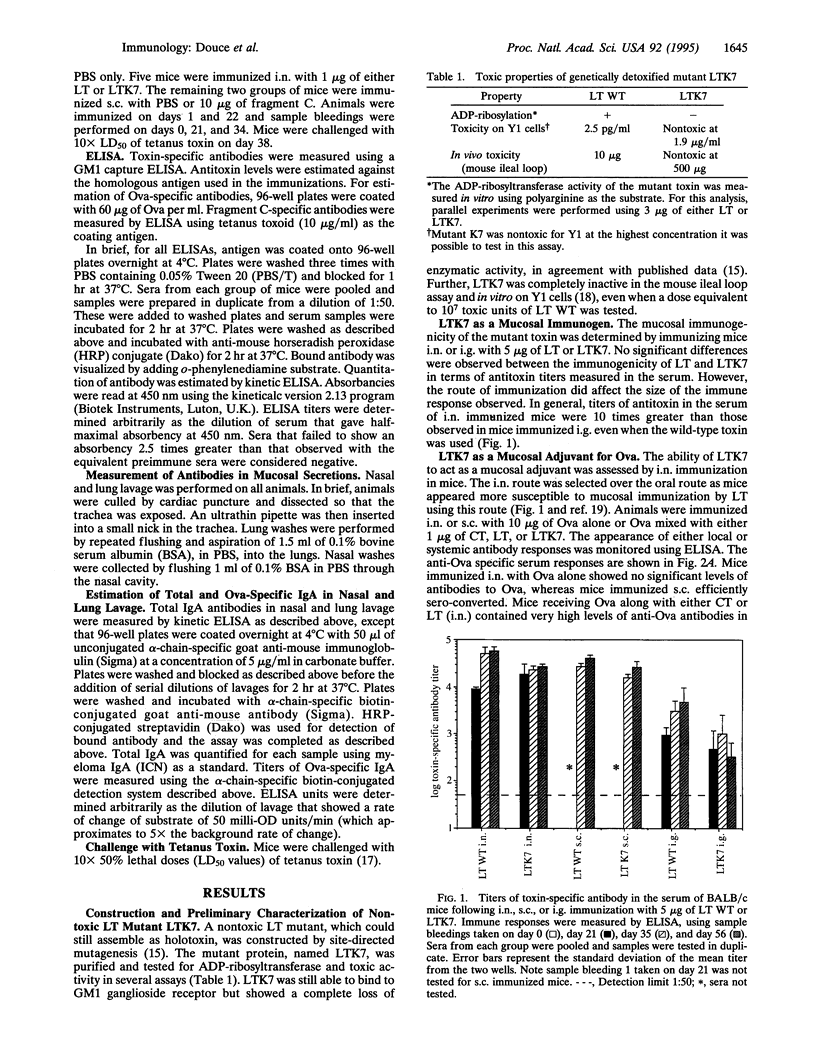
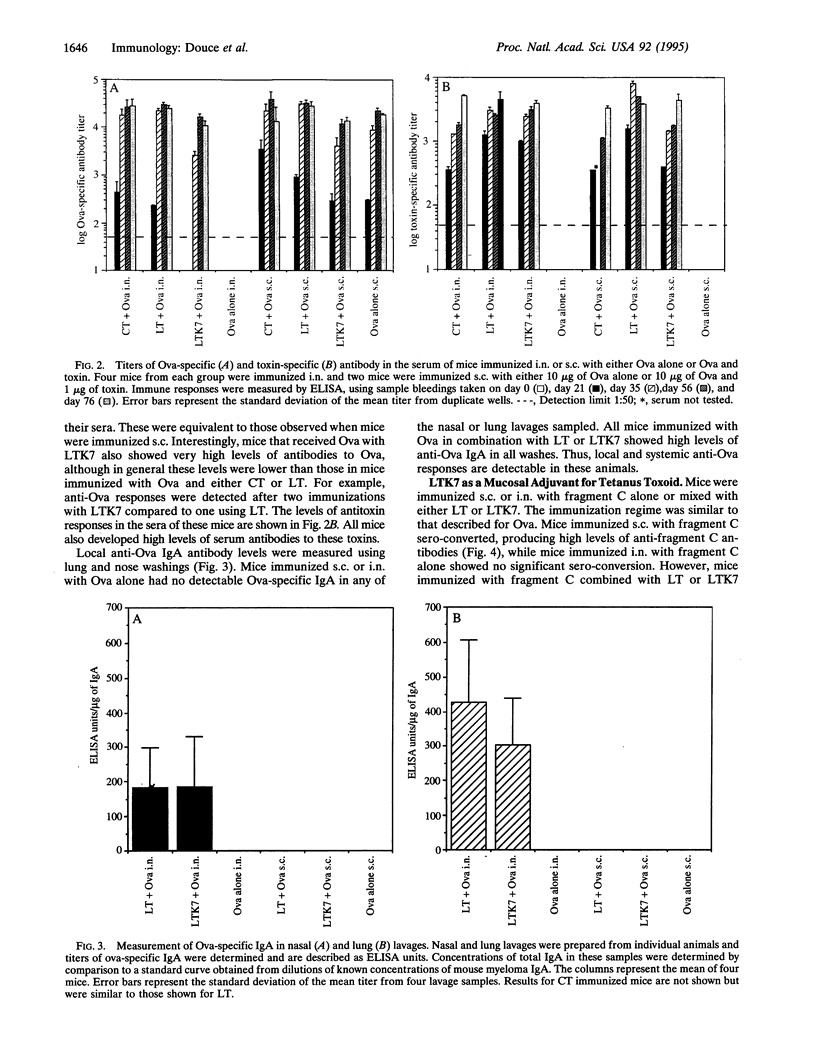
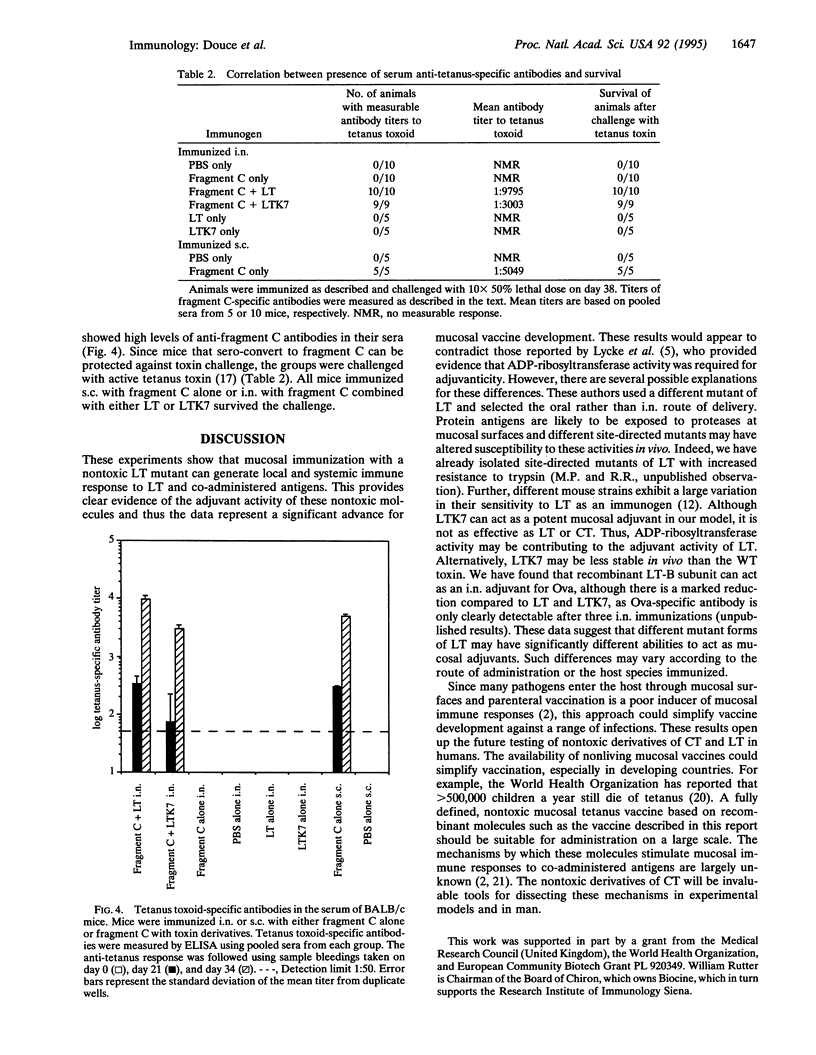
Abstract
A nontoxic mutant (LTK7) of the Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin (LT) lacking ADP-ribosylating activity but retaining holotoxin formation was constructed. By using site-directed mutagenesis, the arginine at position 7 of the A subunit was replaced with lysine. This molecule, which was nontoxic in several assays, was able to bind to eukaryotic cells and acted as a mucosal adjuvant for co-administered proteins; BALB/c mice immunized intranasally with LTK7 and ovalbumin developed high levels of serum and local antibodies to ovalbumin and toxin. In addition, mice immunized intranasally with fragment C of tetanus toxin and LTK7 were protected against lethal challenge with tetanus toxin. Thus nontoxic mutants of heat-labile toxin can act as effective intranasal mucosal adjuvants.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clare J. J., Rayment F. B., Ballantine S. P., Sreekrishna K., Romanos M. A. High-level expression of tetanus toxin fragment C in Pichia pastoris strains containing multiple tandem integrations of the gene. Biotechnology (N Y) 1991 May;9(5):455–460. doi: 10.1038/nbt0591-455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. D., Hartzog N. M., Lyon F. L. Adjuvant activity of Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin and effect on the induction of oral tolerance in mice to unrelated protein antigens. Vaccine. 1988 Jun;6(3):269–277. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(88)90223-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czerkinsky C., Russell M. W., Lycke N., Lindblad M., Holmgren J. Oral administration of a streptococcal antigen coupled to cholera toxin B subunit evokes strong antibody responses in salivary glands and extramucosal tissues. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1072–1077. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1072-1077.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donta S. T., Moon H. W., Whipp S. C. Detection of heat-labile Escherichia coli enterotoxin with the use of adrenal cells in tissue culture. Science. 1974 Jan 25;183(4122):334–336. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4122.334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougan G. 1993 Colworth Prize Lecture. The molecular basis for the virulence of bacterial pathogens: implications for oral vaccine development. Microbiology. 1994 Feb;140(Pt 2):215–224. doi: 10.1099/13500872-140-2-215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elson C. O., Ealding W. Generalized systemic and mucosal immunity in mice after mucosal stimulation with cholera toxin. J Immunol. 1984 Jun;132(6):2736–2741. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairweather N. F., Lyness V. A., Maskell D. J. Immunization of mice against tetanus with fragments of tetanus toxin synthesized in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1987 Nov;55(11):2541–2545. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.11.2541-2545.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirabayashi Y., Kurata H., Funato H., Nagamine T., Aizawa C., Tamura S., Shimada K., Kurata T. Comparison of intranasal inoculation of influenza HA vaccine combined with cholera toxin B subunit with oral or parenteral vaccination. Vaccine. 1990 Jun;8(3):243–248. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(90)90053-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J., Lycke N., Czerkinsky C. Cholera toxin and cholera B subunit as oral-mucosal adjuvant and antigen vector systems. Vaccine. 1993 Sep;11(12):1179–1184. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(93)90039-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. J., Fujihashi K., Xu-Amano J., Kiyono H., Elson C. O., McGhee J. R. Optimizing oral vaccines: induction of systemic and mucosal B-cell and antibody responses to tetanus toxoid by use of cholera toxin as an adjuvant. Infect Immun. 1993 Oct;61(10):4272–4279. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.10.4272-4279.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipscombe M., Charles I. G., Roberts M., Dougan G., Tite J., Fairweather N. F. Intranasal immunization using the B subunit of the Escherichia coli heat-labile toxin fused to an epitope of the Bordetella pertussis P.69 antigen. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Jun;5(6):1385–1392. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00785.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobet Y., Cluff C. W., Cieplak W., Jr Effect of site-directed mutagenic alterations on ADP-ribosyltransferase activity of the A subunit of Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1991 Sep;59(9):2870–2879. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.9.2870-2879.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lycke N., Tsuji T., Holmgren J. The adjuvant effect of Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxins is linked to their ADP-ribosyltransferase activity. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Sep;22(9):2277–2281. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. R., Mestecky J., Dertzbaugh M. T., Eldridge J. H., Hirasawa M., Kiyono H. The mucosal immune system: from fundamental concepts to vaccine development. Vaccine. 1992;10(2):75–88. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(92)90021-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nashar T. O., Amin T., Marcello A., Hirst T. R. Current progress in the development of the B subunits of cholera toxin and Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin as carriers for the oral delivery of heterologous antigens and epitopes. Vaccine. 1993;11(2):235–240. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(93)90023-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spangler B. D. Structure and function of cholera toxin and the related Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin. Microbiol Rev. 1992 Dec;56(4):622–647. doi: 10.1128/mr.56.4.622-647.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson A. D., Robinson A., Irons L., Stokes C. R. Adjuvant action of cholera toxin and pertussis toxin in the induction of IgA antibody response to orally administered antigen. Vaccine. 1993;11(2):113–118. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(93)90004-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



