Abstract
The de novo synthesis of the non-essential amino acid serine is often upregulated in cancer. In this study we demonstrate that the serine catabolic enzyme, mitochondrial serine hydroxymethyltransferase (SHMT2) is induced when Myc-transformed cells are subjected to hypoxia. In mitochondria, SHMT2 can initiate the degradation of serine to CO2 and NH4+ resulting in net production of NADPH from NADP+. Knockdown of SHMT2 in Myc-dependent cells reduced cellular NADPH/NADP+ ratio, increased cellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) and triggered hypoxia-induced cell death. In vivo, SHMT2 suppression led to impaired tumor growth. In myc-amplified neuroblastoma patient samples, there was a significant correlation between SHMT2 and Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 α (HIF-1α) and SHMT2 expression correlated with unfavorable patient prognosis. Together these data demonstrate that mitochondrial serine catabolism supports tumor growth by maintaining mitochondrial redox balance and cell survival.
Keywords: Cancer metabolism, Serine, Hypoxia, Redox, NADPH
Introduction
Since Otto H. Warburg discovered that tumor cells show high glucose consumption in the 1920s (1), oncologists have been interested in finding out how tumor cells adapt metabolic pathways to obtain advantages in cell proliferation and tumor growth. Previously we and others demonstrated that serine is an activator of pyruvate kinase M2 (PKM2), the pyruvate kinase isoform ubiquitously found in cancers that catalyzes the final reaction in glycolysis (2, 3). Intracellular serine depletion reduces PKM2 enzymatic activity, leading to the accumulation of upstream glycolytic intermediates, including 3-phosphoglycerate, which provides the precursor for de novo serine synthesis. Two recent reports suggest that the genomic regions encoding phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase (PHGDH), the first enzyme in the serine synthetic pathway, are amplified in breast cancer and melanomas (4, 5), leading to diversion of the glycolytic intermediate 3-phosphoglycerate to serine synthesis. The cytosolic synthesis of serine in many cancer cells appears to be in excess of that needed to support macromolecular synthesis (4). These observations led us to consider whether serine catabolism also contributes to tumor cell survival and proliferation.
Serine catabolism is initiated by serine hydroxymethyltransferase (SHMT) activity, catalyzed in the cytosol by SHMT1 and in the mitochondrion by SHMT2. SHMTs catalyze a reversible reaction converting serine to glycine, with concurrent methylene-THF generation. Increased SHMT enzyme activity has been detected in human colon cancer and rat sarcoma (6). While it is possible serine catabolism contributes to the anabolic needs of a growing cell for glycine, whether serine catabolism contributes to antioxidative defense for cell survival has not been investigated.
One common problem faced by solid tumors is hypoxia, which refers to oxygen deficiency. The hypoxia-inducible factors (HIFs) are the major transcriptional regulators of hypoxic adaptation of tumor cells. HIFs are heterodimeric transcription factors composed of an oxygen-regulated α subunit and a constitutively expressed β subunit. Under normoxia, the α subunits are hydroxylated on proline residues, enabling recognition by the von-Hippel Lindau (VHL) tumor suppressor followed by proteosomal degradation. As hydroxylation is inhibited under hypoxia, the α subunits accumulate and form heterodimers with the β subunit to regulate the expression of hundreds of genes (7, 8). As oxygen is the terminal electron acceptor of the mitochondrial electron transport chain (ETC), under hypoxia reduced oxygen levels leads to electrons leaking out from ETC, forming reactive oxygen species (ROS) (9, 10). This creates a redox-stress in tumor mitochondria. Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 1 (PDK1), a HIF-1 target, has been shown to suppress pyruvate entry into the TCA cycle, thus reducing ROS generation and cell death (11). However, it is unclear whether there are other metabolic pathway(s) regulated by HIF that influence redox and cell viability in mitochondria.
Here we present evidence for a critical role of mitochondrial serine catabolism in NADPH production and redox regulation under hypoxia. Specifically, we show that the mitochondrial isoform of SHMT, SHMT2, is induced by hypoxic stress through HIF-1. This induction is most apparent in cells overexpressing the oncogenic transcription factor Myc. When such cells are subjected to hypoxia, they require SHMT2 expression to maintain the cellular NADPH/NADP+ ratio. Depletion of SHMT2 in hypoxic cells increases ROS levels, consequently leading to cell death.
Results
The mitochondrial isoform SHMT2 is upregulated in cancers and coexpressed with PHGDH
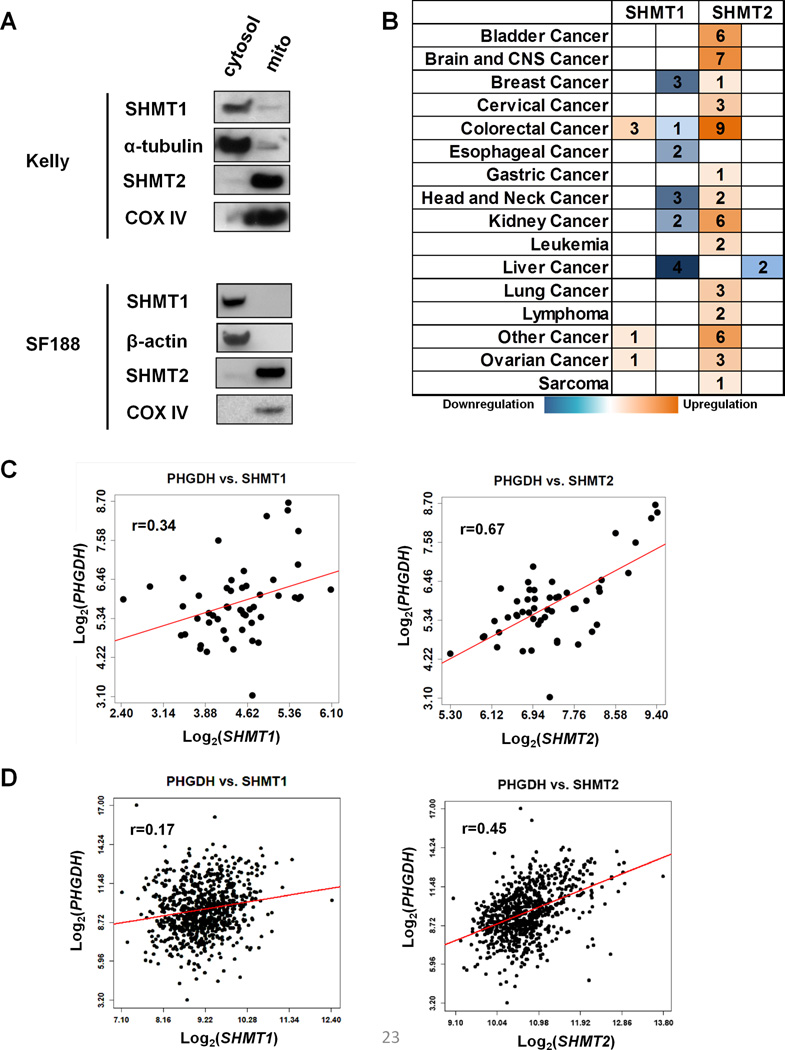
Increased PHGDH enzyme activity is associated with upregulation of SHMT enzyme activity in tumors (6), suggesting that SHMT may be critical for downstream serine catabolism that promotes tumor development. Two SHMT isoforms have been identified in mammals (12, 13): SHMT1 is localized in cytosol, while SHMT2 is in the mitochondrion (Figure 1A). Using the Oncomine database (14), we found that SHMT2 but not SHMT1 is overexpressed in a variety of human cancers (Figure 1B). Since PHGDH, the first enzyme in the de novo serine synthetic pathway, has been shown to be upregulated in cancers (4, 5), we next determined whether either SHMT isoform’s expression was correlated with PHGDH in cancer. We examined the relationship between the two SHMT isoforms with PHGDH in human neuroblastoma samples. SHMT2 showed a stronger correlation with PHGDH expression (r=0.67) compared to that with SHMT1 (r=0.34) (Figure 1C). In addition, the correlation of SHMT2 and PHGDH expression is remarkably more prominent in samples from patients who died from their disease (r=0.9) compared to the correlation found in samples from patients where the neuroblastoma regressed (alive) (r=0.42) (Supplementary Figure 1A). A similar analysis was performed using RNAseq data from human breast cancer samples. Consistently, the correlation of SHMT2 and PHGDH expression (r=0.45) is stronger compared to the correlation of SHMT1 and PHGDH expression (r=0.17) (Figure 1D). Additionally, Kaplan-Meier survival analysis indicated breast cancer patients with low SHMT2 expression survive better than the patients with high SHMT2 expression (Supplementary Figure 1B). Together, these data suggest that the mitochondrial isoform SHMT2 is an important utilizer of serine produced through enhanced PHGDH activity in tumors.
Figure 1. The mitochondrial isoform of SHMT is overexpressed in cancers.
(A) Immunoblots for cytosolic and mitochondrial fractions of Kelly or SF188 cells are shown. COX IV is a mitochondrial marker, α-tubulin and β-actin are cytosolic markers. (B) The expression of SHMT isoforms in human cancers. Analysis was performed using the Oncomine Database. Orange indicates overexpression in cancer, blue indicates downregulation in cancer, the numbers indicate the number of cases for each cancer where the fold changes of gene expression are statistically significant (fold change ≥2, p<1E-4). (C) SHMT2 expression correlates with PHGDH expression in neuroblastoma. Pearson correlation: p (PHGDH vs SHMT1)=0.014 (left), p (PHGDH vs SHMT2)=9.6×10−8 (right). (D) SHMT2 expression correlates with PHGDH expression in breast cancer. p (PHGDH vs SHMT1)=7×10−7 (left), p (PHGDH vs SHMT2)<1×10−8 (right).
SHMT2 is induced upon hypoxia in a HIF-1-dependent manner
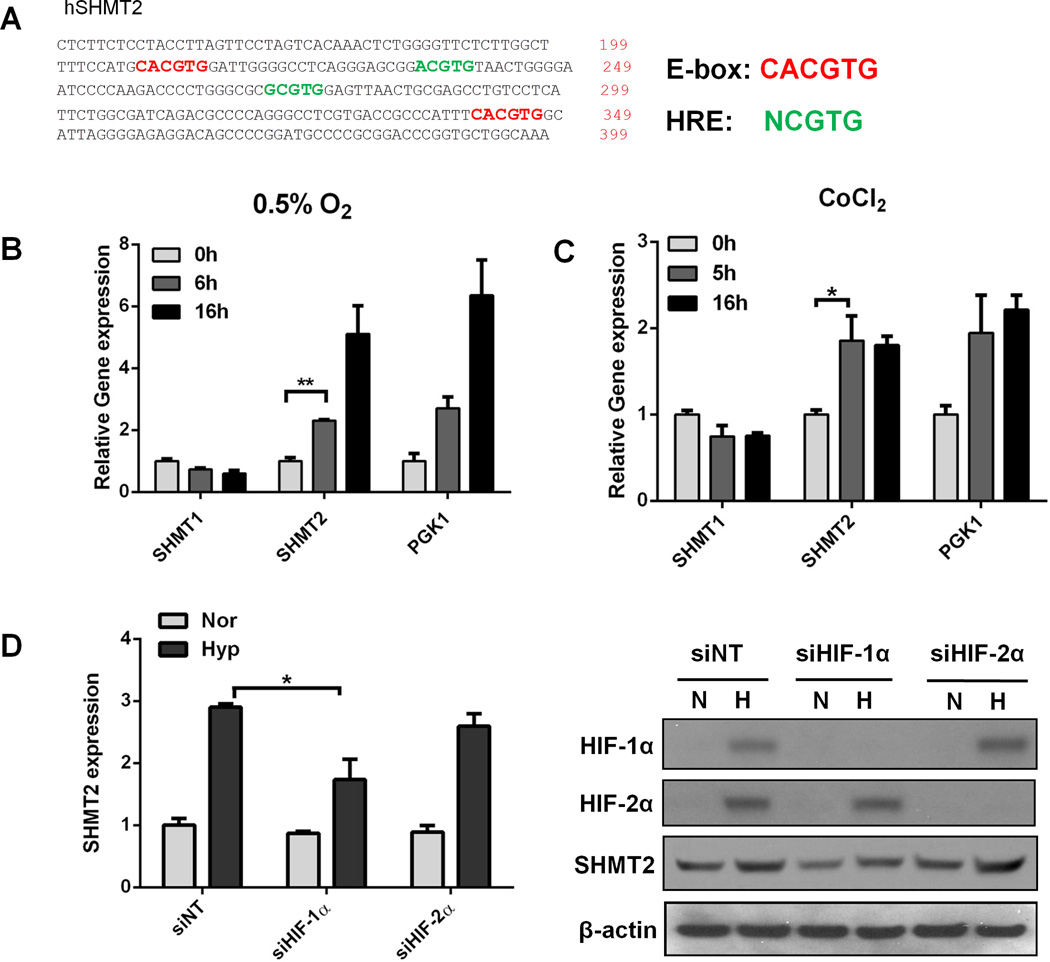
To identify whether changes in other metabolic enzymes were associated with SHMT2 overexpression, we analyzed gene expression data from other cancer samples (15). We found that the expression of phosphoglycerate kinase isoenzyme 1 (PGK1) and lactate dehydrogenese A (LDHA) significantly correlate with SHMT2 expression (r2PGK1vsSHMT2=0.87, p<0.001; r2LDHAvsSHMT2=0.84, p<0.001). Since PGK1 and LDHA are both HIF-1 targets that are induced upon hypoxia (16, 17), we asked whether SHMT2 is also regulated under hypoxia through HIF. A promoter analysis for SHMT2 indentified two hypoxia response elements (HRE), which are the binding sites for HIFs (Figure 2A), suggesting that HIF may be responsible for the upregulation of SHMT2. To test whether SHMT2 is induced upon hypoxia, Kelly cells (a neuroblastoma cell line) were exposed to 0.5% O2 for 6 or 16 hours. Hypoxia significantly induced SHMT2 mRNA expression, while the expression of SHMT1 was not increased (Figure 2B). In addition, treating cells with CoCl2, a HIF stabilizer, also induced SHMT2 expression (Figure 2C). Since HIF-2α expression is tissue-specific while HIF-1α is ubiquitously expressed (8), we next determined which HIF isoform is responsible for the hypoxic induction of SHMT2. The hypoxic induction of SHMT2 was reduced in HIF-1α knockdown cells while knocking down HIF-2α did not affect SHMT2 expression under hypoxia (Figure 2D, Supplementary Figure 2), suggesting that the hypoxic induction of SHMT2 depends on HIF-1.
Figure 2. The hypoxic induction of SHMT2 depends on HIF-1.
(A) The promoter sequence of human SHMT2. E-boxes (CACGTG) are shown in red, HREs (NCGTG) are shown in green. (B) Hypoxia induces SHMT2 expression. Kelly cells were exposed to normoxia or 0.5% O2 for 6 or 16 hours. mRNA levels were measured using Q-PCR and normalized to normoxia control. (C) CoCl2 treatment induces SHMT2 expression. Kelly cells were treated with 50µM CoCl2 for 5 or 16 hours. mRNA levels were measured using Q-PCR and normalized to normoxia control. (D) The hypoxic induction of SHMT2 depends on HIF-1. Kelly cells were transfected with 30nM control siRNA or siRNA targeting HIF-1α or HIF-2α. After 48 hours, cells were exposed to 0.5% O2 for 8 (for Q-PCR) or 16 hours (for immunoblot). mRNA levels were measured using Q-PCR and normalized to normoxia control (left panel). HIF-1α and HIF-2α knockdown were confirmed by immunoblot (right panel). Nor= Normoxia; Hyp= Hypoxia. For panel B-D, data represent Mean ± S.D of triplicate PCR reactions, representative of three independent experiments is shown. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, determined by Student’s two-tailed t-test.
The hypoxic induction of SHMT2 requires Myc amplification
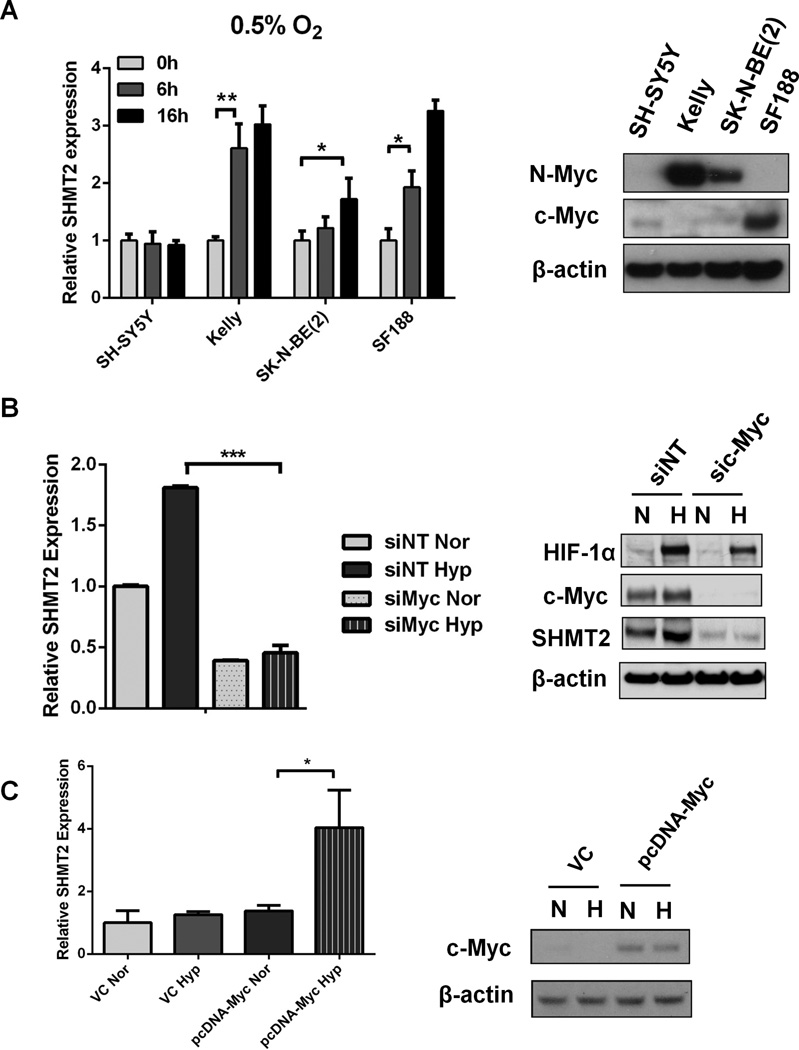
Intriguingly, the hypoxic induction of SHMT2 was not observed in every cell line we tested. Two neuroblastoma cell lines, Kelly and SK-N-BE(2), and one glioblastoma cell line, SF188, showed significant SHMT2 induction under hypoxia, but others (SH-SY5Y, H293T, H1299 and HT1080) did not upregulate SHMT2 upon hypoxia (Figure 3A, Supplementary figure 3). Since SHMT2 is a reported Myc target gene (18, 19), and two Myc binding sites (E-Box) were localized adjacent to the two HREs in the SHMT2 promoter (Figure 2A), we hypothesized that the hypoxic induction of SHMT2 also requires Myc. Indeed, the three cell lines that demonstrated SHMT2 induction under hypoxia all expressed high levels of N-Myc or c-Myc, while the other cell lines had low or undetectable Myc expression (Figure 3A, Supplementary Figure 3). To determine whether Myc is necessary for the hypoxic induction of SHMT2, we repressed Myc activity in SF188 cells using siRNA targeting c-Myc. Downregulation of Myc expression not only reduced basal SHMT2 expression, but also eliminated the hypoxic induction of SHMT2 (Figure 3B). Moreover, overexpressing Myc in SH-SY5Y cells conferred the ability to upregulate SHMT2 under hypoxia (Figure 3C). The fact that cells expressing c-Myc also possess the ability to upregulate SHMT2 indicates that the hypoxic induction of SHMT2 is not limited to N-Myc amplified neuroblastoma. These data are consistent with the recent demonstration that elevated Myc induces transcriptional amplification of adaptive gene expression programs (20).
Figure 3. MYC is required for the hypoxic induction of SHMT2.
(A)SH-SY5Y, Kelly, SK-N-BE(2) and SF188 cells were exposed to 0.5% O2 for 6 or 16 hours. Left: mRNA levels were measured using Q-PCR and normalized to normoxia control. Right: Immunoblots of N-Myc and c-Myc in the four cell lines. (B) SF188 cells were transfected with c-Myc siRNA and exposed to normoxia (Nor) or 0.5% O2 (Hyp) for 8 (for Q-PCR) or 16 hours (for immunoblot), mRNA levels were measured using Q-PCR (left). Protein levels of HIF-1α, Myc and SHMT2 were exammed by immunoblot (right). (C) SH-SY5Y cells were transfected with 2µg pcDNA-c-Myc or vector control (VC). After 48h, transfected cells were exposed to normoxia (Nor) or 0.5% O2 (Hyp) for 8h. mRNA levels were measured using Q-PCR (left). c-Myc overexpression was confirmed using immunoblot (right). For panel A–C, Data represent Mean ± S.D of triplicate PCR reactions, representative of three independent experiments is shown. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, determined by Student’s two-tailed t-test.
SHMT2 is necessary for maintaining redox homeostasis and cell survival under hypoxia
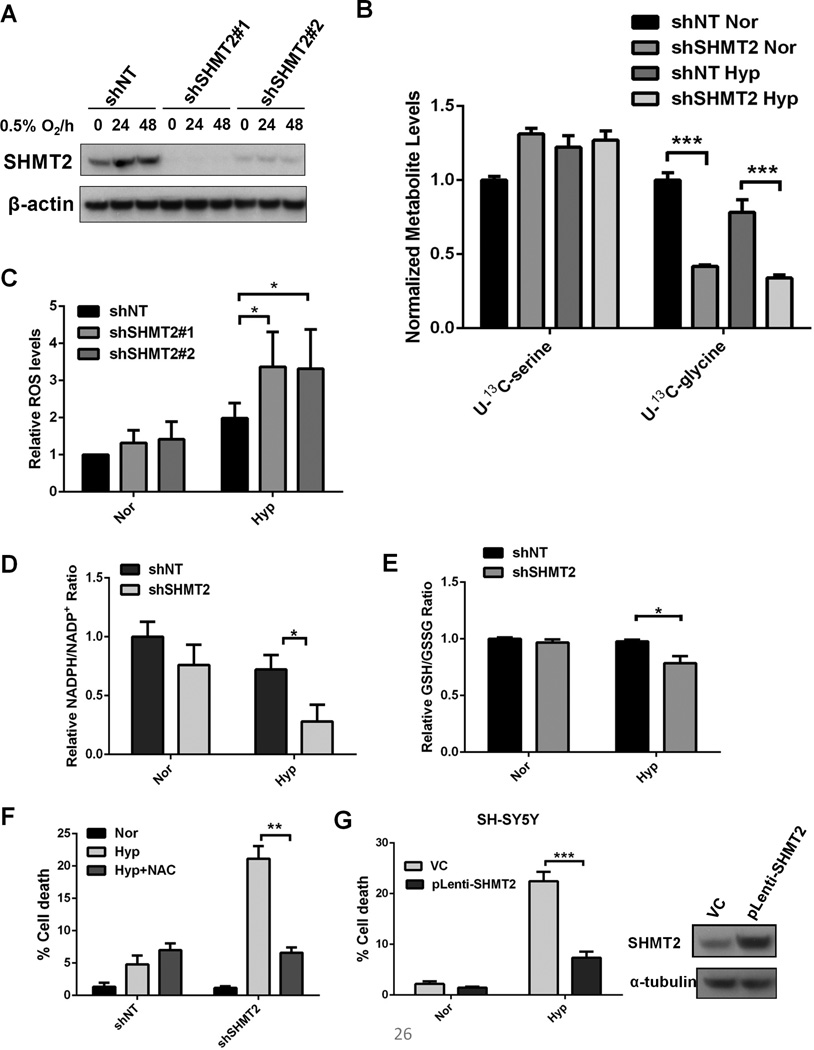
Since transcriptional upregulation of HIF targets contributes to hypoxic adaptation, whether SHMT2 contributes to metabolic adaptation to such conditions was investigated. Stable cell lines were generated through infection with lentiviruses carrying pLKO-shSHMT2 and pLKO-shNT (non-targeting control) vectors. The knockdown efficiency was confirmed by immunoblotting under normoxia and hypoxia (Figure 4A). To measure the metabolic flux from serine to glycine, the shNT and shSHMT2 cells were exposed to normoxia or hypoxia for 16h, and then U-13C-serine was added to their medium. The amounts of U-13C-glycine generated were determined using GC-MS. The metabolic fluxes from serine to glycine had an over 50% reduction in shSHMT2 cells under both normoxia and hypoxia, indicating that in these cells, there is significant flux from serine to glycine catalyzed by SHMT2 (Figure 4B).
Figure 4. SHMT2 is necessary for maintaining redox balance and cell survival under hypoxia.
(A) Kelly cells were infected by lentivirus expressing shRNA targeting SHMT2 (two independent vectors #1 and #2) or a non-targeting control (shNT). After puromycin selection, stable pool of cells was exposed to 0.5% O2 for 24 and 48 hours. SHMT2 knockdown was confirmed by immunoblot. (B) Kelly cells were exposed to 0.5% O2 for 16h, and then labeled with 0.4mM U-13C-serine for 2h in DMEM without serine or glycine. The relative amounts of U-13C-serine and U-13C-glycine were measured using GC-MS. All values are normalized to normoxic shNT control cells (Data represent Mean ± S.D of three biological repeats, representative of two independent experiments is shown). (C) Kelly cells were exposed to normoxia (Nor) or 0.5% O2 (Hyp) for 6h. ROS levels were measured using a flow cytometry-based DCFH assay. All values are normalized to normoxic shNT control cells (Data represent Mean ± S.E.M of three independent experiments). (D) Kelly cells were exposed to normoxia (Nor) or 0.5% O2 (Hyp) for 24 hours. Cellular NADPH and NADP+ were measured using LC-MS (Data represent Mean ± S.E.M of three biological repeats, representative of three independent experiments is shown). (E) Cellular GSH/GSSG ratios were measured using a glutathione colorimetric assay kit. (F) Kelly cells were exposed to normoxia (Nor) or 0.5% O2 (Hyp) for 48 hours with or without 3mM NAC, % cell death was determined using Trypan Blue staining. (G) SH-SY5Y cells were infected by lentivirus expressing pLenti-GIII-CMV-SHMT2 or vector control (VC). After puromycin selection, cells were exposed to normoxia (Nor) or 0.5% O2 (Hyp) for 48 hours. % cell death was determined using Trypan Blue staining. For panels F&G, data represent Mean ± S.D of three biological repeats, representative of three independent experiments is shown. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, determined by Student’s two-tailed t-test.
Methylene-THF produced by SHMT2 can potentially contribute to de novo thymidylate synthesis in the mitochondria. However, the mitochondrial DNA/nuclear DNA ratio of stable shSHMT2 cells was not reduced under either normoxia or hypoxia (Supplemental figure 4A). Methylene-THF can also be oxidized through the folate metabolic enzymes to generate NADPH, which is important for maintaining cellular redox balance (21–24). Consistent with these findings, SHMT2-knockdown cells (shSHMT2) showed a more profound increase of ROS under hypoxia than control cells (shNT) (Figure 4C). Staining with a mitochondrion-specific probe, MitoTracker Red CM-H2Ros (25), confirmed that SHMT2 repression cause elevated ROS in the mitochondria (Supplementary Figure 4B). We also measured NADPH/NADP+ ratio after hypoxic treatment using LC-MS. SHMT2 suppression caused a significant reduction of NADPH/NADP+ ratio under hypoxia (Figure 4D). This decrease was associated with a lower glutathione/glutathione disulfide (GSH/GSSG) ratio (Figure 4E). In addition, using electron microscopy, swollen mitochondria were observed in shSHMT2 cells under hypoxia, indicating these mitochondria are under stress (Supplementary Figure 4C).
Since increased ROS in hypoxic mitochondria leads to cell death, we tested whether repressing SHMT2 expression compromises cell viability under hypoxia. shSHMT2 cells had significantly more cell death than control cells upon hypoxia. The antioxidant N-acetylcysteine (NAC) rescued the death of shSHMT2 cells under hypoxia, indicating that the increased cell death caused by SHMT2 repression was due to elevated ROS (Figure 4F). To determine whether SHMT2 induction is sufficient to protect cells from hypoxic stress, we overexpressed SHMT2 in SH-SY5Y cells, which do not have N-Myc amplification and do not induce SHMT2 under hypoxia (Figure 3A). Forced SHMT2 overexpression significantly promoted the survival of SH-SY5Y cells under hypoxia, suggesting SHMT2 is both necessary and sufficient for protecting cells from hypoxia-induced cell death (Figure 4G). SHMT2 also protects cells from death when exposed to limitations in both oxygen and glucose (Supplementary Figure 5).
SHMT2 is needed for tumor growth in vivo and is upregulated in MYCN amplified and aggressive neuroblastoma samples
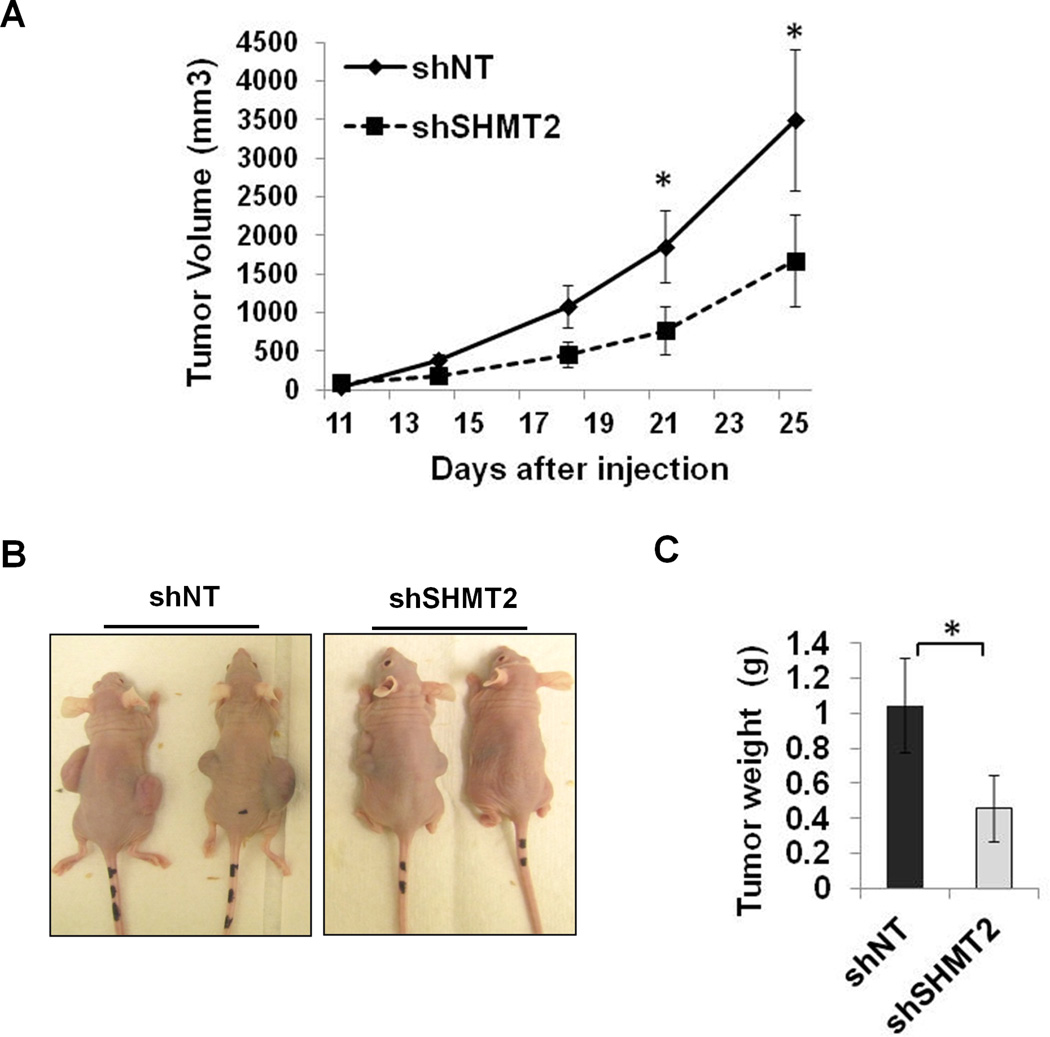
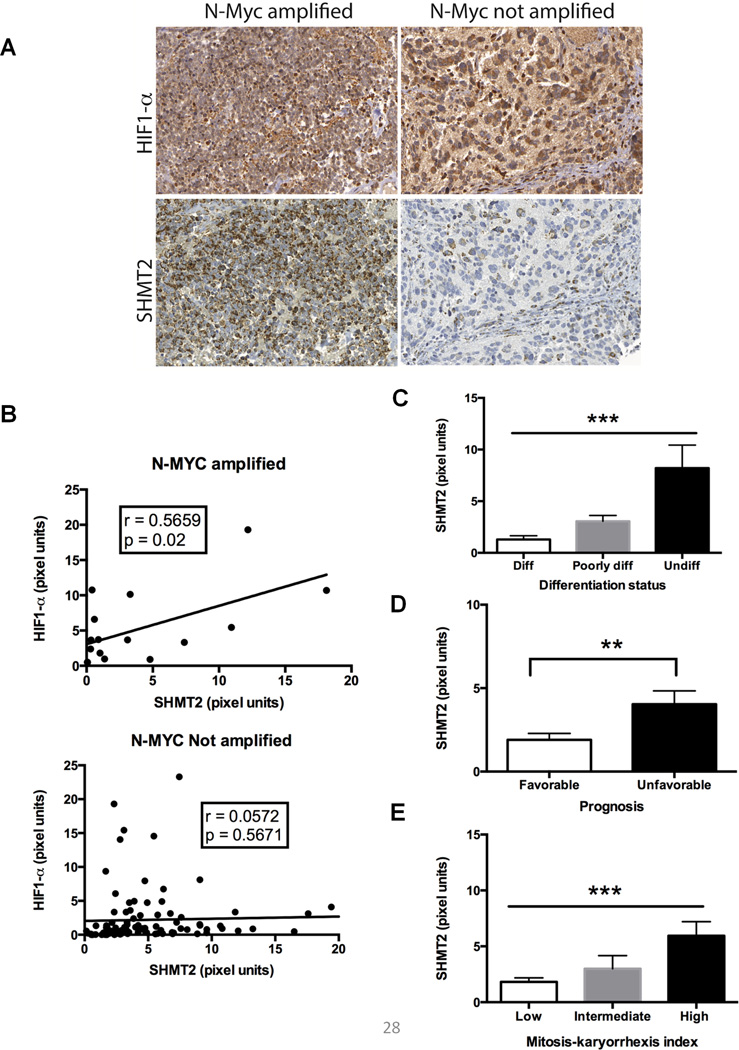
To test whether SHMT2 contributes to tumor growth in vivo, we performed a xenograft experiment by injecting shNT or shSHMT2 Kelly cells in nude mice. SHMT2 knockdown significantly inhibited xenograft tumor growth (Figure 5A–C, Supplementary Table 1). To further examine whether HIF-1-dependent SHMT2 induction is relevant to human tumors, expression of SHMT2 and HIF-1α were studied using immunohistochemistry in a well-characterized human neuroblastoma tissue microarray (26). Consistent with the observation that Myc is required for the hypoxic induction of SHMT2, SHMT2 and HIF-1α show a significant correlation in the N-myc amplified patient group but not in tumor samples without N-myc amplification (Figure 6A&B). Further, SHMT2 is highly expressed in poorly differentiated neuroblastoma and in patient samples with unfavorable prognosis (Figure 6C–E).
Figure 5. Knockdown of SHMT2 reduces xenograft tumor growth in vivo.
Control and shSHMT2 Kelly cells were injected into flanks of athymic nu/nu mice at 2×106 cells/tumor. Tumor volumes were measured twice a week (A). Mice were photographed (B), tumors were harvested and weighed following euthanasia of the mice (C). Data represent Mean ± S.E.M, n=10, *p<0.05, determined by Student’s two-tailed t-test.
Figure 6. Expression of SHMT2 and HIF-1α correlate in aggressive neuroblastomas.
Human neuroblastoma microarray with 123 tumor samples in duplicates were stained for SHMT2 and HIF-1α, staining was quantified using Matlab software. (A) Representative images of HIF-1α and SHMT2 (40×) from N-myc amplified or N-myc non-amplified neuroblastoma samples. (B) SHMT2 and HIF-1α staining correlate in N-Myc amplified tumor samples, but not in tumors without N-myc amplification. (C-E) SHMT2 expression significantly correlates with tumor dedifferentiation and poor prognosis. C: ANOVA, ***p<0.001. D: Student’s test, **p<0.01. E: ANOVA, ***p<0.001.
Discussion
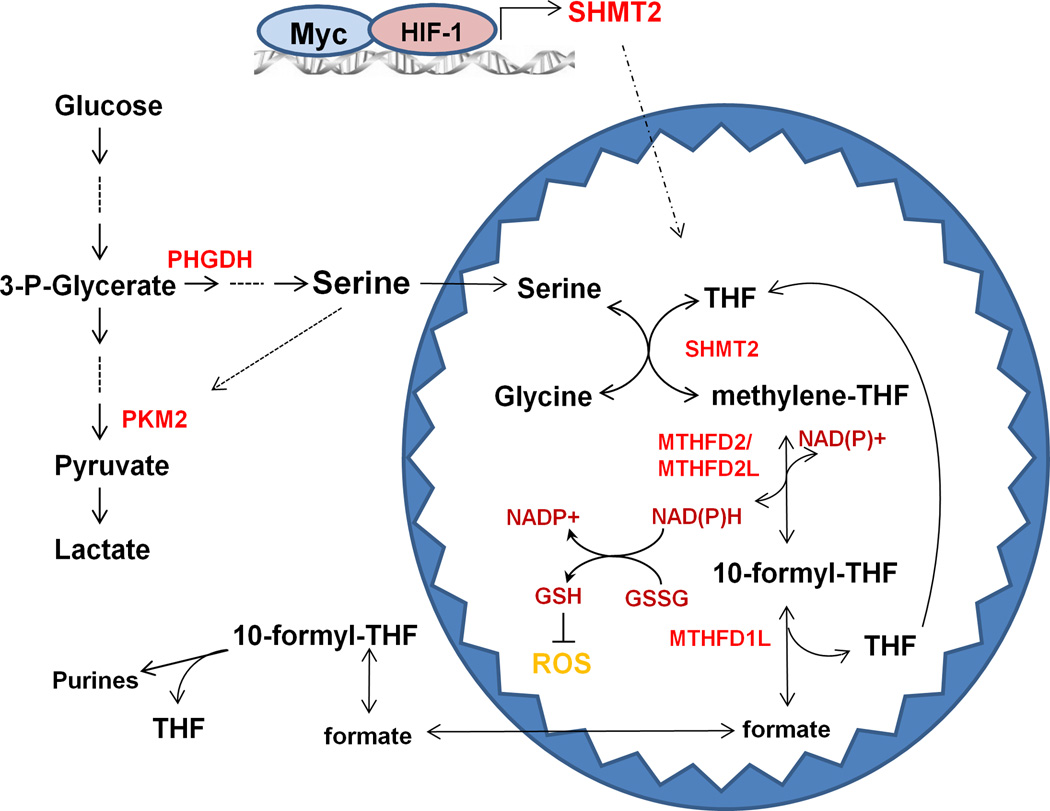
SHMT2 transfers a methyl group from serine to THF, producing glycine and methylene-THF. Glycine and one-carbon units contribute to purine and thymidine synthesis, which are necessary for nucleic acid synthesis and cell proliferation (27–29). Here we demonstrate that methylene-THF is critical for producing NADPH and repressing ROS generation in mitochondria. Cellular NADPH is essential for redox defense and reductive biosynthesis of amino acids, deoxyribonucleotides, and lipids. Previous findings conclude that major NADPH sources are the oxidative pentose phosphate pathway (oxPPP), malic enzyme (ME) and isocitrate dehydrogenese (IDH) (30). In contrast, the folate pathway has been regarded primarily as a one-carbon unit source for de novo nucleotide synthesis, not typically considered as an important NADPH source. However, the present data, suggest that SHMT2-dependent production of methylene-THF in mitochondria contributes to mitochondrial NADPH generation and redox balance during hypoxia (Figure 7).
Figure 7. A model for the role of SHMT2 in maintaining mitochondrial redox control.
Under normoxia, enhanced levels of Myc upregulate SHMT2 to promote serine-dependent one-carbon unit generation in the mitochondria (see Figure 3). The formate released from mitochondria contributes to purine synthesis in the cytosol, thus satisfying cellular needs for proliferation (49, 50). During hypoxia, because proliferation is inhibited, and the reduced demand for purines slows the serine catabolic flux. However, HIF-1α stabilization further induces SHMT2 to compensate, facilitating continued NADPH generation and mitochondrial redox balance (see Figures 2 and 4).
Abbreviations: PKM2, pyruvate kinase M2; PHGDH, phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase; SHMT, serine hydroxymethyltransferase ; MTHFD, methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase; THF, tetrahydrofolate.
During tumor progression, hypoxia develops when tumor growth exceeds the ability of available vasculature to supply tumor cells with oxygen and nutrients. Clinically, tumor hypoxia is a significant obstacle to treatment because hypoxic tumor cells are more resistant to radiation therapy (31) and chemotherapy (32, 33). Hypoxia also contributes to metastasis (34, 35) and angiogenesis. Therefore, it is important to elucidate the mechanisms by which hypoxia affects tumor physiology at the cellular and molecular levels, which can lead to the development of novel therapeutic methods that effectively target hypoxic tumors and ultimately improve patient outcome. HIF-1 and Myc play critical roles in cancer cell metabolism. In fact, both of them can upregulate glycolysis related enzymes, including HK2, LDHA and PDK1 (36, 37). The upregulation of these enzymes not only accelerates glucose uptake and glycolysis, but also promotes the Warburg effect in two ways: on one hand, LDHA channels pyruvate toward lactate production; on the other hand, pyruvate entry into the TCA cycle is blocked by PDK1, which phosphorylates and inhibits pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) activity (11, 38). HIF-1 is able to reprogram cancer cells to anaerobic glycolysis and reduce mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation under low-oxygen conditions, thus protecting cells from ROS accumulation. Here we demonstrate that HIF-1 and Myc cooperatively upregulate SHMT2, resulting in increased NADPH generation and enhanced redox balance during hypoxia. The induction of SHMT2 under conditions of hypoxia likely contributes to maintaining mitochondrial catabolism of serine even when the rate of consumption of one-carbon units for nucleotide metabolism declines. It is likely that SHMT2 is the key enzyme that connects serine metabolism to mitochondrial redox control in cancer. The fact that hypoxic induction of SHMT2 only happens in Myc-amplified cancer cells makes it an attractive target for cancer therapy. The successful usage of antifolate drugs in cancer treatment suggests that the discovery of potent SHMT2 inhibitors may also provide significant benefits for the treatment of cancer.
Material and Methods
Bioinformatic analysis
Expression data of human neuroblastoma tissue samples (GSE16237, Affymetrix Human Genome U133 Plus 2.0 Array) were obtained from NCBI GEO database (39). Expression used in the analysis is the average expression of the multiple probes for the gene. 51 neuroblastoma samples total, including patients who died of their tumors (n = 12) and patients where tumors regressed spontaneously (alive) (n = 39). The RNAseq data of 919 breast cancer samples were obtained from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database. The renal cancer dataset was obtained from Oncomine database.
Cell lines and RNAi
Kelly (36), SK-N-BE(2)(36), SF188(40), H1299 (2), H293T and HT1080 (ATCC) cells were cultured in DMEM. SH-SY5Y (41) cells were cultured in DMEM/F12. All cell lines were tested and found negative for mycoplasma (MycoAlert Mycoplasma Detection Kit, Lonza). These cell lines were not authenticated by the authors. All media were supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum and Pen/Strep. Stable Kelly cell lines expressing SHMT2 shRNA were generated through infection with lentivirus and puromycin selection. To obtain the shRNA-expressing virus, pLKO-shRNA vectors (Sigma-Aldrich) were cotransfected with the third generation lentivirus packaging plasmids (pMDLg, pCMV-VSV-G and pRsv-Rev) into HEK293T cells using FuGENE 6 Transfection Reagent (Promega), fresh media added after 24 h, and viral supernatants collected at 48 h. Target cells were infected by viral supernatant (diluted 1:1 with DMEM; 6 µg/ml polybrene), fresh DMEM was added after 24 h, and selection with 3 µg/ml puromycin initiated at 48 h and allowed to proceed for 2 – 3 days. Thereafter, cells were maintained in DMEM with 1 µg/ml puromycin. SH-SY5Y cells overexpressing SHMT2 were generated using the same packaging system and pLenti-GIII-CMV-SHMT2 plasmid (ABMgood). For HIF-1α, HIF-2α and c-Myc knockdown, siRNA targeting each gene (Ambion, 30nM) were transfected into Kelly or SF188 cells using Lipofectamine™ RNAiMAX (Invitrogen). After 48 hours, cells were subjected to hypoxia treatment.
Glutathione assay
Glutathione assay was performed using a Glutathione colorimetric assay kit (BioVision) following the manufacturer’s protocol.
Mass spectrometry analysis
For measurement of NADPH/NADP+ levels, Kelly cells were exposed to 0.5% oxygen for 24 hours, metabolism was quenched and metabolites extracted by aspirating media and immediately adding 80:20 methanol:water at -80°C. Supernatants from two rounds of methanol:water extraction were combined, dried under nitrogen, resuspended in HPLC water. The LC-MS method involved reversed-phase ion-pairing chromatography coupled by negative mode electrospray ionization to a stand-alone orbitrap mass spectrometer (Thermo Scientific) scanning from m/z 85–1000 at 1 Hz at 100,000 resolution (42–44) with LC separation on a Synergy Hydro-RP column (100 mm × 2 mm, 2.5 µm particle size, Phenomenex, Torrance, CA) using a gradient of solvent A (97:3 H2O/MeOH with 10 mM tributylamine and 15 mM acetic acid), and solvent B (100% MeOH). The gradient was 0 min, 0% B; 2.5 min, 0% B; 5 min, 20% B; 7.5 min, 20% B; 13 min, 55% B; 15.5 min, 95% B; 18.5 min, 95% B; 19 min, 0% B; 25 min, 0% B. Injection volume was 10 µL, flow rate 200µl/min, and column temperature 25°C. Data were analyzed using the MAVEN software suite(45).
For isotope labeling and tracing experiment, Kelly cells were exposed to 21% or 0.5% oxygen for 16 hours, and then labeled with 0.4mM U-13C-serine for 2h in DMEM without serine or glycine. After washing twice with ice-cold PBS, metabolites were extracted using 80:20 methanol:water at -80°C containg 20µM D-2HG (D-2-hydroxyglutaric-2,3,3,4,4-d5 acid) as internal standard. Supernatants were dried in an evaporator (Genevac EZ-2, Stoneridge, NY) under nitrogen and dissolved in methoxamine/pyridine (40mg/ml) and derivatized using acetonitrile:N-methyl-N-tertbutyldimethylsilyltrifluoroacetamide (MTBSTFA; Regis, Morton Grove, IL, USA) and heated at 37°C for 30 min to derivatize metabolites. Gas chromatography mass spectroscopy (GC-MS) was conducted. The signal of U-13C-serine and U-13C-glycine were normalized to internal standard and packed cell volume. Natural isotope abundance were corrected using IsoCor (46).
Immunoblot
The following antibodies were used: SHMT1, SHMT2 (Sigma), HIF-1α, HIF-2α (Novus), c-Myc, N-Myc (Santa Cruz) and COX IV (Abcam).
Reverse transcription and Real-time PCR
Total RNA was extracted following the TRIzol® Reagent (Invitrogen) protocol. 3µg total RNA was used in reverse transcription following SuperScript™ III (Invitrogen) protocol. Quantitative PCR was performed on a 7900HT Sequence Detection System (Applied Biosystems) using Taqman Gene Expression Assays (Applied Biosystems). Gene expression data was normalized to 18S rRNA.
ROS measurement and cell death assay
Cellular ROS was measured according to published protocols (47). Briefly, Kelly cells were exposed to hypoxia for 6h, and then incubated with 5 µM CM-H2DCFDA (Invitrogen) for 30 min. Cells were trypsinized, and mean FL1 fluorescence was measured by flow cytometry. Mitochondrial ROS were measured using MitoTracker Red CM-H2Ros dye (Invitrogen)(25). Kelly cells were exposed to hypoxia for 6h, and then incubated with 0.5 µM MitoTracker Red CM-H2Ros dye for 30mins. To measure cell death, cells were stained with Trypan Blue. Stained/unstained cells were counted and cell death percentages were calculated.
Immunohistochemistry and automated scoring
Neuroblastoma cases were obtained from the University of Pennsylvania following approval from the Institutional Review Board. All cases were de-identified prior to analysis and were contained in a previously well-characterized tissue microarray (26). Tumor samples consisted of 123 neuroblastomas (34 differentiated, 89 poorly differentiated), 33 ganglioneuroblastomas (17 intermixed, 16 nodular) and 11 ganglioneuromas. Control tissues included brain, adrenal, placenta and tonsil. All samples were documented with the age at diagnosis, disease stage, MYCN gene amplification status, mitosis-karyorrhexis index, prognosis and histopathologic classification according to the International Neuroblastoma Pathologic Classification, Children’s Oncology Group (INPC, COG). An independent pathologist evaluated all cases before analyses.
Immunohistochemical studies and quantification were performed as previously described (48). In brief, immunostaining was performed using the Discovery XT processor (Ventana Medical Systems). Tissue sections were blocked for 30 min in 10% normal goat serum in 2% BSA in PBS. Sections were incubated for 5 h with the rabbit anti-SHMT2 (Sigma, concentration 0.3 µg/ml) or mouse anti-HIF1-α (concentration 10 µg/ml) antibodies. Tissue sections were then incubated for 60 min with biotinylated goat anti-rabbit or anti-mouse IgG (Vector labs) at 1:200 dilution. Blocker D, Streptavidin- HRP and DAB detection kit (Ventana Medical Systems) were used according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Slides were scanned using an Aperio Scanscope Scanner (Aperio Vista, CA) and viewed through Aperio ImageScope software program. For automated scoring, an individual blinded to the experimental design captured JPEG images from each tissue core (circular area of 315 cm2 corresponding to the entire core) at 10× magnification on the Aperio ImageScope viewing program. Automated quantification of immunostaining (described as pixel units) on each JPEG was conducted using an automated analysis program with Matlab’s image processing toolbox based on previously described methodology. The algorithm was based on color segmentation with RGB color differentiation, K-Means Clustering and background-foreground separation with Otsu’s thresholding. To arrive at a score for each tissue core, the number of extracted pixels was multiplied by their average intensity for each core (depicted as pixel units). The final score for SHMT2 or HIF-1α for a given case was calculated by averaging the score of two cores (for each case).
Supplementary Material
Statement of significance.
In this study we demonstrate that the mitochondrial enzyme SHMT2 is induced upon hypoxic stress and is critical for maintaining NADPH production and redox balance to support tumor cell survival and growth.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Nai-Kong Chueng, MSKCC for providing us with the SH-SY5Y cell line. We also thank the Cell Metabolism, Flow Cytometry and the Molecular Cytology Core Facilities of the MSKCC for their help with mass spectrometry, flow cytometry and tissue staining analysis. This work was supported by NIH R01 grant CA105463 and P01 grant CA104838. Jing Fan is a Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI) international student research fellow.
Footnotes
Conflict of interest disclosure:
Craig B. Thompson is a co-founder of Agios Pharmaceuticals and a member of the Board of Directors of Merck.
References
- 1.Warburg O, Wind F, Negelein E. The Metabolism of Tumors in the Body. The Journal of general physiology. 1927;8:519–530. doi: 10.1085/jgp.8.6.519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Ye J, Mancuso A, Tong X, Ward PS, Fan J, Rabinowitz JD, et al. Pyruvate kinase M2 promotes de novo serine synthesis to sustain mTORC1 activity and cell proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109:6904–6909. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1204176109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Chaneton B, Hillmann P, Zheng L, Martin AC, Maddocks OD, Chokkathukalam A, et al. Serine is a natural ligand and allosteric activator of pyruvate kinase M2. Nature. 2012 doi: 10.1038/nature11540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Possemato R, Marks KM, Shaul YD, Pacold ME, Kim D, Birsoy K, et al. Functional genomics reveal that the serine synthesis pathway is essential in breast cancer. Nature. 2011;476:346–350. doi: 10.1038/nature10350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Locasale JW, Grassian AR, Melman T, Lyssiotis CA, Mattaini KR, Bass AJ, et al. Phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase diverts glycolytic flux and contributes to oncogenesis. Nat Genet. 2011;43:869–874. doi: 10.1038/ng.890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Snell K, Natsumeda Y, Eble JN, Glover JL, Weber G. Enzymic imbalance in serine metabolism in human colon carcinoma and rat sarcoma. Br J Cancer. 1988;57:87–90. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1988.15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Semenza GL. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1: regulator of mitochondrial metabolism and mediator of ischemic preconditioning. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011;1813:1263–1268. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2010.08.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Mucaj V, Shay JE, Simon MC. Effects of hypoxia and HIFs on cancer metabolism. Int J Hematol. 2012;95:464–470. doi: 10.1007/s12185-012-1070-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Chandel NS, McClintock DS, Feliciano CE, Wood TM, Melendez JA, Rodriguez AM, et al. Reactive Oxygen Species Generated at Mitochondrial Complex III Stabilize Hypoxia-inducible Factor-1α during Hypoxia A MECHANISM OF O2 SENSING. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2000;275:25130–25138. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M001914200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Guzy RD, Hoyos B, Robin E, Chen H, Liu L, Mansfield KD, et al. Mitochondrial complex III is required for hypoxia-induced ROS production and cellular oxygen sensing. Cell Metab. 2005;1:401–408. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2005.05.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kim JW, Tchernyshyov I, Semenza GL, Dang CV. HIF-1-mediated expression of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase: a metabolic switch required for cellular adaptation to hypoxia. Cell Metab. 2006;3:177–185. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2006.02.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Fujioka M. Purification and properties of serine hydroxymethylase from soluble and mitochondrial fractions of rabbit liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969;185:338–349. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(69)90427-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Garrow TA, Brenner AA, Whitehead VM, Chen XN, Duncan RG, Korenberg JR, et al. Cloning of human cDNAs encoding mitochondrial and cytosolic serine hydroxymethyltransferases and chromosomal localization. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:11910–11916. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Rhodes DR, Kalyana-Sundaram S, Mahavisno V, Varambally R, Yu J, Briggs BB, et al. Oncomine 3.0: genes, pathways, and networks in a collection of 18,000 cancer gene expression profiles. Neoplasia. 2007;9:166–180. doi: 10.1593/neo.07112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Gumz ML, Zou H, Kreinest PA, Childs AC, Belmonte LS, LeGrand SN, et al. Secreted frizzled-related protein 1 loss contributes to tumor phenotype of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13:4740–4749. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-0143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Firth JD, Ebert BL, Pugh CW, Ratcliffe PJ. Oxygen-regulated control elements in the phosphoglycerate kinase 1 and lactate dehydrogenase A genes: similarities with the erythropoietin 3' enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994;91:6496–6500. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.14.6496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Semenza GL, Roth PH, Fang HM, Wang GL. Transcriptional regulation of genes encoding glycolytic enzymes by hypoxia-inducible factor 1. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:23757–23763. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Nikiforov MA, Chandriani S, O'Connell B, Petrenko O, Kotenko I, Beavis A, et al. A functional screen for Myc-responsive genes reveals serine hydroxymethyltransferase, a major source of the one-carbon unit for cell metabolism. Mol Cell Biol. 2002;22:5793–5800. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.16.5793-5800.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Haggerty TJ, Zeller KI, Osthus RC, Wonsey DR, Dang CV. A strategy for identifying transcription factor binding sites reveals two classes of genomic c-Myc target sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100:5313–5318. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0931346100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Lin CY, Loven J, Rahl PB, Paranal RM, Burge CB, Bradner JE, et al. Transcriptional amplification in tumor cells with elevated c-Myc. Cell. 2012;151:56–67. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.08.026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Fan J, Ye J, Kamphorst JJ, Shlomi T, Thompson CB, Rabinowitz JD. Quantitative flux analysis reveals folate-dependent NADPH production. Nature. 2014 doi: 10.1038/nature13236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Bolusani S, Young BA, Cole NA, Tibbetts AS, Momb J, Bryant JD, et al. Mammalian MTHFD2L encodes a mitochondrial methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase isozyme expressed in adult tissues. J Biol Chem. 2011;286:5166–5174. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.196840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Patel H, Di Pietro E, Mejia N, MacKenzie RE. NAD- and NADP-dependent mitochondrially targeted methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase-cyclohydrolases can rescue mthfd2 null fibroblasts. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2005;442:133–139. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2005.07.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Lewis CA, Parker SJ, Fiske BP, McCloskey D, Gui DY, Green CR, et al. Tracing compartmentalized NADPH metabolism in the cytosol and mitochondria of Mammalian cells. Mol Cell. 2014;55:253–263. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2014.05.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Kuznetsov AV, Kehrer I, Kozlov AV, Haller M, Redl H, Hermann M, et al. Mitochondrial ROS production under cellular stress: comparison of different detection methods. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2011;400:2383–2390. doi: 10.1007/s00216-011-4764-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Winter C, Pawel B, Seiser E, Zhao H, Raabe E, Wang Q, et al. Neural cell adhesion molecule (NCAM) isoform expression is associated with neuroblastoma differentiation status. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2008;51:10–16. doi: 10.1002/pbc.21475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Jain M, Nilsson R, Sharma S, Madhusudhan N, Kitami T, Souza AL, et al. Metabolite profiling identifies a key role for glycine in rapid cancer cell proliferation. Science. 2012;336:1040–1044. doi: 10.1126/science.1218595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Zhang WC, Shyh-Chang N, Yang H, Rai A, Umashankar S, Ma S, et al. Glycine decarboxylase activity drives non-small cell lung cancer tumor-initiating cells and tumorigenesis. Cell. 2012;148:259–272. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.11.050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Labuschagne CF, van den Broek NJ, Mackay GM, Vousden KH, Maddocks OD. Serine, but not glycine, supports one-carbon metabolism and proliferation of cancer cells. Cell Rep. 2014;7:1248–1258. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2014.04.045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Stanton RC. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, NADPH, and cell survival. IUBMB Life. 2012;64:362–369. doi: 10.1002/iub.1017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Nordsmark M, Overgaard M, Overgaard J. Pretreatment oxygenation predicts radiation response in advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Radiother Oncol. 1996;41:31–39. doi: 10.1016/s0167-8140(96)91811-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Wike-Hooley JL, Haveman J, Reinhold HS. The relevance of tumour pH to the treatment of malignant disease. Radiother Oncol. 1984;2:343–366. doi: 10.1016/s0167-8140(84)80077-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Sutherland RM, Eddy HA, Bareham B, Reich K, Vanantwerp D. Resistance to adriamycin in multicellular spheroids. International journal of radiation oncology, biology, physics. 1979;5:1225–1230. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(79)90643-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Hockel M, Schlenger K, Aral B, Mitze M, Schaffer U, Vaupel P. Association between tumor hypoxia and malignant progression in advanced cancer of the uterine cervix. Cancer research. 1996;56:4509–4515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Brizel DM, Scully SP, Harrelson JM, Layfield LJ, Bean JM, Prosnitz LR, et al. Tumor oxygenation predicts for the likelihood of distant metastases in human soft tissue sarcoma. Cancer research. 1996;56:941–943. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Qing G, Skuli N, Mayes PA, Pawel B, Martinez D, Maris JM, et al. Combinatorial regulation of neuroblastoma tumor progression by N-Myc and hypoxia inducible factor HIF-1alpha. Cancer Res. 2010;70:10351–10361. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-0740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Kim JW, Gao P, Liu YC, Semenza GL, Dang CV. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 and dysregulated c-Myc cooperatively induce vascular endothelial growth factor and metabolic switches hexokinase 2 and pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 1. Mol Cell Biol. 2007;27:7381–7393. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00440-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Papandreou I, Cairns RA, Fontana L, Lim AL, Denko NC. HIF-1 mediates adaptation to hypoxia by actively downregulating mitochondrial oxygen consumption. Cell Metab. 2006;3:187–197. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2006.01.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Ohtaki M, Otani K, Hiyama K, Kamei N, Satoh K, Hiyama E. A robust method for estimating gene expression states using Affymetrix microarray probe level data. BMC Bioinformatics. 2010;11:183. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-11-183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Wise DR, Ward PS, Shay JE, Cross JR, Gruber JJ, Sachdeva UM, et al. Hypoxia promotes isocitrate dehydrogenase-dependent carboxylation of alpha-ketoglutarate to citrate to support cell growth and viability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108:19611–19616. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1117773108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Huang R, Cheung NK, Vider J, Cheung IY, Gerald WL, Tickoo SK, et al. MYCN and MYC regulate tumor proliferation and tumorigenesis directly through BMI1 in human neuroblastomas. FASEB J. 2011;25:4138–4149. doi: 10.1096/fj.11-185033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Munger J, Bennett BD, Parikh A, Feng XJ, McArdle J, Rabitz HA, et al. Systems-level metabolic flux profiling identifies fatty acid synthesis as a target for antiviral therapy. Nat Biotechnol. 2008;26:1179–1186. doi: 10.1038/nbt.1500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Lemons JM, Feng XJ, Bennett BD, Legesse-Miller A, Johnson EL, Raitman I, et al. Quiescent fibroblasts exhibit high metabolic activity. PLoS Biol. 2010;8:e1000514. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Lu W, Clasquin MF, Melamud E, Amador-Noguez D, Caudy AA, Rabinowitz JD. Metabolomic analysis via reversed-phase ion-pairing liquid chromatography coupled to a stand alone orbitrap mass spectrometer. Anal Chem. 2010;82:3212–3221. doi: 10.1021/ac902837x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Melamud E, Vastag L, Rabinowitz JD. Metabolomic analysis and visualization engine for LC-MS data. Anal Chem. 2010;82:9818–9826. doi: 10.1021/ac1021166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Millard P, Letisse F, Sokol S, Portais JC. IsoCor: correcting MS data in isotope labeling experiments. Bioinformatics. 2012;28:1294–1296. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Eruslanov E, Kusmartsev S. Identification of ROS using oxidized DCFDA and flow-cytometry. Methods Mol Biol. 2010;594:57–72. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60761-411-1_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Venneti S, Garimella MT, Sullivan LM, Martinez D, Huse JT, Heguy A, et al. Evaluation of histone 3 lysine 27 trimethylation (H3K27me3) and enhancer of Zest 2 (EZH2) in pediatric glial and glioneuronal tumors shows decreased H3K27me3 in H3F3A K27M mutant glioblastomas. Brain Pathol. 2013;23:558–564. doi: 10.1111/bpa.12042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Barlowe CK, Appling DR. In vitro evidence for the involvement of mitochondrial folate metabolism in the supply of cytoplasmic one-carbon units. Biofactors. 1988;1:171–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Tibbetts AS, Appling DR. Compartmentalization of Mammalian folate-mediated one-carbon metabolism. Annu Rev Nutr. 2010;30:57–81. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nutr.012809.104810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.