Abstract
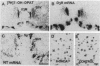
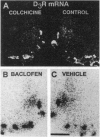
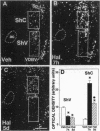
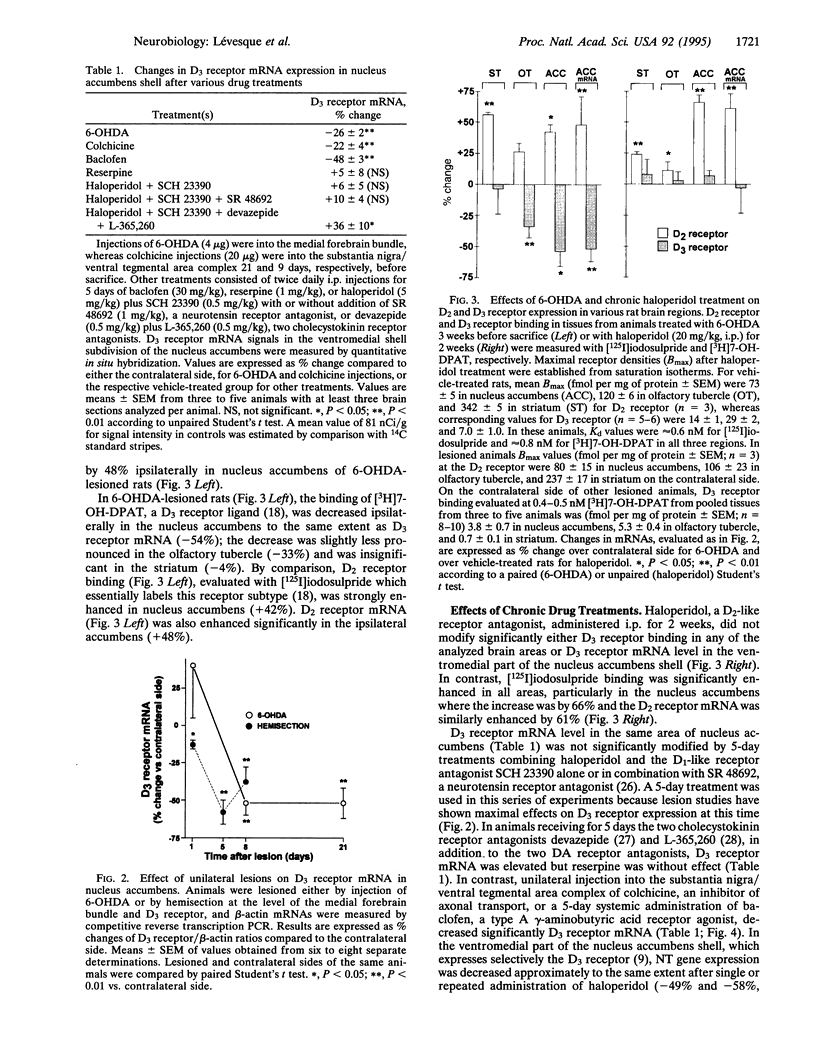
The effects of interruption of dopaminergic transmission or sustained blockade of dopamine receptors by neuroleptics on the dopamine D3 receptor in the shell of the nucleus accumbens were investigated in rats. In this brain area the D3 receptor is abundant and may mediate antipsychotic drug effects. The D3 receptor density and mRNA abundance were evaluated with 7-[3H]hydroxy-N,N-di-n-propyl-2-aminotetralin and by quantitative PCR or image analysis of in situ hybridization signals, respectively. Unilateral dopamine neuron degeneration by 6-hydroxydopamine or sections triggered, after a few days, a marked decrease (up to 50%) in D3 receptor binding and mRNA in the nucleus accumbens. In contrast, a 2-week treatment with the neuroleptic haloperidol (20 mg/kg) had no effect on D3 receptor density and mRNA but enhanced D2 receptor density and mRNA level by > 50%. In addition, tolerance to the haloperidol-induced change of neurotensin mRNA mediated by the D2 receptor developed, but there was no tolerance to the opposite change mediated by the D3 receptor. Reserpine, a monoamine-depleting drug with antipsychotic activity, did not modify D3 receptor mRNA. These observations reinforce the idea that the D3 receptor may be an important target for neuroleptics whose antipsychotic actions, but not extrapyramidal motor actions, do not display tolerance. The D3 receptor mRNA level was also decreased by a unilateral injection in dopamine cell body areas of colchicine, a drug blocking the anterograde axonal transport, or by baclofen, a type A gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor agonist reducing dopamine neuron activity, but not by sustained blockade of D1-like and D2-like, neurotensin, or cholecystokinin receptors. We therefore propose that an anterograde factor present in mesolimbic dopaminergic neurons, but distinct from dopamine and known peptide cotransmitters, plays a positive role on transcription of the D3 receptor gene.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agid Y., Javoy F., Glowinski J. Hyperactivity of remaining dopaminergic neurones after partial destruction of the nigro-striatal dopaminergic system in the rat. Nat New Biol. 1973 Oct 3;245(144):150–151. doi: 10.1038/newbio245150a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard V., Le Moine C., Bloch B. Striatal neurons express increased level of dopamine D2 receptor mRNA in response to haloperidol treatment: a quantitative in situ hybridization study. Neuroscience. 1991;45(1):117–126. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(91)90108-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bock M. G., DiPardo R. M., Evans B. E., Rittle K. E., Whitter W. L., Veber D. E., Anderson P. S., Freidinger R. M. Benzodiazepine gastrin and brain cholecystokinin receptor ligands: L-365,260. J Med Chem. 1989 Jan;32(1):13–16. doi: 10.1021/jm00121a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouthenet M. L., Souil E., Martres M. P., Sokoloff P., Giros B., Schwartz J. C. Localization of dopamine D3 receptor mRNA in the rat brain using in situ hybridization histochemistry: comparison with dopamine D2 receptor mRNA. Brain Res. 1991 Nov 15;564(2):203–219. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)91456-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer P. A., Trembleau A., Leviel V., Arluison M. Effects of intranigral injections of colchicine on the expression of some neuropeptides in the rat forebrain: an immunohistochemical and in situ hybridization study. Brain Res Bull. 1994;33(5):541–560. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(94)90081-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckland P. R., O'Donovan M. C., McGuffin P. Changes in dopamine D1, D2 and D3 receptor mRNA levels in rat brain following antipsychotic treatment. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1992;106(4):479–483. doi: 10.1007/BF02244818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckland P. R., O'Donovan M. C., McGuffin P. Clozapine and sulpiride up-regulate dopamine D3 receptor mRNA levels. Neuropharmacology. 1993 Sep;32(9):901–907. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(93)90146-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunney B. S., Grace A. A. Acute and chronic haloperidol treatment: comparison of effects on nigral dopaminergic cell activity. Life Sci. 1978 Oct 23;23(16):1715–1727. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(78)90471-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang R. S., Lotti V. J. Biochemical and pharmacological characterization of an extremely potent and selective nonpeptide cholecystokinin antagonist. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4923–4926. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chio C. L., Lajiness M. E., Huff R. M. Activation of heterologously expressed D3 dopamine receptors: comparison with D2 dopamine receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1994 Jan;45(1):51–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen A. I., Todd R. D., Harmon S., O'Malley K. L. Photoreceptors of mouse retinas possess D4 receptors coupled to adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 15;89(24):12093–12097. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.24.12093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creese I., Sibley D. R. Receptor adaptations to centrally acting drugs. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1981;21:357–391. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.21.040181.002041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crow T. J., Cross A. J., Johnstone E. C., Longden A., Owen F., Ridley R. M. Time course of the antipsychotic effect in schizophrenia and some changes in postmortem brain and their relation to neuroleptic medication. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol. 1980;24:495–503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz J., Lévesque D., Griffon N., Lammers C. H., Martres M. P., Sokoloff P., Schwartz J. C. Opposing roles for dopamine D2 and D3 receptors on neurotensin mRNA expression in nucleus accumbens. Eur J Neurosci. 1994 Aug 1;6(8):1384–1387. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1994.tb00329.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishburn C. S., David C., Carmon S., Fuchs S. The effect of haloperidol on D2 dopamine receptor subtype mRNA levels in the brain. FEBS Lett. 1994 Feb 14;339(1-2):63–66. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)80385-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontaine B., Klarsfeld A., Changeux J. P. Calcitonin gene-related peptide and muscle activity regulate acetylcholine receptor alpha-subunit mRNA levels by distinct intracellular pathways. J Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;105(3):1337–1342. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.3.1337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fremeau R. T., Jr, Duncan G. E., Fornaretto M. G., Dearry A., Gingrich J. A., Breese G. R., Caron M. G. Localization of D1 dopamine receptor mRNA in brain supports a role in cognitive, affective, and neuroendocrine aspects of dopaminergic neurotransmission. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3772–3776. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerfen C. R., Engber T. M., Mahan L. C., Susel Z., Chase T. N., Monsma F. J., Jr, Sibley D. R. D1 and D2 dopamine receptor-regulated gene expression of striatonigral and striatopallidal neurons. Science. 1990 Dec 7;250(4986):1429–1432. doi: 10.1126/science.2147780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giros B., el Mestikawy S., Bertrand L., Caron M. G. Cloning and functional characterization of a cocaine-sensitive dopamine transporter. FEBS Lett. 1991 Dec 16;295(1-3):149–154. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)81406-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gully D., Canton M., Boigegrain R., Jeanjean F., Molimard J. C., Poncelet M., Gueudet C., Heaulme M., Leyris R., Brouard A. Biochemical and pharmacological profile of a potent and selective nonpeptide antagonist of the neurotensin receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 1;90(1):65–69. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.1.65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess E. J., Norman A. B., Creese I. Chronic treatment with dopamine receptor antagonists: behavioral and pharmacologic effects on D1 and D2 dopamine receptors. J Neurosci. 1988 Jul;8(7):2361–2370. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-07-02361.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hökfelt T., Everitt B. J., Theodorsson-Norheim E., Goldstein M. Occurrence of neurotensinlike immunoreactivity in subpopulations of hypothalamic, mesencephalic, and medullary catecholamine neurons. J Comp Neurol. 1984 Feb 1;222(4):543–559. doi: 10.1002/cne.902220407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hökfelt T., Rehfeld J. F., Skirboll L., Ivemark B., Goldstein M., Markey K. Evidence for coexistence of dopamine and CCK in meso-limbic neurones. Nature. 1980 Jun 12;285(5765):476–478. doi: 10.1038/285476a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joyce J. N. Differential response of striatal dopamine and muscarinic cholinergic receptor subtypes to the loss of dopamine. II. Effects of 6-hydroxydopamine or colchicine microinjections into the VTA or reserpine treatment. Exp Neurol. 1991 Sep;113(3):277–290. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(91)90017-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalivas P. W., Duffy P., Eberhardt H. Modulation of A10 dopamine neurons by gamma-aminobutyric acid agonists. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 May;253(2):858–866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopp J., Lindefors N., Brené S., Hall H., Persson H., Sedvall G. Effect of raclopride on dopamine D2 receptor mRNA expression in rat brain. Neuroscience. 1992;47(4):771–779. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(92)90028-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lévesque D., Diaz J., Pilon C., Martres M. P., Giros B., Souil E., Schott D., Morgat J. L., Schwartz J. C., Sokoloff P. Identification, characterization, and localization of the dopamine D3 receptor in rat brain using 7-[3H]hydroxy-N,N-di-n-propyl-2-aminotetralin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 1;89(17):8155–8159. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.17.8155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malmberg A., Jackson D. M., Eriksson A., Mohell N. Unique binding characteristics of antipsychotic agents interacting with human dopamine D2A, D2B, and D3 receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1993 May;43(5):749–754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansour A., Meador-Woodruff J. H., Zhou Q., Civelli O., Akil H., Watson S. J. A comparison of D1 receptor binding and mRNA in rat brain using receptor autoradiographic and in situ hybridization techniques. Neuroscience. 1992;46(4):959–971. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(92)90197-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martres M. P., Bouthenet M. L., Sales N., Sokoloff P., Schwartz J. C. Widespread distribution of brain dopamine receptors evidenced with [125I]iodosulpride, a highly selective ligand. Science. 1985 May 10;228(4700):752–755. doi: 10.1126/science.3838821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martres M. P., Sokoloff P., Giros B., Schwartz J. C. Effects of dopaminergic transmission interruption on the D2 receptor isoforms in various cerebral tissues. J Neurochem. 1992 Feb;58(2):673–679. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb09770.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilon C., Lévesque D., Dimitriadou V., Griffon N., Martres M. P., Schwartz J. C., Sokoloff P. Functional coupling of the human dopamine D3 receptor in a transfected NG 108-15 neuroblastoma-glioma hybrid cell line. Eur J Pharmacol. 1994 Jul 15;268(2):129–139. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(94)90182-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porceddu M. L., Ongini E., Biggio G. [3H]SCH 23390 binding sites increase after chronic blockade of D-1 dopamine receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Dec 3;118(3):367–370. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90151-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz J. C., Llorens Cortes C., Rose C., Quach T. T., Pollard H. Adaptive changes of neurotransmitter receptor mechanisms in the central nervous system. Prog Brain Res. 1983;58:117–129. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)60012-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebert P. D., Larrick J. W. Competitive PCR. Nature. 1992 Oct 8;359(6395):557–558. doi: 10.1038/359557a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokoloff P., Andrieux M., Besançon R., Pilon C., Martres M. P., Giros B., Schwartz J. C. Pharmacology of human dopamine D3 receptor expressed in a mammalian cell line: comparison with D2 receptor. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Apr 10;225(4):331–337. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(92)90107-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokoloff P., Giros B., Martres M. P., Bouthenet M. L., Schwartz J. C. Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel dopamine receptor (D3) as a target for neuroleptics. Nature. 1990 Sep 13;347(6289):146–151. doi: 10.1038/347146a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg R., Brun P., Fournier M., Souilhac J., Rodier D., Mons G., Terranova J. P., Le Fur G., Soubrié P. SR 48692, a non-peptide neurotensin receptor antagonist differentially affects neurotensin-induced behaviour and changes in dopaminergic transmission. Neuroscience. 1994 Apr;59(4):921–929. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(94)90295-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Tol H. H., Bunzow J. R., Guan H. C., Sunahara R. K., Seeman P., Niznik H. B., Civelli O. Cloning of the gene for a human dopamine D4 receptor with high affinity for the antipsychotic clozapine. Nature. 1991 Apr 18;350(6319):610–614. doi: 10.1038/350610a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahm D. S., Johnson S. N. Asymmetrical distribution of neurotensin immunoreactivity following unilateral injection of 6-hydroxydopamine in rat ventral tegmental area (VTA). Brain Res. 1989 Apr 3;483(2):301–311. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90174-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Tol H. H., Riva M., Civelli O., Creese I. Lack of effect of chronic dopamine receptor blockade on D2 dopamine receptor mRNA level. Neurosci Lett. 1990 Apr 6;111(3):303–308. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(90)90279-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]