Abstract
The title compound, C18H12Br2O6, was synthesized from Morita–Baylis–Hillman adducts. It incorporates the brominated spiro-hexadienone moiety typically exhibited by compounds of this class that exhibit biological activity. Both the brominated cyclohexadienone and the central five-membered rings are nearly planar (r.m.s. deviations of 0.044 and 0.016 Å, respectively), being almost perpendicularly oriented [interplanar angle = 89.47 (5)°]. With respect to the central five-membered ring, the brominated cyclohexadienone ring, the benzodioxol ring and the carboxylate fragment make C—O—C—C, O—C—C—C and C—C—C—O dihedral angles of −122.11 (8), −27.20 (11) and −8.40 (12)°, respectively. An intramolecular C—H⋯O hydrogen bond occurs. In the crystal, molecules are linked by non-classical C—H⋯O and C—H⋯Br hydrogen bonds resulting in a molecular packing in which the brominated rings are in a head-to-head orientation, forming well marked planes parallel to the b axis.
Keywords: Single-crystal X-ray study, spiro-hexadienone structure, Morita–Baylis–Hillman adducts
Related literature
For compounds that contain a spiro-hexadienone moiety in their structures, related biological activities and examples of brominated spiro-hexadienones, see: König & Wright (1993 ▶); Lou (2012 ▶); Sorek et al. (2009 ▶). For strategies for the synthesis of spiro-hexadienones from Morita–Baylis–Hillman aducts, see: Martins et al. (2014 ▶); Barontini et al. (2013 ▶).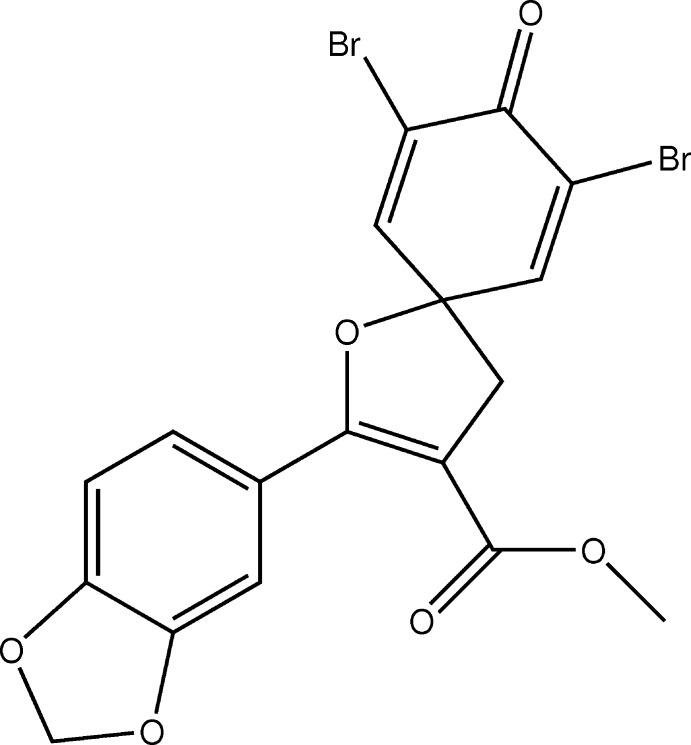
Experimental
Crystal data
C18H12Br2O6
M r = 484.10
Triclinic,
a = 8.1929 (13) Å
b = 8.4811 (14) Å
c = 12.761 (2) Å
α = 84.485 (4)°
β = 80.007 (5)°
γ = 78.077 (4)°
V = 852.7 (2) Å3
Z = 2
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 4.79 mm−1
T = 100 K
0.32 × 0.17 × 0.16 mm
Data collection
Bruker APEX CCD detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2010 ▶) T min = 0.309, T max = 0.515
27788 measured reflections
7098 independent reflections
6288 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.017
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.018
wR(F 2) = 0.047
S = 1.02
7098 reflections
236 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.57 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.39 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2010 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2010 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXLE (Hübschle et al., 2011 ▶) and SHELXL2014 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: Mercury (Macrae et al., 2006 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: OLEX2 (Dolomanov et al., 2003 ▶), PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶) and publCIF (Westrip, 2010 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, New_Global_Publ_Block. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814024763/hg5413sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814024763/hg5413Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814024763/hg5413Isup4.cdx
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814024763/hg5413Isup4.cml
. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814024763/hg5413fig1.tif
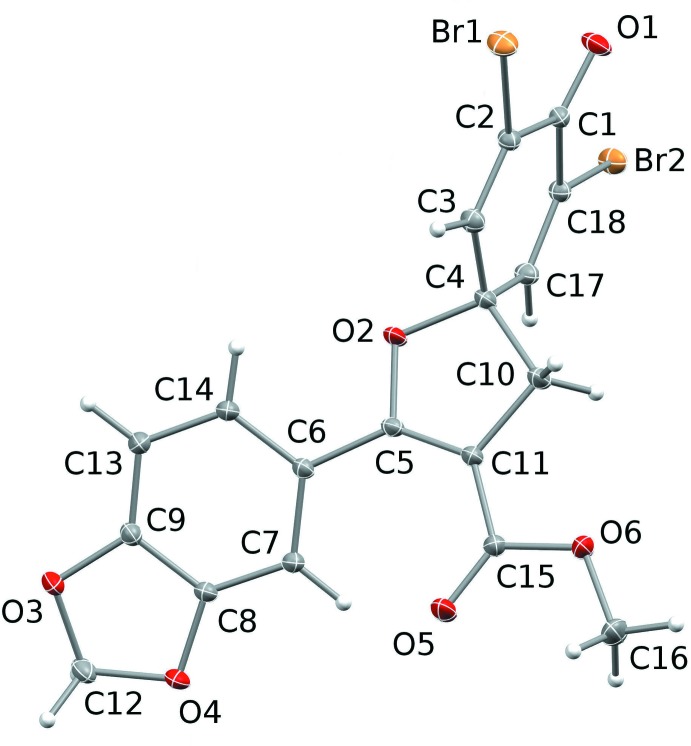
The molecular structure of the title compound with atom labels and 50% probability displacement ellipsoids.
. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814024763/hg5413fig2.tif
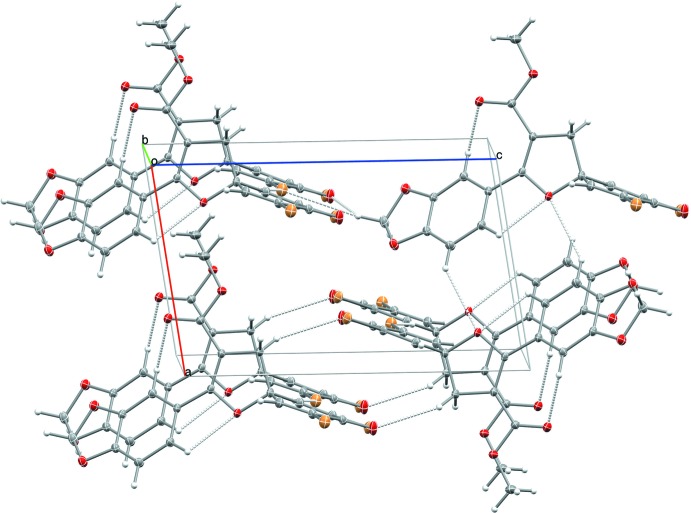
Crystal packing of the title compound, showing hydrogen bonding interactions.
CCDC reference: 1033626
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (, ).
| DHA | DH | HA | D A | DHA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C3H3O5i | 0.95 | 2.61 | 3.4272(13) | 144 |
| C7H7O5 | 0.95 | 2.34 | 2.9441(13) | 121 |
| C10H10AO1ii | 0.99 | 2.55 | 3.3995(13) | 143 |
| C12H12ABr1iii | 0.99 | 2.96 | 3.9411(12) | 173 |
| C12H12AO1iii | 0.99 | 2.53 | 3.0852(13) | 116 |
| C13H13O2iv | 0.95 | 2.63 | 3.3909(13) | 137 |
| C16H16CO5v | 0.98 | 2.59 | 3.2434(14) | 124 |
| C17H17Br1vi | 0.95 | 3.03 | 3.9069(11) | 153 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 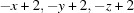 ; (ii)
; (ii) 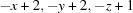 ; (iii)
; (iii) 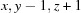 ; (iv)
; (iv) 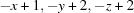 ; (v)
; (v) 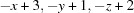 ; (vi)
; (vi)  .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge Dr Jorge Henrique Monteiro for preliminary structure refinement. This work was supported by the Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP 2009/18390–4 and 2009/51602–5), the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES) and the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq). RA is the recipient of a research grant from CNPq.
supplementary crystallographic information
S1. Introduction
Compounds containing a spiro-hexadienone moiety typically exhibit biological activity, also sharing a structural architecture observed in some natural products (König & Wright, 1993; Sorek et al., 2009). In view of the importance of this class of compounds, recent efforts resulted in a new synthetic strategy, which starts from Morita-Baylis-Hillman adducts as building blocks for organic synthesis (Martins et al., 2014). Based on this methodology, it was possible to obtain a brominated spiro-hexadienone which resulted, to our knowledge, in the first report of a halogenated spiro-hexadienone crystal structure.
S2. Experimental
S2.1. Synthesis and crystallization
Methyl 2-(2H-1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-7,9-dibromo-8-oxo-1-oxaspiro[4.5]deca-2,6,9-triene-3-carboxylate was prepared from a subset of β-ketoesters following the experimental protocol recently described by Barontini et al. (2013). A separable mixture of mono- and dibrominated (in majority) derivatives in good overall yields was obtained.
After chromatographic separation, the dibrominated compounds were easily transformed into halogenated spiro-hexadienones, in three steps procedure, starting with the Morita-Baylis-Hillman adducts.
Methyl 2-(2H-1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-7,9-dibromo-8-oxo-1-oxaspiro[4.5]deca-2,6,9-triene-3-carboxylate (48 mg, 0.1 mmoL) was dissolved in absolute chloroform-D1 (1 mL), followed by stirring until total dissolution was achieved. The solution was kept in the freezer. After two weeks, the resulting material was filtered under vacuum, washed with small portions of cold chloroform and dried in a desiccator to furnish pale yellow single crystals suitable for X-ray diffraction data collection.
S2.2. Refinement
The C-bound H atoms were positioned with idealized geometry and treated as riding atoms: phenyl, methyl and methylene C—H bond lengths were 0.95, 0.98 and 0.99 Å, respectively. The isotropic displacement parameters values (Uiso(H)) were fixed at 1.5Ueq(C) for methyl H atoms and 1.2Ueq(C) for all other attached H atoms.
S3. Results and discussion
The title compound (Fig. 1) crystallized in the space group P1 assuming a conformational structure determined by non-classical intramolecular C—H—O and intermolecular C—H—O and C—H—Br bonding (Table 1, Fig. 2). The molecule contains one six-membered (brominated ciclohexadienone) and one central five-membered rings connected by a spiro-carbon C4. The mean plane of these planar rings, C1—C2—C4—C17—C18 (r.m.s.= 0.044 Å) and C4—C10—C11—C5—O2 (r.m.s. = 0.016 Å), are almost perpendicularly oriented, making a plane-plane angle of 90.53°. With respect to the central five-membered ring, the brominated spiro-hexadienone and the benzodioxol rings make dihedral angles C5—O2—C4—C3 = -122.11 (8)° and O2—C5—C6—C14 = -27.20 (11)°, respectively, while the dihedral angle with the carboxylate fragment C10—C11—C15—O6 is -8.40 (12)°.
In the hexadienone ring of the title compound, the C2—C3, C17—C18 and C1—O1 bond lengths are 1.3351 (13), 1.3354 (13) and 1.2139 (11) Å, respectively, and the bond length between the spiro-carbon (C4) and the oxygen atom C4—O2 is 1.4684 (11) Å, similar to those reported for a related oxaspiro structure (Lou, 2012). In the latter, the plane-plane angle between the mean planes of the six-membered and the central five-membered rings in the spiro-carbon is 96.06°, slightly different from that observed in the title compound (90.53°). Further comparison also reveals different orientations of the carboxylate moiety, which makes a dihedral angle of 170.6 (1)° (C10—C11—C15—O5) in the title compound, with a corresponding angle equal to 11.3 (3)° in the related structure (Lou, 2012). This large difference is consistent with an observed C7—H7—O5 intramolecular hydrogen bond (Table 1) in the title compound, which results in a favourable conformation of the carboxylate group.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound with atom labels and 50% probability displacement ellipsoids.
Fig. 2.
Crystal packing of the title compound, showing hydrogen bonding interactions.
Crystal data
| C18H12Br2O6 | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 484.10 | F(000) = 476 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.885 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: -P 1 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 8.1929 (13) Å | Cell parameters from 9887 reflections |
| b = 8.4811 (14) Å | θ = 3.2–35.1° |
| c = 12.761 (2) Å | µ = 4.79 mm−1 |
| α = 84.485 (4)° | T = 100 K |
| β = 80.007 (5)° | Block, pale yellow |
| γ = 78.077 (4)° | 0.32 × 0.17 × 0.16 mm |
| V = 852.7 (2) Å3 |
Data collection
| Bruker APEX CCD detector diffractometer | 7098 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 6288 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Detector resolution: 8.3333 pixels mm-1 | Rint = 0.017 |
| phi and ω scans | θmax = 34.3°, θmin = 3.0° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2010) | h = −12→12 |
| Tmin = 0.309, Tmax = 0.515 | k = −13→13 |
| 27788 measured reflections | l = −20→20 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | 0 restraints |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.018 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.047 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0245P)2 + 0.2583P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.02 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.003 |
| 7098 reflections | Δρmax = 0.57 e Å−3 |
| 236 parameters | Δρmin = −0.39 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Br1 | 0.81611 (2) | 1.44904 (2) | 0.62579 (2) | 0.01782 (3) | |
| Br2 | 0.72560 (2) | 0.85491 (2) | 0.49155 (2) | 0.01638 (3) | |
| O1 | 0.75814 (11) | 1.20677 (9) | 0.48397 (6) | 0.01915 (14) | |
| O2 | 0.81234 (9) | 0.93071 (9) | 0.86474 (5) | 0.01450 (12) | |
| O3 | 0.57197 (10) | 0.68379 (9) | 1.33065 (6) | 0.01608 (13) | |
| O4 | 0.81596 (9) | 0.50402 (9) | 1.26861 (6) | 0.01609 (13) | |
| O5 | 1.24024 (10) | 0.67487 (10) | 1.01728 (6) | 0.01916 (14) | |
| O6 | 1.37041 (9) | 0.72220 (9) | 0.84968 (6) | 0.01529 (12) | |
| C1 | 0.79228 (12) | 1.13898 (10) | 0.56785 (7) | 0.01214 (14) | |
| C2 | 0.83286 (12) | 1.22429 (10) | 0.65381 (7) | 0.01222 (14) | |
| C3 | 0.88062 (12) | 1.14902 (11) | 0.74351 (7) | 0.01357 (15) | |
| H3 | 0.8963 | 1.2114 | 0.7977 | 0.016* | |
| C4 | 0.91021 (12) | 0.96878 (11) | 0.76100 (7) | 0.01264 (15) | |
| C5 | 0.91926 (12) | 0.83972 (10) | 0.92957 (7) | 0.01135 (14) | |
| C6 | 0.82769 (11) | 0.79788 (10) | 1.03513 (7) | 0.01106 (14) | |
| C7 | 0.88494 (12) | 0.65586 (11) | 1.09690 (7) | 0.01202 (14) | |
| H7 | 0.9864 | 0.5828 | 1.0731 | 0.014* | |
| C8 | 0.78592 (12) | 0.62914 (11) | 1.19325 (7) | 0.01182 (14) | |
| C9 | 0.63896 (12) | 0.73620 (11) | 1.23042 (7) | 0.01254 (14) | |
| C10 | 1.09810 (12) | 0.89627 (12) | 0.77135 (7) | 0.01504 (16) | |
| H10A | 1.1501 | 0.8183 | 0.7164 | 0.018* | |
| H10B | 1.1655 | 0.9820 | 0.7656 | 0.018* | |
| C11 | 1.08297 (12) | 0.81321 (11) | 0.88176 (7) | 0.01190 (14) | |
| C12 | 0.66357 (14) | 0.52054 (12) | 1.34563 (8) | 0.01708 (17) | |
| H12A | 0.6912 | 0.5003 | 1.4188 | 0.020* | |
| H12B | 0.5948 | 0.4422 | 1.3344 | 0.020* | |
| C13 | 0.58111 (12) | 0.87530 (11) | 1.17181 (8) | 0.01435 (15) | |
| H13 | 0.4809 | 0.9486 | 1.1975 | 0.017* | |
| C14 | 0.67762 (12) | 0.90331 (11) | 1.07223 (7) | 0.01288 (15) | |
| H14 | 0.6401 | 0.9965 | 1.0287 | 0.015* | |
| C15 | 1.23289 (12) | 0.72953 (11) | 0.92621 (7) | 0.01239 (14) | |
| C16 | 1.52864 (13) | 0.64225 (14) | 0.88280 (9) | 0.02125 (19) | |
| H16A | 1.5418 | 0.6880 | 0.9478 | 0.032* | |
| H16B | 1.6222 | 0.6580 | 0.8261 | 0.032* | |
| H16C | 1.5291 | 0.5265 | 0.8969 | 0.032* | |
| C17 | 0.85126 (12) | 0.88535 (11) | 0.68028 (7) | 0.01319 (15) | |
| H17 | 0.8524 | 0.7728 | 0.6918 | 0.016* | |
| C18 | 0.79718 (12) | 0.96291 (10) | 0.59287 (7) | 0.01170 (14) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Br1 | 0.02471 (5) | 0.00997 (4) | 0.01954 (5) | −0.00466 (3) | −0.00492 (4) | 0.00072 (3) |
| Br2 | 0.02188 (5) | 0.01408 (4) | 0.01473 (4) | −0.00300 (3) | −0.00654 (3) | −0.00306 (3) |
| O1 | 0.0307 (4) | 0.0153 (3) | 0.0107 (3) | −0.0017 (3) | −0.0063 (3) | 0.0023 (2) |
| O2 | 0.0119 (3) | 0.0197 (3) | 0.0100 (3) | −0.0004 (2) | −0.0030 (2) | 0.0048 (2) |
| O3 | 0.0186 (3) | 0.0160 (3) | 0.0112 (3) | −0.0020 (2) | 0.0011 (2) | 0.0023 (2) |
| O4 | 0.0173 (3) | 0.0147 (3) | 0.0138 (3) | −0.0009 (2) | −0.0019 (2) | 0.0056 (2) |
| O5 | 0.0146 (3) | 0.0278 (4) | 0.0125 (3) | 0.0000 (3) | −0.0034 (2) | 0.0045 (3) |
| O6 | 0.0106 (3) | 0.0196 (3) | 0.0133 (3) | 0.0005 (2) | −0.0009 (2) | 0.0011 (2) |
| C1 | 0.0137 (4) | 0.0115 (3) | 0.0101 (3) | −0.0011 (3) | −0.0008 (3) | −0.0001 (3) |
| C2 | 0.0144 (4) | 0.0101 (3) | 0.0119 (4) | −0.0024 (3) | −0.0017 (3) | 0.0000 (3) |
| C3 | 0.0153 (4) | 0.0137 (3) | 0.0123 (4) | −0.0032 (3) | −0.0034 (3) | −0.0009 (3) |
| C4 | 0.0137 (4) | 0.0143 (3) | 0.0091 (3) | −0.0018 (3) | −0.0025 (3) | 0.0023 (3) |
| C5 | 0.0129 (4) | 0.0113 (3) | 0.0096 (3) | −0.0011 (3) | −0.0037 (3) | 0.0010 (3) |
| C6 | 0.0123 (4) | 0.0117 (3) | 0.0093 (3) | −0.0021 (3) | −0.0028 (3) | 0.0004 (3) |
| C7 | 0.0128 (4) | 0.0113 (3) | 0.0114 (3) | −0.0009 (3) | −0.0024 (3) | 0.0003 (3) |
| C8 | 0.0135 (4) | 0.0111 (3) | 0.0109 (3) | −0.0020 (3) | −0.0036 (3) | 0.0012 (3) |
| C9 | 0.0139 (4) | 0.0133 (3) | 0.0101 (3) | −0.0028 (3) | −0.0012 (3) | −0.0001 (3) |
| C10 | 0.0131 (4) | 0.0196 (4) | 0.0110 (4) | −0.0014 (3) | −0.0027 (3) | 0.0036 (3) |
| C11 | 0.0122 (4) | 0.0133 (3) | 0.0095 (3) | −0.0010 (3) | −0.0024 (3) | 0.0009 (3) |
| C12 | 0.0219 (5) | 0.0149 (4) | 0.0127 (4) | −0.0037 (3) | 0.0000 (3) | 0.0027 (3) |
| C13 | 0.0139 (4) | 0.0140 (4) | 0.0130 (4) | 0.0005 (3) | −0.0006 (3) | 0.0004 (3) |
| C14 | 0.0131 (4) | 0.0127 (3) | 0.0116 (4) | −0.0004 (3) | −0.0026 (3) | 0.0015 (3) |
| C15 | 0.0115 (4) | 0.0132 (3) | 0.0117 (4) | −0.0005 (3) | −0.0023 (3) | −0.0003 (3) |
| C16 | 0.0119 (4) | 0.0287 (5) | 0.0201 (5) | 0.0015 (4) | −0.0019 (3) | 0.0012 (4) |
| C17 | 0.0151 (4) | 0.0114 (3) | 0.0126 (4) | −0.0018 (3) | −0.0031 (3) | 0.0012 (3) |
| C18 | 0.0134 (4) | 0.0110 (3) | 0.0108 (3) | −0.0018 (3) | −0.0025 (3) | −0.0011 (3) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Br1—C2 | 1.8863 (9) | C6—C14 | 1.4001 (13) |
| Br2—C18 | 1.8887 (9) | C6—C7 | 1.4158 (12) |
| O1—C1 | 1.2139 (11) | C7—C8 | 1.3775 (13) |
| O2—C5 | 1.3772 (11) | C7—H7 | 0.9500 |
| O2—C4 | 1.4684 (11) | C8—C9 | 1.3900 (13) |
| O3—C9 | 1.3721 (11) | C9—C13 | 1.3777 (13) |
| O3—C12 | 1.4444 (12) | C10—C11 | 1.5104 (13) |
| O4—C8 | 1.3746 (11) | C10—H10A | 0.9900 |
| O4—C12 | 1.4397 (13) | C10—H10B | 0.9900 |
| O5—C15 | 1.2158 (11) | C11—C15 | 1.4623 (13) |
| O6—C15 | 1.3520 (11) | C12—H12A | 0.9900 |
| O6—C16 | 1.4459 (13) | C12—H12B | 0.9900 |
| C1—C2 | 1.4887 (13) | C13—C14 | 1.4026 (13) |
| C1—C18 | 1.4904 (12) | C13—H13 | 0.9500 |
| C2—C3 | 1.3351 (13) | C14—H14 | 0.9500 |
| C3—C4 | 1.4985 (13) | C16—H16A | 0.9800 |
| C3—H3 | 0.9500 | C16—H16B | 0.9800 |
| C4—C17 | 1.4996 (13) | C16—H16C | 0.9800 |
| C4—C10 | 1.5585 (14) | C17—C18 | 1.3354 (13) |
| C5—C11 | 1.3563 (13) | C17—H17 | 0.9500 |
| C5—C6 | 1.4733 (12) | ||
| C5—O2—C4 | 109.46 (7) | C11—C10—H10A | 111.3 |
| C9—O3—C12 | 104.80 (7) | C4—C10—H10A | 111.3 |
| C8—O4—C12 | 105.13 (7) | C11—C10—H10B | 111.3 |
| C15—O6—C16 | 115.44 (8) | C4—C10—H10B | 111.3 |
| O1—C1—C2 | 122.93 (8) | H10A—C10—H10B | 109.2 |
| O1—C1—C18 | 122.50 (8) | C5—C11—C15 | 128.64 (8) |
| C2—C1—C18 | 114.57 (8) | C5—C11—C10 | 110.13 (8) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 123.31 (8) | C15—C11—C10 | 121.07 (8) |
| C3—C2—Br1 | 121.81 (7) | O4—C12—O3 | 106.94 (7) |
| C1—C2—Br1 | 114.87 (6) | O4—C12—H12A | 110.3 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 121.73 (8) | O3—C12—H12A | 110.3 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 119.1 | O4—C12—H12B | 110.3 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 119.1 | O3—C12—H12B | 110.3 |
| O2—C4—C3 | 107.32 (7) | H12A—C12—H12B | 108.6 |
| O2—C4—C17 | 106.47 (7) | C9—C13—C14 | 116.62 (9) |
| C3—C4—C17 | 114.33 (8) | C9—C13—H13 | 121.7 |
| O2—C4—C10 | 105.43 (7) | C14—C13—H13 | 121.7 |
| C3—C4—C10 | 111.56 (8) | C6—C14—C13 | 121.91 (8) |
| C17—C4—C10 | 111.13 (8) | C6—C14—H14 | 119.0 |
| C11—C5—O2 | 112.55 (8) | C13—C14—H14 | 119.0 |
| C11—C5—C6 | 135.58 (8) | O5—C15—O6 | 122.92 (9) |
| O2—C5—C6 | 111.85 (8) | O5—C15—C11 | 127.60 (9) |
| C14—C6—C7 | 120.45 (8) | O6—C15—C11 | 109.47 (8) |
| C14—C6—C5 | 117.27 (8) | O6—C16—H16A | 109.5 |
| C7—C6—C5 | 122.27 (8) | O6—C16—H16B | 109.5 |
| C8—C7—C6 | 116.53 (8) | H16A—C16—H16B | 109.5 |
| C8—C7—H7 | 121.7 | O6—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| C6—C7—H7 | 121.7 | H16A—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| O4—C8—C7 | 127.79 (8) | H16B—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| O4—C8—C9 | 109.53 (8) | C18—C17—C4 | 122.64 (8) |
| C7—C8—C9 | 122.61 (8) | C18—C17—H17 | 118.7 |
| O3—C9—C13 | 128.16 (9) | C4—C17—H17 | 118.7 |
| O3—C9—C8 | 109.94 (8) | C17—C18—C1 | 122.38 (8) |
| C13—C9—C8 | 121.85 (8) | C17—C18—Br2 | 121.91 (7) |
| C11—C10—C4 | 102.30 (7) | C1—C18—Br2 | 115.70 (6) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C3—H3···O5i | 0.95 | 2.61 | 3.4272 (13) | 144 |
| C7—H7···O5 | 0.95 | 2.34 | 2.9441 (13) | 121 |
| C10—H10A···O1ii | 0.99 | 2.55 | 3.3995 (13) | 143 |
| C12—H12A···Br1iii | 0.99 | 2.96 | 3.9411 (12) | 173 |
| C12—H12A···O1iii | 0.99 | 2.53 | 3.0852 (13) | 116 |
| C13—H13···O2iv | 0.95 | 2.63 | 3.3909 (13) | 137 |
| C16—H16C···O5v | 0.98 | 2.59 | 3.2434 (14) | 124 |
| C17—H17···Br1vi | 0.95 | 3.03 | 3.9069 (11) | 153 |
| C14—H14···O2 | 0.95 | 2.36 | 2.6937 (12) | 100 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+2, −y+2, −z+2; (ii) −x+2, −y+2, −z+1; (iii) x, y−1, z+1; (iv) −x+1, −y+2, −z+2; (v) −x+3, −y+1, −z+2; (vi) x, y−1, z.
Footnotes
Supporting information for this paper is available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: HG5413).
References
- Barontini, M., Proietti Silvestri, I., Nardi, V., Crisante, F., Pepe, G., Pari, L., Gallucci, F., Bovicelli, P. & Righi, G. (2013). Med. Chem. Res. 22, 674–680.
- Bruker (2010). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Dolomanov, O. V., Blake, A. J., Champness, N. R. & Schröder, M. (2003). J. Appl. Cryst. 36, 1283–1284.
- Hübschle, C. B., Sheldrick, G. M. & Dittrich, B. (2011). J. Appl. Cryst. 44, 1281–1284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- König, G. M. & Wright, A. D. (1993). Heterocycles, 36, 1351–1358.
- Lou, Y. (2012). Acta Cryst. E68, o1152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Macrae, C. F., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Shields, G. P., Taylor, R., Towler, M. & van de Streek, J. (2006). J. Appl. Cryst. 39, 453–457.
- Martins, L. J., Ferreira, B. V., Almeida, W. P., Lancellotti, M. & Coelho, F. (2014). Tetrahedron Lett. 55, 5264–5267.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sorek, H., Rudi, A., Goldberg, I., Aknin, M. & Kashman, Y. (2009). J. Nat. Prod. 72, 784–786. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Westrip, S. P. (2010). J. Appl. Cryst. 43, 920–925.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, New_Global_Publ_Block. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814024763/hg5413sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814024763/hg5413Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814024763/hg5413Isup4.cdx
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814024763/hg5413Isup4.cml
. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814024763/hg5413fig1.tif
The molecular structure of the title compound with atom labels and 50% probability displacement ellipsoids.
. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814024763/hg5413fig2.tif
Crystal packing of the title compound, showing hydrogen bonding interactions.
CCDC reference: 1033626
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report