Abstract
In the title compound, C11H11N3O3S·3H2O, the non-H atoms of the main molecule are approximately planar, with an r.m.s. deviation of 0.030 Å. There is a bifurcated intramolecular N—H⋯(O,S) hydrogen bond present forming S(6) and S(5) ring motifs. In the crystal, O—H⋯O and N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds link the molecules into a three-dimensional network.
Keywords: crystal structure; benzohydrazide; 1,3-thiazolidene; hydrogen bonding; biological activity
Related literature
For the biological activities of thiazolidin-4-one compounds, see: Jain et al. (2012 ▶); Verma & Saraf (2008 ▶); Singh et al. (1981 ▶). For the synthesis, see: Brown (1961 ▶).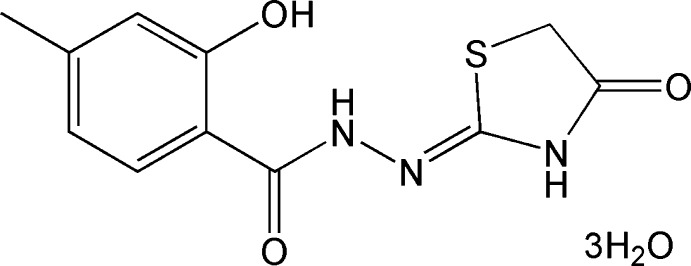
Experimental
Crystal data
C11H11N3O3S·3H2O
M r = 319.33
Triclinic,

a = 7.3739 (12) Å
b = 8.5110 (13) Å
c = 12.493 (2) Å
α = 103.047 (2)°
β = 101.385 (2)°
γ = 92.532 (2)°
V = 745.5 (2) Å3
Z = 2
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.25 mm−1
T = 296 K
0.21 × 0.20 × 0.18 mm
Data collection
Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996 ▶) T min = 0.950, T max = 0.957
5460 measured reflections
2731 independent reflections
2266 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.020
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.052
wR(F 2) = 0.154
S = 1.10
2731 reflections
191 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.53 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.44 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2001 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2001 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL2014 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶) and PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814023356/lh5733sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814023356/lh5733Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814023356/lh5733Isup3.cml
. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814023356/lh5733fig1.tif
The molecular structure of (I), showing 30% probability displacement ellipsoids. The solvent water molecules have been omitted for clarity. Dashed lines indicate hydrogen bonds.
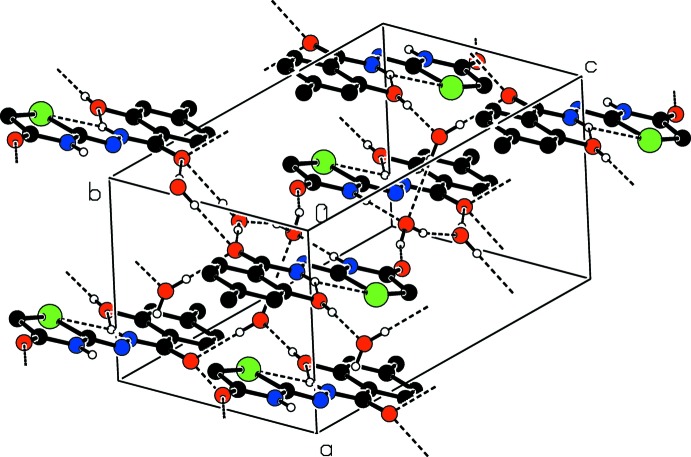
. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814023356/lh5733fig2.tif
Part of the crystal structure of (I) showing hydrogen bonds as dashed lines.
CCDC reference: 1030606
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (, ).
| DHA | DH | HA | D A | DHA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1H1OO5i | 0.84 | 1.83 | 2.655(3) | 167 |
| N1H1AS1 | 0.86 | 2.51 | 2.941(2) | 112 |
| N1H1AO1 | 0.86 | 1.92 | 2.609(3) | 137 |
| N3H3BO4 | 0.86 | 1.89 | 2.739(4) | 170 |
| O4H4OAO3ii | 0.84 | 2.10 | 2.813(4) | 143 |
| O4H4OBO6 | 0.81 | 1.81 | 2.587(4) | 161 |
| O5H5OAO2iii | 0.84 | 2.02 | 2.864(3) | 178 |
| O5H5OBO4 | 0.84 | 2.40 | 3.239(6) | 180 |
| O6H6OAO2iv | 0.84 | 2.11 | 2.947(4) | 180 |
| O6H6OBO2 | 0.84 | 2.02 | 2.862(3) | 180 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  ; (iv)
; (iv)  .
.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Key Project of the Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province, China (grant No. 2008CDA067) and the Students Science and Technology Innovation Funds of the South-Central University for Nationalities.
supplementary crystallographic information
S1. Comment
4-Thiazolidinones are compounds which have a sulfur atom at position 1, a nitrogen atom at position 3 and a carbonyl group at position 4. Derivatives of 4-thiazolidinone exhibit prominent biological activites such as antibacterial, antifungal, antitubercular, anticancer, antiinflammtory, analgesic, anticonvulsant, antidepressant, antiviral/anti-HIV, antidiabetic, muscarinic receptor 1 agonist, FSH receptor agonist, trypanocidal (anti-epimastigote) and antiarrhythmic activity (Jain, et al., 2012; Verma & Saraf, 2008; Singh et al., 1981). Several hydrogen bond acceptor sites exist in these compounds, which could potentially lead to the formation of supermolecular structures. As part of our ongoing studies, the preparation and X-ray structure determination of the title compound, (I), was undertaken.
In the title molecule (Fig. 1) the bond lengths show normal ranges of values. The non-hydrogen atoms of the main molecule are approximately planar with an r.m.s. deviation of 0.030Å. There is a bifurcated intramolecular N—H···(O,S) hydrogen bond present forming S(6) and S(5) ring motifs. In the crystal, O—H···O and N—H···O hydrogen bonds form a three-dimensional network (Fig. 2).
S2. Experimental
The synthesis followed the prodecures of Brown (1961). 4-(4-Methyl salicyloyl) thiosemicarbazide (2.25 g, 0.01 mol), ethyl bromoacetate (3.34 g, 0.02 mol) and 50 ml of ethyl alcohol were added to a round-bottom flask. The mixture was stirred for 10 minutes, then slowly warmed to boiling and stirred for 8 h. After cooling to room temperature, 40 ml of water were added and the reaction mixture was left for 12 h. The resulting precipitate was filtered and recrystallized with ethyl alcohol to give 2.30 g of the title compound. Single crystals suitable for X-ray diffraction analysis were growned by slow evaporation of a solution of the title compound in methanol/water/ether (20:7:5) at room temperature.
S3. Refinement
H atoms bonded to C and N atoms were placed in calculated positions and included in a riding-model approximation with C—H = 0.93–0.97Å, N—H = 0.86Å and Uiso(H)=1.2Ueq(C,N) or 1.5Ueq(Cmethyl). The hydroxyl H atom was placed in an 'as found' position and refined as riding with Uiso(H)=1.5Ueq(O). The H atoms bonded to the solvent water molecules were included in positions which gave the most sensible and consistent hydrogen bond interactions and were refined as riding with Uiso(H)=1.5Ueq(O).
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of (I), showing 30% probability displacement ellipsoids. The solvent water molecules have been omitted for clarity. Dashed lines indicate hydrogen bonds.
Fig. 2.
Part of the crystal structure of (I) showing hydrogen bonds as dashed lines.
Crystal data
| C11H11N3O3S·3H2O | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 319.33 | F(000) = 336 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.423 Mg m−3 |
| a = 7.3739 (12) Å | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| b = 8.5110 (13) Å | Cell parameters from 2596 reflections |
| c = 12.493 (2) Å | θ = 2.5–31.1° |
| α = 103.047 (2)° | µ = 0.25 mm−1 |
| β = 101.385 (2)° | T = 296 K |
| γ = 92.532 (2)° | Block, yellow |
| V = 745.5 (2) Å3 | 0.21 × 0.20 × 0.18 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer | 2266 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | Rint = 0.020 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 25.5°, θmin = 1.7° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996) | h = −8→8 |
| Tmin = 0.950, Tmax = 0.957 | k = −10→10 |
| 5460 measured reflections | l = −14→15 |
| 2731 independent reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | 0 restraints |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: mixed |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.052 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.154 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0721P)2 + 0.5146P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.10 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 2731 reflections | Δρmax = 0.53 e Å−3 |
| 191 parameters | Δρmin = −0.44 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| S1 | 0.43631 (10) | −0.07307 (8) | 0.18232 (6) | 0.0437 (2) | |
| O1 | 0.2052 (3) | −0.2057 (2) | −0.11504 (16) | 0.0516 (5) | |
| H1O | 0.2170 | −0.3043 | −0.1393 | 0.077* | |
| O2 | 0.1220 (3) | 0.2836 (2) | −0.06337 (16) | 0.0554 (6) | |
| O3 | 0.6060 (3) | 0.2112 (3) | 0.47760 (17) | 0.0650 (6) | |
| N1 | 0.2365 (3) | 0.0858 (3) | 0.01408 (17) | 0.0383 (5) | |
| H1A | 0.2525 | −0.0154 | 0.0060 | 0.046* | |
| N2 | 0.3037 (3) | 0.1936 (2) | 0.11730 (17) | 0.0394 (5) | |
| N3 | 0.4615 (3) | 0.2237 (3) | 0.30031 (18) | 0.0424 (5) | |
| H3B | 0.4541 | 0.3266 | 0.3168 | 0.051* | |
| C1 | 0.0805 (3) | 0.0165 (3) | −0.1811 (2) | 0.0348 (5) | |
| C2 | 0.1095 (4) | −0.1485 (3) | −0.2005 (2) | 0.0385 (6) | |
| C3 | 0.0424 (4) | −0.2507 (3) | −0.3061 (2) | 0.0459 (7) | |
| H3A | 0.0628 | −0.3597 | −0.3176 | 0.055* | |
| C4 | −0.0540 (4) | −0.1944 (3) | −0.3946 (2) | 0.0444 (6) | |
| C5 | −0.0822 (4) | −0.0295 (3) | −0.3762 (2) | 0.0436 (6) | |
| H5A | −0.1456 | 0.0114 | −0.4345 | 0.052* | |
| C6 | −0.0159 (4) | 0.0715 (3) | −0.2714 (2) | 0.0394 (6) | |
| H6A | −0.0360 | 0.1806 | −0.2603 | 0.047* | |
| C7 | −0.1260 (5) | −0.3079 (4) | −0.5088 (3) | 0.0658 (9) | |
| H7A | −0.1713 | −0.4104 | −0.4996 | 0.099* | |
| H7B | −0.0272 | −0.3230 | −0.5489 | 0.099* | |
| H7C | −0.2251 | −0.2622 | −0.5504 | 0.099* | |
| C8 | 0.1471 (4) | 0.1390 (3) | −0.0727 (2) | 0.0365 (6) | |
| C9 | 0.3903 (3) | 0.1303 (3) | 0.1930 (2) | 0.0361 (6) | |
| C10 | 0.5429 (4) | 0.1475 (4) | 0.3782 (2) | 0.0450 (6) | |
| C11 | 0.5482 (4) | −0.0303 (4) | 0.3291 (2) | 0.0484 (7) | |
| H11A | 0.4837 | −0.0940 | 0.3678 | 0.058* | |
| H11B | 0.6758 | −0.0574 | 0.3373 | 0.058* | |
| O4 | 0.4027 (6) | 0.5448 (4) | 0.3300 (3) | 0.1451 (18) | |
| H4OA | 0.3560 | 0.5885 | 0.3846 | 0.218* | |
| H4OB | 0.3221 | 0.5540 | 0.2778 | 0.218* | |
| O5 | 0.7047 (5) | 0.5074 (3) | 0.1718 (3) | 0.1071 (12) | |
| H5OA | 0.7543 | 0.5677 | 0.1388 | 0.161* | |
| H5OB | 0.6264 | 0.5168 | 0.2128 | 0.161* | |
| O6 | 0.1984 (7) | 0.5417 (4) | 0.1356 (3) | 0.160 (2) | |
| H6OA | 0.1074 | 0.5918 | 0.1148 | 0.241* | |
| H6OB | 0.1766 | 0.4661 | 0.0771 | 0.241* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| S1 | 0.0523 (4) | 0.0375 (4) | 0.0412 (4) | 0.0101 (3) | 0.0083 (3) | 0.0095 (3) |
| O1 | 0.0767 (14) | 0.0345 (10) | 0.0386 (10) | 0.0106 (9) | −0.0014 (9) | 0.0093 (8) |
| O2 | 0.0862 (15) | 0.0350 (10) | 0.0397 (11) | 0.0137 (10) | 0.0006 (10) | 0.0076 (8) |
| O3 | 0.0801 (15) | 0.0747 (15) | 0.0328 (11) | 0.0121 (12) | −0.0027 (10) | 0.0094 (10) |
| N1 | 0.0508 (13) | 0.0315 (10) | 0.0296 (11) | 0.0045 (9) | 0.0029 (9) | 0.0056 (8) |
| N2 | 0.0496 (13) | 0.0344 (11) | 0.0309 (11) | 0.0037 (9) | 0.0039 (9) | 0.0050 (9) |
| N3 | 0.0535 (13) | 0.0363 (11) | 0.0323 (11) | 0.0036 (10) | 0.0002 (10) | 0.0058 (9) |
| C1 | 0.0363 (13) | 0.0376 (13) | 0.0311 (12) | 0.0036 (10) | 0.0081 (10) | 0.0083 (10) |
| C2 | 0.0431 (14) | 0.0394 (14) | 0.0330 (13) | 0.0032 (11) | 0.0072 (11) | 0.0098 (10) |
| C3 | 0.0568 (17) | 0.0372 (14) | 0.0395 (15) | 0.0060 (12) | 0.0054 (12) | 0.0046 (11) |
| C4 | 0.0447 (15) | 0.0492 (15) | 0.0341 (14) | 0.0044 (12) | 0.0026 (11) | 0.0044 (12) |
| C5 | 0.0424 (14) | 0.0534 (16) | 0.0342 (13) | 0.0114 (12) | 0.0046 (11) | 0.0105 (12) |
| C6 | 0.0419 (14) | 0.0410 (14) | 0.0356 (13) | 0.0098 (11) | 0.0074 (11) | 0.0094 (11) |
| C7 | 0.080 (2) | 0.059 (2) | 0.0419 (17) | 0.0092 (17) | −0.0070 (15) | −0.0042 (14) |
| C8 | 0.0416 (13) | 0.0350 (13) | 0.0330 (13) | 0.0040 (10) | 0.0073 (10) | 0.0089 (10) |
| C9 | 0.0383 (13) | 0.0352 (13) | 0.0343 (13) | 0.0014 (10) | 0.0081 (10) | 0.0079 (10) |
| C10 | 0.0467 (15) | 0.0555 (16) | 0.0342 (14) | 0.0067 (12) | 0.0068 (12) | 0.0149 (12) |
| C11 | 0.0536 (17) | 0.0538 (17) | 0.0426 (15) | 0.0139 (13) | 0.0107 (13) | 0.0194 (13) |
| O4 | 0.216 (4) | 0.0616 (18) | 0.097 (2) | 0.052 (2) | −0.072 (2) | −0.0211 (16) |
| O5 | 0.162 (3) | 0.0516 (15) | 0.139 (3) | 0.0217 (17) | 0.088 (3) | 0.0362 (17) |
| O6 | 0.285 (5) | 0.0653 (19) | 0.073 (2) | 0.074 (3) | −0.067 (3) | −0.0197 (15) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| S1—C9 | 1.759 (3) | C3—H3A | 0.9300 |
| S1—C11 | 1.803 (3) | C4—C5 | 1.401 (4) |
| O1—C2 | 1.357 (3) | C4—C7 | 1.511 (4) |
| O1—H1O | 0.8400 | C5—C6 | 1.376 (4) |
| O2—C8 | 1.236 (3) | C5—H5A | 0.9300 |
| O3—C10 | 1.224 (3) | C6—H6A | 0.9300 |
| N1—C8 | 1.334 (3) | C7—H7A | 0.9600 |
| N1—N2 | 1.387 (3) | C7—H7B | 0.9600 |
| N1—H1A | 0.8600 | C7—H7C | 0.9600 |
| N2—C9 | 1.271 (3) | C10—C11 | 1.504 (4) |
| N3—C10 | 1.349 (3) | C11—H11A | 0.9700 |
| N3—C9 | 1.382 (3) | C11—H11B | 0.9700 |
| N3—H3B | 0.8600 | O4—H4OA | 0.8430 |
| C1—C6 | 1.396 (4) | O4—H4OB | 0.8119 |
| C1—C2 | 1.404 (4) | O5—H5OA | 0.8400 |
| C1—C8 | 1.489 (3) | O5—H5OB | 0.8399 |
| C2—C3 | 1.388 (4) | O6—H6OA | 0.8400 |
| C3—C4 | 1.385 (4) | O6—H6OB | 0.8400 |
| C9—S1—C11 | 91.62 (12) | C1—C6—H6A | 118.8 |
| C2—O1—H1O | 108.8 | C4—C7—H7A | 109.5 |
| C8—N1—N2 | 120.0 (2) | C4—C7—H7B | 109.5 |
| C8—N1—H1A | 120.0 | H7A—C7—H7B | 109.5 |
| N2—N1—H1A | 120.0 | C4—C7—H7C | 109.5 |
| C9—N2—N1 | 114.6 (2) | H7A—C7—H7C | 109.5 |
| C10—N3—C9 | 117.5 (2) | H7B—C7—H7C | 109.5 |
| C10—N3—H3B | 121.2 | O2—C8—N1 | 121.3 (2) |
| C9—N3—H3B | 121.2 | O2—C8—C1 | 121.7 (2) |
| C6—C1—C2 | 117.5 (2) | N1—C8—C1 | 117.0 (2) |
| C6—C1—C8 | 117.0 (2) | N2—C9—N3 | 120.5 (2) |
| C2—C1—C8 | 125.5 (2) | N2—C9—S1 | 128.4 (2) |
| O1—C2—C3 | 120.8 (2) | N3—C9—S1 | 111.13 (18) |
| O1—C2—C1 | 119.0 (2) | O3—C10—N3 | 125.6 (3) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 120.1 (2) | O3—C10—C11 | 122.5 (3) |
| C4—C3—C2 | 121.7 (3) | N3—C10—C11 | 111.9 (2) |
| C4—C3—H3A | 119.2 | C10—C11—S1 | 107.76 (18) |
| C2—C3—H3A | 119.2 | C10—C11—H11A | 110.2 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 118.5 (2) | S1—C11—H11A | 110.2 |
| C3—C4—C7 | 120.8 (3) | C10—C11—H11B | 110.2 |
| C5—C4—C7 | 120.7 (3) | S1—C11—H11B | 110.2 |
| C6—C5—C4 | 119.7 (2) | H11A—C11—H11B | 108.5 |
| C6—C5—H5A | 120.1 | H4OA—O4—H4OB | 100.2 |
| C4—C5—H5A | 120.1 | H5OA—O5—H5OB | 135.7 |
| C5—C6—C1 | 122.5 (2) | H6OA—O6—H6OB | 95.3 |
| C5—C6—H6A | 118.8 | ||
| C8—N1—N2—C9 | −178.4 (2) | C6—C1—C8—O2 | −1.6 (4) |
| C6—C1—C2—O1 | 179.0 (2) | C2—C1—C8—O2 | 177.2 (3) |
| C8—C1—C2—O1 | 0.2 (4) | C6—C1—C8—N1 | 178.9 (2) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −0.4 (4) | C2—C1—C8—N1 | −2.3 (4) |
| C8—C1—C2—C3 | −179.2 (2) | N1—N2—C9—N3 | −178.8 (2) |
| O1—C2—C3—C4 | −179.4 (3) | N1—N2—C9—S1 | 0.7 (4) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 0.0 (4) | C10—N3—C9—N2 | 176.4 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.5 (4) | C10—N3—C9—S1 | −3.1 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—C7 | −180.0 (3) | C11—S1—C9—N2 | −177.6 (3) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −0.6 (4) | C11—S1—C9—N3 | 1.9 (2) |
| C7—C4—C5—C6 | 179.9 (3) | C9—N3—C10—O3 | −177.0 (3) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | 0.2 (4) | C9—N3—C10—C11 | 2.8 (4) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | 0.3 (4) | O3—C10—C11—S1 | 178.6 (2) |
| C8—C1—C6—C5 | 179.2 (2) | N3—C10—C11—S1 | −1.2 (3) |
| N2—N1—C8—O2 | −0.1 (4) | C9—S1—C11—C10 | −0.4 (2) |
| N2—N1—C8—C1 | 179.4 (2) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O1—H1O···O5i | 0.84 | 1.83 | 2.655 (3) | 167 |
| N1—H1A···S1 | 0.86 | 2.51 | 2.941 (2) | 112 |
| N1—H1A···O1 | 0.86 | 1.92 | 2.609 (3) | 137 |
| N3—H3B···O4 | 0.86 | 1.89 | 2.739 (4) | 170 |
| O4—H4OA···O3ii | 0.84 | 2.10 | 2.813 (4) | 143 |
| O4—H4OB···O6 | 0.81 | 1.81 | 2.587 (4) | 161 |
| O5—H5OA···O2iii | 0.84 | 2.02 | 2.864 (3) | 178 |
| O5—H5OB···O4 | 0.84 | 2.40 | 3.239 (6) | 180 |
| O6—H6OA···O2iv | 0.84 | 2.11 | 2.947 (4) | 180 |
| O6—H6OB···O2 | 0.84 | 2.02 | 2.862 (3) | 180 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, −y, −z; (ii) −x+1, −y+1, −z+1; (iii) −x+1, −y+1, −z; (iv) −x, −y+1, −z.
Footnotes
Supporting information for this paper is available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: LH5733).
References
- Brown, F. C. (1961). Chem. Rev. 61, 463–521.
- Bruker (2001). APEX2 and SAINT. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Jain, A. K., Vaidya, A., Ravichandran, V., Kashaw, S. K. & Agrawal, R. K. (2012). Bioorg. Med. Chem. 20, 3378–3395. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (1996). SADABS. University of Göttingen, Germany.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Singh, S. P., Parmar, S. S., Raman, K. & Stenberg, V. I. (1981). Chem. Rev. 81, 175–203.
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Verma, A. & Saraf, S. K. (2008). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 43, 897–905. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814023356/lh5733sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814023356/lh5733Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814023356/lh5733Isup3.cml
. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814023356/lh5733fig1.tif
The molecular structure of (I), showing 30% probability displacement ellipsoids. The solvent water molecules have been omitted for clarity. Dashed lines indicate hydrogen bonds.
. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814023356/lh5733fig2.tif
Part of the crystal structure of (I) showing hydrogen bonds as dashed lines.
CCDC reference: 1030606
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report