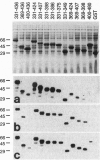
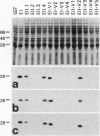
Abstract
To understand the relationship between antibodies present in patients with anti-nuclear dot (ND) autoimmune disease and the proteins they recognize, epitopes that react with the autoantibodies were mapped. A panel of fusion proteins containing different portions of the ND protein were overproduced in Escherichia coli. Immunoblot analysis with anti-ND antibodies revealed that most (10 of 12) sera recognize two major autoepitopes that are each a maximum of 8 amino acids long. The other two sera recognize one of the two epitopes. In addition to the short linear autoepitopes, a conformational epitope appears to be present on the ND antigen. Each of the two linear epitope sequences shares sequence similarities with those of several viral proteins found in the databases. Furthermore, two fusion proteins containing short Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) protein sequences that are similar to the ND epitopes were recognized by the human autoimmune sera, indicating that the autoepitopes are present in EBV protein sequences. Our results are consistent with the hypothesis that ND autoimmune disease might be associated with EBV infections.
Full text
PDF

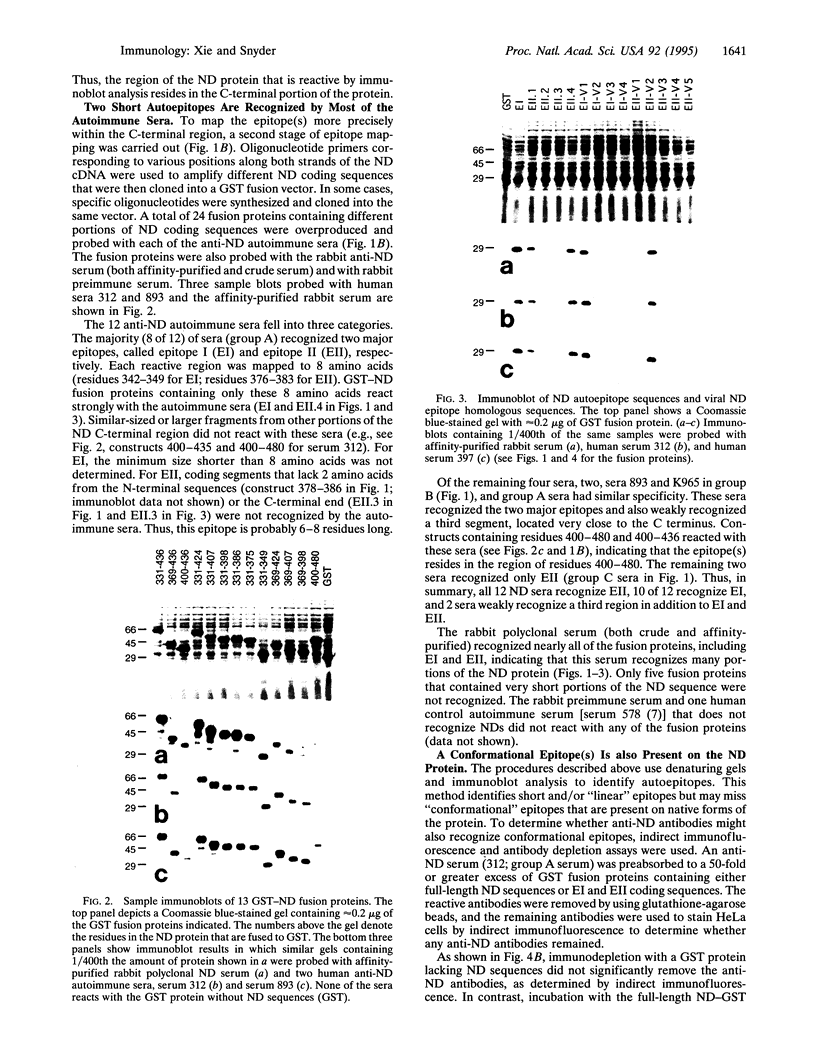


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ascoli C. A., Maul G. G. Identification of a novel nuclear domain. J Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;112(5):785–795. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.5.785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baer R., Bankier A. T., Biggin M. D., Deininger P. L., Farrell P. J., Gibson T. J., Hatfull G., Hudson G. S., Satchwell S. C., Séguin C. DNA sequence and expression of the B95-8 Epstein-Barr virus genome. Nature. 1984 Jul 19;310(5974):207–211. doi: 10.1038/310207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baranski B., Armstrong G., Truman J. T., Quinnan G. V., Jr, Straus S. E., Young N. S. Epstein-Barr virus in the bone marrow of patients with aplastic anemia. Ann Intern Med. 1988 Nov 1;109(9):695–704. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-109-9-695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodansky H. J., Grant P. J., Dean B. M., McNally J., Bottazzo G. F., Hambling M. H., Wales J. K. Islet-cell antibodies and insulin autoantibodies in association with common viral infections. Lancet. 1986 Dec 13;2(8520):1351–1353. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)92003-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan E. K., Francoeur A. M., Tan E. M. Epitopes, structural domains, and asymmetry of amino acid residues in SS-B/La nuclear protein. J Immunol. 1986 May 15;136(10):3744–3749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheeseman S. H. Infectious mononucleosis. Semin Hematol. 1988 Jul;25(3):261–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Depper J. M., Zvaifler N. J. Epstein-Barr virus. Its relationship to the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1981 Jun;24(6):755–761. doi: 10.1002/art.1780240601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guldner H. H., Netter H. J., Szostecki C., Jaeger E., Will H. Human anti-p68 autoantibodies recognize a common epitope of U1 RNA containing small nuclear ribonucleoprotein and influenza B virus. J Exp Med. 1990 Mar 1;171(3):819–829. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.3.819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koerner T. J., Hill J. E., Myers A. M., Tzagoloff A. High-expression vectors with multiple cloning sites for construction of trpE fusion genes: pATH vectors. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:477–490. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94036-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopelman R. G., Zolla-Pazner S. Association of human immunodeficiency virus infection and autoimmune phenomena. Am J Med. 1988 Jan;84(1):82–88. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(88)90012-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littler E., Zeuthen J., McBride A. A., Trøst Sørensen E., Powell K. L., Walsh-Arrand J. E., Arrand J. R. Identification of an Epstein-Barr virus-coded thymidine kinase. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):1959–1966. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04450.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maisch B., Trostel-Soeder R., Stechemesser E., Berg P. A., Kochsiek K. Diagnostic relevance of humoral and cell-mediated immune reactions in patients with acute viral myocarditis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Jun;48(3):533–545. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maul G. G., Jimenez S. A., Riggs E., Ziemnicka-Kotula D. Determination of an epitope of the diffuse systemic sclerosis marker antigen DNA topoisomerase I: sequence similarity with retroviral p30gag protein suggests a possible cause for autoimmunity in systemic sclerosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8492–8496. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra R., Venables P. J., Plater-Zyberk C., Watkins P. F., Maini R. N. Anti-cardiolipin antibodies in infectious mononucleosis react with the membrane of activated lymphocytes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1989 Jan;75(1):35–40. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moroi Y., Peebles C., Fritzler M. J., Steigerwald J., Tan E. M. Autoantibody to centromere (kinetochore) in scleroderma sera. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1627–1631. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schattner A., Rager-Zisman B. Virus-induced autoimmunity. Rev Infect Dis. 1990 Mar-Apr;12(2):204–222. doi: 10.1093/clinids/12.2.204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schooley R. T., Densen P., Harmon D., Felsenstein D., Hirsch M. S., Henle W., Weitzman S. Antineutrophil antibodies in infectious mononucleosis. Am J Med. 1984 Jan;76(1):85–90. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(84)90754-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwimmbeck P. L., Dyrberg T., Drachman D. B., Oldstone M. B. Molecular mimicry and myasthenia gravis. An autoantigenic site of the acetylcholine receptor alpha-subunit that has biologic activity and reacts immunochemically with herpes simplex virus. J Clin Invest. 1989 Oct;84(4):1174–1180. doi: 10.1172/JCI114282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szostecki C., Guldner H. H., Netter H. J., Will H. Isolation and characterization of cDNA encoding a human nuclear antigen predominantly recognized by autoantibodies from patients with primary biliary cirrhosis. J Immunol. 1990 Dec 15;145(12):4338–4347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toh B. H., Yildiz A., Sotelo J., Osung O., Holborow E. J., Kanakoudi F., Small J. V. Viral infections and IgM autoantibodies to cytoplasmic intermediate filaments. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Jul;37(1):76–82. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittingham S., McNeilage J., Mackay I. R. Primary Sjögren's syndrome after infectious mononucleosis. Ann Intern Med. 1985 Apr;102(4):490–493. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-102-4-490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xie K., Lambie E. J., Snyder M. Nuclear dot antigens may specify transcriptional domains in the nucleus. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Oct;13(10):6170–6179. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.10.6170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang C. H., Lambie E. J., Hardin J., Craft J., Snyder M. Higher order structure is present in the yeast nucleus: autoantibody probes demonstrate that the nucleolus lies opposite the spindle pole body. Chromosoma. 1989 Aug;98(2):123–128. doi: 10.1007/BF00291048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]