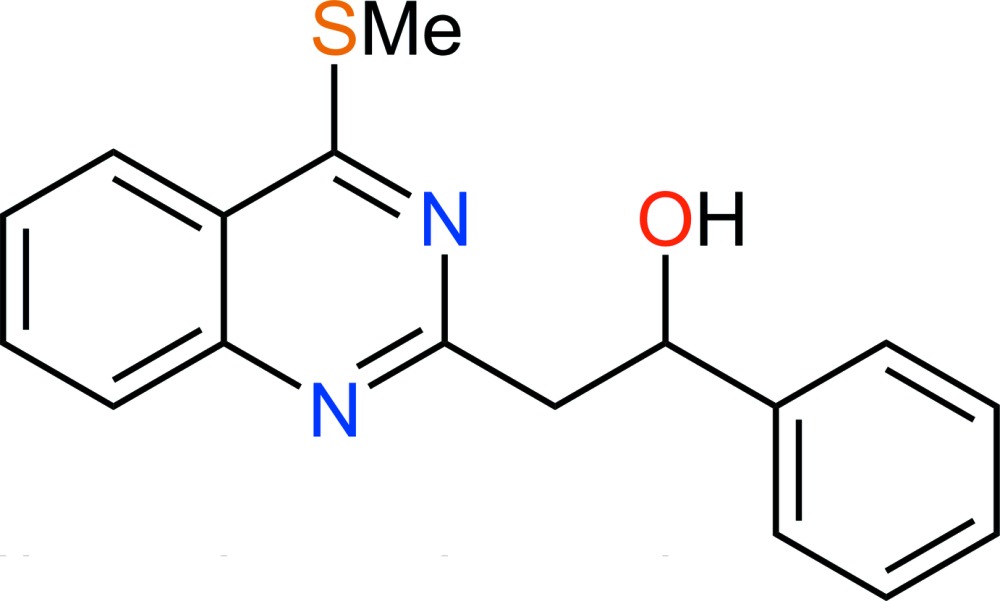
Abstract
In the molecule of the title compound, C17H16N2OS, the almost planar methylsulfanylquinazoline group [the methyl C atom deviates by 0.032 (2) Å from the plane through the ring system] forms an interplanar angle of 76.26 (4)° with the plane of the phenyl group. An intramolecular O—H⋯N hydrogen bond is present between the quinazoline and hydroxy groups. In the crystal, molecules are stacked along the b-axis direction.
Keywords: crystal structure, 4-(methylsulfanyl)quinazoline derivative, hydrogen bonding
Related literature
For the synthesis of 4-(methylsulfanyl)quinazoline derivatives, see: Smith et al. (2005a
▶,b
▶); Leonard & Curtin (1946 ▶); Meerwein et al. (1956 ▶). For the crystal structures of related compounds, see: Alshammari et al. (2014a
▶,b
▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
C17H16N2OS
M r = 296.38
Monoclinic,
a = 15.6142 (3) Å
b = 5.6142 (1) Å
c = 17.2355 (3) Å
β = 101.138 (2)°
V = 1482.43 (5) Å3
Z = 4
Cu Kα radiation
μ = 1.93 mm−1
T = 293 K
0.32 × 0.19 × 0.14 mm
Data collection
Agilent SuperNova (Dual, Cu at zero, Atlas) diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Agilent, 2014 ▶) T min = 0.867, T max = 1.000
9606 measured reflections
2938 independent reflections
2688 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.014
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.032
wR(F 2) = 0.094
S = 1.06
2938 reflections
192 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.16 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.28 e Å−3
Data collection: CrysAlis PRO (Agilent, 2014 ▶); cell refinement: CrysAlis PRO; data reduction: CrysAlis PRO; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS2013 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL2013 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: Mercury (Macrae et al., 2006 ▶), ORTEP-3 for Windows (Farrugia, 2012 ▶) and CHEMDRAW Ultra (Cambridge Soft, 2001 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: publCIF (Westrip, 2010 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, New_Global_Publ_Block. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814019990/gg2141sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814019990/gg2141Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814019990/gg2141Isup3.cml
17 16 2 . DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814019990/gg2141fig1.tif
A molecule of C17H16N2OS with atom labels and 50% probability displacement ellipsoids for nonhydrogen atoms.
b . DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814019990/gg2141fig2.tif
Crystal structure packing viewed down the b axis.
CCDC reference: 1022918
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1—H1⋯N1 | 0.82 | 2.12 | 2.7531 (15) | 134 |
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Cornea Research Chair, Department of Optometry, College of Applied Medical Sciences, King Saud University, for funding this research.
supplementary crystallographic information
S1. Comment
In C17H16N2OS (Fig. 1), the methylsulfanylquinazoline group is planar and is oriented at an angle of 76.26 (4)° with the phenyl group. The hydroxyl group forms an intramolecular hydrogen bond to one of the quinazoline ring nitrogen atoms (Table 1) whereas the second N atom is not involved in hydrogen bonding. In the crystal structure, molecules are stacked along the b-axis direction (Fig. 2).
S2. Experimental
Synthesis and crystallization: 2-(2-hydroxy-2-phenylethyl)-4-(methylsulfanyl)quinazoline was obtained in 83% yield from lithiation of 2-methyl-4-(methylsulfanyl)quinazoline with n-butyllithium at 78°C in anhydrous THF under nitrogen followed by reaction with benzaldehyde (Smith et al., 2005b). Crystallization from a mixture of ethyl acetate and diethyl ether (1:3 by volume) gave the title compound as colorless crystals. The NMR and low and high resolution mass spectra for the title compound were consistent with those reported (Smith et al., 2005b).
S3. Refinement
H atoms were positioned geometrically and refined using a riding model with Uiso(H) constrained to be 1.2 times Ueq(C) except for the methyl group where it was 1.5 times with free rotation about the C—C bond. For the OH group, Uiso(H) 1.5 times Ueq(O) was used with free rotation about the C—O bond.
Figures
Fig. 1.

A molecule of C17H16N2OS with atom labels and 50% probability displacement ellipsoids for nonhydrogen atoms.
Fig. 2.
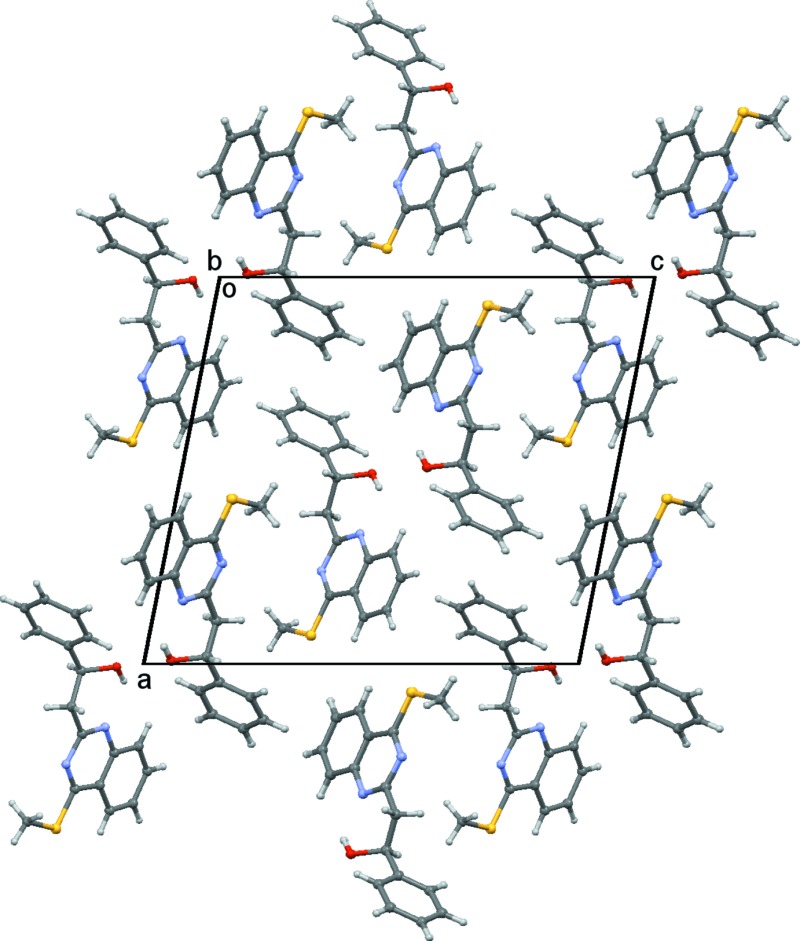
Crystal structure packing viewed down the b axis.
Crystal data
| C17H16N2OS | F(000) = 624 |
| Mr = 296.38 | Dx = 1.328 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Cu Kα radiation, λ = 1.54184 Å |
| a = 15.6142 (3) Å | Cell parameters from 5816 reflections |
| b = 5.6142 (1) Å | θ = 3.5–73.7° |
| c = 17.2355 (3) Å | µ = 1.93 mm−1 |
| β = 101.138 (2)° | T = 293 K |
| V = 1482.43 (5) Å3 | Block, colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.32 × 0.19 × 0.14 mm |
Data collection
| Agilent SuperNova (Dual, Cu at 0, Atlas) diffractometer | 2688 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| ω scans | Rint = 0.014 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Agilent, 2014) | θmax = 74.0°, θmin = 3.5° |
| Tmin = 0.867, Tmax = 1.000 | h = −19→19 |
| 9606 measured reflections | k = −6→6 |
| 2938 independent reflections | l = −11→21 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | 0 restraints |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.032 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.094 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0507P)2 + 0.2343P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.06 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 2938 reflections | Δρmax = 0.16 e Å−3 |
| 192 parameters | Δρmin = −0.28 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Experimental. Absorption correction: CrysAlisPro, Agilent Technologies, Version 1.171.36.28 (release 01-02-2013 CrysAlis171 .NET) (compiled Feb 1 2013,16:14:44) Empirical absorption correction in SCALE3 ABSPACK. |
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | 0.67633 (8) | 0.0261 (2) | 0.10297 (7) | 0.0458 (3) | |
| C2 | 0.68632 (8) | −0.1600 (2) | 0.04845 (7) | 0.0450 (3) | |
| C3 | 0.62090 (9) | −0.3225 (3) | 0.01440 (8) | 0.0553 (3) | |
| H3 | 0.5652 | −0.3110 | 0.0258 | 0.066* | |
| C4 | 0.63923 (10) | −0.4967 (3) | −0.03523 (9) | 0.0601 (4) | |
| H4 | 0.5961 | −0.6048 | −0.0569 | 0.072* | |
| C5 | 0.72249 (10) | −0.5136 (3) | −0.05366 (8) | 0.0569 (3) | |
| H5 | 0.7342 | −0.6336 | −0.0873 | 0.068* | |
| C6 | 0.78660 (9) | −0.3561 (3) | −0.02273 (8) | 0.0523 (3) | |
| H6 | 0.8413 | −0.3669 | −0.0363 | 0.063* | |
| C7 | 0.76994 (8) | −0.1775 (2) | 0.02961 (7) | 0.0444 (3) | |
| C8 | 0.81859 (8) | 0.1354 (2) | 0.11131 (7) | 0.0445 (3) | |
| C9 | 0.59215 (12) | 0.3019 (3) | 0.19721 (11) | 0.0734 (5) | |
| H9A | 0.6392 | 0.2626 | 0.2400 | 0.110* | |
| H9B | 0.5401 | 0.3312 | 0.2176 | 0.110* | |
| H9C | 0.6070 | 0.4421 | 0.1708 | 0.110* | |
| C10 | 0.88942 (8) | 0.3057 (2) | 0.14745 (8) | 0.0479 (3) | |
| H10A | 0.8870 | 0.3261 | 0.2029 | 0.058* | |
| H10B | 0.8775 | 0.4595 | 0.1220 | 0.058* | |
| C11 | 0.98167 (8) | 0.2298 (2) | 0.14133 (7) | 0.0429 (3) | |
| H11 | 0.9941 | 0.0764 | 0.1683 | 0.051* | |
| C12 | 1.04767 (8) | 0.4094 (2) | 0.18105 (7) | 0.0414 (3) | |
| C13 | 1.06970 (9) | 0.6065 (2) | 0.14024 (8) | 0.0483 (3) | |
| H13 | 1.0441 | 0.6280 | 0.0873 | 0.058* | |
| C14 | 1.12977 (9) | 0.7713 (2) | 0.17802 (9) | 0.0538 (3) | |
| H14 | 1.1449 | 0.9011 | 0.1499 | 0.065* | |
| C15 | 1.16716 (9) | 0.7448 (2) | 0.25659 (9) | 0.0544 (3) | |
| H15 | 1.2075 | 0.8556 | 0.2815 | 0.065* | |
| C16 | 1.14426 (9) | 0.5519 (3) | 0.29825 (8) | 0.0541 (3) | |
| H16 | 1.1681 | 0.5350 | 0.3517 | 0.065* | |
| C17 | 1.08585 (8) | 0.3841 (2) | 0.26030 (8) | 0.0477 (3) | |
| H17 | 1.0720 | 0.2526 | 0.2883 | 0.057* | |
| N1 | 0.83603 (7) | −0.0253 (2) | 0.06177 (6) | 0.0475 (3) | |
| N2 | 0.74020 (7) | 0.1686 (2) | 0.13399 (6) | 0.0475 (3) | |
| O1 | 0.99198 (7) | 0.2036 (2) | 0.06187 (6) | 0.0606 (3) | |
| H1 | 0.9563 | 0.1070 | 0.0393 | 0.091* | |
| S1 | 0.57374 (2) | 0.05921 (7) | 0.12865 (2) | 0.06185 (14) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0408 (6) | 0.0551 (7) | 0.0426 (6) | 0.0077 (5) | 0.0110 (5) | 0.0052 (5) |
| C2 | 0.0415 (6) | 0.0531 (7) | 0.0399 (6) | 0.0044 (5) | 0.0071 (5) | 0.0040 (5) |
| C3 | 0.0463 (7) | 0.0683 (9) | 0.0517 (7) | −0.0049 (6) | 0.0101 (6) | −0.0006 (6) |
| C4 | 0.0609 (8) | 0.0649 (8) | 0.0529 (8) | −0.0122 (7) | 0.0070 (6) | −0.0060 (6) |
| C5 | 0.0654 (9) | 0.0565 (8) | 0.0487 (7) | 0.0011 (7) | 0.0105 (6) | −0.0077 (6) |
| C6 | 0.0504 (7) | 0.0597 (8) | 0.0474 (7) | 0.0065 (6) | 0.0107 (5) | −0.0063 (6) |
| C7 | 0.0414 (6) | 0.0508 (7) | 0.0405 (6) | 0.0059 (5) | 0.0065 (5) | 0.0007 (5) |
| C8 | 0.0398 (6) | 0.0514 (7) | 0.0418 (6) | 0.0076 (5) | 0.0072 (5) | −0.0004 (5) |
| C9 | 0.0777 (11) | 0.0691 (10) | 0.0845 (11) | 0.0061 (8) | 0.0435 (9) | −0.0105 (8) |
| C10 | 0.0431 (6) | 0.0510 (7) | 0.0492 (7) | 0.0052 (5) | 0.0078 (5) | −0.0062 (5) |
| C11 | 0.0433 (6) | 0.0459 (6) | 0.0410 (6) | 0.0028 (5) | 0.0123 (5) | 0.0009 (5) |
| C12 | 0.0376 (6) | 0.0434 (6) | 0.0451 (6) | 0.0061 (5) | 0.0129 (5) | −0.0006 (5) |
| C13 | 0.0508 (7) | 0.0475 (7) | 0.0482 (6) | 0.0057 (5) | 0.0139 (5) | 0.0037 (5) |
| C14 | 0.0538 (7) | 0.0434 (6) | 0.0691 (8) | 0.0010 (6) | 0.0244 (6) | 0.0017 (6) |
| C15 | 0.0451 (7) | 0.0510 (7) | 0.0677 (8) | −0.0014 (6) | 0.0123 (6) | −0.0110 (6) |
| C16 | 0.0479 (7) | 0.0604 (8) | 0.0517 (7) | 0.0045 (6) | 0.0038 (6) | −0.0037 (6) |
| C17 | 0.0468 (6) | 0.0489 (7) | 0.0477 (6) | 0.0037 (5) | 0.0098 (5) | 0.0039 (5) |
| N1 | 0.0390 (5) | 0.0554 (6) | 0.0482 (5) | 0.0046 (4) | 0.0084 (4) | −0.0067 (5) |
| N2 | 0.0429 (5) | 0.0546 (6) | 0.0462 (5) | 0.0072 (5) | 0.0116 (4) | −0.0021 (5) |
| O1 | 0.0655 (6) | 0.0740 (7) | 0.0477 (5) | −0.0177 (5) | 0.0247 (4) | −0.0148 (5) |
| S1 | 0.0459 (2) | 0.0755 (3) | 0.0698 (2) | 0.00317 (16) | 0.02499 (17) | −0.00692 (17) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| C1—N2 | 1.3092 (17) | C9—H9C | 0.9600 |
| C1—C2 | 1.4340 (18) | C10—C11 | 1.5252 (16) |
| C1—S1 | 1.7521 (13) | C10—H10A | 0.9700 |
| C2—C7 | 1.4083 (17) | C10—H10B | 0.9700 |
| C2—C3 | 1.4100 (19) | C11—O1 | 1.4173 (14) |
| C3—C4 | 1.365 (2) | C11—C12 | 1.5082 (17) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | C11—H11 | 0.9800 |
| C4—C5 | 1.400 (2) | C12—C17 | 1.3880 (17) |
| C4—H4 | 0.9300 | C12—C13 | 1.3894 (18) |
| C5—C6 | 1.365 (2) | C13—C14 | 1.3873 (19) |
| C5—H5 | 0.9300 | C13—H13 | 0.9300 |
| C6—C7 | 1.4065 (18) | C14—C15 | 1.375 (2) |
| C6—H6 | 0.9300 | C14—H14 | 0.9300 |
| C7—N1 | 1.3713 (17) | C15—C16 | 1.384 (2) |
| C8—N1 | 1.3067 (16) | C15—H15 | 0.9300 |
| C8—N2 | 1.3678 (16) | C16—C17 | 1.3843 (19) |
| C8—C10 | 1.5032 (18) | C16—H16 | 0.9300 |
| C9—S1 | 1.7902 (17) | C17—H17 | 0.9300 |
| C9—H9A | 0.9600 | O1—H1 | 0.8200 |
| C9—H9B | 0.9600 | ||
| N2—C1—C2 | 122.82 (11) | C11—C10—H10A | 108.5 |
| N2—C1—S1 | 119.58 (10) | C8—C10—H10B | 108.5 |
| C2—C1—S1 | 117.60 (10) | C11—C10—H10B | 108.5 |
| C7—C2—C3 | 119.24 (12) | H10A—C10—H10B | 107.5 |
| C7—C2—C1 | 115.14 (11) | O1—C11—C12 | 108.24 (10) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 125.62 (12) | O1—C11—C10 | 112.40 (10) |
| C4—C3—C2 | 120.08 (13) | C12—C11—C10 | 110.70 (10) |
| C4—C3—H3 | 120.0 | O1—C11—H11 | 108.5 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 120.0 | C12—C11—H11 | 108.5 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 120.48 (13) | C10—C11—H11 | 108.5 |
| C3—C4—H4 | 119.8 | C17—C12—C13 | 118.57 (12) |
| C5—C4—H4 | 119.8 | C17—C12—C11 | 120.28 (11) |
| C6—C5—C4 | 120.70 (13) | C13—C12—C11 | 121.12 (11) |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.7 | C14—C13—C12 | 120.31 (12) |
| C4—C5—H5 | 119.7 | C14—C13—H13 | 119.8 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 120.01 (13) | C12—C13—H13 | 119.8 |
| C5—C6—H6 | 120.0 | C15—C14—C13 | 120.65 (13) |
| C7—C6—H6 | 120.0 | C15—C14—H14 | 119.7 |
| N1—C7—C6 | 119.03 (12) | C13—C14—H14 | 119.7 |
| N1—C7—C2 | 121.49 (11) | C14—C15—C16 | 119.52 (13) |
| C6—C7—C2 | 119.47 (12) | C14—C15—H15 | 120.2 |
| N1—C8—N2 | 126.28 (12) | C16—C15—H15 | 120.2 |
| N1—C8—C10 | 118.73 (11) | C15—C16—C17 | 119.99 (13) |
| N2—C8—C10 | 114.98 (11) | C15—C16—H16 | 120.0 |
| S1—C9—H9A | 109.5 | C17—C16—H16 | 120.0 |
| S1—C9—H9B | 109.5 | C16—C17—C12 | 120.92 (12) |
| H9A—C9—H9B | 109.5 | C16—C17—H17 | 119.5 |
| S1—C9—H9C | 109.5 | C12—C17—H17 | 119.5 |
| H9A—C9—H9C | 109.5 | C8—N1—C7 | 117.30 (11) |
| H9B—C9—H9C | 109.5 | C1—N2—C8 | 116.95 (11) |
| C8—C10—C11 | 115.00 (10) | C11—O1—H1 | 109.5 |
| C8—C10—H10A | 108.5 | C1—S1—C9 | 102.08 (7) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O1—H1···N1 | 0.82 | 2.12 | 2.7531 (15) | 134 |
Footnotes
Supporting information for this paper is available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: GG2141).
References
- Agilent (2014). CrysAlis PRO Agilent Technologies, Yarnton, Oxfordshire, England.
- Alshammari, M. B., Smith, K., Hegazy, A. S., Kariuki, B. M. & El-Hiti, G. A. (2014a). Acta Cryst. E70, o919–o920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Alshammari, M. B., Smith, K., Hegazy, A. S., Kariuki, B. M. & El-Hiti, G. A. (2014b). Acta Cryst. E70, o953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Cambridge Soft (2001). CHEMDRAW Ultra Cambridge Soft Corporation, Cambridge, Massachusetts, USA.
- Farrugia, L. J. (2012). J. Appl. Cryst. 45, 849–854.
- Leonard, N. J. & Curtin, D. Y. (1946). J. Org. Chem. 11, 349–352. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Macrae, C. F., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Shields, G. P., Taylor, R., Towler, M. & van de Streek, J. (2006). J. Appl. Cryst. 39, 453–457.
- Meerwein, H., Laasch, P., Mersch, R. & Nentwig, J. (1956). Chem. Ber. 89, 224–238.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Smith, K., El-Hiti, G. A. & Hegazy, A. S. (2005a). J. Sulfur Chem. 26, 121–131.
- Smith, K., El-Hiti, G. A. & Hegazy, A. S. (2005b). Synthesis, pp. 2951–2961.
- Westrip, S. P. (2010). J. Appl. Cryst. 43, 920–925.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, New_Global_Publ_Block. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814019990/gg2141sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814019990/gg2141Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814019990/gg2141Isup3.cml
17 16 2 . DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814019990/gg2141fig1.tif
A molecule of C17H16N2OS with atom labels and 50% probability displacement ellipsoids for nonhydrogen atoms.
b . DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814019990/gg2141fig2.tif
Crystal structure packing viewed down the b axis.
CCDC reference: 1022918
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report


