Abstract
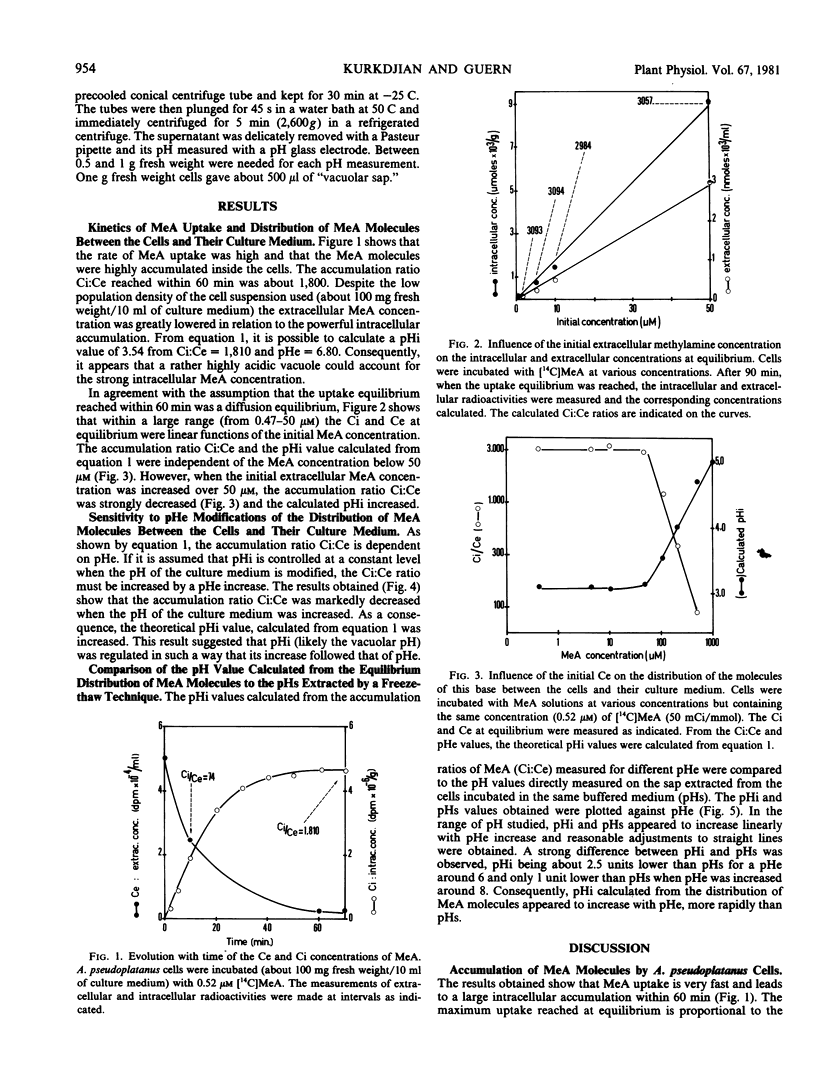
[14C]Methylamine is rapidly accumulated by Acer pseudoplatanus cells cultivated in liquid medium. The accumulation ratio of intracellular concentration to the extracellular one reaches, within 60 minutes, values as high as 3,000. This lipophilic amine appears to enter the cells through a diffusion process and is probably mainly accumulated as a cation inside the large acidic vacuolar compartment.
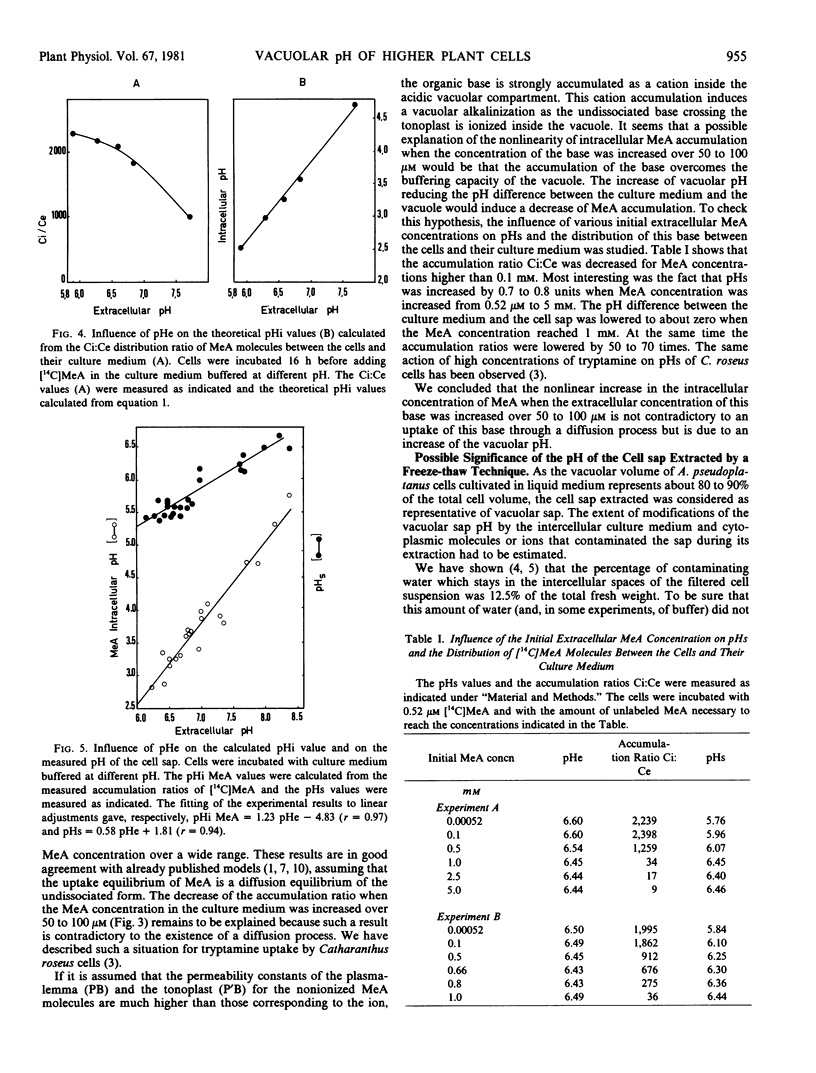
A large discrepancy has been observed between the vacuolar pH calculated from the distribution of methylamine molecules between the cells and their culture medium and the pH of the sap extracted from frozen-thawed cells, the pH of the sap being higher than the calculated values.
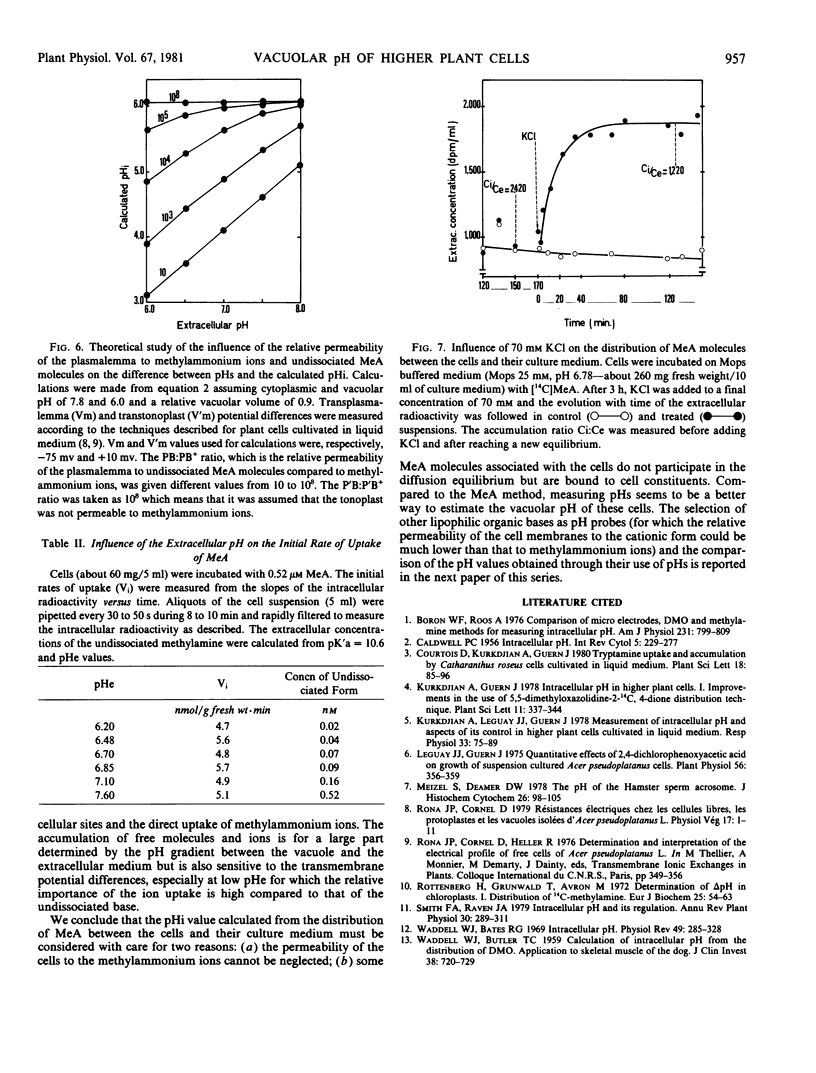
The pH estimated through the use of the methylamine method must be considered with some care as evidence has been obtained showing that the intracellular accumulation of this base depends not only on the vacuolar pH but also on: (a) the transplasmalemma and transtonoplast potential differences; (b) the relative permeabilities of these membranes to the nonionized and ionized form of the base; and (c) the adsorption of methylamine on cellular constituents.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boron W. F., Roos A. Comparison of microelectrode, DMO, and methylamine methods for measuring intracellular pH. Am J Physiol. 1976 Sep;231(3):799–809. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.231.3.799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurkdjian A., Leguay J. J., Guern J. Measurement of intracellular pH and aspects of its control in higher plant cells cultivated in liquid medium. Respir Physiol. 1978 Apr;33(1):75–89. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(78)90086-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leguay J. J., Guern J. Quantitative Effects of 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic Acid on Growth of Suspension-cultured Acer pseudoplatanus Cells. Plant Physiol. 1975 Sep;56(3):356–359. doi: 10.1104/pp.56.3.356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meizel S., Deamer D. W. The pH of the hamster sperm acrosome. J Histochem Cytochem. 1978 Feb;26(2):98–105. doi: 10.1177/26.2.24069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottenberg H., Grunwald T., Avron M. Determination of pH in chloroplasts. I. Distribution of ( 14 C) methylamine. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Jan 31;25(1):54–63. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01666.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WADDELL W. J., BUTLER T. C. Calculation of intracellular pH from the distribution of 5,5-dimethyl-2,4-oxazolidinedione (DMO); application to skeletal muscle of the dog. J Clin Invest. 1959 May;38(5):720–729. doi: 10.1172/JCI103852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waddell W. J., Bates R. G. Intracellular pH. Physiol Rev. 1969 Apr;49(2):285–329. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1969.49.2.285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


