Abstract
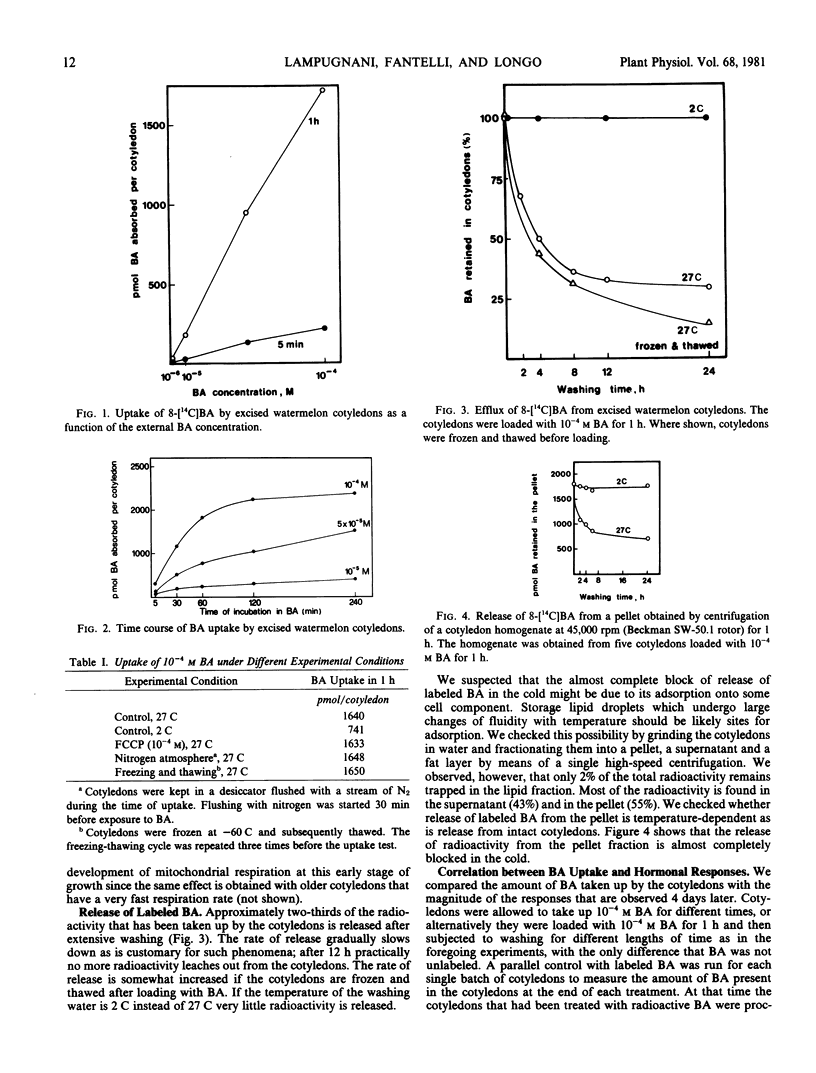
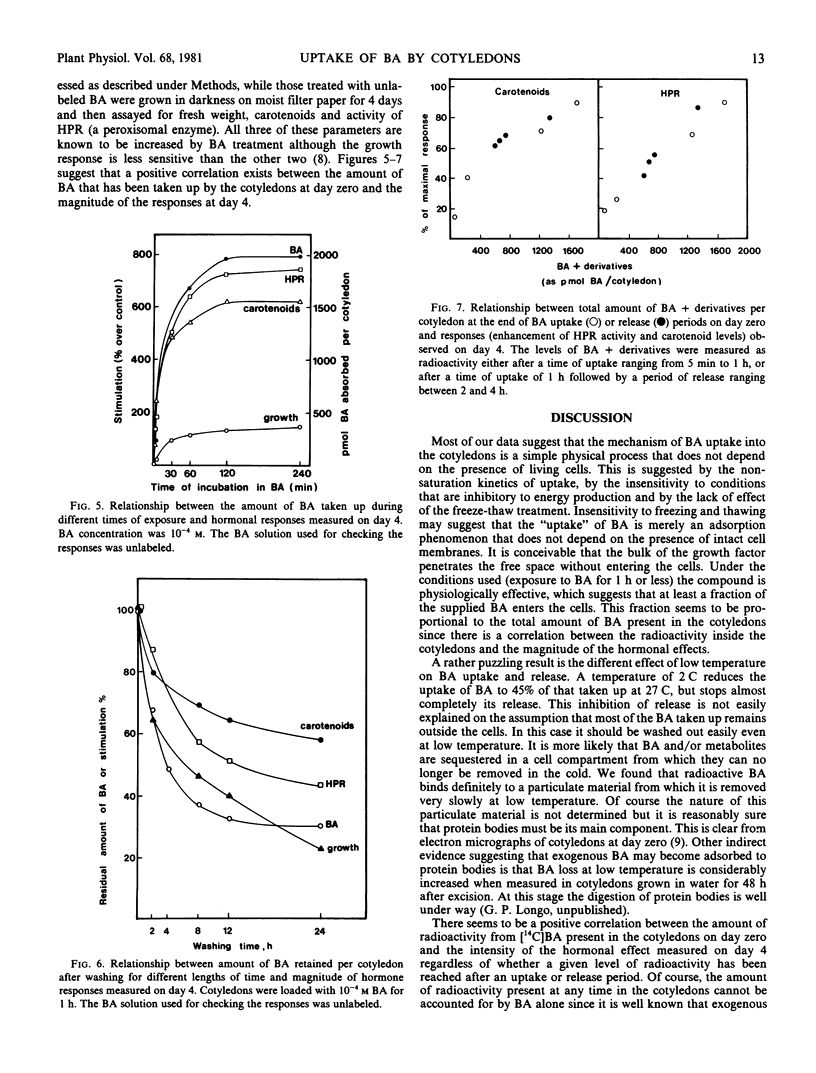
The uptake of 8-[14C]N6-benzyladenine (BA) was studied in excised watermelon (Citrullus vulgaris Schrad.) cotyledons 24 hours after the start of imbibition. The passive nature of this uptake is suggested by the following evidence: (a) no sign of saturation on increasing external concentration of BA; (b) no decrease in uptake under conditions that inhibit ATP synthesis; (c) no change in amount of radioactivity absorbed when cotyledons are frozen and thawed before the uptake test. About two-thirds of the radioactivity taken up is released after 12 hours of washing. If the washing is performed at 2 C very little radioactivity is released.
There seems to be a correlation between the level of radioactivity (i.e. of BA + derivatives) present in the cotyledons and the magnitude of hormonal responses that are observed four days after uptake. This relationship holds regardless of whether a given level of radioactivity has been reached after a short period of uptake or after a long period of uptake followed by washing.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Elliott D. C. Analysis of Variability in the Amaranthus Bioassay for Cytokinins: Effects of Water Stress on Benzyladenine- and Fusicoccin-dependent Responses. Plant Physiol. 1979 Feb;63(2):269–273. doi: 10.1104/pp.63.2.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



