Abstract
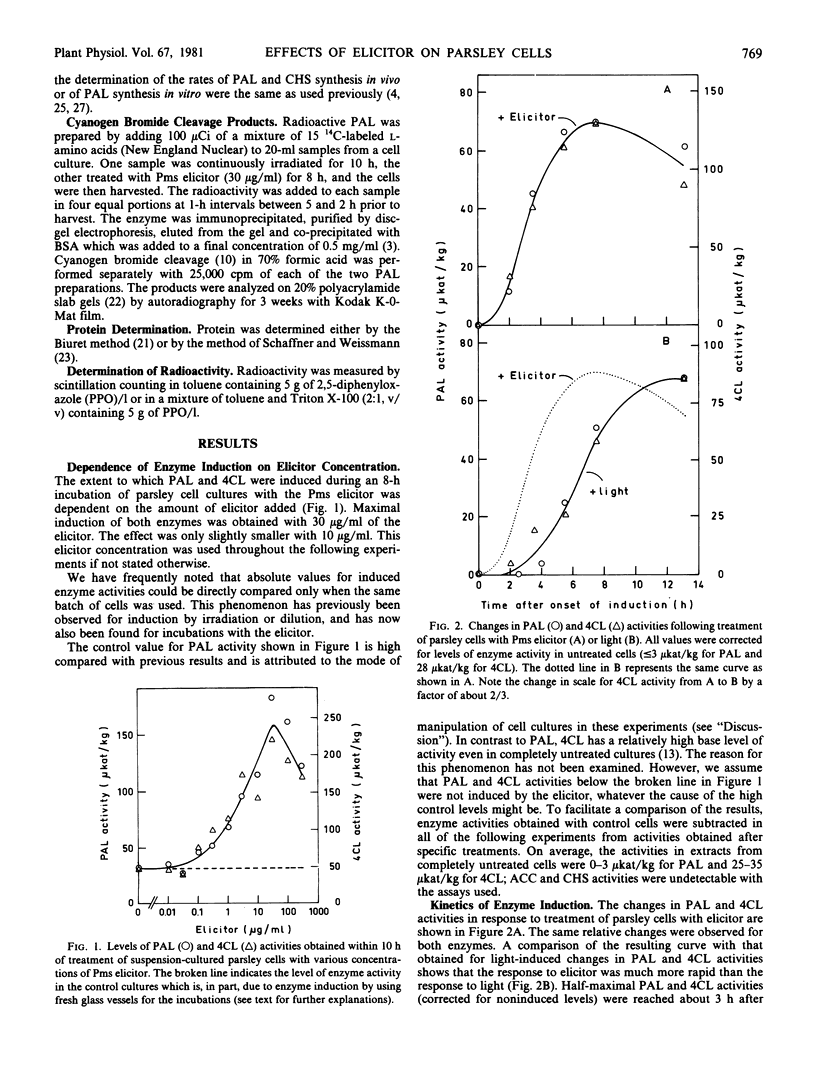
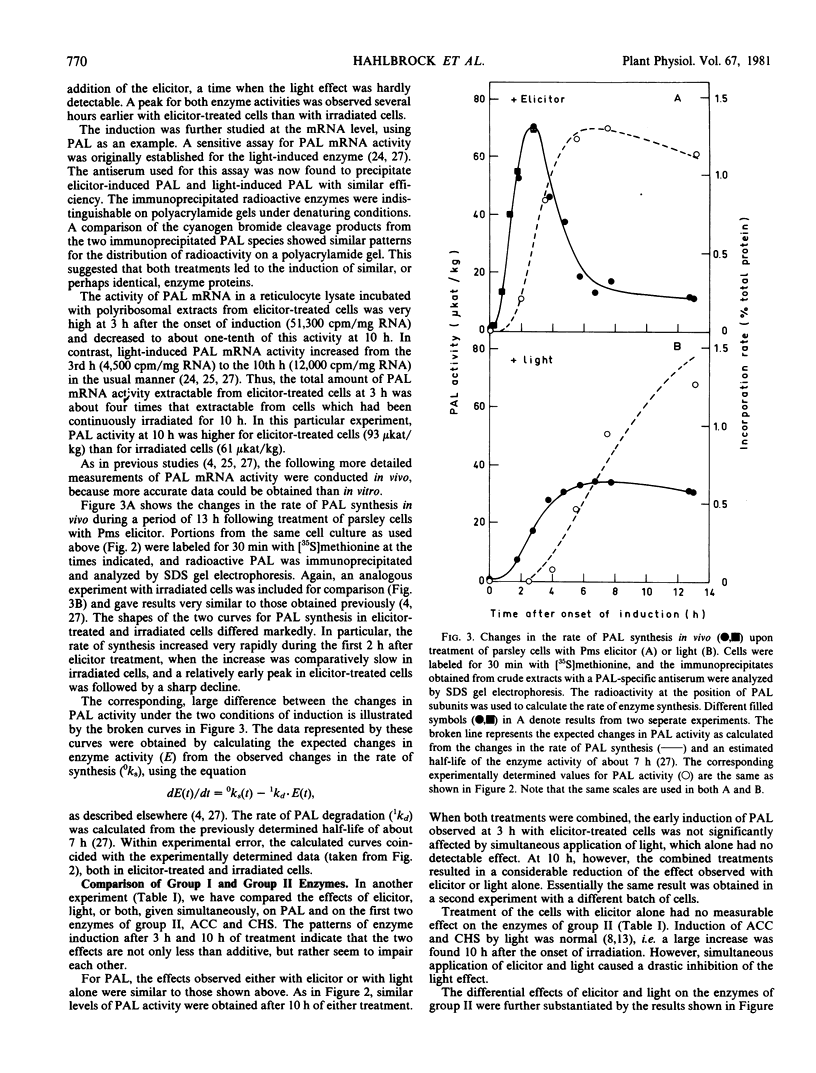
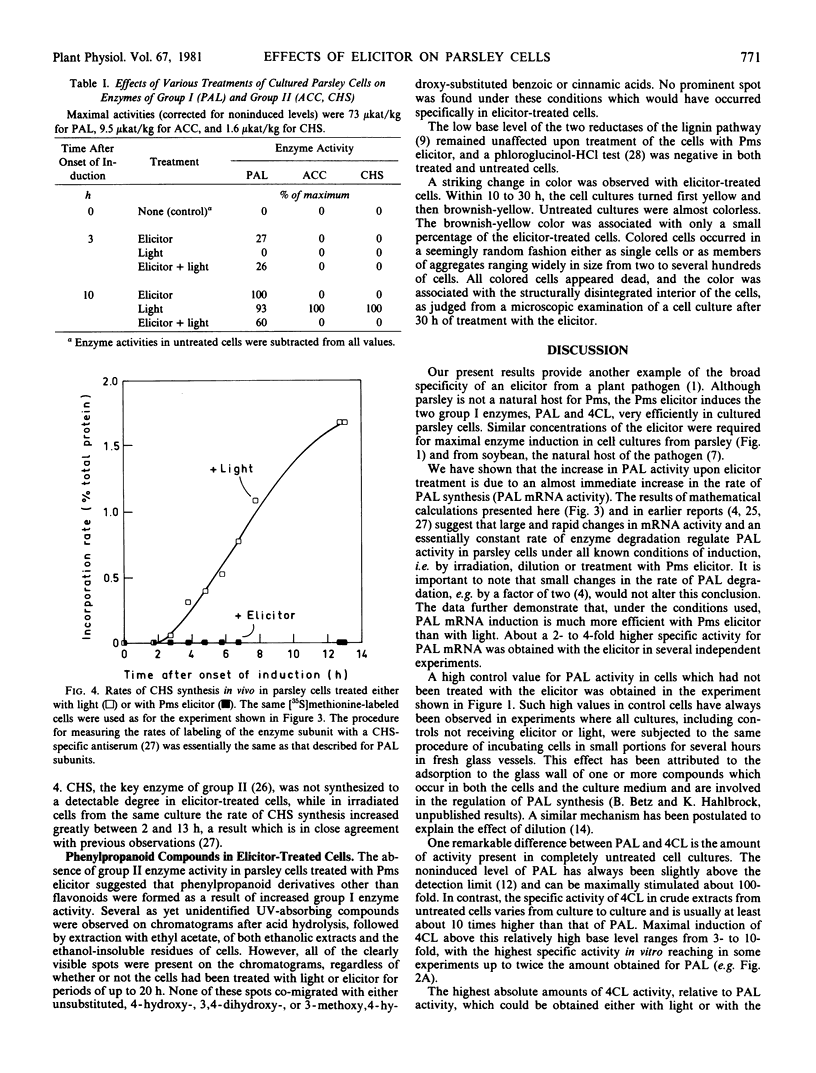
Large and rapid increases in the activities of two enzymes of general phenylpropanoid metabolism, phenylalanine ammonia-lyase and 4-coumarate:CoA ligase, occurred in suspension-cultured parsley cells (Petroselinum hortense) treated with an elicitor preparation from Phytophthora megasperma var. sojae. Highest enzyme activities were obtained with an elicitor concentration similar to that required for maximal phenylalanine ammonialyase induction in cell suspension cultures of soybean, a natural host of the fungal pathogen.
The changes in phenylalanine ammonia-lyase activity in parsley cells were caused by corresponding changes in the mRNA activity for this enzyme. Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase mRNA activity increased much faster and transiently reached a much higher level in elicitor-treated than in irradiated cell cultures. In contrast to irradiation, treatment of the cells with the elicitor did not induce the enzymes of the flavonoid glycoside pathway, as demonstrated for acetyl-CoA carboxylase and chalcone synthase. Induction of these enzymes by light was abolished by simultaneous application of the elicitor.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albersheim P., Valent B. S. Host-pathogen interactions in plants. Plants, when exposed to oligosaccharides of fungal origin, defend themselves by accumulating antibiotics. J Cell Biol. 1978 Sep;78(3):627–643. doi: 10.1083/jcb.78.3.627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayers A. R., Ebel J., Finelli F., Berger N., Albersheim P. Host-Pathogen Interactions: IX. Quantitative Assays of Elicitor Activity and Characterization of the Elicitor Present in the Extracellular Medium of Cultures of Phytophthora megasperma var. sojae. Plant Physiol. 1976 May;57(5):751–759. doi: 10.1104/pp.57.5.751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betz B., Hahlbrock K. Identity of differently-induced phenylalanine ammonia-lyases from cell suspension cultures of Petroselinum hortense. FEBS Lett. 1979 Nov 1;107(1):233–236. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80503-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betz B., Schäfer E., Hahlbrock K. Light-induced phenylalanine ammonia-lyase in cell-suspension cultures of Petroselinum hortense. Quantitative comparison of rates of synthesis and degradation. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Sep;190(1):126–135. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90259-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebel J., Ayers A. R., Albersheim P. Host-Pathogen Interactions: XII. Response of Suspension-cultured Soybean Cells to the Elicitor Isolated from Phytophthora megasperma var. sojae, a Fungal Pathogen of Soybeans. Plant Physiol. 1976 May;57(5):775–779. doi: 10.1104/pp.57.5.775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebel J., Hahlbrock K. Enzymes of flavone and flavonol-glycoside biosynthesis. Coordinated and selective induction in cell-suspension cultures of Petroselinum hortense. Eur J Biochem. 1977 May 2;75(1):201–209. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11518.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HATCH M. D., STUMPF P. K. Fat metabolism in higher plants. XVI. Acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase and acyl coenzyme A-malonyl coenzyme A transcarboxylase from wheat germ. J Biol Chem. 1961 Nov;236:2879–2885. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahlbrock K., Knobloch K. H., Kreuzaler F., Potts J. R., Wellmann E. Coordinated induction and subsequent activity changes of two groups of metabolically interrelated enzymes. Light-induced synthesis of flavonoid glycosides in cell suspension cultures of Petroselinum hortense. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Jan 2;61(1):199–206. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10012.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahlbrock K. Regulation of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase activity in cell-suspension cultures of Petroselinum hortense. Apparent rates of enzyme synthesis and degradation. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Mar 16;63(1):137–145. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10216.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahlbrock K., Schröder J. Specific effects on enzyme activities upon ditution of petroselinum hortense cell cultures into water. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Dec;171(2):500–506. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90059-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahlbrock K., Wellmann E. Light-independent induction of enzymes related to phenylpropanoid metabolism in cell suspension cultures from parsley. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 May 28;304(3):702–706. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(73)90215-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller W., Egin-Bühler B., Gardiner S. E., Knobloch K. H., Matern U., Ebel J., Hahlbrock K. Enzymes of General Phenylpropanoid Metabolism and of Flavonoid Glycoside Biosynthesis in Parsley: Differential Inducibility by Light during the Growth of Cell Suspension Cultures. Plant Physiol. 1979 Sep;64(3):371–373. doi: 10.1104/pp.64.3.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knobloch K. H., Hahlbrock K. 4-Coumarate:CoA ligase from cell suspension cultures of Petroselinum hortense Hoffm. Partial purification, substrate specificity, and further properties. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Nov;184(1):237–248. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90347-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knobloch K. H., Hahlbrock K. Isoenzymes of p-coumarate: CoA ligase from cell suspension cultures of Glycine max. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Mar 17;52(2):311–320. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb03999.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Meijers J., Peters R., van der Hoek P., van Alphen L. Electrophoretic resolution of the "major outer membrane protein" of Escherichia coli K12 into four bands. FEBS Lett. 1975 Oct 15;58(1):254–258. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80272-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner W., Weissmann C. A rapid, sensitive, and specific method for the determination of protein in dilute solution. Anal Biochem. 1973 Dec;56(2):502–514. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90217-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder J., Betz B., Hahlbrock K. Messenger RNA-controlled Increase of Phenylalanine Ammonia-Lyase Activity in Parsley: Light-Independent Induction by Dilution of Cell Suspension Cultures into Water. Plant Physiol. 1977 Sep;60(3):440–445. doi: 10.1104/pp.60.3.440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder J., Kreuzaler F., Schäfer E., Hahlbrock K. Concomitant induction of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase and flavanone synthase mRNAs in irradiated plant cells. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jan 10;254(1):57–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder J. Light-induced increase of messenger RNA for phenylalanine ammonia-lyase in cell suspension cultures of Petroselinum hortense. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Aug;182(2):488–496. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90529-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegei S., Frost P., Porto F. Effects of Indoleacetic Acid and Other Oxidation Regulators on in Vitro Peroxidation and Experimental Conversion of Eugenol to Lignin. Plant Physiol. 1960 Mar;35(2):163–167. doi: 10.1104/pp.35.2.163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann S., Hahlbrock K. Light-induced changes of enzyme activities in parsley cell suspension cultures. Purification and some properties of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (E.C.4.3.1.5). Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Jan;166(1):54–62. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90364-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zähringer U., Ebel J., Grisebach H. Induction of phytoalexin synthesis in soybean. Elicitor-induced increase in enzyme activities of flavonoid biosynthesis and incorporation of mevalonate into glyceollin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Jun;188(2):450–455. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(78)80029-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


