Abstract
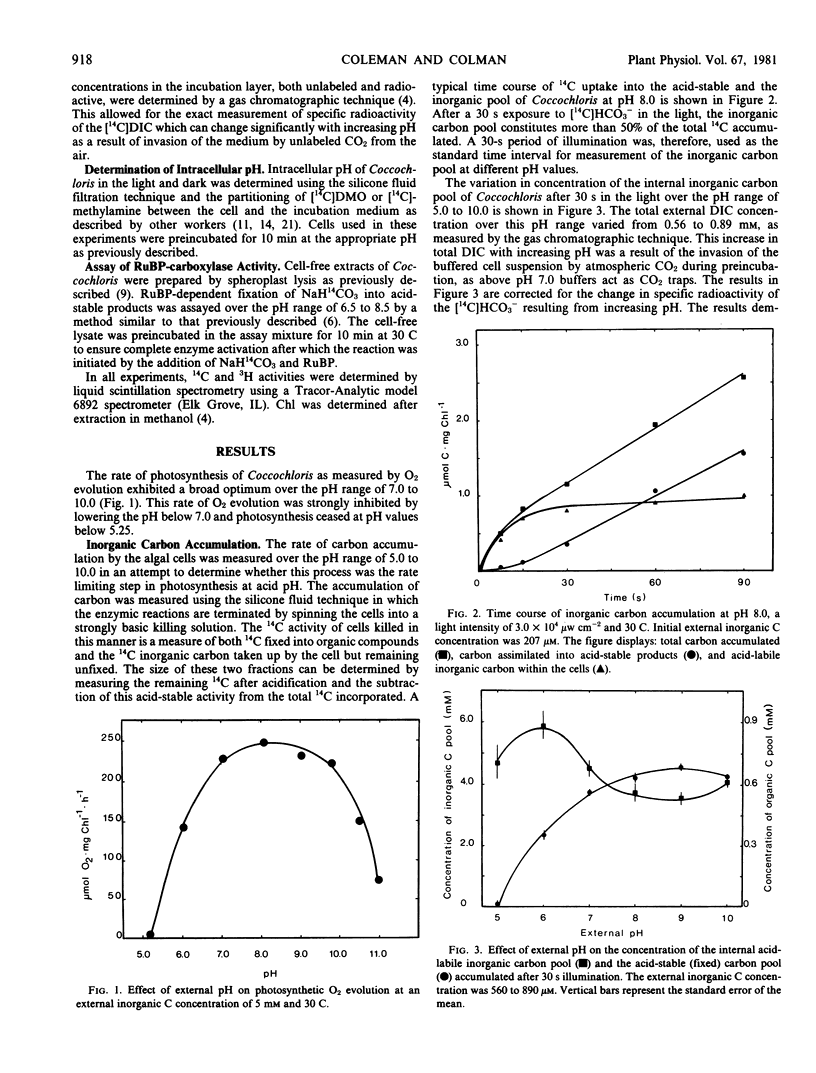
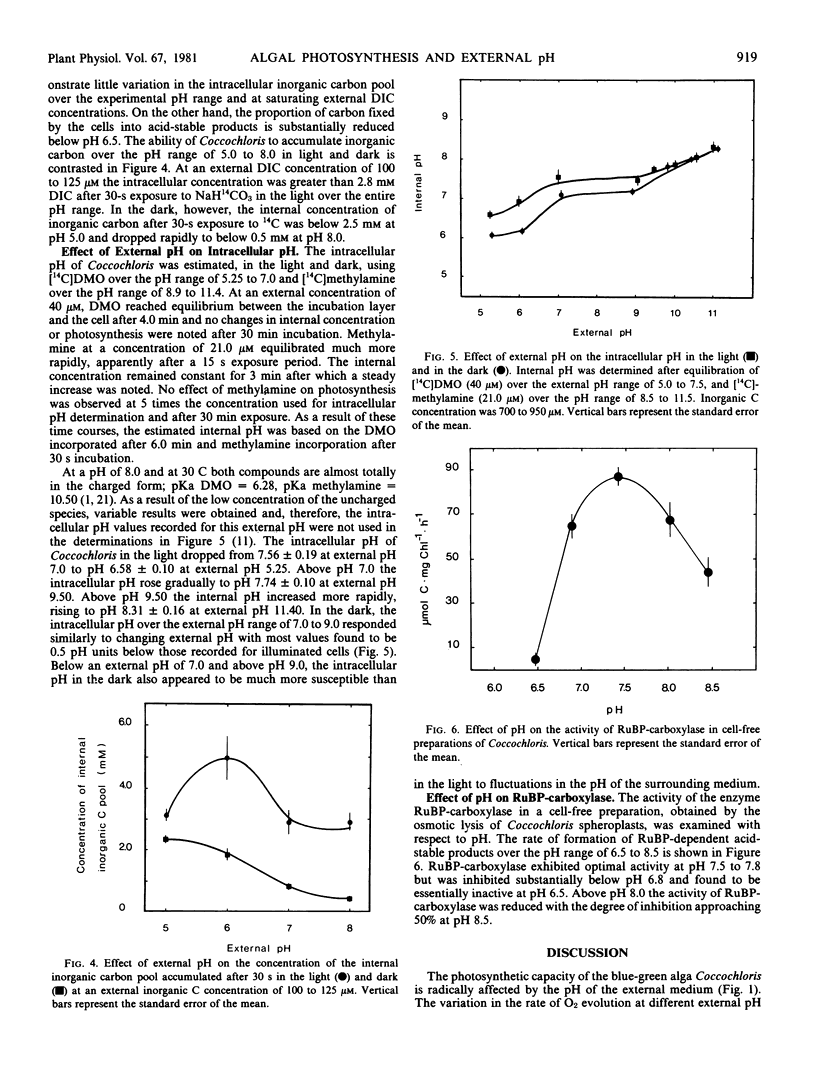
The blue-green alga Coccochloris peniocystis photosynthesizes optimally over the pH range of 7.0 to 10.0, but the O2-evolution rate is inhibited below pH 7.0 and ceases below pH 5.25. Measurement of the inorganic carbon pool in this alga in the light, using the silicone-fluid filtration technique demonstrated that the rate of accumulation of dissolved inorganic carbon remained relatively constant over a wide pH range. At external dissolved inorganic carbon concentrations of 0.56 to 0.89 millimolar the internal concentration after 30 seconds illumination was greater than 3.5 millimolar over the entire pH range. Intracellular pH measured in the light using [14C]5,5-dimethyloxazolidine-2,4-dione and [14C]methylamine dropped from pH 7.6 at an external pH of 7.0 to pH 6.6 at an external pH of 5.25. Above an external pH of 7.0 the intracellular pH rose gradually to pH 7.9 at an external pH 10.0. Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase activity of cell-free algal extracts exhibited optimal activity at pH 7.5 to 7.8 but was inactive below pH 6.5. It is suggested that the inability of Coccochloris to maintain its intracellular pH when in an acidic environment restricts its photosynthetic capacity by a direct pH effect on the principal CO2 fixing enzyme.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Addanki A., Cahill F. D., Sotos J. F. Determination of intramitochondrial pH and intramitochondrial-extramitochondrial pH gradient of isolated heart mitochondria by the use of 5,5-dimethyl-2,4-oxazolidinedione. I. Changes during respiration and adenosine triphosphate-dependent transport of Ca++, Mg++, and Zn++. J Biol Chem. 1968 May 10;243(9):2337–2348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badger M. R. Kinetic properties of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase from Anabaena variabilis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1980 Apr 15;201(1):247–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(80)90509-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birmingham B. C., Colman B. Measurement of carbon dioxide compensation points of freshwater algae. Plant Physiol. 1979 Nov;64(5):892–895. doi: 10.1104/pp.64.5.892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman J. R., Colman B. Effect of oxygen and temperature on the efficiency of photosynthetic carbon assimilation in two microscopic algae. Plant Physiol. 1980 May;65(5):980–983. doi: 10.1104/pp.65.5.980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkner G., Horner F. pH Changes in the Cytoplasm of the Blue-Green Alga Anacystis nidulans Caused by Light-dependent Proton Flux into the Thylakoid Space. Plant Physiol. 1976 Dec;58(6):717–718. doi: 10.1104/pp.58.6.717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaensslen R. E., McCarty R. E. Determination of solute accumulation in chloroplasts by rapid centrifugal transfer through silicone fluid layers. Anal Biochem. 1972 Aug;48(2):504–514. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90105-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarino L. A., Cohen S. S. Uptake and accumulation of putrescine and its lethality in Anacystis nidulans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3184–3188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. G., Colman B. Active transport and accumulation of bicarbonate by a unicellular cyanobacterium. J Bacteriol. 1980 Sep;143(3):1253–1259. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.3.1253-1259.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. G., Colman B. Evidence for HCO(3) Transport by the Blue-Green Alga (Cyanobacterium) Coccochloris peniocystis. Plant Physiol. 1980 Feb;65(2):397–402. doi: 10.1104/pp.65.2.397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padan E., Zilberstein D., Rottenberg H. The proton electrochemical gradient in Escherichia coli cells. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Apr 1;63(2):533–541. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10257.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werdan K., Heldt H. W. Accumulation of bicarbonate in intact chloroplasts following a pH gradient. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Dec 14;283(3):430–441. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(72)90260-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



