlier, few ovarian angiosarcomas have been treated with adjuvant chemotherapy, and the associated effects have been poorly characterized. However, several regimens have been reported to effectively treat angiosarcoma, regardless of origin. Combination therapy with anthracyclines and ifosfamide has been proved to be effective for the treatment of metastatic soft-tissue sarcoma, including angiosarcoma23. Doxorubicin-based and weekly paclitaxel regimens have demonstrated similar efficacy ranges for metastatic angiosarcomas30. However, we selected gemcitabine in the present case because several publications had reported its efficacy in angiosarcoma treatment34,35. After we initiated chemotherapy for our patient, gemcitabine monotherapy was reported to effectively treat advanced angiosarcoma36. Although the clinical diagnosis of bone metastases in our case was not definitive because no bone biopsy was conducted for histologic confirmation, the patient’s clinical outcome is consistent with reports proposing that gemcitabine-based chemotherapy regimens could be considered effective for angiosarcomas, including advanced disease.
After surgery, serum levels of the tumour markers cancer antigen 125, carbohydrate antigen 19–9, and carcinoembryonic antigen promptly declined to within their reference ranges, even before chemotherapy for angiosarcoma control was introduced. Those levels remained normal for 7 years. Mucinous cystadenomas are known to elevate levels of those markers above their normal range37,38. Assuming that bone metastases were truly present, the initially elevated tumour marker levels might have been primarily a result of the mucinous cystadenoma component of the tumour rather than the angiosarcoma component.
To the best of our knowledge, this report is the fourth of an ovarian angiosarcoma arising from a mucinous cystadenoma4,12,25 and the first to be treated with postoperative chemotherapy. In our retrospective analysis, the mural nodule of the mucinous cystadenoma was identified as angiosarcoma with MYC gene amplification and c-Myc protein overexpression. This case is therefore also extremely rare pathologically, because ovarian mucinous tumours are rarely associated with mural nodules reflecting any type of sarcoma-like (benign) disease, sarcoma, or carcinoma39,40. The features as described suggest that the primary ovarian angiosarcoma in this case developed sequentially as a mural nodule from the mucinous cystadenoma. During angiosarcoma formation, which appears to have been prompted by a mucinous cystadenoma, alterations in the molecular signatures similar to those observed in secondary angiosarcomas might have occurred. One such similarity might have been the observed MYC amplification in the present case32.
The c-Myc protein regulates numerous processes, including cell cycle progression, epithelial–mesenchymal transition, stem-cell progression, and angiogenesis, thereby facilitating tumour initiation and progression. Gong et al. showed that gemcitabine downregulates MYC gene expression and induces apoptosis in HL-60 cells37, a finding that might partly explain that agent’s therapeutic efficacy in this case. Also, reduced MYC expression in tumour cells was recently proposed to induce sensitivity to dna-damaging reagents such as cisplatin by stimulating BIN1 transcription and disrupting parp1 activity41. Therefore, gemcitabine administration might also have facilitated the antitumour efficacy of cisplatin.
In the present case, a gemcitabine based-regimen treated a primary ovarian angiosarcoma with MYC gene amplification and c-Myc protein overexpression extremely effectively. Although further studies with more enrolled cases are needed to statistically prove the effectiveness of this gemcitabine-based regimen and the correlation between MYC status and clinical outcomes, this remarkable case suggests that gemcitabine-based regimens could be a therapeutic option and even a first-line chemotherapy for the treatment of angiosarcomas.
4. SUMMARY
The patient reported here experienced 7 years of progression-free survival after treatment with a gemcitabine-based regimen for a primary ovarian angiosarcoma with MYC gene amplification. MYC amplification and the effectiveness of gemcitabine-based regimens in primary angiosarcomas should be addressed in future analyses and studies.
5. CONFLICT OF INTEREST DISCLOSURES
The authors declare that they have no financial conflicts of interest.
6. REFERENCES
- 1.Weiss SW, Lasota J, Miettinem MM. Angiosarcoma of soft tissue. In: Fletcher CDM, Unni KK, Mertens F, editors. World Health Organization Classification of Tumours: Pathology and Genetics of Tumours of Soft Tissue and Bone. Lyon, France: IARC Press; 2002. pp. 175–7. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Budd GT. Management of angiosarcoma. Curr Oncol Rep. 2002;4:515–19. doi: 10.1007/s11912-002-0066-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kruse AJ, Sep S, Slangen BF, et al. Angiosarcomas of primary gynecologic origin: a clinicopathologic review and quantitative analysis of survival. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2014;24:4–12. doi: 10.1097/IGC.0000000000000020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ongkasuwan C, Taylor JE, Tang CK, Prempree T. Angiosarcomas of the uterus and ovary: clinicopathologic report. Cancer. 1982;49:1469–75. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19820401)49:7<1469::AID-CNCR2820490726>3.0.CO;2-K. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Patel T, Ohri SK, Sundaresan M, et al. Metastatic angiosarcoma of the ovary. Eur J Surg Oncol. 1991;17:295–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Cunningham MJ, Brooks JS, Noumoff JS. Treatment of primary ovarian angiosarcoma with ifosfamide and doxorubicin. Gynecol Oncol. 1994;53:265–8. doi: 10.1006/gyno.1994.1128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Nara M, Sasaki T, Shimura S, et al. Diffuse alveolar hemorrhage caused by lung metastasis of ovarian angiosarcoma. Intern Med. 1996;35:653–6. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.35.653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Nielsen GP, Young RH, Prat J, Scully RE. Primary angiosarcoma of the ovary: a report of seven cases and review of the literature. Int J Gynecol Pathol. 1997;16:378–82. doi: 10.1097/00004347-199710000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Furihata M, Takeuchi T, Iwata J, et al. Primary ovarian angiosarcoma: a case report and literature review. Pathol Int. 1998;48:967–73. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.1998.tb03868.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Lifschitz–Mercer B, Leider–Trejo L, Messer G, Peyser MR, Czernobilsky B. Primary angiosarcoma of the ovary: a clinicopathologic, immunohistochemical and electronmicroscopic study. Pathol Res Pract. 1998;194:183–7. doi: 10.1016/S0344-0338(98)80020-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Nucci MR, Krausz T, Lifschitz–Mercer B, Chan JK, Fletcher CD. Angiosarcoma of the ovary: clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical analysis of four cases with a broad morphologic spectrum. Am J Surg Pathol. 1998;22:620–30. doi: 10.1097/00000478-199805000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Jylling AM, Jorgensen L, Holund B. Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma in combination with hemangiosarcoma in the ovary. Pathol Oncol Res. 1999;5:318–19. doi: 10.1053/paor.1999.0213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Platt JS, Rogers SJ, Flynn EA, Taylor RR. Primary angiosarcoma of the ovary: a case report and review of the literature. Gynecol Oncol. 1999;73:443–6. doi: 10.1006/gyno.1998.5335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Twu NF, Juang CM, Yeng MS, Lu CJ, Lai CZ, Chao KC. Treatment of primary pure angiosarcoma of ovary with multiple lung metastases: a case report. Eur J Gynaecol Oncol. 1999;20:383–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Pillay K, Essa AS, Chetty R. Borderline serous cystadeno-carcinoma with coexistent angiosarcoma: an unusual form of ovarian carcinosarcoma. Int J Surg Pathol. 2001;9:317–21. doi: 10.1177/106689690100900411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Davidson B, Abeler VM. Primary ovarian angiosarcoma presenting as malignant cells in ascites: case report and review of the literature. Diagn Cytopathol. 2005;32:307–9. doi: 10.1002/dc.20245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Quesenberry CD, Li C, Chen AH, Zweizig SL, Ball HG., 3rd Primary angiosarcoma of the ovary: a case report of stage i disease. Gynecol Oncol. 2005;99:218–21. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2005.05.044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Jha S, Chan KK, Poole CJ, Rollason TP. Pregnancy following recurrent angiosarcoma of the ovary—a case report and review of literature. Gynecol Oncol. 2005;97:935–7. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2005.02.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.den Bakker MA, Ansink AC, Ewing–Graham PC. “Cutaneous-type” angiosarcoma arising in a mature cystic teratoma of the ovary. J Clin Pathol. 2006;59:658–60. doi: 10.1136/jcp.2005.029751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Contreras AL, Malpica A. Angiosarcoma arising in mature cystic teratoma of the ovary: a case report and review of the literature. Int J Gynecol Pathol. 2009;28:453–7. doi: 10.1097/PGP.0b013e31819d4574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Bradford L, Swartz K, Rose S. Primary angiosarcoma of the ovary complicated by hemoperitoneum: a case report and review of the literature. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2010;281:145–50. doi: 10.1007/s00404-009-1092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Cambruzzi E, Pegas KL, Milani DM, Cruz RP, Guerra EH, Ferrari MB. Angiosarcoma arising in an ovarian fibroma: a case report. Patholog Res Int. 2010;2010:842592. doi: 10.4061/2010/842592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Serrano C, Garcia A, Brana I, Perez–Benavente A, Oaknin A. Angiosarcoma of the ovary: is it always a lethal disease? J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:e675–7. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2010.30.0830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Iljazovic E, Tomic S, Mustedanagic–Mujanovic J, et al. Angiosarcoma of the ovary in an 11 year old girl: case report and review of the literature. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2011;11:132–6. doi: 10.17305/bjbms.2011.2599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Aragon L, Terreros D, Ho H, Greenberg H, Kupesic Plavsic S. Angiosarcoma of the ovary arising in a mucinous cystadenoma. J Clin Ultrasound. 2011;39:351–5. doi: 10.1002/jcu.20821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Bosmuller H, Gruber C, Haitchi–Petnehazy S, Wagner D, Webersinke G, Hauptmann S. Primary angiosarcoma of the ovary with prominent fibrosis of the ovarian stroma. Case report of an 81-year old patient. Diagn Pathol. 2011;6:65. doi: 10.1186/1746-1596-6-65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Takahashi H, Chaopotong P, Kajita S, Hashimura M, Yamazaki H, Saegusa M. Mixed angiosarcoma, clear cell adenocarcinoma and mature teratoma elements in an ovarian tumor: a case report and literature review. Pathol Int. 2012;62:538–42. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.2012.02831.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Guseh SH, Bradford LS, Hariri LP, Schorge JO. Ovarian angiosarcoma: extended survival following optimal cytoreductive surgery and adjuvant chemotherapy. Gynecol Oncol Case Rep. 2012;4:23–5. doi: 10.1016/j.gynor.2012.12.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Yaqoob N, Nemenqani D, Khoja H, Hafez M, Tulbah A, Al-Dayel F. Ovarian angiosarcoma: a case report and review of the literature. J Med Case Rep. 2014;8:47. doi: 10.1186/1752-1947-8-47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Penel N, Italiano A, Ray–Coquard I, et al. on behalf of the French Sarcoma Group (gsf/geto) Metastatic angiosarcomas: doxorubicin-based regimens, weekly paclitaxel and metastasectomy significantly improve the outcome. Ann Oncol. 2012;23:517–23. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdr138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Italiano A, Thomas R, Breen M, et al. The miR-17-92 cluster and its target thbs1 are differentially expressed in angiosarcomas dependent on MYC amplification. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2012;51:569–78. doi: 10.1002/gcc.21943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Ginter PS, Mosquera JM, MacDonald TY, D’Alfonso TM, Rubin MA, Shin SJ. Diagnostic utility of MYC amplification and anti-MYC immunohistochemistry in atypical vascular lesions, primary or radiation-induced mammary angiosarcomas, and primary angiosarcomas of other sites. Hum Pathol. 2014;45:709–16. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2013.11.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Kurisetty V, Bryan BA. Aberrations in angiogenic signaling and MYC amplifications are distinguishing features of angiosarcoma. Angiol. 2013;1:102. doi: 10.4172/2329-9495.1000102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Patel SR, Gandhi V, Jenkins J, et al. Phase ii clinical investigation of gemcitabine in advanced soft tissue sarcomas and window evaluation of dose rate on gemcitabine triphosphate accumulation. J Clin Oncol. 2001;19:3483–9. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2001.19.15.3483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Leu KM, Ostruszka LJ, Shewach D, et al. Laboratory and clinical evidence of synergistic cytotoxicity of sequential treatment with gemcitabine followed by docetaxel in the treatment of sarcoma. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22:1706–12. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2004.08.043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Stacchiotti S, Palassini E, Sanfilippo R, et al. Gemcitabine in advanced angiosarcoma: a retrospective case series analysis from the Italian Rare Cancer Network. Ann Oncol. 2012;23:501–8. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdr066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Gong HT, Sun L, Ren XJ, Liu L, Han XF. Influence of gemcitabine on expression of c-MYC gene and its apoptosis-inducing effect on HL-60 cells [Chinese] Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2010;18:317–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Jacobs I, Bast RC., Jr The CA125 tumour-associated antigen: a review of the literature. Hum Reprod. 1989;4:1–12. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.humrep.a136832. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Scully RE, Young RH, Clement PB. Atlas of Tumor Pathology: Tumors of the Ovary, Maldeveloped Gonads, Fallopian Tube and Broad Ligament. Washington, DC: Armed Forces Institute of Pathology; 1998. [Google Scholar]
- 40.Hart WR. Mucinous tumors of the ovary: a review. Int J Gynecol Pathol. 2005;24:4–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Pyndiah S, Tanida S, Ahmed KM, Cassimere EK, Choe C, Sakamuro D. c-Myc suppresses BIN1 to release poly(adpribose) polymerase 1: a mechanism by which cancer cells acquire cisplatin resistance. Sci Signal. 2011;4:ra19. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2001556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]