In the title compound, the acenapthylene ring system and the hydrazinecarbothioamide unit (=N—NH—C=S—NH–) are essentially coplanar, making a dihedral angle of 1.59 (9)°. The molecular conformation is stabilized by two weak intramolecular hydrogen bonds (N—H⋯O and N—H⋯N), which generate S(6) and S(5) ring motifs.
Keywords: crystal structure, acenaphthylene, hydrazinecarbothioamide, thiosemicarbazones, hydrogen bonding, C—H⋯π interactions
Abstract
In the title compound, C14H11N3OS, the acenaphthylene ring system and hydrazinecarbothioamide unit (=N—NH—C=S—NH–) are essentially coplanar [with maximum deviations from their mean planes of −0.009 (2) and 0.033 (2) Å, respectively], and make a dihedral angle of 1.59 (9)°. The molecular conformation is stabilized by two weak intramolecular hydrogen bonds (N—H⋯O and N—H⋯N), which generate S(6) and S(5) ring motifs. In the crystal, molecules are linked by N—H⋯S hydrogen bonds, forming chains along [010]. The chains are linked via pairs of C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, enclosing R 2 2(10) ring motifs, and C—H⋯π interactions, forming a three-dimensional framework. The absolute structure of the title compound was determined by resonant scattering.
Chemical context
The design and synthesis of thiosemicarbazones are of considerable interest because of their versatile chemistry and various biological activities, such as antitumor, antibacterial, antiviral, antiamoebic and antimalarial (Kelly et al., 1996 ▶). They comprise an intriguing class of chelating molecules, which possess a wide range of beneficial medicinal properties (Prabhakaran et al. 2008 ▶). Thiosemicarbazones are a versatile class of ligands that have been studied for their biological activity (Chellan et al., 2010 ▶), their interesting binding motifs (Lobana et al., 2009 ▶) and their use as ligands in catalysis (Xie et al., 2010 ▶). In view of their biological importance, the crystal structure of the title compound has been determined and the results are presented herein.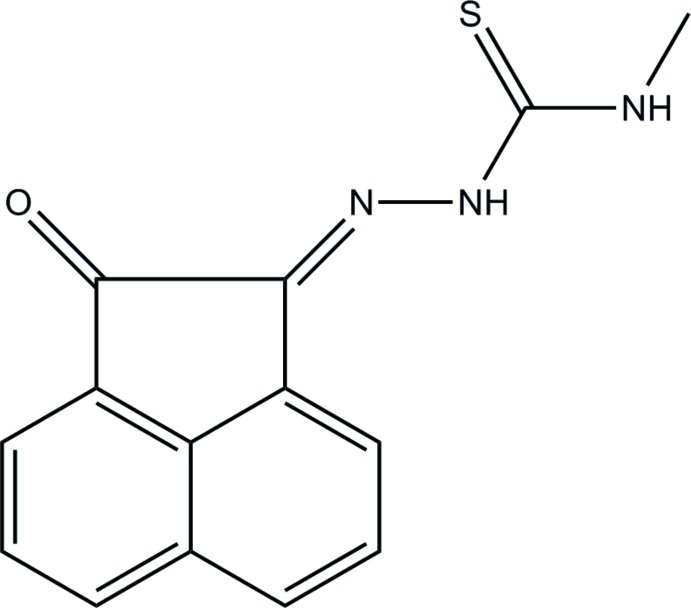
Structural commentary
The molecular structure of the title compound is illustrated in Fig. 1 ▶. The atoms of both the acenaphthylene ring system and the =N—NH—C=S—NH– segment are essentially coplanar, the maximum deviations from their mean planes being −0.009 (2) and 0.033 (2) Å for atoms C12 and C14, respectively. The dihedral angle between the benzene and cyclopentane rings of the acenapthalene unit is 1.59 (9)°. The molecular structure is stabilized by N—H⋯O and N—H⋯N hydrogen bonds, forming S(6) and S(5) ring motifs, respectively (Table 1 ▶ and Fig. 1 ▶).
Figure 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound, with the atom labelling. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 30% probability level. Hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines (see Table 1 ▶ for details).
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (, ).
Cg is the centroid of ring C1/C6C10.
| DHA | DH | HA | D A | DHA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N2H2O1 | 0.86 | 2.03 | 2.7178(19) | 136 |
| N3H3N1 | 0.86 | 2.26 | 2.6437(19) | 107 |
| N3H3S1i | 0.86 | 2.64 | 3.4407(15) | 156 |
| C4H4O1ii | 0.93 | 2.47 | 3.246(2) | 141 |
| C2H2A Cg iii | 0.93 | 2.76 | 3.502(2) | 137 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  .
.
Supramolecular features
In the crystal, molecules are linked by N—H⋯S hydrogen bonds (Table 1 ▶ and Fig. 2 ▶), forming chains along [010]. The chains are linked via pairs of C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, enclosing  (10) ring motifs, and C—H⋯π interactions, forming a three-dimensional framework (Table 1 ▶ and Fig. 2 ▶).
(10) ring motifs, and C—H⋯π interactions, forming a three-dimensional framework (Table 1 ▶ and Fig. 2 ▶).
Figure 2.
The crystal packing of the title compound viewed along the a axis. Hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines (see Table 1 ▶ for details; H atoms not involved in hydrogen bonding have been omitted for clarity).
Database survey
A search of the Cambridge Structural Database (Version 5.35, last update May 2014; Groom & Allen, 2014 ▶) for the substructure 2-(imino)acenaphthylen-1(2H)-one gave 13 hits, including that of the ethyl analogue of the title compound, acenaphthylene-1,2-dione 4-ethylthiosemicarbazone (GURHAD; Pascu et al., 2010 ▶). The two molecules differ in the dihedral angle between the mean planes of the acenaphthylene ring system and hydrazinecarbothioamide unit (=N—NH—C=S—NH–) which is 1.59 (9)° in the title compound but 9.14 (6)° in the ethyl analogue (GURHAD; Pascu et al., 2010 ▶). In the crystals of both compounds, molecules are linked via N—H⋯S hydrogen bonds, forming chains along [010].
Synthesis and crystallization
An ethanolic solution of N-methylhydrazinecarbothioamide (0.01 mol) was added to an ethanolic solution (50 ml) containing acenaphthylene-1,2-dione (0.01 mol). The mixture was refluxed for 2 h during which time a yellow precipitate separated out. The reaction mixture was then cooled to room temperature and the precipitate was filtered off. It was then washed with ethanol and dried under vacuum. The yield of the isolated product was 89%. Single crystals suitable for X-ray diffraction were obtained by slow evaporation of a solution of the title compound in ethanol at room temperature.
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 2 ▶. All H atoms were fixed geometrically and allowed to ride on their parent atoms: N—H = 0.86 and C—H = 0.93–0.97 Å and with U iso(H) = 1.5U eq(C) for methyl H atoms and = 1.2U eq(C) for other H atoms. The absolute structure of the title compound was determined by resonant scattering, with a Flack parameter of 0.02 (8).
Table 2. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | C14H11N3OS |
| M r | 269.33 |
| Crystal system, space group | Orthorhombic, P212121 |
| Temperature (K) | 293 |
| a, b, c () | 6.1110(6), 10.0547(11), 21.497(2) |
| V (3) | 1320.8(2) |
| Z | 4 |
| Radiation type | Mo K |
| (mm1) | 0.24 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.30 0.25 0.20 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Bruker SMART APEXII CCD |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2008 ▶) |
| T min, T max | 0.932, 0.954 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2(I)] reflections | 23135, 3941, 2929 |
| R int | 0.030 |
| (sin /)max (1) | 0.708 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.035, 0.100, 0.99 |
| No. of reflections | 3941 |
| No. of parameters | 173 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters constrained |
| max, min (e 3) | 0.19, 0.21 |
| Absolute structure | Flack (1983 ▶); Friedel pairs |
| Absolute structure parameter | 0.02(8) |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814023216/su2796sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814023216/su2796Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814023216/su2796Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 1030348
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr Babu Varghese, SAIF, IIT, Chennai, India for the data collection.
supplementary crystallographic information
Crystal data
| C14H11N3OS | Z = 4 |
| Mr = 269.33 | F(000) = 560 |
| Orthorhombic, P212121 | Dx = 1.354 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: P 2ac 2ab | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 6.1110 (6) Å | µ = 0.24 mm−1 |
| b = 10.0547 (11) Å | T = 293 K |
| c = 21.497 (2) Å | Block, yellow |
| V = 1320.8 (2) Å3 | 0.30 × 0.25 × 0.20 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART APEXII CCD diffractometer | 3941 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2929 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.030 |
| ω and φ scans | θmax = 30.2°, θmin = 2.2° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2008) | h = −8→8 |
| Tmin = 0.932, Tmax = 0.954 | k = −13→14 |
| 23135 measured reflections | l = −29→29 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.035 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.100 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0532P)2 + 0.2048P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 0.99 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 3941 reflections | Δρmax = 0.19 e Å−3 |
| 173 parameters | Δρmin = −0.21 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Absolute structure: Flack (1983); Friedel pairs |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Absolute structure parameter: −0.02 (8) |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R-factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| S1 | 0.25692 (8) | 0.16757 (4) | 0.21243 (2) | 0.04960 (13) | |
| N1 | 0.7542 (2) | −0.05741 (12) | 0.17414 (6) | 0.0365 (3) | |
| C6 | 1.2232 (3) | −0.09719 (15) | 0.07905 (7) | 0.0371 (3) | |
| O1 | 0.8428 (2) | 0.16301 (14) | 0.08374 (6) | 0.0550 (4) | |
| N2 | 0.6084 (2) | 0.04380 (14) | 0.17558 (7) | 0.0416 (3) | |
| H2 | 0.6259 | 0.1109 | 0.1513 | 0.050* | |
| C7 | 1.0847 (3) | −0.14650 (15) | 0.12619 (7) | 0.0342 (3) | |
| C13 | 0.4342 (3) | 0.04074 (16) | 0.21510 (8) | 0.0380 (3) | |
| N3 | 0.4208 (2) | −0.06205 (15) | 0.25248 (7) | 0.0445 (3) | |
| H3 | 0.5225 | −0.1210 | 0.2506 | 0.053* | |
| C12 | 0.9103 (3) | −0.04864 (16) | 0.13442 (7) | 0.0350 (3) | |
| C5 | 1.1533 (3) | 0.02565 (17) | 0.05510 (8) | 0.0425 (4) | |
| C11 | 0.9539 (3) | 0.06370 (17) | 0.08912 (8) | 0.0403 (4) | |
| C8 | 1.1346 (3) | −0.26514 (17) | 0.15336 (8) | 0.0416 (4) | |
| H8 | 1.0445 | −0.3015 | 0.1838 | 0.050* | |
| C9 | 1.3268 (3) | −0.3313 (2) | 0.13404 (9) | 0.0492 (4) | |
| H9 | 1.3632 | −0.4114 | 0.1530 | 0.059* | |
| C14 | 0.2450 (4) | −0.0824 (2) | 0.29673 (10) | 0.0634 (5) | |
| H14A | 0.2421 | −0.0099 | 0.3258 | 0.095* | |
| H14B | 0.2686 | −0.1642 | 0.3187 | 0.095* | |
| H14C | 0.1080 | −0.0866 | 0.2750 | 0.095* | |
| C1 | 1.4122 (3) | −0.16161 (19) | 0.05877 (8) | 0.0435 (4) | |
| C2 | 1.5292 (4) | −0.0968 (2) | 0.01114 (10) | 0.0604 (6) | |
| H2A | 1.6559 | −0.1356 | −0.0045 | 0.072* | |
| C4 | 1.2699 (4) | 0.0860 (2) | 0.00894 (9) | 0.0578 (5) | |
| H4 | 1.2252 | 0.1668 | −0.0078 | 0.069* | |
| C3 | 1.4596 (4) | 0.0221 (2) | −0.01250 (11) | 0.0671 (6) | |
| H3A | 1.5408 | 0.0621 | −0.0439 | 0.080* | |
| C10 | 1.4618 (3) | −0.2829 (2) | 0.08867 (9) | 0.0505 (5) | |
| H10 | 1.5867 | −0.3300 | 0.0775 | 0.061* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| S1 | 0.0421 (2) | 0.0413 (2) | 0.0654 (3) | 0.0080 (2) | 0.0033 (2) | −0.01024 (19) |
| N1 | 0.0345 (6) | 0.0331 (6) | 0.0420 (7) | 0.0008 (6) | 0.0020 (7) | −0.0007 (5) |
| C6 | 0.0373 (9) | 0.0370 (8) | 0.0369 (8) | −0.0031 (7) | −0.0004 (7) | −0.0047 (6) |
| O1 | 0.0621 (8) | 0.0423 (7) | 0.0605 (8) | 0.0123 (7) | 0.0046 (7) | 0.0140 (6) |
| N2 | 0.0397 (7) | 0.0361 (7) | 0.0488 (8) | 0.0054 (6) | 0.0055 (7) | 0.0043 (6) |
| C7 | 0.0353 (8) | 0.0338 (8) | 0.0336 (7) | 0.0004 (6) | −0.0001 (6) | −0.0013 (6) |
| C13 | 0.0337 (8) | 0.0365 (8) | 0.0438 (8) | −0.0028 (6) | 0.0001 (7) | −0.0089 (7) |
| N3 | 0.0401 (8) | 0.0406 (7) | 0.0528 (8) | 0.0015 (6) | 0.0077 (7) | −0.0009 (7) |
| C12 | 0.0356 (8) | 0.0326 (7) | 0.0368 (7) | 0.0007 (6) | −0.0014 (7) | 0.0021 (6) |
| C5 | 0.0498 (10) | 0.0395 (9) | 0.0381 (8) | −0.0029 (8) | 0.0047 (8) | −0.0009 (7) |
| C11 | 0.0436 (9) | 0.0357 (8) | 0.0415 (8) | −0.0005 (7) | −0.0003 (7) | 0.0040 (7) |
| C8 | 0.0454 (10) | 0.0386 (9) | 0.0407 (9) | 0.0029 (8) | 0.0000 (8) | 0.0019 (7) |
| C9 | 0.0523 (10) | 0.0432 (9) | 0.0521 (10) | 0.0129 (9) | −0.0088 (8) | −0.0013 (8) |
| C14 | 0.0583 (12) | 0.0610 (12) | 0.0707 (13) | −0.0037 (11) | 0.0226 (12) | 0.0021 (9) |
| C1 | 0.0388 (9) | 0.0476 (9) | 0.0441 (9) | −0.0044 (8) | 0.0042 (7) | −0.0129 (8) |
| C2 | 0.0513 (12) | 0.0702 (14) | 0.0596 (12) | −0.0090 (10) | 0.0196 (10) | −0.0180 (10) |
| C4 | 0.0742 (14) | 0.0496 (10) | 0.0495 (10) | −0.0103 (11) | 0.0164 (11) | 0.0068 (8) |
| C3 | 0.0747 (16) | 0.0684 (15) | 0.0581 (12) | −0.0179 (12) | 0.0285 (12) | −0.0009 (10) |
| C10 | 0.0397 (10) | 0.0547 (11) | 0.0572 (11) | 0.0100 (8) | −0.0044 (8) | −0.0157 (9) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| S1—C13 | 1.6744 (17) | C5—C11 | 1.472 (3) |
| N1—C12 | 1.283 (2) | C8—C9 | 1.412 (2) |
| N1—N2 | 1.3528 (19) | C8—H8 | 0.9300 |
| C6—C1 | 1.394 (2) | C9—C10 | 1.367 (3) |
| C6—C5 | 1.405 (2) | C9—H9 | 0.9300 |
| C6—C7 | 1.410 (2) | C14—H14A | 0.9600 |
| O1—C11 | 1.213 (2) | C14—H14B | 0.9600 |
| N2—C13 | 1.362 (2) | C14—H14C | 0.9600 |
| N2—H2 | 0.8600 | C1—C2 | 1.409 (3) |
| C7—C8 | 1.363 (2) | C1—C10 | 1.411 (3) |
| C7—C12 | 1.461 (2) | C2—C3 | 1.367 (3) |
| C13—N3 | 1.312 (2) | C2—H2A | 0.9300 |
| N3—C14 | 1.449 (2) | C4—C3 | 1.403 (3) |
| N3—H3 | 0.8600 | C4—H4 | 0.9300 |
| C12—C11 | 1.515 (2) | C3—H3A | 0.9300 |
| C5—C4 | 1.364 (3) | C10—H10 | 0.9300 |
| C12—N1—N2 | 116.93 (13) | C7—C8—H8 | 120.9 |
| C1—C6—C5 | 123.08 (16) | C9—C8—H8 | 120.9 |
| C1—C6—C7 | 123.95 (16) | C10—C9—C8 | 122.95 (18) |
| C5—C6—C7 | 112.96 (15) | C10—C9—H9 | 118.5 |
| N1—N2—C13 | 120.78 (14) | C8—C9—H9 | 118.5 |
| N1—N2—H2 | 119.6 | N3—C14—H14A | 109.5 |
| C13—N2—H2 | 119.6 | N3—C14—H14B | 109.5 |
| C8—C7—C6 | 118.78 (16) | H14A—C14—H14B | 109.5 |
| C8—C7—C12 | 134.48 (16) | N3—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| C6—C7—C12 | 106.73 (13) | H14A—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| N3—C13—N2 | 116.67 (15) | H14B—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| N3—C13—S1 | 125.49 (13) | C6—C1—C2 | 115.65 (19) |
| N2—C13—S1 | 117.84 (13) | C6—C1—C10 | 115.92 (16) |
| C13—N3—C14 | 124.05 (16) | C2—C1—C10 | 128.43 (18) |
| C13—N3—H3 | 118.0 | C3—C2—C1 | 121.1 (2) |
| C14—N3—H3 | 118.0 | C3—C2—H2A | 119.4 |
| N1—C12—C7 | 125.20 (14) | C1—C2—H2A | 119.4 |
| N1—C12—C11 | 127.56 (15) | C5—C4—C3 | 117.9 (2) |
| C7—C12—C11 | 107.22 (14) | C5—C4—H4 | 121.1 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 119.92 (18) | C3—C4—H4 | 121.1 |
| C4—C5—C11 | 132.73 (18) | C2—C3—C4 | 122.4 (2) |
| C6—C5—C11 | 107.34 (15) | C2—C3—H3A | 118.8 |
| O1—C11—C5 | 129.05 (16) | C4—C3—H3A | 118.8 |
| O1—C11—C12 | 125.21 (16) | C9—C10—C1 | 120.19 (17) |
| C5—C11—C12 | 105.74 (14) | C9—C10—H10 | 119.9 |
| C7—C8—C9 | 118.19 (17) | C1—C10—H10 | 119.9 |
| C12—N1—N2—C13 | 178.14 (14) | C6—C5—C11—C12 | −0.95 (18) |
| C1—C6—C7—C8 | −1.1 (2) | N1—C12—C11—O1 | −0.7 (3) |
| C5—C6—C7—C8 | −179.95 (15) | C7—C12—C11—O1 | −179.08 (17) |
| C1—C6—C7—C12 | 178.56 (15) | N1—C12—C11—C5 | 179.18 (16) |
| C5—C6—C7—C12 | −0.34 (19) | C7—C12—C11—C5 | 0.76 (18) |
| N1—N2—C13—N3 | 2.3 (2) | C6—C7—C8—C9 | 1.7 (2) |
| N1—N2—C13—S1 | −178.08 (12) | C12—C7—C8—C9 | −177.74 (17) |
| N2—C13—N3—C14 | −179.01 (17) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | −1.3 (3) |
| S1—C13—N3—C14 | 1.4 (3) | C5—C6—C1—C2 | −1.3 (2) |
| N2—N1—C12—C7 | 179.26 (15) | C7—C6—C1—C2 | 179.96 (16) |
| N2—N1—C12—C11 | 1.1 (2) | C5—C6—C1—C10 | 178.58 (16) |
| C8—C7—C12—N1 | 0.8 (3) | C7—C6—C1—C10 | −0.2 (2) |
| C6—C7—C12—N1 | −178.75 (15) | C6—C1—C2—C3 | 0.6 (3) |
| C8—C7—C12—C11 | 179.24 (18) | C10—C1—C2—C3 | −179.2 (2) |
| C6—C7—C12—C11 | −0.29 (17) | C6—C5—C4—C3 | −0.7 (3) |
| C1—C6—C5—C4 | 1.4 (3) | C11—C5—C4—C3 | 178.57 (19) |
| C7—C6—C5—C4 | −179.72 (17) | C1—C2—C3—C4 | 0.0 (4) |
| C1—C6—C5—C11 | −178.08 (15) | C5—C4—C3—C2 | 0.1 (3) |
| C7—C6—C5—C11 | 0.83 (19) | C8—C9—C10—C1 | 0.0 (3) |
| C4—C5—C11—O1 | −0.5 (4) | C6—C1—C10—C9 | 0.7 (2) |
| C6—C5—C11—O1 | 178.88 (19) | C2—C1—C10—C9 | −179.5 (2) |
| C4—C5—C11—C12 | 179.7 (2) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
Cg is the centroid of ring C1/C6–C10.
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N2—H2···O1 | 0.86 | 2.03 | 2.7178 (19) | 136 |
| N3—H3···N1 | 0.86 | 2.26 | 2.6437 (19) | 107 |
| N3—H3···S1i | 0.86 | 2.64 | 3.4407 (15) | 156 |
| C4—H4···O1ii | 0.93 | 2.47 | 3.246 (2) | 141 |
| C2—H2A···Cgiii | 0.93 | 2.76 | 3.502 (2) | 137 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, y−1/2, −z+1/2; (ii) x+1/2, −y+1/2, −z; (iii) x+1/2, −y−1/2, −z.
References
- Bruker (2008). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Chellan, P., Shunmoogam-Gounden, N., Hendricks, D. T., Gut, J., Rosenthal, P. J., Lategan, C., Smith, P. J., Chibale, K. & Smith, G. S. (2010). Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. pp, 3520–3528.
- Farrugia, L. J. (2012). J. Appl. Cryst. 45, 849–854.
- Flack, H. D. (1983). Acta Cryst. A39, 876–881.
- Groom, C. R. & Allen, F. H. (2014). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 53, 662–671. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Kelly, P. F., Slawin, A. M. Z. & Soriano-Rama, A. (1996). J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. pp. 53–59.
- Lobana, T. S., Sharma, R., Bawa, G. & Khanna, S. (2009). Coord. Chem. Rev. 253, 977–1055.
- Pascu, S. I., Waghorn, P. A., Kennedy, B. W. C., Arrowsmith, R. L., Bayly, S. R., Dilworth, J. R., Christlieb, M., Tyrrell, R. M., Zhong, J., Kowalczyk, R. M., Collison, D., Aley, P. K., Churchill, G. C. & Aigbirhio, F. I. (2010). Chem. Asian J. 5, 506–519. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Prabhakaran, R., Huang, R., Renukadevi, S. V., Karvembu, R., Zeller, M. & Natarajan, K. (2008). Inorg. Chim. Acta, 361, 2547–2552.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Xie, G., Chellan, P., Mao, J., Chibale, K. & Smith, G. S. (2010). Adv. Synth. Catal. 352, 1641–1647.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814023216/su2796sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814023216/su2796Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814023216/su2796Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 1030348
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




