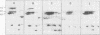Abstract
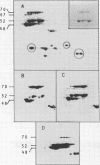
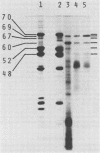
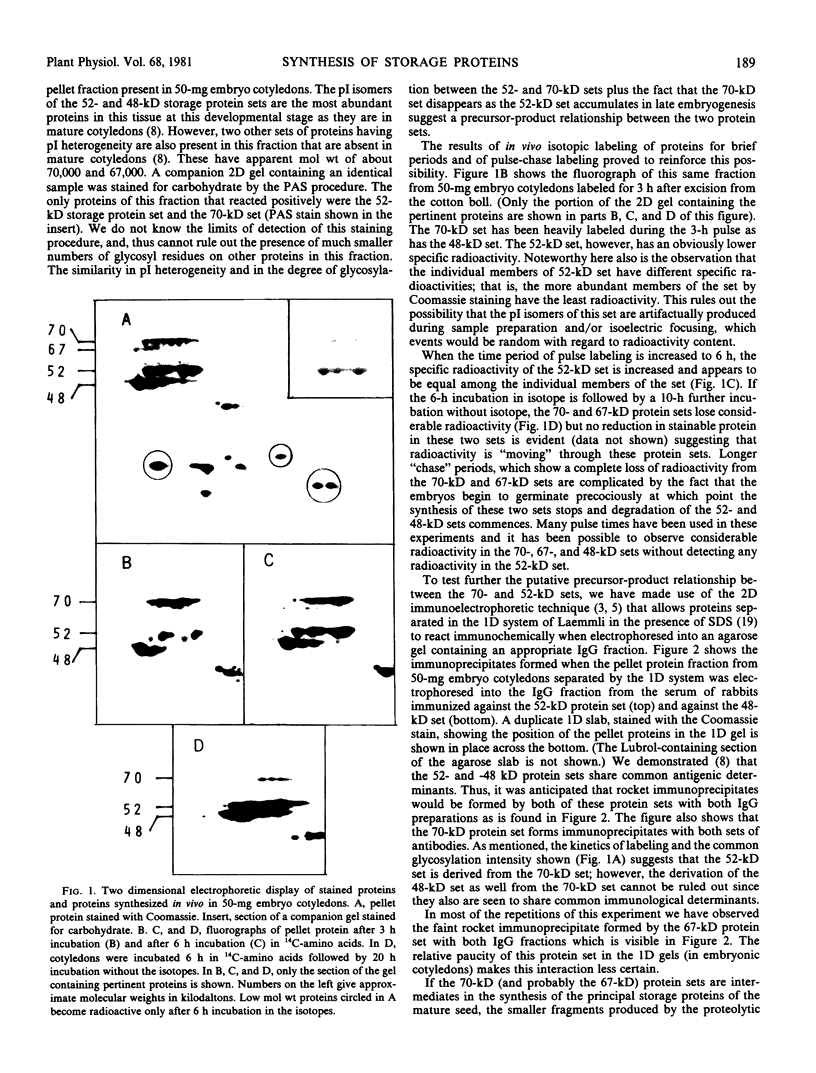
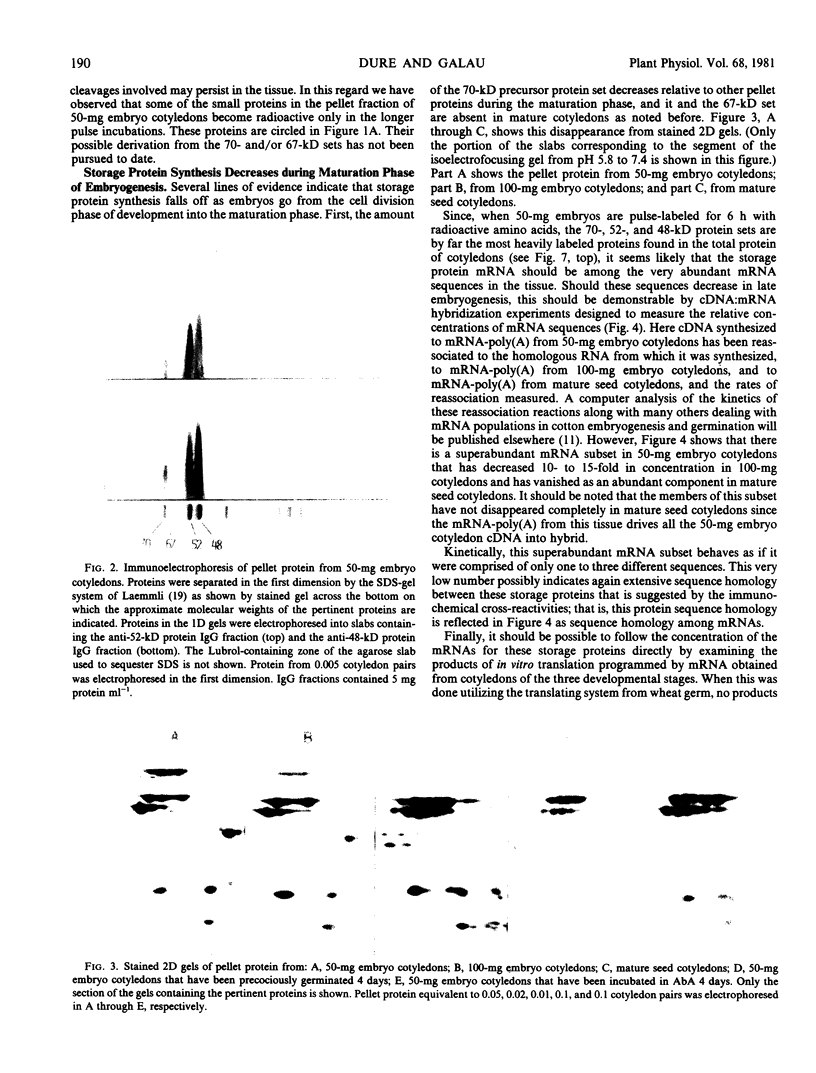
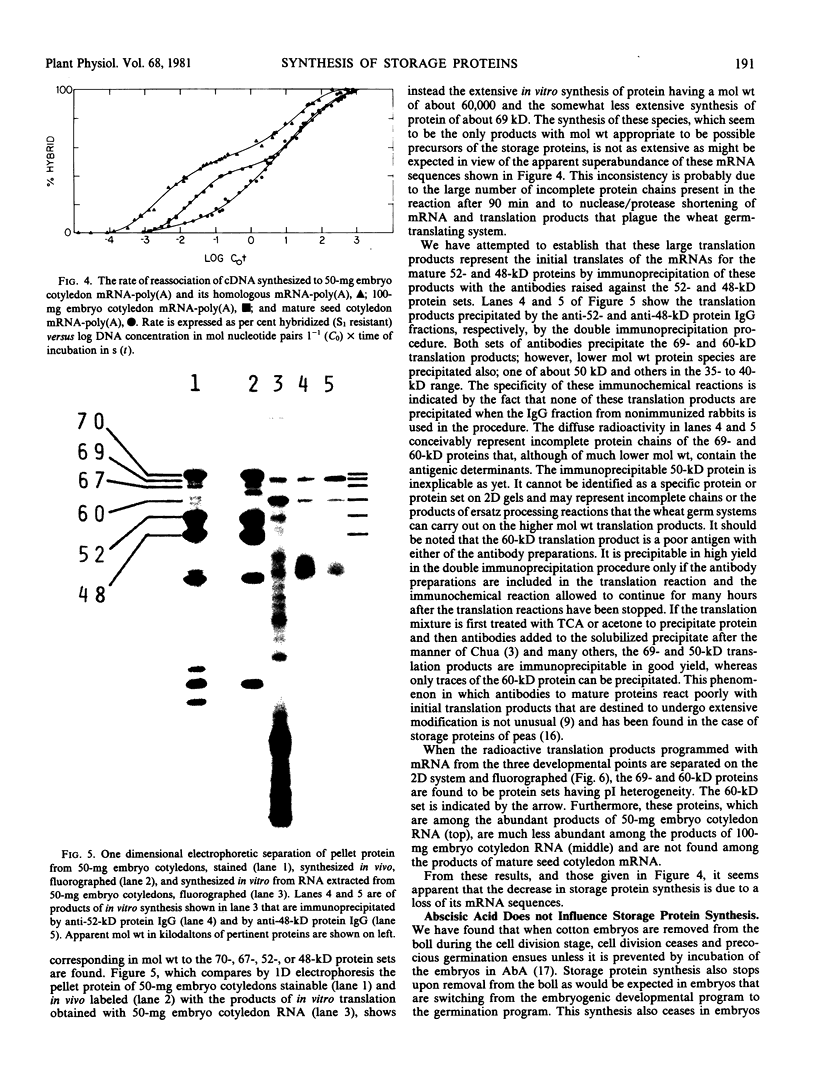
The synthesis of the principal cottonseed storage proteins during embryogenesis has been followed by analyses of stained protein gels and of fluorographs of protein synthesized in vivo and from purified RNA in vitro in the wheat germ system. The kinetics of in vivo labeling as well as immunochemical cross-reactivity indicate that the 52- and 48-kilodalton mature storage protein sets are derived from 70- and 67-kilodalton precursor protein sets that are abundant proteins in embryonic cotyledons and disappear in late embryogenesis. Identification of the initial translation products of the storage protein mRNA has not been clearly established although products of apparent molecular weights of 69,000 and 60,000 are the likely storage protein precursors.
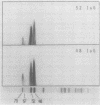
Storage protein synthesis falls off markedly in late embryogenesis simultaneously with the loss of a superabundant class of mRNAs (shown by cDNA:RNA reassociation) that are presumed to be those for the storage proteins. The synthesis of these proteins ceases abruptly when immature embryos are removed from the boll and allowed to germinate precociously or when this precocious germination is prevented by incubation in abscisic acid. Thus, abscisic acid is not implicated in the expression of the storage protein genes.
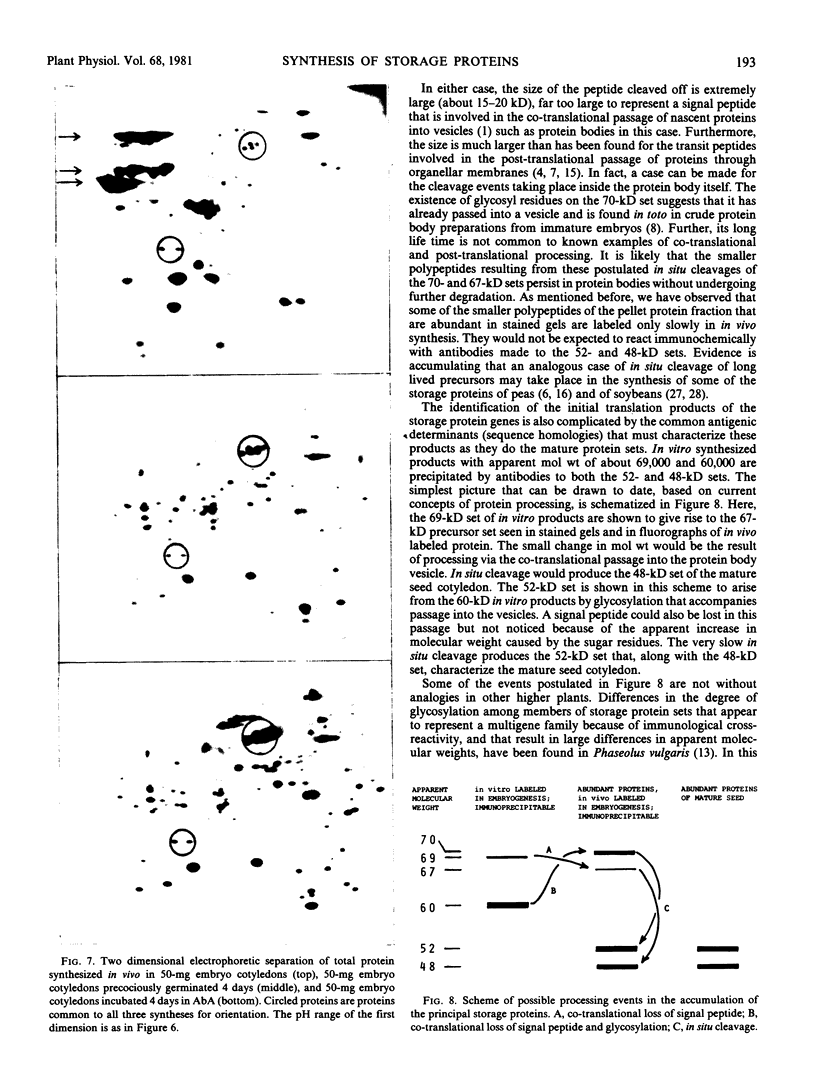
A scheme involving co-translational processing into vesicles, glycosylation, and slow in situ cleavage to produce the mature storage proteins is proposed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blobel G., Dobberstein B. Transfer of proteins across membranes. I. Presence of proteolytically processed and unprocessed nascent immunoglobulin light chains on membrane-bound ribosomes of murine myeloma. J Cell Biol. 1975 Dec;67(3):835–851. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.3.835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chua N. H., Blomberg F. Immunochemical studies of thylakoid membrane polypeptides from spinach and Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. A modified procedure for crossed immunoelectrophoresis of dodecyl sulfate.protein complexes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jan 10;254(1):215–223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chua N. H., Schmidt G. W. Transport of proteins into mitochondria and chloroplasts. J Cell Biol. 1979 Jun;81(3):461–483. doi: 10.1083/jcb.81.3.461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Converse C. A., Papermaster D. S. Membrane protein analysis by two-dimensional immunoelectrophoresis. Science. 1975 Aug 8;189(4201):469–472. doi: 10.1126/science.1154021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobberstein B., Blobel G., Chua N. H. In vitro synthesis and processing of a putative precursor for the small subunit of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1082–1085. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dure L., Chlan C. Developmental Biochemistry of Cottonseed Embryogenesis and Germination : XII. PURIFICATION AND PROPERTIES OF PRINCIPAL STORAGE PROTEINS. Plant Physiol. 1981 Jul;68(1):180–186. doi: 10.1104/pp.68.1.180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster J. A., Rich C. B., Fletcher S., Karr S. R., Przybyla A. Translation of chick aortic elastin messenger ribonucleic acid. Comparison to elastin synthesis in chick aorta organ culture. Biochemistry. 1980 Mar 4;19(5):857–864. doi: 10.1021/bi00546a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galau G. A., Legocki A. B., Greenway S. C., Dure L. S., 3rd Cotton messenger RNA sequences exist in both polyadenylated and nonpolyadenylated forms. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 10;256(5):2551–2560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris B., Dure L., 3rd Developmental regulation in cotton seed germination: polyadenylation of stored messenger RNA. Biochemistry. 1978 Aug 8;17(16):3250–3256. doi: 10.1021/bi00609a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihle J. N., Dure L. S., 3rd The developmental biochemistry of cottonseed embryogenesis and germination. 3. Regulation of the biosynthesis of enzymes utilized in germination. J Biol Chem. 1972 Aug 25;247(16):5048–5055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Rapid isolation of antigens from cells with a staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent: parameters of the interaction of antibody-antigen complexes with protein A. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1617–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcu K., Dudock B. Characterization of a highly efficient protein synthesizing system derived from commercial wheat germ. Nucleic Acids Res. 1974 Nov;1(11):1385–1397. doi: 10.1093/nar/1.11.1385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell I. H., Van Ness J., Hahn W. E. Assay of DNA-RNA hybrids by S1 nuclease digestion and adsorption to DEAE-cellulose filters. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Jun;5(6):2033–2038. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.6.2033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palacios R., Palmiter R. D., Schimke R. T. Identification and isolation of ovalbumin-synthesizing polysomes. I. Specific binding of 125 I-anti-ovalbumin to polysomes. J Biol Chem. 1972 Apr 25;247(8):2316–2321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walbot V., Dure L. S., 3rd Developmental biochemistry of cotton seed embryogenesis and germination. VII. Characterization of the cotton genome. J Mol Biol. 1976 Mar 15;101(4):503–536. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90242-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]