The crystal structures of the 1:1 salts of nicotine with 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid and with 5-sulfosalicylic acid both show polymeric hydrogen-bonded and π–π-bonded structures but these differ in that in the first example, cations and anions form separate cation chains or anion columns which are unassociated through formal hydrogen bonds while in the second, hydrogen-bonded cation–anion chains are found.
Keywords: crystal structure; nicotine; proton-transfer salts; 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid; 5-sulfosalicylic acid; hydrogen-bonding; π–π interactions
Abstract
The structures of the 1:1 anhydrous salts of nicotine (NIC) with 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid (DNSA) and 5-sulfosalicylic acid (5-SSA), namely (1R,2S)-1-methyl-2-(pyridin-3-yl)-1H-pyrrolidin-1-ium 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolate, C10H15N2 +·C7H3N2O7 −, (I), and (1R,2S)-1-methyl-2-(pyridin-3-yl)-1H-pyrrolidin-1-ium 3-carboxy-4-hydroxybenzenesulfonate, C10H15N2 +·C7H5O6S−, (II), are reported. The asymmetric units of both (I) and (II) comprise two independent nicotinium cations (C and D) and either two DNSA or two 5-SSA anions (A and B), respectively. One of the DNSA anions shows a 25% rotational disorder in the benzene ring system. In the crystal of (I), inter-unit pyrrolidinium N—H⋯Npyridine hydrogen bonds generate zigzag NIC cation chains which extend along a, while the DNSA anions are not involved in any formal inter-species hydrogen bonding but instead form π–π-associated stacks which are parallel to the NIC cation chains along a [ring-centroid separation = 3.857 (2) Å]. Weak C—H⋯O interactions between chain substructures give an overall three-dimensional structure. In the crystal of (II), A and B anions form independent zigzag chains with C and D cations, respectively, through carboxylic acid O—H⋯Npyridine hydrogen bonds. These chains, which extend along b, are pseudocentrosymmetrically related and give π–π interactions between the benzene rings of anions A and B and the pyridine rings of the NIC cations C and D, respectively [ring centroid separations = 3.6422 (19) and 3.7117 (19) Å]. Also present are weak C—H⋯O hydrogen-bonding interactions between the chains, giving an overall three-dimensional structure.
Chemical context
Nicotine [3-(2S-1-methylpyrrolidin-2-yl)pyridine] is well known as a toxic liquid alkaloid which is found in the leaves of the tobacco plants Nicotiana tabacum and N. rustica (Rodgman & Parfetti, 2009 ▶). Because of these properties, nicotine and its compounds have been of commercial interest and have been used in the past as insecticides and as veterinary ectoparasiticides (usually as the sulfate) (Ujváry, 1999 ▶), as well as in limited medical applications as the bitartrate (Eudermol) for the treatment of smoking-withdrawal syndrome (Enzell et al., 1977 ▶). However, its veterinary use is restricted due to its toxicity with even topical applications, resulting in the total ban on its use in the USA early in 2014.
As a Lewis base, nicotine is potentially capable of forming both monocationic and dicationic species (pK a1 = 3.10 and pK a2 = 8.01) and the sulfate, dihydrochloride, bitartrate and bipicrate salts have been reported (O’Neil, 2001 ▶). However, the only example of a simple dicationic salt in the crystallographic literature is the dihydroiodide (Koo & Kim, 1965 ▶). Some metal complexes with the dication as a counter-ion are known, e.g. tetrachloridocopper(II) nicotinate (Choi et al., 2002 ▶). More commonly, monocationic salt structures are reported, e.g. the iodide (Barlow et al., 1986 ▶), the picrate (Arnaud et al., 2007 ▶) and the salicylate (Kim & Jeffrey, 1971 ▶).
3,5-Dinitrosalicylic acid (DNSA) (pK
a = 2.18) and 3-carboxy-4-hydroxybenzenesulfonic acid (5-sulfosalicylic acid: 5-SSA) (pK
a < 1) are capable of forming salts with most Lewis bases and have been used for the formation of crystalline salts suitable for X-ray analysis, e.g. with 5-SSA (Baskar Raj et al., 2003 ▶; Smith et al., 2006 ▶) and with DNSA, where the majority of the salts formed are phenolates rather than carboxylates (Smith et al., 2007 ▶). The title salts C10H15N2
+ C7H3N2O7
−, (I) and C10H15N2
+ C7H5O6S−, (II) were prepared from the reaction of nicotine (NIC) with DNSA and with 5-SSA, respectively, and the structures are reported herein.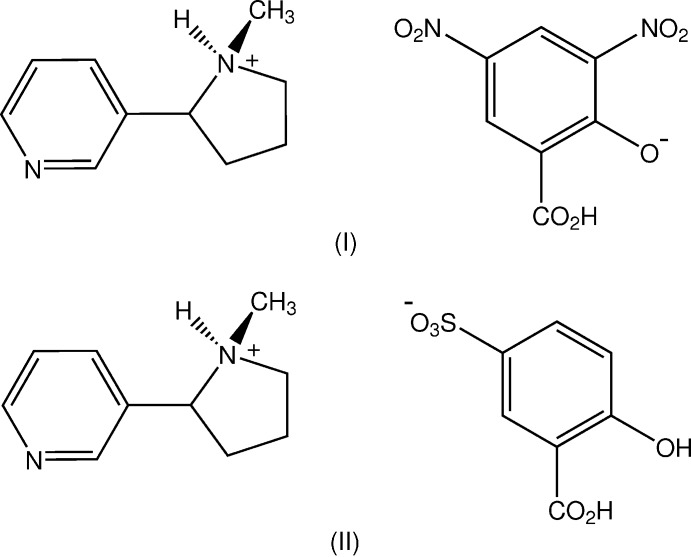
Structural commentary
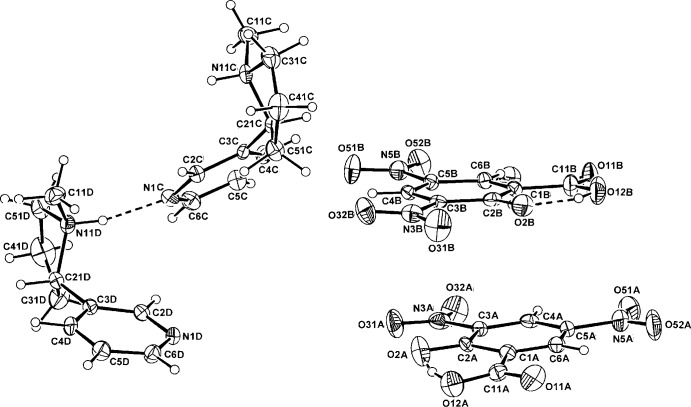
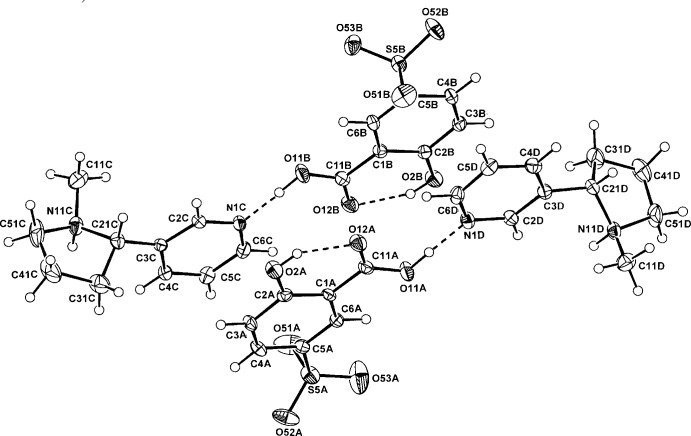
In both the nicotinium salts of DNSA (I) and 5-SSA (II), proton-transfer to the pyrrolidine N-atom of nicotine has occurred as expected, generating an N11(R) chiral centre relative to the known C21(S) centre. Also, in both (I) and (II) (Figs. 1 ▶ and 2 ▶), the asymmetric units comprise two independent NIC+ cations (C and D) and either, for (I), two DNSA phenolate monoanions or two 5-SSA carboxylate monoanions (A and B) (Figs. 1 ▶, 2 ▶). With (II), the two independent anion and cation pairs are pseudo-centrosymmetrically related but the presence of the inversion centre is obviated by the fact that both of the NIC cations have the same N11(R), C21(S) absolute configuration.
Figure 1.
The molecular conformation and atom labelling for the two NIC cations (C and D) and the two DNSA anions (A and B) in the asymmetric unit of (I), with displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 40% probability level. Inter-species hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines (see Table 1 ▶).
Figure 2.
The molecular conformation and atom labelling for the two NIC cations (C and D) and the two 5-SSA anions (A and B) in the asymmetric unit of (II), with displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 40% probability level. Inter-species hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines (see Table 2 ▶).
In (I), the nicotinium C and D cations are conformationally similar but in (II), they are different. However, in both, the pyrrolidinium plane is significantly rotated with respect to that of the benzene ring [the torsion angles C2C/D—C3C/D—C21C/D—N11C/D are −71.9 (4) (C) and −68.8 (4)° (D) in (I) and −45.7 (4) (C) and 125.7 (3)° (D) in (II)]. This conformation with the two rings antiplanar is usual for cationic nicotine structures, e.g. Arnaud et al. (2007 ▶). The substituent carboxyl and nitro groups of the DNSA anions in (I) are essentially coplanar with the benzene ring, with the maximum deviation among the three defining torsion angles for each anion (C2A/B—C1A/B—C11A/B—O2A/B, C2A/B —C3A/B—N3A/B—O32A/B and C4A/B—C5A/B—N5A/B—O52A/B) being for the C3B nitro group [173.7 (3)°]. In the B anion, there is 25% rotational disorder about the C1⋯C4 ring vector, which generates a second phenolic O-component (O21B). This phenomenon has precedence in DNSA salt structures, e.g. with the nicotinamide salt (Koman et al., 2003 ▶; 24% disorder). The C3 nitro group is most often associated with deviation from planarity in the DNSA phenolate salts (Smith et al., 2007 ▶) and is the more interactive and sterically crowded group. In the case of (I), the uncommon planarity is probably associated with the presence of anion π-bonding associations.
With the 5-SSA anions, the carboxylic acid group is essentially coplanar with the benzene ring, which is expected in this salicylic acid species, invariably having the short intramolecular carboxylic acid O—H⋯Ophenol hydrogen bond (Table 2 ▶) (Smith et al., 2006 ▶). This interaction is also present in the phenolate anion in (I) in which the carboxylic acid H-atom is anti-related (Table 1 ▶).
Table 2. Hydrogen-bond geometry (, ) for (II) .
| DHA | DH | HA | D A | DHA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O2AH2AO12A | 0.84 | 1.80 | 2.549(4) | 147 |
| O2BH2BO12B | 0.84 | 1.82 | 2.561(4) | 146 |
| O11AH11AN1D | 0.95 | 1.60 | 2.555(4) | 179 |
| O11BH11BN1C | 0.95 | 1.61 | 2.558(4) | 179 |
| N11CH11CO51B i | 0.93 | 2.32 | 3.022(5) | 132 |
| N11CH11CO53B i | 0.93 | 2.15 | 3.029(5) | 157 |
| N11DH11DO52A ii | 0.93 | 1.85 | 2.735(4) | 158 |
| C11DH12DO2B iii | 0.98 | 2.51 | 3.491(5) | 174 |
| C2CH2CO53B i | 0.95 | 2.29 | 3.201(5) | 160 |
| C2DH2DO53A iv | 0.95 | 2.45 | 3.359(4) | 160 |
| C11CH12CO2A v | 0.98 | 2.52 | 3.481(5) | 165 |
| C11CH13CO52B vi | 0.98 | 2.46 | 3.290(5) | 142 |
| C11DH13DO51A iv | 0.98 | 2.37 | 3.251(5) | 150 |
| C21CH21CO52B vi | 1.00 | 2.42 | 3.331(5) | 151 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 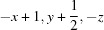 ; (ii)
; (ii) 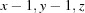 ; (iii)
; (iii) 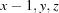 ; (iv)
; (iv) 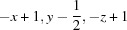 ; (v)
; (v) 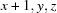 ; (vi)
; (vi) 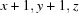 .
.
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (, ) for (I) .
| DHA | DH | HA | D A | DHA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O12AH12AO2A | 0.84 | 1.71 | 2.475(4) | 150 |
| O12BH12BO2B | 0.84 | 1.63 | 2.411(4) | 152 |
| N11CH11CN1D i | 0.93 | 1.89 | 2.809(4) | 169 |
| N11DH11DN1C | 0.93 | 1.90 | 2.817(5) | 168 |
| C2CH2CO11A ii | 0.95 | 2.42 | 3.228(5) | 143 |
| C4CH4CO31A i | 0.95 | 2.59 | 3.452(5) | 151 |
| C6CH6CO32A iii | 0.95 | 2.27 | 3.054(5) | 139 |
| C11CH13CO32B i | 0.98 | 2.48 | 3.151(6) | 126 |
| C11DH14DO51A iv | 0.98 | 2.55 | 3.373(6) | 141 |
| C21CH21CO2A i | 1.00 | 2.27 | 3.163(5) | 148 |
| C21DH21DO11B v | 1.00 | 2.44 | 3.307(5) | 144 |
| C51CH52CO11A ii | 0.99 | 2.54 | 3.534(6) | 177 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 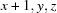 ; (ii)
; (ii) 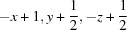 ; (iii)
; (iii) 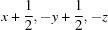 ; (iv)
; (iv) 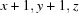 ; (v)
; (v) 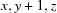 .
.
Supramolecular features
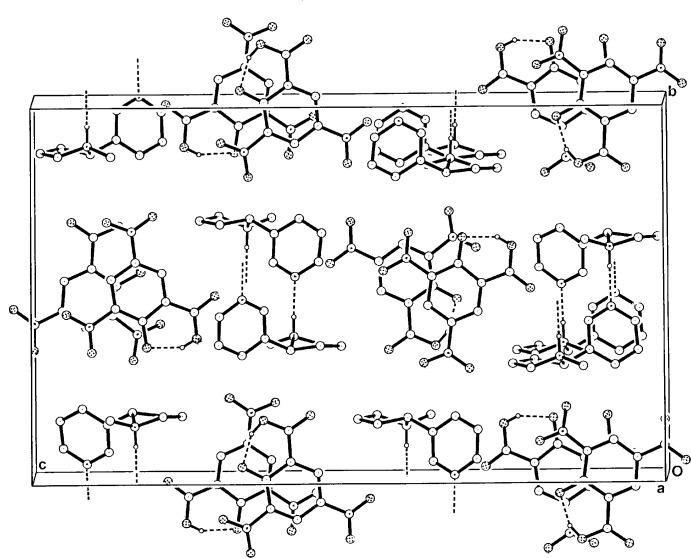
In the supramolecular structure of (I), the two independent NIC cations C and D interact through N1C —H⋯N11D i and N1D —H⋯N11C hydrogen bonds (Table 1 ▶), giving zigzag chains extending along a (Fig. 3 ▶). With the DNSA anions, there are no formal hydrogen-bonding interactions either between A and B anions or with the NIC chain structures. Instead, these anions form π–π-bonded stacks which are parallel to the NIC+ chains down a [ring-centroid separation = 3.857 (2) Å]. The presence of π–π stacking is unusual in DNSA cation structures. In the crystal, there are a number of intermolecular CC/D—H⋯OA/B hydrogen-bonding interactions, which give an overall three-dimensional structure.
Figure 3.
The alternating hydrogen-bonded C–D cationic columns and π-bonded A–B anion stacks in the structure of (I), viewed along the stacks in the unit cell.
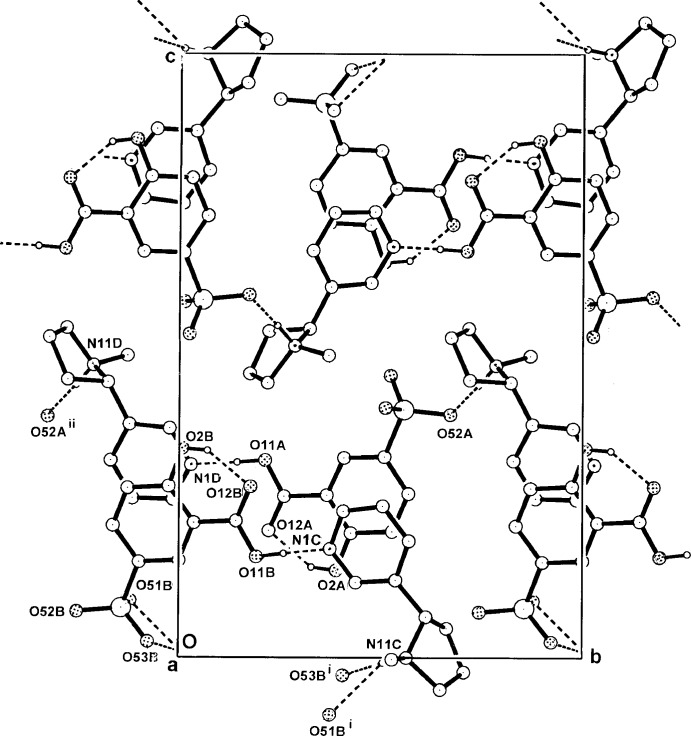
In the crystal of (II), the independent A and B 5-SSA anions form carboxylic acid O—H⋯Npyridine hydrogen bonds with the D and C NIC cations, respectively (Table 2 ▶) (see Fig. 2 ▶). These cation–anion subunits are then extended into independent chain structures through pyrrolidinium N—H⋯Osulfonate hydrogen bonds, which with anion C is three-centre (O51B i and O53B i) and with anion D, linear (O52A ii). These give independent zigzag chain substructures which extend along b. Although there are no formal hydrogen-bonding links between the two chains, there are π–π interactions between 5-SSA anion A and B benzene rings and C and D NIC cation pyridine rings, respectively [ring-centroid separations = 3.6422 (19) and 3.7117 (19) Å] (Fig. 4 ▶). The presence of a number of intermolecular C—H⋯O hydrogen-bonding interactions to carboxyl, nitro and phenolic O-atom acceptors gives rise to an overall three-dimensional structure.
Figure 4.
The hydrogen-bonded A–C and B–D chain structures in (II), extending along b. Non-associative H atoms have been omitted. For symmetry codes, see Table 2 ▶.
Synthesis and crystallization
The title salts (I) and (II) were prepared by refluxing equimolar quantities of nicotine (160 mg) and the respective acids, 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid (230 mg) for (I) or 3-carboxy-4-hydroxybenzenesulfonic acid (220 mg) for (II) in 30 ml of ethanol for 10 min, after which room temperature evaporation of the solutions gave, for (I), thin yellow needles and for (II) colourless prisms, from which specimens were cleaved for the X-ray analyses.
Refinement details
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 3 ▶. H atoms on all potentially interactive O—H and N—H groups in all molecular species, were located by difference-Fourier methods but these and the carbon-bound H-atoms were subsequently set as riding on the parent atoms in the refinement in calculated positions [O—H = 0.88, N—H = 0.94, C—H = 0.95–1.00 Å] and with U iso(H) = 1.5U eq(O or methyl-C) or 1.2U eq(C, N).
Table 3. Experimental details.
| (I) | (II) | |
|---|---|---|
| Crystal data | ||
| Chemical formula | C10H15N2 +C7H3N2O7 | C10H15N2 +C7H5O6S |
| M r | 390.35 | 380.41 |
| Crystal system, space group | Orthorhombic, P212121 | Monoclinic, P21 |
| Temperature (K) | 200 | 200 |
| a, b, c () | 6.8096(5), 17.6403(15), 29.3604(19) | 7.1568(3), 12.6416(5), 19.1519(8) |
| , , () | 90, 90, 90 | 90, 93.729(4), 90 |
| V (3) | 3526.9(4) | 1729.07(12) |
| Z | 8 | 4 |
| Radiation type | Mo K | Mo K |
| (mm1) | 0.12 | 0.23 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.40 0.10 0.08 | 0.35 0.30 0.12 |
| Data collection | ||
| Diffractometer | Oxford Diffraction Gemini-S CCD detector | Oxford Diffraction Gemini-S CCD detector |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Agilent, 2013 ▶) | Multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Agilent, 2013 ▶) |
| T min, T max | 0.807, 0.980 | 0.909, 0.981 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2(I)] reflections | 8840, 6476, 4303 | 7764, 5104, 4424 |
| R int | 0.028 | 0.031 |
| (sin /)max (1) | 0.617 | 0.680 |
| Refinement | ||
| R[F 2 > 2(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.072, 0.122, 1.07 | 0.046, 0.108, 1.01 |
| No. of reflections | 6476 | 5104 |
| No. of parameters | 508 | 469 |
| No. of restraints | 2 | 1 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters constrained | H-atom parameters constrained |
| max, min (e 3) | 0.44, 0.19 | 0.49, 0.36 |
| Absolute structure | Flack (1983 ▶), 2983 Friedel pairs | Flack (1983 ▶), 4361 Friedel pairs |
| Absolute structure parameter | 0.2(16) | 0.02(9) |
The site occupancy factors for the rotationally disordered phenolate components (O2B) and its other component (O21B) in anion B of (I) were determined as 0.752 (4): 0.248 (4) and were subsequently set at 0.75:0.25 in the refinement.
In both structures, the known C21(S) absolute configuration was invoked. The Flack parameter for (I) [0.2 (16)] has no physical meaning. The absolute structure of compound (II) was confirmed by resonant scattering [Flack parameter = −0.02 (9)].
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I, II. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814023253/lh5736sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814023253/lh5736Isup2.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) II. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814023253/lh5736IIsup3.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814023253/lh5736Isup4.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814023253/lh5736IIsup5.cml
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
supplementary crystallographic information
Crystal data
| C10H15N2+·C7H5O6S− | F(000) = 800 |
| Mr = 380.41 | Dx = 1.461 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: P 2yb | Cell parameters from 2239 reflections |
| a = 7.1568 (3) Å | θ = 3.4–27.5° |
| b = 12.6416 (5) Å | µ = 0.23 mm−1 |
| c = 19.1519 (8) Å | T = 200 K |
| β = 93.729 (4)° | Prism, colourless |
| V = 1729.07 (12) Å3 | 0.35 × 0.30 × 0.12 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Oxford Diffraction Gemini-S CCD-detector diffractometer | 5104 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: Enhance (Mo) X-ray source | 4424 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.031 |
| Detector resolution: 16.077 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 28.9°, θmin = 3.2° |
| ω scans | h = −8→9 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Agilent, 2013) | k = −17→8 |
| Tmin = 0.909, Tmax = 0.981 | l = −24→14 |
| 7764 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.046 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.108 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0448P)2 + 0.6152P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.01 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 5104 reflections | Δρmax = 0.49 e Å−3 |
| 469 parameters | Δρmin = −0.36 e Å−3 |
| 1 restraint | Absolute structure: Flack (1983), 4361 Friedel pairs |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Absolute structure parameter: −0.02 (9) |
Special details
| Geometry. Bond distances, angles etc. have been calculated using the rounded fractional coordinates. All su's are estimated from the variances of the (full) variance-covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account in the estimation of distances, angles and torsion angles |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| S5A | 0.68704 (12) | 0.55842 (7) | 0.41012 (4) | 0.0263 (3) | |
| O2A | 0.3397 (4) | 0.3912 (2) | 0.14516 (12) | 0.0340 (8) | |
| O11A | 0.3204 (4) | 0.2139 (2) | 0.32641 (13) | 0.0348 (8) | |
| O12A | 0.2584 (4) | 0.2236 (2) | 0.21069 (13) | 0.0337 (8) | |
| O51A | 0.8728 (4) | 0.5131 (3) | 0.41339 (15) | 0.0508 (10) | |
| O52A | 0.6922 (4) | 0.6735 (2) | 0.40180 (14) | 0.0422 (9) | |
| O53A | 0.5792 (4) | 0.5253 (2) | 0.46723 (12) | 0.0393 (9) | |
| C1A | 0.4129 (4) | 0.3676 (3) | 0.26886 (17) | 0.0221 (9) | |
| C2A | 0.4124 (5) | 0.4284 (3) | 0.20674 (17) | 0.0222 (10) | |
| C3A | 0.4845 (5) | 0.5304 (3) | 0.20917 (17) | 0.0240 (10) | |
| C4A | 0.5643 (4) | 0.5705 (3) | 0.27120 (17) | 0.0239 (9) | |
| C5A | 0.5696 (4) | 0.5108 (3) | 0.33217 (17) | 0.0211 (9) | |
| C6A | 0.4930 (5) | 0.4106 (3) | 0.33044 (18) | 0.0234 (10) | |
| C11A | 0.3243 (5) | 0.2614 (3) | 0.26686 (19) | 0.0259 (11) | |
| S5B | 0.30149 (14) | −0.14181 (8) | 0.08257 (5) | 0.0345 (3) | |
| O2B | 0.6834 (4) | 0.0076 (2) | 0.34578 (12) | 0.0344 (8) | |
| O11B | 0.7029 (4) | 0.1928 (2) | 0.16767 (13) | 0.0347 (8) | |
| O12B | 0.7680 (4) | 0.1780 (2) | 0.28273 (13) | 0.0335 (8) | |
| O51B | 0.1062 (4) | −0.1205 (3) | 0.09470 (17) | 0.0625 (11) | |
| O52B | 0.3370 (4) | −0.2529 (2) | 0.07618 (16) | 0.0480 (10) | |
| O53B | 0.3571 (6) | −0.0759 (3) | 0.02651 (16) | 0.0801 (15) | |
| C1B | 0.6053 (4) | 0.0375 (3) | 0.22345 (17) | 0.0206 (9) | |
| C2B | 0.6058 (5) | −0.0256 (3) | 0.28333 (17) | 0.0233 (10) | |
| C3B | 0.5299 (5) | −0.1274 (3) | 0.28007 (18) | 0.0255 (10) | |
| C4B | 0.4433 (5) | −0.1631 (3) | 0.21848 (19) | 0.0261 (10) | |
| C5B | 0.4331 (5) | −0.0982 (3) | 0.15869 (17) | 0.0231 (10) | |
| C6B | 0.5145 (4) | 0.0004 (3) | 0.16130 (17) | 0.0222 (10) | |
| C11B | 0.6976 (5) | 0.1427 (3) | 0.22658 (19) | 0.0260 (11) | |
| N1C | 0.8536 (4) | 0.3758 (3) | 0.18074 (15) | 0.0270 (9) | |
| N11C | 0.9801 (4) | 0.5668 (3) | −0.00002 (14) | 0.0295 (9) | |
| C2C | 0.8558 (5) | 0.4408 (3) | 0.12534 (19) | 0.0253 (10) | |
| C3C | 0.9371 (4) | 0.5393 (3) | 0.12903 (18) | 0.0257 (10) | |
| C4C | 1.0161 (5) | 0.5724 (3) | 0.19371 (18) | 0.0294 (10) | |
| C5C | 1.0096 (5) | 0.5074 (3) | 0.25102 (18) | 0.0296 (11) | |
| C6C | 0.9288 (5) | 0.4092 (3) | 0.24258 (19) | 0.0297 (11) | |
| C11C | 1.1769 (5) | 0.5314 (4) | −0.0030 (2) | 0.0392 (14) | |
| C21C | 0.9336 (5) | 0.6148 (3) | 0.06816 (18) | 0.0290 (11) | |
| C31C | 0.7439 (6) | 0.6662 (4) | 0.0489 (2) | 0.0493 (16) | |
| C41C | 0.7621 (7) | 0.7097 (4) | −0.0242 (2) | 0.0529 (17) | |
| C51C | 0.9232 (6) | 0.6511 (4) | −0.0534 (2) | 0.0476 (16) | |
| N1D | 0.1735 (4) | 0.0297 (2) | 0.31881 (15) | 0.0257 (8) | |
| N11D | −0.0524 (4) | −0.2131 (3) | 0.48368 (14) | 0.0327 (10) | |
| C2D | 0.1839 (5) | −0.0236 (3) | 0.37895 (18) | 0.0239 (10) | |
| C3D | 0.1071 (4) | −0.1235 (3) | 0.38558 (16) | 0.0211 (9) | |
| C4D | 0.0196 (5) | −0.1695 (3) | 0.32573 (17) | 0.0256 (10) | |
| C5D | 0.0119 (5) | −0.1153 (3) | 0.26338 (18) | 0.0283 (11) | |
| C6D | 0.0898 (5) | −0.0152 (3) | 0.26175 (19) | 0.0284 (11) | |
| C11D | −0.1872 (6) | −0.1290 (4) | 0.4998 (2) | 0.0430 (14) | |
| C21D | 0.1287 (5) | −0.1769 (3) | 0.45539 (17) | 0.0267 (10) | |
| C31D | 0.2434 (6) | −0.2778 (4) | 0.4595 (2) | 0.0442 (14) | |
| C41D | 0.1992 (8) | −0.3244 (4) | 0.5301 (2) | 0.0626 (19) | |
| C51D | 0.0103 (7) | −0.2808 (4) | 0.5453 (2) | 0.0564 (16) | |
| H2A | 0.30050 | 0.32920 | 0.15050 | 0.0510* | |
| H3A | 0.47890 | 0.57260 | 0.16810 | 0.0290* | |
| H4A | 0.61610 | 0.63970 | 0.27220 | 0.0290* | |
| H6A | 0.49510 | 0.37020 | 0.37230 | 0.0280* | |
| H11A | 0.26610 | 0.14530 | 0.32280 | 0.0520* | |
| H2B | 0.71920 | 0.07050 | 0.34230 | 0.0520* | |
| H3B | 0.53810 | −0.17170 | 0.32020 | 0.0310* | |
| H4B | 0.39000 | −0.23190 | 0.21620 | 0.0310* | |
| H6B | 0.50900 | 0.04360 | 0.12060 | 0.0270* | |
| H11B | 0.75890 | 0.26070 | 0.17310 | 0.0520* | |
| H2C | 0.79870 | 0.41780 | 0.08180 | 0.0300* | |
| H4C | 1.07430 | 0.63980 | 0.19820 | 0.0350* | |
| H5A | 1.06000 | 0.53000 | 0.29570 | 0.0350* | |
| H6C | 0.92630 | 0.36360 | 0.28190 | 0.0360* | |
| H11C | 0.90280 | 0.50850 | −0.00850 | 0.0350* | |
| H12C | 1.20770 | 0.48160 | 0.03520 | 0.0580* | |
| H13C | 1.26050 | 0.59270 | 0.00170 | 0.0580* | |
| H21C | 1.02610 | 0.67240 | 0.07990 | 0.0350* | |
| H31C | 0.64180 | 0.61330 | 0.04910 | 0.0590* | |
| H32C | 0.71820 | 0.72360 | 0.08200 | 0.0590* | |
| H41C | 0.64530 | 0.69750 | −0.05370 | 0.0630* | |
| H42C | 0.78790 | 0.78660 | −0.02240 | 0.0630* | |
| H51C | 1.02880 | 0.69990 | −0.06010 | 0.0570* | |
| H52C | 0.88390 | 0.61850 | −0.09900 | 0.0570* | |
| H134 | 1.19250 | 0.49640 | −0.04800 | 0.0580* | |
| H12D | −0.21690 | −0.08640 | 0.45780 | 0.0650* | |
| H2D | 0.24650 | 0.00810 | 0.41890 | 0.0290* | |
| H4D | −0.03450 | −0.23790 | 0.32810 | 0.0310* | |
| H5D | −0.04590 | −0.14600 | 0.22220 | 0.0340* | |
| H6D | 0.08380 | 0.02270 | 0.21880 | 0.0340* | |
| H11D | −0.11170 | −0.25710 | 0.45020 | 0.0390* | |
| H21D | 0.18880 | −0.12540 | 0.48950 | 0.0320* | |
| H13D | −0.13180 | −0.08360 | 0.53710 | 0.0650* | |
| H14D | −0.30210 | −0.16130 | 0.51510 | 0.0650* | |
| H31D | 0.37870 | −0.26240 | 0.45810 | 0.0530* | |
| H32D | 0.20480 | −0.32650 | 0.42080 | 0.0530* | |
| H41D | 0.19550 | −0.40260 | 0.52770 | 0.0750* | |
| H42D | 0.29520 | −0.30300 | 0.56690 | 0.0750* | |
| H51D | −0.07990 | −0.33910 | 0.55110 | 0.0680* | |
| H52D | 0.01960 | −0.23820 | 0.58870 | 0.0680* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| S5A | 0.0295 (4) | 0.0253 (5) | 0.0232 (4) | −0.0031 (4) | −0.0062 (3) | 0.0026 (4) |
| O2A | 0.0467 (15) | 0.0280 (15) | 0.0261 (13) | −0.0022 (13) | −0.0058 (11) | −0.0012 (11) |
| O11A | 0.0456 (15) | 0.0234 (14) | 0.0352 (14) | −0.0115 (13) | 0.0018 (11) | 0.0042 (12) |
| O12A | 0.0397 (14) | 0.0249 (14) | 0.0360 (14) | −0.0065 (13) | −0.0013 (11) | −0.0045 (12) |
| O51A | 0.0347 (14) | 0.073 (2) | 0.0424 (16) | 0.0124 (17) | −0.0146 (12) | 0.0011 (17) |
| O52A | 0.0580 (18) | 0.0242 (14) | 0.0417 (16) | −0.0116 (14) | −0.0180 (13) | 0.0052 (13) |
| O53A | 0.0496 (15) | 0.0460 (17) | 0.0219 (12) | −0.0115 (15) | −0.0002 (10) | 0.0003 (12) |
| C1A | 0.0201 (16) | 0.0212 (17) | 0.0249 (16) | 0.0028 (16) | 0.0010 (12) | 0.0024 (15) |
| C2A | 0.0238 (17) | 0.0227 (18) | 0.0197 (16) | 0.0035 (15) | −0.0009 (13) | 0.0010 (14) |
| C3A | 0.0271 (17) | 0.0256 (18) | 0.0193 (16) | 0.0050 (16) | 0.0008 (13) | 0.0056 (14) |
| C4A | 0.0213 (15) | 0.0197 (17) | 0.0305 (17) | −0.0002 (16) | 0.0009 (13) | 0.0055 (16) |
| C5A | 0.0221 (16) | 0.0196 (17) | 0.0210 (16) | −0.0011 (16) | −0.0025 (12) | 0.0008 (14) |
| C6A | 0.0264 (18) | 0.0203 (18) | 0.0233 (17) | 0.0010 (16) | 0.0002 (13) | 0.0055 (14) |
| C11A | 0.0231 (17) | 0.0221 (19) | 0.0326 (19) | 0.0001 (15) | 0.0022 (14) | −0.0005 (16) |
| S5B | 0.0413 (5) | 0.0300 (5) | 0.0305 (5) | −0.0046 (5) | −0.0110 (4) | −0.0026 (4) |
| O2B | 0.0499 (15) | 0.0292 (14) | 0.0227 (12) | −0.0051 (14) | −0.0078 (11) | −0.0009 (11) |
| O11B | 0.0440 (15) | 0.0269 (15) | 0.0330 (14) | −0.0111 (13) | 0.0007 (11) | 0.0065 (12) |
| O12B | 0.0442 (15) | 0.0270 (14) | 0.0286 (14) | −0.0052 (13) | −0.0029 (11) | −0.0020 (12) |
| O51B | 0.0379 (16) | 0.070 (2) | 0.075 (2) | 0.0237 (18) | −0.0305 (15) | −0.029 (2) |
| O52B | 0.0402 (16) | 0.0333 (17) | 0.068 (2) | 0.0016 (14) | −0.0145 (14) | −0.0229 (16) |
| O53B | 0.126 (3) | 0.084 (3) | 0.0272 (16) | −0.057 (3) | −0.0197 (18) | 0.0087 (18) |
| C1B | 0.0202 (15) | 0.0139 (17) | 0.0277 (16) | 0.0026 (14) | 0.0020 (12) | −0.0005 (13) |
| C2B | 0.0234 (17) | 0.0248 (19) | 0.0218 (17) | 0.0048 (16) | 0.0013 (13) | −0.0008 (15) |
| C3B | 0.0310 (18) | 0.0187 (17) | 0.0263 (17) | 0.0035 (17) | −0.0021 (13) | 0.0067 (15) |
| C4B | 0.0242 (17) | 0.0175 (18) | 0.0358 (19) | 0.0016 (15) | −0.0052 (14) | 0.0029 (15) |
| C5B | 0.0211 (16) | 0.0219 (18) | 0.0260 (17) | 0.0044 (15) | −0.0002 (13) | 0.0007 (15) |
| C6B | 0.0222 (16) | 0.0218 (18) | 0.0224 (16) | 0.0028 (15) | −0.0001 (13) | 0.0025 (14) |
| C11B | 0.0249 (17) | 0.0193 (18) | 0.034 (2) | 0.0029 (15) | 0.0047 (14) | 0.0001 (16) |
| N1C | 0.0256 (14) | 0.0258 (17) | 0.0294 (15) | 0.0004 (14) | 0.0003 (11) | 0.0076 (14) |
| N11C | 0.0363 (15) | 0.0269 (16) | 0.0251 (14) | −0.0033 (15) | 0.0003 (11) | 0.0064 (14) |
| C2C | 0.0250 (18) | 0.0242 (19) | 0.0263 (17) | 0.0007 (16) | −0.0012 (13) | 0.0008 (15) |
| C3C | 0.0225 (16) | 0.0238 (19) | 0.0312 (18) | 0.0015 (15) | 0.0041 (13) | 0.0038 (15) |
| C4C | 0.0239 (16) | 0.0269 (19) | 0.0375 (19) | −0.0031 (16) | 0.0036 (14) | −0.0039 (17) |
| C5C | 0.0255 (18) | 0.038 (2) | 0.0249 (18) | 0.0011 (17) | −0.0003 (14) | −0.0009 (17) |
| C6C | 0.0263 (18) | 0.035 (2) | 0.0278 (18) | 0.0032 (17) | 0.0025 (14) | 0.0108 (17) |
| C11C | 0.038 (2) | 0.044 (3) | 0.036 (2) | −0.003 (2) | 0.0049 (16) | −0.006 (2) |
| C21C | 0.0339 (19) | 0.0202 (17) | 0.0333 (19) | 0.0005 (16) | 0.0064 (14) | 0.0042 (16) |
| C31C | 0.048 (2) | 0.043 (3) | 0.058 (3) | 0.020 (2) | 0.013 (2) | 0.024 (2) |
| C41C | 0.064 (3) | 0.038 (3) | 0.055 (3) | 0.005 (2) | −0.009 (2) | 0.020 (2) |
| C51C | 0.060 (3) | 0.048 (3) | 0.035 (2) | 0.003 (2) | 0.0038 (19) | 0.024 (2) |
| N1D | 0.0265 (14) | 0.0213 (15) | 0.0299 (15) | −0.0009 (13) | 0.0067 (11) | 0.0047 (13) |
| N11D | 0.0428 (18) | 0.0322 (17) | 0.0230 (15) | −0.0165 (15) | 0.0009 (12) | −0.0011 (14) |
| C2D | 0.0264 (17) | 0.0190 (17) | 0.0265 (17) | 0.0002 (15) | 0.0033 (13) | 0.0007 (14) |
| C3D | 0.0215 (15) | 0.0182 (17) | 0.0239 (16) | 0.0011 (15) | 0.0033 (12) | −0.0009 (14) |
| C4D | 0.0266 (17) | 0.0226 (18) | 0.0278 (18) | −0.0038 (15) | 0.0038 (13) | 0.0005 (15) |
| C5D | 0.0253 (18) | 0.035 (2) | 0.0241 (17) | −0.0020 (17) | −0.0020 (13) | 0.0008 (16) |
| C6D | 0.0281 (18) | 0.033 (2) | 0.0245 (18) | 0.0016 (17) | 0.0058 (14) | 0.0052 (16) |
| C11D | 0.040 (2) | 0.052 (3) | 0.038 (2) | −0.010 (2) | 0.0113 (17) | −0.012 (2) |
| C21D | 0.0310 (18) | 0.0252 (18) | 0.0231 (17) | −0.0095 (16) | −0.0031 (13) | −0.0007 (14) |
| C31D | 0.058 (3) | 0.037 (2) | 0.036 (2) | 0.012 (2) | −0.0081 (19) | 0.005 (2) |
| C41D | 0.099 (4) | 0.039 (3) | 0.048 (3) | 0.011 (3) | −0.008 (3) | 0.019 (2) |
| C51D | 0.077 (3) | 0.061 (3) | 0.030 (2) | −0.022 (3) | −0.006 (2) | 0.023 (2) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| S5A—O51A | 1.445 (3) | C3B—H3B | 0.9500 |
| S5A—O52A | 1.464 (3) | C4B—H4B | 0.9500 |
| S5A—O53A | 1.441 (3) | C6B—H6B | 0.9500 |
| S5A—C5A | 1.770 (3) | C2C—C3C | 1.374 (5) |
| S5B—O51B | 1.457 (3) | C3C—C21C | 1.506 (5) |
| S5B—O52B | 1.434 (3) | C3C—C4C | 1.392 (5) |
| S5B—O53B | 1.436 (4) | C4C—C5C | 1.374 (5) |
| S5B—C5B | 1.771 (4) | C5C—C6C | 1.375 (5) |
| O2A—C2A | 1.343 (4) | C21C—C31C | 1.529 (6) |
| O11A—C11A | 1.291 (4) | C31C—C41C | 1.518 (6) |
| O12A—C11A | 1.242 (4) | C41C—C51C | 1.508 (7) |
| O2A—H2A | 0.8400 | C2C—H2C | 0.9500 |
| O11A—H11A | 0.9500 | C4C—H4C | 0.9500 |
| O2B—C2B | 1.352 (4) | C5C—H5A | 0.9500 |
| O11B—C11B | 1.297 (4) | C6C—H6C | 0.9500 |
| O12B—C11B | 1.241 (4) | C11C—H134 | 0.9800 |
| O2B—H2B | 0.8400 | C11C—H12C | 0.9800 |
| O11B—H11B | 0.9500 | C11C—H13C | 0.9800 |
| N1C—C6C | 1.337 (5) | C21C—H21C | 1.0000 |
| N1C—C2C | 1.343 (5) | C31C—H32C | 0.9900 |
| N11C—C11C | 1.483 (5) | C31C—H31C | 0.9900 |
| N11C—C51C | 1.514 (6) | C41C—H41C | 0.9900 |
| N11C—C21C | 1.497 (5) | C41C—H42C | 0.9900 |
| N11C—H11C | 0.9300 | C51C—H52C | 0.9900 |
| N1D—C2D | 1.332 (4) | C51C—H51C | 0.9900 |
| N1D—C6D | 1.338 (5) | C2D—C3D | 1.386 (5) |
| N11D—C51D | 1.503 (5) | C3D—C21D | 1.497 (5) |
| N11D—C11D | 1.482 (6) | C3D—C4D | 1.397 (5) |
| N11D—C21D | 1.508 (5) | C4D—C5D | 1.375 (5) |
| N11D—H11D | 0.9300 | C5D—C6D | 1.384 (5) |
| C1A—C2A | 1.416 (5) | C21D—C31D | 1.516 (6) |
| C1A—C11A | 1.484 (5) | C31D—C41D | 1.527 (6) |
| C1A—C6A | 1.388 (5) | C41D—C51D | 1.506 (7) |
| C2A—C3A | 1.389 (5) | C2D—H2D | 0.9500 |
| C3A—C4A | 1.381 (5) | C4D—H4D | 0.9500 |
| C4A—C5A | 1.389 (5) | C5D—H5D | 0.9500 |
| C5A—C6A | 1.380 (5) | C6D—H6D | 0.9500 |
| C3A—H3A | 0.9500 | C11D—H12D | 0.9800 |
| C4A—H4A | 0.9500 | C11D—H13D | 0.9800 |
| C6A—H6A | 0.9500 | C11D—H14D | 0.9800 |
| C1B—C6B | 1.399 (5) | C21D—H21D | 1.0000 |
| C1B—C11B | 1.484 (5) | C31D—H31D | 0.9900 |
| C1B—C2B | 1.397 (5) | C31D—H32D | 0.9900 |
| C2B—C3B | 1.397 (5) | C41D—H41D | 0.9900 |
| C3B—C4B | 1.373 (5) | C41D—H42D | 0.9900 |
| C4B—C5B | 1.407 (5) | C51D—H51D | 0.9900 |
| C5B—C6B | 1.375 (5) | C51D—H52D | 0.9900 |
| O51A—S5A—O52A | 111.65 (19) | N11C—C21C—C31C | 101.9 (3) |
| O51A—S5A—O53A | 112.86 (17) | C21C—C31C—C41C | 104.4 (3) |
| O51A—S5A—C5A | 106.66 (17) | C31C—C41C—C51C | 106.1 (4) |
| O52A—S5A—O53A | 112.94 (16) | N11C—C51C—C41C | 105.9 (3) |
| O52A—S5A—C5A | 105.07 (17) | N1C—C2C—H2C | 119.00 |
| O53A—S5A—C5A | 107.03 (15) | C3C—C2C—H2C | 119.00 |
| O51B—S5B—C5B | 105.99 (18) | C5C—C4C—H4C | 120.00 |
| O51B—S5B—O52B | 111.8 (2) | C3C—C4C—H4C | 120.00 |
| O51B—S5B—O53B | 109.1 (2) | C4C—C5C—H5A | 121.00 |
| O53B—S5B—C5B | 106.1 (2) | C6C—C5C—H5A | 121.00 |
| O52B—S5B—O53B | 116.4 (2) | C5C—C6C—H6C | 119.00 |
| O52B—S5B—C5B | 106.70 (18) | N1C—C6C—H6C | 119.00 |
| C2A—O2A—H2A | 109.00 | N11C—C11C—H13C | 109.00 |
| C11A—O11A—H11A | 113.00 | H12C—C11C—H13C | 109.00 |
| C2B—O2B—H2B | 109.00 | N11C—C11C—H12C | 109.00 |
| C11B—O11B—H11B | 112.00 | H13C—C11C—H134 | 109.00 |
| C2C—N1C—C6C | 118.8 (4) | N11C—C11C—H134 | 109.00 |
| C11C—N11C—C21C | 114.9 (3) | H12C—C11C—H134 | 109.00 |
| C11C—N11C—C51C | 113.6 (3) | C31C—C21C—H21C | 108.00 |
| C21C—N11C—C51C | 103.8 (3) | C3C—C21C—H21C | 108.00 |
| C51C—N11C—H11C | 108.00 | N11C—C21C—H21C | 108.00 |
| C21C—N11C—H11C | 108.00 | C41C—C31C—H32C | 111.00 |
| C11C—N11C—H11C | 108.00 | C21C—C31C—H31C | 111.00 |
| C2D—N1D—C6D | 119.2 (3) | C41C—C31C—H31C | 111.00 |
| C11D—N11D—C51D | 114.2 (3) | H31C—C31C—H32C | 109.00 |
| C11D—N11D—C21D | 116.3 (3) | C21C—C31C—H32C | 111.00 |
| C21D—N11D—C51D | 103.6 (3) | C51C—C41C—H41C | 110.00 |
| C51D—N11D—H11D | 107.00 | H41C—C41C—H42C | 109.00 |
| C11D—N11D—H11D | 107.00 | C31C—C41C—H42C | 111.00 |
| C21D—N11D—H11D | 107.00 | C31C—C41C—H41C | 110.00 |
| C6A—C1A—C11A | 121.9 (3) | C51C—C41C—H42C | 110.00 |
| C2A—C1A—C11A | 119.4 (3) | H51C—C51C—H52C | 109.00 |
| C2A—C1A—C6A | 118.7 (3) | N11C—C51C—H51C | 111.00 |
| O2A—C2A—C1A | 121.8 (3) | C41C—C51C—H52C | 111.00 |
| O2A—C2A—C3A | 118.5 (3) | C41C—C51C—H51C | 111.00 |
| C1A—C2A—C3A | 119.7 (3) | N11C—C51C—H52C | 111.00 |
| C2A—C3A—C4A | 120.1 (3) | N1D—C2D—C3D | 122.7 (3) |
| C3A—C4A—C5A | 120.7 (3) | C2D—C3D—C21D | 118.3 (3) |
| C4A—C5A—C6A | 119.3 (3) | C2D—C3D—C4D | 117.6 (3) |
| S5A—C5A—C4A | 120.7 (3) | C4D—C3D—C21D | 124.1 (3) |
| S5A—C5A—C6A | 119.9 (3) | C3D—C4D—C5D | 119.7 (3) |
| C1A—C6A—C5A | 121.4 (3) | C4D—C5D—C6D | 118.8 (3) |
| O11A—C11A—C1A | 115.6 (3) | N1D—C6D—C5D | 121.9 (3) |
| O12A—C11A—C1A | 120.5 (3) | C3D—C21D—C31D | 116.7 (3) |
| O11A—C11A—O12A | 123.9 (3) | N11D—C21D—C3D | 114.6 (3) |
| C2A—C3A—H3A | 120.00 | N11D—C21D—C31D | 101.6 (3) |
| C4A—C3A—H3A | 120.00 | C21D—C31D—C41D | 103.2 (3) |
| C3A—C4A—H4A | 120.00 | C31D—C41D—C51D | 105.7 (4) |
| C5A—C4A—H4A | 120.00 | N11D—C51D—C41D | 106.4 (3) |
| C5A—C6A—H6A | 119.00 | N1D—C2D—H2D | 119.00 |
| C1A—C6A—H6A | 119.00 | C3D—C2D—H2D | 119.00 |
| C6B—C1B—C11B | 121.0 (3) | C3D—C4D—H4D | 120.00 |
| C2B—C1B—C11B | 120.1 (3) | C5D—C4D—H4D | 120.00 |
| C2B—C1B—C6B | 118.9 (3) | C4D—C5D—H5D | 121.00 |
| C1B—C2B—C3B | 120.6 (3) | C6D—C5D—H5D | 121.00 |
| O2B—C2B—C3B | 117.5 (3) | N1D—C6D—H6D | 119.00 |
| O2B—C2B—C1B | 121.9 (3) | C5D—C6D—H6D | 119.00 |
| C2B—C3B—C4B | 119.6 (3) | N11D—C11D—H12D | 109.00 |
| C3B—C4B—C5B | 120.3 (3) | N11D—C11D—H13D | 110.00 |
| C4B—C5B—C6B | 120.0 (3) | N11D—C11D—H14D | 109.00 |
| S5B—C5B—C4B | 119.0 (3) | H12D—C11D—H13D | 109.00 |
| S5B—C5B—C6B | 120.9 (3) | H12D—C11D—H14D | 109.00 |
| C1B—C6B—C5B | 120.5 (3) | H13D—C11D—H14D | 109.00 |
| O12B—C11B—C1B | 120.8 (3) | N11D—C21D—H21D | 108.00 |
| O11B—C11B—C1B | 116.1 (3) | C3D—C21D—H21D | 108.00 |
| O11B—C11B—O12B | 123.1 (3) | C31D—C21D—H21D | 108.00 |
| C2B—C3B—H3B | 120.00 | C21D—C31D—H31D | 111.00 |
| C4B—C3B—H3B | 120.00 | C21D—C31D—H32D | 111.00 |
| C3B—C4B—H4B | 120.00 | C41D—C31D—H31D | 111.00 |
| C5B—C4B—H4B | 120.00 | C41D—C31D—H32D | 111.00 |
| C5B—C6B—H6B | 120.00 | H31D—C31D—H32D | 109.00 |
| C1B—C6B—H6B | 120.00 | C31D—C41D—H41D | 111.00 |
| N1C—C2C—C3C | 122.7 (3) | C31D—C41D—H42D | 111.00 |
| C2C—C3C—C4C | 117.7 (3) | C51D—C41D—H41D | 111.00 |
| C4C—C3C—C21C | 118.9 (3) | C51D—C41D—H42D | 111.00 |
| C2C—C3C—C21C | 123.3 (3) | H41D—C41D—H42D | 109.00 |
| C3C—C4C—C5C | 119.9 (3) | N11D—C51D—H51D | 110.00 |
| C4C—C5C—C6C | 118.8 (3) | N11D—C51D—H52D | 111.00 |
| N1C—C6C—C5C | 122.1 (3) | C41D—C51D—H51D | 110.00 |
| N11C—C21C—C3C | 115.2 (3) | C41D—C51D—H52D | 110.00 |
| C3C—C21C—C31C | 115.2 (3) | H51D—C51D—H52D | 109.00 |
| O51A—S5A—C5A—C4A | −95.6 (3) | C6B—C1B—C2B—O2B | −176.9 (3) |
| O51A—S5A—C5A—C6A | 80.1 (3) | C6B—C1B—C2B—C3B | 5.0 (5) |
| O52A—S5A—C5A—C4A | 23.0 (3) | C11B—C1B—C2B—C3B | −175.9 (3) |
| O52A—S5A—C5A—C6A | −161.3 (3) | C2B—C1B—C6B—C5B | −2.3 (5) |
| O53A—S5A—C5A—C4A | 143.4 (3) | C11B—C1B—C6B—C5B | 178.6 (3) |
| O53A—S5A—C5A—C6A | −41.0 (3) | C2B—C1B—C11B—O11B | 175.1 (3) |
| O53B—S5B—C5B—C6B | 19.4 (4) | C2B—C1B—C11B—O12B | −3.5 (5) |
| O52B—S5B—C5B—C4B | −40.0 (3) | C6B—C1B—C11B—O11B | −5.8 (5) |
| O51B—S5B—C5B—C4B | 79.3 (3) | C11B—C1B—C2B—O2B | 2.2 (5) |
| O51B—S5B—C5B—C6B | −96.5 (3) | C6B—C1B—C11B—O12B | 175.6 (3) |
| O52B—S5B—C5B—C6B | 144.1 (3) | O2B—C2B—C3B—C4B | 177.5 (3) |
| O53B—S5B—C5B—C4B | −164.8 (3) | C1B—C2B—C3B—C4B | −4.2 (5) |
| C2C—N1C—C6C—C5C | −0.6 (5) | C2B—C3B—C4B—C5B | 0.8 (5) |
| C6C—N1C—C2C—C3C | 1.9 (5) | C3B—C4B—C5B—C6B | 1.7 (5) |
| C21C—N11C—C51C—C41C | −30.3 (4) | C3B—C4B—C5B—S5B | −174.1 (3) |
| C11C—N11C—C21C—C3C | −67.9 (4) | C4B—C5B—C6B—C1B | −1.0 (5) |
| C11C—N11C—C51C—C41C | −155.8 (4) | S5B—C5B—C6B—C1B | 174.8 (2) |
| C51C—N11C—C21C—C31C | 41.9 (4) | N1C—C2C—C3C—C4C | −1.4 (5) |
| C11C—N11C—C21C—C31C | 166.6 (4) | N1C—C2C—C3C—C21C | −177.4 (3) |
| C51C—N11C—C21C—C3C | 167.4 (3) | C2C—C3C—C4C—C5C | −0.5 (5) |
| C2D—N1D—C6D—C5D | 0.6 (5) | C21C—C3C—C4C—C5C | 175.7 (3) |
| C6D—N1D—C2D—C3D | −1.6 (5) | C2C—C3C—C21C—N11C | −45.7 (4) |
| C51D—N11D—C21D—C3D | 169.5 (3) | C2C—C3C—C21C—C31C | 72.5 (5) |
| C11D—N11D—C21D—C31D | 168.9 (3) | C4C—C3C—C21C—C31C | −103.4 (4) |
| C21D—N11D—C51D—C41D | −27.3 (4) | C4C—C3C—C21C—N11C | 138.4 (3) |
| C51D—N11D—C21D—C31D | 42.6 (3) | C3C—C4C—C5C—C6C | 1.7 (5) |
| C11D—N11D—C51D—C41D | −154.9 (4) | C4C—C5C—C6C—N1C | −1.2 (6) |
| C11D—N11D—C21D—C3D | −64.3 (4) | N11C—C21C—C31C—C41C | −38.1 (4) |
| C2A—C1A—C11A—O12A | 3.6 (5) | C3C—C21C—C31C—C41C | −163.5 (3) |
| C2A—C1A—C11A—O11A | −175.9 (3) | C21C—C31C—C41C—C51C | 19.6 (5) |
| C6A—C1A—C11A—O11A | 2.6 (5) | C31C—C41C—C51C—N11C | 6.2 (5) |
| C6A—C1A—C11A—O12A | −178.0 (3) | N1D—C2D—C3D—C4D | 1.4 (5) |
| C6A—C1A—C2A—C3A | −2.6 (5) | N1D—C2D—C3D—C21D | 179.3 (3) |
| C11A—C1A—C2A—O2A | −2.4 (5) | C2D—C3D—C4D—C5D | −0.2 (5) |
| C11A—C1A—C2A—C3A | 176.0 (3) | C21D—C3D—C4D—C5D | −177.9 (3) |
| C2A—C1A—C6A—C5A | 0.6 (5) | C2D—C3D—C21D—N11D | 125.7 (3) |
| C11A—C1A—C6A—C5A | −177.9 (3) | C2D—C3D—C21D—C31D | −115.7 (4) |
| C6A—C1A—C2A—O2A | 179.1 (3) | C4D—C3D—C21D—N11D | −56.6 (5) |
| C1A—C2A—C3A—C4A | 3.1 (5) | C4D—C3D—C21D—C31D | 62.0 (5) |
| O2A—C2A—C3A—C4A | −178.5 (3) | C3D—C4D—C5D—C6D | −0.8 (5) |
| C2A—C3A—C4A—C5A | −1.6 (5) | C4D—C5D—C6D—N1D | 0.6 (5) |
| C3A—C4A—C5A—C6A | −0.4 (5) | N11D—C21D—C31D—C41D | −41.6 (4) |
| C3A—C4A—C5A—S5A | 175.3 (3) | C3D—C21D—C31D—C41D | −167.0 (3) |
| C4A—C5A—C6A—C1A | 0.9 (5) | C21D—C31D—C41D—C51D | 25.0 (5) |
| S5A—C5A—C6A—C1A | −174.9 (3) | C31D—C41D—C51D—N11D | 1.3 (5) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O2A—H2A···O12A | 0.84 | 1.80 | 2.549 (4) | 147 |
| O2B—H2B···O12B | 0.84 | 1.82 | 2.561 (4) | 146 |
| O11A—H11A···N1D | 0.95 | 1.60 | 2.555 (4) | 179 |
| O11B—H11B···N1C | 0.95 | 1.61 | 2.558 (4) | 179 |
| N11C—H11C···O51Bi | 0.93 | 2.32 | 3.022 (5) | 132 |
| N11C—H11C···O53Bi | 0.93 | 2.15 | 3.029 (5) | 157 |
| N11D—H11D···O52Aii | 0.93 | 1.85 | 2.735 (4) | 158 |
| C11D—H12D···O2Biii | 0.98 | 2.51 | 3.491 (5) | 174 |
| C2C—H2C···O53Bi | 0.95 | 2.29 | 3.201 (5) | 160 |
| C2D—H2D···O53Aiv | 0.95 | 2.45 | 3.359 (4) | 160 |
| C4A—H4A···O52A | 0.95 | 2.54 | 2.914 (4) | 103 |
| C6B—H6B···O53B | 0.95 | 2.54 | 2.913 (5) | 103 |
| C11C—H12C···O2Av | 0.98 | 2.52 | 3.481 (5) | 165 |
| C11C—H13C···O52Bvi | 0.98 | 2.46 | 3.290 (5) | 142 |
| C11D—H13D···O51Aiv | 0.98 | 2.37 | 3.251 (5) | 150 |
| C21C—H21C···O52Bvi | 1.00 | 2.42 | 3.331 (5) | 151 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, y+1/2, −z; (ii) x−1, y−1, z; (iii) x−1, y, z; (iv) −x+1, y−1/2, −z+1; (v) x+1, y, z; (vi) x+1, y+1, z.
References
- Agilent (2013). CrysAlis PRO. Agilent Technologies Ltd, Yarnton, England.
- Altomare, A., Cascarano, G., Giacovazzo, C. & Guagliardi, A. (1993). J. Appl. Cryst. 26, 343–350.
- Arnaud, V., Berthelot, M., Evain, M., Graton, J. & Le Questel, J. Y. (2007). Chem. Eur. J. 13, 1499–1510. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Barlow, R. B., Howard, J. A. K. & Johnson, O. (1986). Acta Cryst. C42, 853–856.
- Baskar Raj, P., Sethuraman, V., Francis, S., Hemamalini, M., Muthiah, P. T., Bocelli, A., Cantoni, A., Rychlewska, M. & Warzajtis, B. (2003). CrystEngComm, 5, 70–76.
- Choi, S.-N., Lee, Y.-M., Lee, H.-W., Kang, S. K. & Kim, Y.-I. (2002). Acta Cryst. E58, m583–m585.
- Enzell, C. R., Wahlberg, I. & Aasen, A. J. (1977). Isoprenoids and Alkaloids of Tobacco, in Progress in the Chemistry of Organic Natural Products, Vol. 34, pp. 1–74. Vienna: Springer-Verlag.
- Farrugia, L. J. (2012). J. Appl. Cryst. 45, 849–854.
- Flack, H. D. (1983). Acta Cryst. A39, 876–881.
- Kim, H. S. & Jeffrey, G. A. (1971). Acta Cryst. B27, 1123–1131.
- Koman, M., Martiška, L., Valigura, D. & Glowiak, T. (2003). Acta Cryst. E59, o441–o442.
- Koo, C. H. & Kim, H. S. (1965). J. Korean Chem. Soc. 9, 134–141.
- O’Neil, M. A. (2001). Editor. The Merck Index, 13th ed., p. 1169. Whitehouse Station, NJ: Merck & Co. Inc.
- Rodgman, A. & Parfetti, T. A. (2009). In The Chemical Components of Tobacco and Tobacco Smoke. Boca Raton, Florida, USA: CRC Press.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Smith, G., Wermuth, U. D. & Healy, P. C. (2006). J. Chem. Crystallogr. 36, 841–849.
- Smith, G., Wermuth, U. D., Healy, P. C. & White, J. M. (2007). Aust. J. Chem. 60, 264–277.
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Ujváry, I. (1999). In Nicotinoid Insecticides, edited by I. Yamamoto & J. Casida. Tokyo: Springer-Verlag.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I, II. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814023253/lh5736sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814023253/lh5736Isup2.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) II. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814023253/lh5736IIsup3.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814023253/lh5736Isup4.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814023253/lh5736IIsup5.cml
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report