Abstract
Pyruvate kinase M2 (PKM2) is expressed at high levels during embryonic development and tumor progression and is important for cell growth. However, it is not known whether it directly controls cell division. Here, we found that Aurora B phosphorylates PKM2, but not PKM1, at T45; this phosphorylation is required for PKM2's localization and interaction with myosin light chain 2 (MLC2) in the contractile ring region of mitotic cells during cytokinesis. PKM2 phosphorylates MLC2 at Y118, which primes the binding of ROCK2 to MLC2 and subsequent ROCK2-dependent MLC2 S15 phosphorylation. PKM2-regulated MLC2 phosphorylation, which is greatly enhanced by EGF stimulation or EGFRvIII, K-Ras G12V, and B-Raf V600E mutant expression, plays a pivotal role in cytokinesis, cell proliferation, and brain tumor development. These findings underscore the instrumental function of PKM2 in oncogenic EGFR-, K-Ras-, and B-Raf-regulated cytokinesis and tumorigenesis.
Keywords: PKM2, Aurora B, ROCK2, MLC2, EGFR, K-Ras, B-Raf, phosphorylation, cytokinesis
Cytokinesis is the final stage of cell division, during which the two daughter cells separate completely 1, 2. A failure in cytokinesis completion can lead to polyploidy, a state in which cells contain more than two sets of chromosomes; this results in cell cycle arrest and cell growth inhibition 3. Cellular myosin II, the conventional two-headed myosin that was first identified in muscle tissue, is the primary motor protein responsible for cytokinesis. Myosin II comprises a parallel dimer of heavy chains, each of which binds to an essential light chain and a regulatory myosin light chain (RMLC) 4. RMLC has smooth muscle isoforms (MRLC1 or MLC-2C, encoded by MYL9), non-muscle isoforms (encoded by the highly homologous MYL12A and MYL12B, referred to as MYLB12A and MYLB12B hereafter), and cardiac ventricular muscle isoform (MLC2 or MLC2v, encoded by MYL2). Phosphorylation of MRLC1 and MYLB12A/B at Ser19 (or Thr18/Ser19) in higher eukaryotes and phosphorylation of human MLC2 at Ser15 allow myosin II to interact with actin, assemble an actomyosin complex, and initiate contraction 5, 6, 7. Thus, RMLC phosphorylation controls both the assembly and contractility of the actomyosin contractile apparatus 8.
Pyruvate kinase regulates the final rate-limiting step of glycolysis, which catalyzes the transfer of a phosphate group from phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) to adenosine diphosphate for the production of pyruvate and adenosine triphosphate (ATP) 9, 10. Alternate splicing of PKM pre-mRNA by hnRNP A1/2 and polypyrimidine tract binding (PTB) protein splicing factors leads to PKM2 generation by the inclusion of exon 10 and the exclusion of exon 9, which is specific for PKM1 11, 12. Besides its cytosolic roles in glycolysis 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, PKM2, which is upregulated by growth factor receptor activation and phosphorylated by extracellular signal-regulated kinase, translocates into the nucleus and binds to c-Src-phosphorylated Y333 of β-catenin, which is essential for β-catenin transactivation 19, 20, 21, 22. Histone H3-interacted PKM2 phosphorylates histone H3 at T11, leading to H3-K9 acetylation and gene transcription, including MYC and CCND1 (encoding for cyclin D1) 23, 24. c-Myc expression results in the upregulation of GLUT1, lactate dehydrogenase A, and in a positive feedback loop, PTB-dependent PKM2 expression, which leads to an enhanced Warburg effect 21. Cyclin D1 expression, in turn, promotes G1-S phase transition 19, 23, 25. In addition to its specific role in regulating G1-S transition, PKM2 binds to and phosphorylates the spindle checkpoint protein Bub3, thereby regulating correct kinetochore-microtubule attachment, the spindle-assembly checkpoint, and accurate chromosome segregation 26. However, whether PKM2 plays a role in in other phases of the cell cycle besides the G1-S phase transition and mitotic checkpoint is not known.
In this study, we found that Aurora B phosphorylates PKM2 at T45 and that this phosphorylation is required for PKM2 to localize in the contractile ring of dividing cells, where it binds to MLC2 and phosphorylates MLC2 Y118. MLC2 Y118 phosphorylation primes ROCK2-mediated MLC2 S15 phosphorylation and is required for oncogenic protein-regulated cytokinesis progression.
RESULTS
PKM2 Interacts with MLC2 and Is Critical for Cytokinesis
To determine whether PKM2 has functions in cytokinesis, we immunostained U87 human glioblastoma (GBM) cells and found that PKM2 was localized in the contractile ring or cleavage furrow as well as in the equator region of a large percentage of dividing cells (Fig. 1a, Supplementary Fig. 1a). Localization of PKM2 in these regions was also observed in HeLa cervical cancer cells and U87 cells expressing active epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) vIII mutant (Supplementary Fig. 1a), which lacks 267 amino acids from the extracellular domain of EGFR and is commonly found in GBM as well as in breast, ovarian, prostate, and lung carcinomas 27.
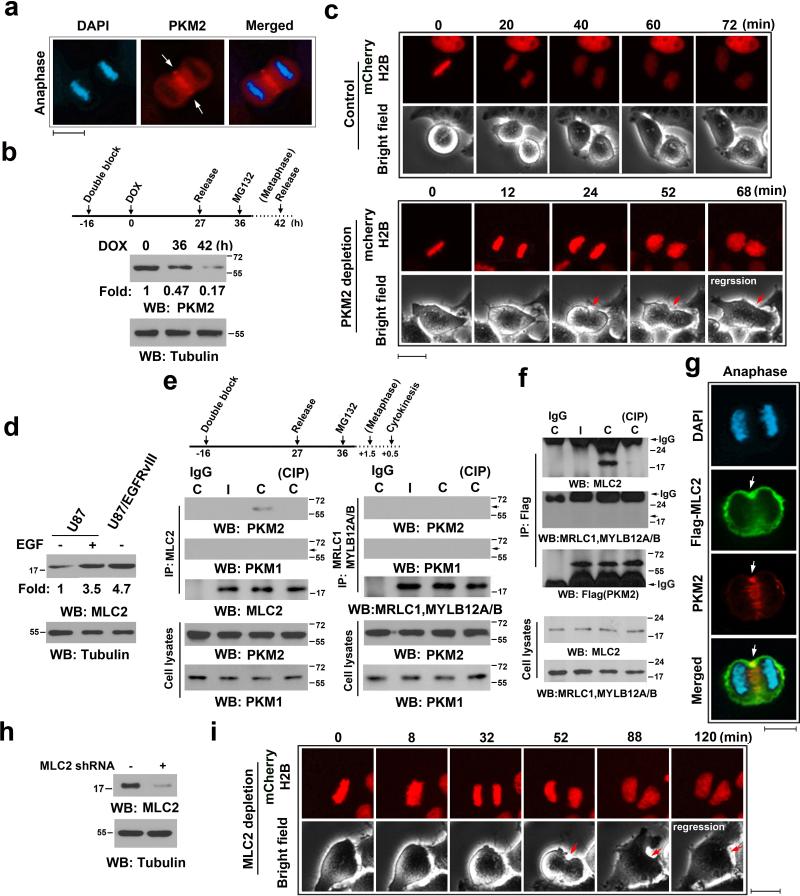
Figure 1. PKM2 Interacts with MLC2 and Is Critical for Cytokinesis.
Immunoblotting (b, d-f, h) and immunofluorescence (a, c, g, i) analyses were performed with the indicated antibodies. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue).
(a) U87 cells in cytokinesis were immunostained with the indicated antibodies. Scale bars, 10 μm.
(b) U87/EGFRvIII cells, synchronized by thymidine double block (2 mM), were released for the indicated time periods. Doxycycline (500 ng/ml) was added at the indicated time point to induce PKM2 shRNA expression. MG132 (25 μM) was added at the indicated time point to sustain the cells in metaphase for 6 h.
(c) U87/EGFRvIII cells expressing mCherry-histone H2B (for chromosome staining) were synchronized by thymidine double block. PKM2 shRNA was induced by doxycycline, as described in (b). MG132 was removed after 6 h incubation, followed by imaging analyses using a DeltaVision deconvolution microscope with a 20 × lens in a CO2 environment chamber. Selected time points are shown. Scale bars, 10 μm.
(d) The indicated cells were treated with or without EGF (100 ng/ml) for 24 h.
(e, f) U87 cells (e) or U87 cells expressing Flag-PKM2 (f), which had been synchronized by double thymidine block (2 mM) for 43 h, were unreleased or released for 9 h, followed by MG132 (25 μM) treatment for 1.5 h to arrest cells at metaphase. MG132 was removed for 30 min before cell harvesting. Immunoprecipitates with the indicated antibodies were incubated with or without CIP (10 units) for 30 min at 37°C and were washed with PBS three times. C, cytokinesis; I, interphase (no thymidine release).
(g) Flag-MLC2-expressing U87 cells, synchronized by double thymidine block (2 mM) for 43 h, were released for 10 h (anaphase). Scale bars, 10 μm.
(h) Control or MLC2 shRNA was expressed in U87/EGFRvIII cells.
(i) U87/EGFRvIII cells expressing MLC2 shRNA and mCherry-histone H2B were synchronized. MG132 (25 μM) was added at the indicated time point as shown in (b) and incubated with the cells for 1.5 h to sustain the cells in metaphase. MG132 were then removed, followed by imaging analyses using a DeltaVision deconvolution microscope. Selected time points are shown. Scale bars, 10 μm.
To avoid the effect of PKM2 depletion on G1-S transition and chromosome segregation and determine whether PKM2 regulates cytokinesis, we expressed doxycycline-inducible PKM2 shRNA in U87/EGFRvIII cells. These cells were synchronized from a double-thymidine block and release and arrested at metaphase by MG132 treatment; this was followed by removal of MG132 for cytokinesis 28. As demonstrated in Fig. 1b, PKM2 was largely depleted at the time that MG132 was removed. About 10%-12% cells could not recover from arrested metaphase because of the toxic effect of MG132, and the rest of the cells underwent cell division. Live cell analyses revealed that a large percentage of U87/EGFRvIII cells with PKM2 depletion failed to complete cytokinesis and cell division, with regression of the cleavage furrow (Fig. 1c and Supplementary Fig. 1b). PKM2 depletion-induced retarded cleavage furrow formation and failure of cell division were also observed by immunofluorescence (IF) analyses (Supplementary Fig. 1c). Some cells exhibited a chromosome segregation defect that resulted from incomplete cell synchronization and PKM2 depletion in early mitosis that affected correct kinetochore-microtubule attachment 26. These results indicate that PKM2 is involved in regulating tumor cell cytokinesis.
Myosin II, including its component RMLC, directly regulates contractile ring progression during cytokinesis. Quantitative PCR analyses of several human GBM cell lines and mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) showed expression of MLC2, MYL9, and MYL12A/B (Supplementary Fig. 1d). Intriguingly, expression of EGFRvIII mutant significantly enhanced MLC2 mRNA levels in U87 GBM cells (Supplementary Fig. 1d). Immunoblotting analyses showed that EGF treatment and EGFRvIII expression led to greatly increased MLC2 protein levels (Fig. 1d). These results indicate that EGFR activation, which greatly enhances PKM2 expression 22, also upregulates MLC2 expression in tumor cells.
The specific contractile ring localization of PKM2 suggests that it interacts with RMLC, which is a regulatory component of myosin II. To test this assumption, we synchronized U87 cells with a double thymidine block and release and MG132 treatment. We next immunoblotted immunoprecipitated MLC2 or MRLC1 and MYLB12A/B with antibodies for PKM2 and PKM1. We found that PKM2 rather than PKM1 bound to endogenous MLC2 (Fig. 1e, left panels) but not MRLC1 and MYLB12A/B (Fig. 1e, right panels) in U87 cells in cytokinesis, but not in interphase. This finding was further confirmed by reciprocal immunoprecipitation of Flag-tagged PKM2 in U87 (Fig. 1f) and U87/EGFRvIII (Supplementary Fig. 1e) cells and immunoblotting analyses with an anti-MLC2 antibody and an antibody for MRLC1 and MYLB12A/B. In addition, IF analysis indicates PKM2 partially co-localized with MLC2 in the contractile ring region (Fig. 1g and Supplementary Fig. 1f). Intriguingly, incubating the precipitates with calf intestinal phosphatase (CIP) abrogated the interaction between PKM2 and MLC2 (Figs. 1e and 1f, and Supplementary Fig. 1e), and this abrogated effect was blocked by including phosphatase inhibitors (sodium orthovanadate, sodium pyrophosphate, and sodium fluoride) (Supplementary Fig. 1e). These results suggest that protein phosphorylation is required for the binding of PKM2 to MLC2. Live cell analyses revealed that the expression of MLC2 shRNA in U87/EGFRvIII cells (Fig. 1h) blocked cytokinesis and cell division, with regression of the cleavage furrow, in a large percentage of the cells (Fig. 1i and Supplementary Fig. 1g). These results indicate that PKM2 interacts with MLC2 in a phosphorylation-dependent manner and that both PKM2 and MLC2 play a critical role in tumor cell cytokinesis.
Aurora B-phosphorylated PKM2 T45 Interacts with MLC2
To determine whether PKM2 is phosphorylated during cytokinesis and whether the phosphorylation of PKM2 is required for its binding to MLC2, we conducted liquid chromatography-coupled ion trap mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) analyses of tryptic digests of PKM2 in the MLC2 immunoprecipitates and found that PKM2 was phosphorylated at T45 (Fig. 2a).
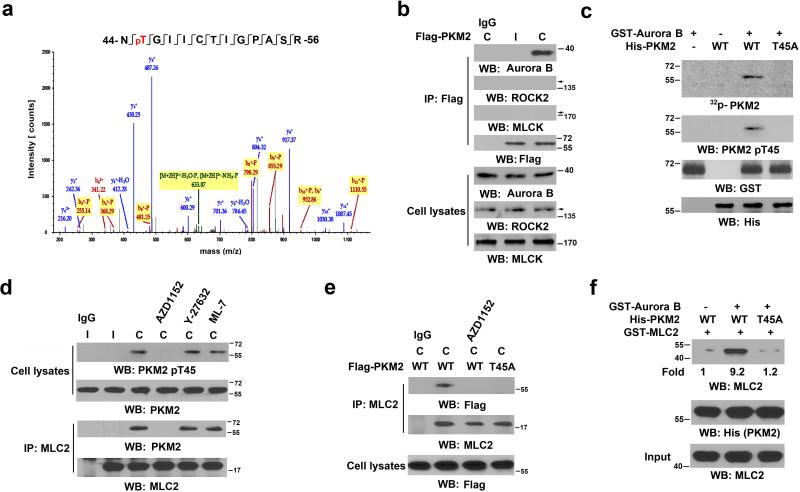
Figure 2. Aurora B-phosphorylated PKM2 T45 interacts with MLC2.
(a) PKM2, which was in the immunoprecipitate with an anti-MLC2 antibody from U87 cells in cytokinesis, was analyzed by mass spectrometry. The results of a fragment spectrometrum of a tryptic peptide at m/z 691.827 (mass error, −2.39 ppm) matched the doubly charged peptide 44-NTGIICTIGPASR-56, suggesting that T45 was phosphorylated. The Sequest score for this match was Xcorr = 3.19. The Mascot score was 46, and the expectation value was 5.1e-4.
(b) U87 cells that had been synchronized by double thymidine block (2 mM) for 43 h were unreleased or released for 10 h. Immunoprecipitation analyses with the indicated antibodies were performed. C, cytokinesis; I, interphase (no thymidine release).
(c) In vitro kinase assays were performed by mixing purified recombinant GST-Aurora B, His-PKM2 proteins, and 32P-ATP.
(d) U87 cells that had been synchronized by double thymidine block (2 mM) for 43 h were unreleased or released for 9 h, followed by MG132 (25 μM) treatment for 1.5 h to arrest cells at metaphase. MG132 was removed, and the cells were treated with or without AZD1152 (100 nM), Y-27632 (10 μM), or ML-7 (10 μM) for 30 min before cell harvesting.
(e) U87 cells that had been synchronized by double thymidine block (2 mM) for 43 h were released for 9 h, followed by MG132 (25 μM) treatment for 1.5 h. MG132 was removed, and the cells were treated with or without AZD1152 (100 nM) for 30 min before cell harvesting. Immunoprecipitation with the indicated antibodies was performed.
(f) WT His-PKM2 or His-PKM2 T45A on agarose beads was incubated with or without purified Aurora B protein for a kinase assay; it was then washed in PBS three times and incubated with recombinant GST-MLC2.
Several Ser/Thr protein kinases, including Aurora B, Rho-associated protein kinase (ROCK), and MLC kinase (MLCK), are known to be involved in cytokinesis 2, 29. Co-immunoprecipitation analyses revealed that PKM2 was associated only with Aurora B in cytokinesis but not in the interphase of U87 cells (Fig. 2b), and PKM2 largely co-localized with Aurora B in the spindle midzone of the cells (Supplementary Fig. 2a). In addition, this association was enhanced in U87/EGFRvIII cells (Supplementary Fig. 2b). We performed an in vitro kinase assay in which purified recombinant glutathione S-transferase (GST)-Aurora B was incubated with His-PKM2 proteins; Aurora B phosphorylated wild-type (WT) PKM2, but not PKM2 T45A, which was detected by both autoradiography and a specific anti-phospho-PKM2 T45 antibody (Fig. 2c and Supplementary Fig. 2c). Treating U87 cells with AZD1152 Aurora B inhibitor, Y-27632 ROCK inhibitor, and ML-7 MLCK inhibitor (inhibiting MRLC1 S19 phosphorylation) inhibited their respective kinase activity (Supplementary Fig. 2d), revealing that phosphorylation of WT PKM2 and the interaction between PKM2 and MLC2 in U87 cells in cytokinesis were inhibited only by AZD1152 (Fig. 2d). In contrast to its Flag-tagged WT counterpart, PKM2 T45A mutant largely lost its ability to interact with MLC2 (Fig. 2e).
To further evaluate the role of Aurora B in the interaction between PKM2 and MLC2, we mixed immobilized recombinant WT His-PKM2 or His-PKM2 T45A on agarose beads with recombinant GST-MLC2, with or without purified Aurora B protein for PKM2 phosphorylation. Fig. 2f shows that Aurora B enhanced the binding of WT PKM2, but not PKM2 T45A mutant, to MLC2. In addition, PKM1, unlike PKM2, was unable to bind to MLC2 (Supplementary Fig. 2e). These results indicate that Aurora B phosphorylates PKM2 at T45, leading to an enhanced interaction between PKM2 and MLC2 during cytokinesis.
Mutations of the polar or hydrophobic surface residues of R400, L401, P403, L404, D407, P408, T409, and K433, coded by the PKM2-specific exon 10, and the expression of these mutants showed that the K433E mutant, but not others, reduced the binding ability of PKM2 to Aurora B (Supplementary Fig. 2f) and was resistant to be phosphorylated at T45 during cytokinesis (Supplementary Fig. 2g). PKM2 K433 can bind Tyr-phosphorylated proteins 19, 30. Incubating the PKM2 precipitates with CIP abrogated the interaction between PKM2 and Aurora B (Supplementary Fig. 2h), suggesting that a phosphorylation event is involved in the formation of the complex. In addition, immunofluorescence studies showed that Flag-PKM2 K433E was unable to translocate to the contractile ring or co-localize with MLC2 (Supplementary Fig. 2i) during cytokinesis. These results indicate that PKM2 K433 is involved in binding to Aurora B and is required for translocation of PKM2 to the contractile ring region during cytokinesis.
PKM2 Phosphorylates MLC2 at Y118
PKM2 can act as a dual-specificity protein kinase that phosphorylates both the Ser/Thr and Tyr residues of its substrates 23, 31. To determine whether MLC2 is a substrate of PKM2 kinase activity, we performed an in vitro kinase assay by mixing recombinant Aurora B and MLC2 with WT PKM2, PKM2 K367M inactive mutant, or PKM1. Fig. 3a shows that PKM2, but not PKM2 K367M or PKM1, phosphorylated MLC2; MLC2 phosphorylation was detected by autoradiography using 32P-labeled PEP (the physiological phosphate group donor of PKM2) and anti-phospho-Tyr, but not anti-phospho-Ser or anti-phospho-Thr antibodies. Of note, this phosphorylation did not occur in the presence of ATP, the physiological phosphate group donor of classic protein kinases. An LC-MS/MS analysis of MLC2 phosphorylated by PKM2 showed that MLC2 is phosphorylated at Y118 (Fig. 3b). Mutations of Y118 and Y152, which are the only two Tyr residues in MLC2, into phenylalanine revealed that only MLC2 Y118F, not WT MLC2 or MLC2 Y152F, was resistant to PKM2-mediated phosphorylation, as detected by autoradiography and an antibody that specifically recognizes phosphorylated MLC2 Y118 (Fig. 3c and Supplementary Fig. 3a). In addition, PKM2 T45A, which largely reduced its binding to MLC2, inefficiently phosphorylated MLC2 Y118 (Supplementary Fig. 3b). These results indicate that Aurora B-phosphorylated PKM2 phosphorylates MLC2 Y118 in vitro.
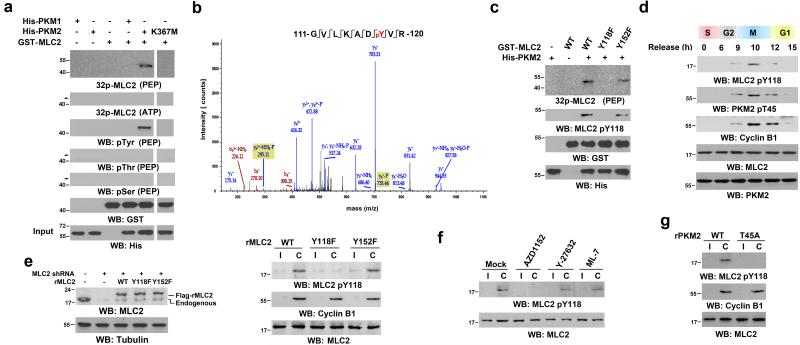
Figure 3. PKM2 Phosphorylates MLC2 at Y118.
a, c-g, Immunoblotting analyses were performed with the indicated antibodies. C, cytokinesis; I, interphase (no thymidine release).
(a) WT His-PKM2, His-PKM2 K367M, or His-PKM1 on agarose beads was incubated with purified Aurora B protein for a kinase assay; it was then washed in PBS three times and incubated with recombinant GST-MLC2 to proceed the kinase assay in the presence of 32P-labeled PEP or ATP for autoradiography.
(b) In vitro kinase assays were performed by mixing purified recombinant GST-MLC2 with His-PKM2. MLC2 was analyzed by mass spectrometry. The results of a mass spectrometric analysis of a tryptic fragment at m/z 550.779 (mass error, −0.16 ppm) matched those of the doubly charged peptide 111-GVLKADYVR-120, suggesting that Y118 was phosphorylated. The Sequest score for this match was Xcorr =2.83. The Mascot score was 51, and the expectation value was 1.1e-4.
(c) In vitro kinase assays were performed by mixing the indicated GST-MLC2 proteins with WT His-PKM2 in the presence of 32P-PEP for autoradiography.
(d) U87 cells that had been synchronized by double thymidine block (2 mM) for 43 h were released for the indicated time periods.
(e) U87 cells, with and without MLC2 shRNA expression, were reconstituted with or without expression of WT rMLC2, rMLC2 Y118F, or rMLC2 Y152F (left panel). The cells were synchronized by double thymidine block (2 mM) for 43 h and then unreleased or released for 10 h (right panel).
(f) U87 cells synchronized by double thymidine block (2 mM) for 43 h were unreleased or released for 9 h, followed by MG132 (25 μM) treatment for 1.5 h to arrest cells at metaphase. MG132 was replaced with AZD1152 (100 nM), Y-27632 (10 μM), or ML-7 (10 μM) for 30 min before cell harvesting.
(g) U87 cells with PKM2 depletion were stably transfected with a vector expressing WT rPKM2 or rPKM2 T45A. These cells were synchronized by double thymidine block (2 mM) for 43 h and then unreleased or released for 10 h.
Synchronized U87 (Fig. 3d) and HeLa (Supplementary Fig. 3c) cells with a double thymidine block and release had prominent MLC2 Y118 and PKM2 T45 phosphorylations at late-stage mitosis/cytokinesis (as indicated by cyclin B1 expression levels, which started to decrease at the beginning of anaphase 32), and these phosphorylations were decreased in the G1 phase of the cell cycle. In addition, depletion of MLC2 with MLC2 shRNA and reconstituted expression of RNAi-resistant (r)MLC2 WT, rMLC2 Y118F, or rMLC2 Y152F in U87 (Fig. 3e, left panel) and U251 (Supplementary Fig. 3d) GBM cells revealed that rMLC2 Y118F, but not WT rMLC2 and rMLC2 Y152F, was resistant to the enhanced phosphorylation during cytokinesis of U87 (Fig. 3e, right panel) and U251 (Supplementary Fig. 3e) cells. Immunofluorescence studies showed that MLC2 Y118F and Y152F mutations did not affect MLC2 localization during cytokinesis (Supplementary Fig. S3f), suggesting that the resistance of MLC2 Y118F to phosphorylation was not due to its mis-localization.
Consistent with the role of Aurora B in the interaction between PKM2 and MLC2, AZD1152 Aurora B inhibitor, but not Y-27632 ROCK or ML-7 MLCK inhibitor, blocked PKM2-dependent phosphorylation of MLC2 at Y118 in cytokinesis (Fig. 3f) and in the contractile ring region of mitotic cells (Supplementary Fig. 3g). Furthermore, PKM2 depletion with PKM2 shRNA and reconstituted WT rPKM2 or rPKM2 T45A expression in U87 (Supplementary Fig. 3h, left panel) or U251 cells (Supplementary Fig. 3h, right panel) revealed that rPKM2 T45A expression abrogated MLC2 Y118 phosphorylation in the cytokinesis of U87 (Fig. 3g) and U251 (Supplementary Fig. 3i) cells and the contractile ring region of dividing cells (Supplementary Fig. 3j). Thus, these results indicate that Aurora B-dependent PKM2 phosphorylation at T45 is required for PKM2-dependent MLC2 phosphorylation at Y118 during cytokinesis.
MLC2 pY118 Primes ROCK2-mediated MLC2 pS15
Human MLC2 phosphorylation at S15 is known to be critical for actomyosin contraction 6, 33, 34. To determine whether MLC2 Y118 phosphorylation has a regulatory effect on MLC2 S15 phosphorylation, we performed immunoblotting and immunofluorescence studies with a specific MLC2 pS15 antibody (Supplementary Fig. 4a); these studies revealed that MLC2 S15 phosphorylation primarily occurred in cytokinesis, not in the interphase (Fig. 4a, left panel). In addition, this phosphorylation was restricted in the contractile ring region in U87 cells with reconstituted expression of WT rMLC2, but not rMLC2 Y118F, in the presence of MLC2 shRNA expression (Fig. 4a, middle and right panels, single cell; Supplementary Fig. 4b, multiple cells). In contrast, rMLC2 Y118F expression did not affect S19 phosphorylation of MRLC1 and MYLB12A/B (Supplementary Fig. 4c). Furthermore, depletion of endogenous MLC2 and reconstituted expression of WT rMLC2 or rMLC2 S15A in U87 cells revealed that the MLC2 S15A mutation did not affect MLC2 phosphorylation at Y118 (Supplementary Fig. 4d). These results indicate that MLC2 Y118 phosphorylation primes MLC2 S15 phosphorylation.
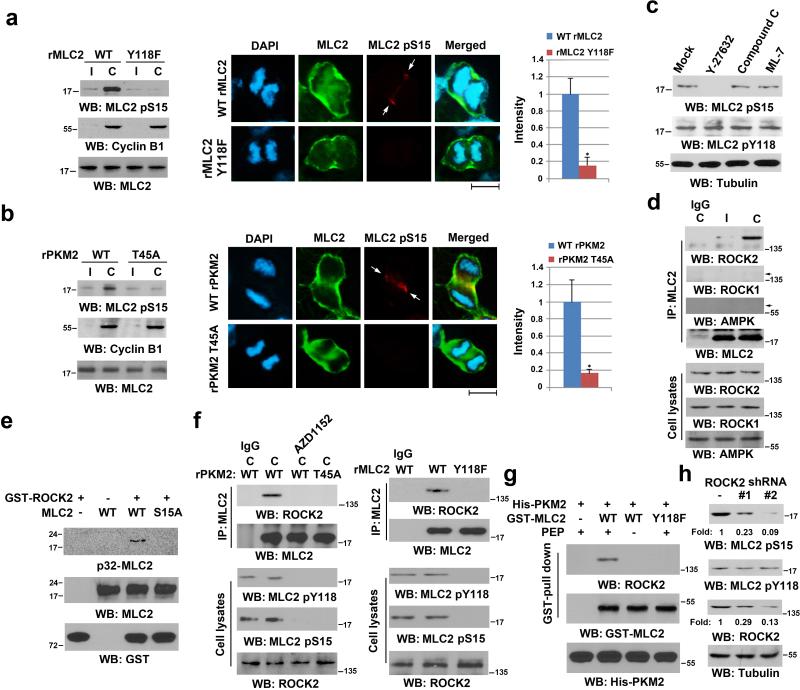
Figure 4. MLC2 pY118 Primes ROCK2-mediated MLC2 pS15.
Immunoblotting analyses were performed with the indicated antibodies. C, cytokinesis; I, interphase (no thymidine release).
(a, b) U87 cells with reconstituted expression of WT rMLC2, or rMLC2 Y118F (a), WT rPKM2, or rPKM2 T45A (b) were synchronized by double thymidine block (2 mM) for 43 h, with or without release for 10 h (left panel). Immunofluorescence analyses of cells in cytokinesis were performed with the indicated antibodies (middle panel). Scale bars, 10 μm. The relative fluorescence intensity of the indicated proteins in the contractile ring of 100 cells from each cell line was quantified. Data represent the mean ± SD of three independent experiments (right panel). *P<0.01: statistically significant value in relation to U87 cells with PKM2 depletion and reconstituted expression of WT rPKM2, Student's t-test.
(c) U87 cells, synchronized by double thymidine block (2 mM) for 43 h, were released for 9 h, followed by MG132 (25 μM) treatment for 1.5 h to arrest cells at metaphase. MG132 was then replaced with Y-27632 (10 μM), compound C (20 μM), or ML-7 (10 μM) for 30 min before cell harvesting.
(d) U87 cells were synchronized by double thymidine block (2 mM) for 43 h, followed by no release or release for 10 h. Immunoprecipitation analyses were performed.
(e) In vitro kinase assays were performed by mixing purified recombinant active GST-ROCK2 with purified PKM2-phosphorylated MLC2 for autoradiography.
(f) U87 cells with depleted PKM2 or MLC2 and reconstituted expression of WT rPKM2 or rPKM2 T45A (left panel), WT rMLC2 or rMLC2 Y118F (right panel) were synchronized and arrested at metaphase, as described in (c). MG132 was then replaced with AZD1152 (100 nM) for 30 min before cell harvesting (left panel). Immunoprecipitation analyses were performed.
(g) WT GST-MLC2 on agarose beads was incubated with purified Aurora B-phosphorylated His-PKM2 protein for a kinase assay in the presence or absence of PEP, which was followed by incubation with the lysate of HeLa cells synchronized by double thymidine block (2 mM) for 43 h and release for 10 h.
(h) U87 cells that expressed a control or two different ROCK2 shRNAs were synchronized by double thymidine block (2 mM) for 43 h and release for 10 h.
Depletion of endogenous PKM2 and reconstituted rPKM2 T45A expression in U87 cells (Supplementary Fig. 3h) revealed inhibited MLC2 S15 phosphorylation in cytokinesis and in the contractile ring region of dividing cells (Fig. 4b; Supplementary Fig. 4e, multiple cells). These results indicate that Aurora B-dependent PKM2 T45 phosphorylation, which regulates MLC2 Y118 phosphorylation, is required for MLC2 S15 phosphorylation. The evidence that MLC2 S15A was still detected in the contractile ring region (Supplementary Fig. 4f) and that MLC2 S15A and Y118F mutants still interacted with PKM2 during cytokinesis (Supplementary Fig. 4g) further support that Aurora B-dependent PKM2 T45 phosphorylation is required for the interaction between PKM2 and MLC2.
AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) 35, 36, MLCK 37, and ROCK2 38 have been found to directly or indirectly regulate the phosphorylation of different RMLC isoforms. We treated U87 cells with Y-27632 ROCK inhibitor, compound C AMPK inhibitor (blocking downstream acetyl-CoA carboxylase [ACC] phosphorylation), and ML-7 MLCK inhibitor, which inhibited their respective kinase activities (Supplementary Figs. 2d and 4h); MLC2 S15 phosphorylation was primarily blocked by ROCK inhibition (Fig. 4c). ROCK1 and ROCK2 are known to be involved in cytokinesis 29, 39. Co-immunoprecipitation analyses revealed that MLC2 interacted with ROCK2, but not ROCK1 or AMPK, in cytokinesis (Fig. 4d). In addition, an in vitro kinase assay with mixed recombinant GST-ROCK2 and MLC2 revealed that ROCK2 phosphorylated WT MLC2, but not MLC2 S15A mutant, indicating that it phosphorylates MLC2 at S15 in vitro (Fig. 4e).
We found that Aurora B-dependent PKM2 T45 phosphorylation is required for PKM2-dependent MLC2 Y118 phosphorylation, which primes ROCK2-dependent MLC2 S15 phosphorylation. In line with these findings, we showed that Aurora B inhibition with AZD1152 and reconstituted expression of rPKM2 T45A (Fig. 4f, left panel) or rMLC2 Y118F (Fig. 4f, right panel) mutants, which abrogated MLC2 Y118 phosphorylation, blocked the interaction between MLC2 and ROCK2 and the phosphorylation of MLC2 at S15. The requirement of PKM2-dependent MLC2 phosphorylation for the interaction between MLC2 and ROCK2 was further supported by the results of a GST-MLC2 pull-down assay. GST-MLC2 but not GST-MLC2 Y118F mutant interacted with ROCK2 in the presence of PKM2 and PEP (Fig. 4g). In addition, separate expression of two different ROCK2 shRNAs inhibited phosphorylation of MLC2 at S15 but not Y118 in cytokinesis (Fig. 4h). These results indicate that PKM2-phosphorylated MLC2 at Y118 is required for the interaction between ROCK2 and MLC2 and ROCK2-phosphorylated MLC2 at S15.
MLC2 Phosphorylation by PKM2 is Critical for Cytokinesis
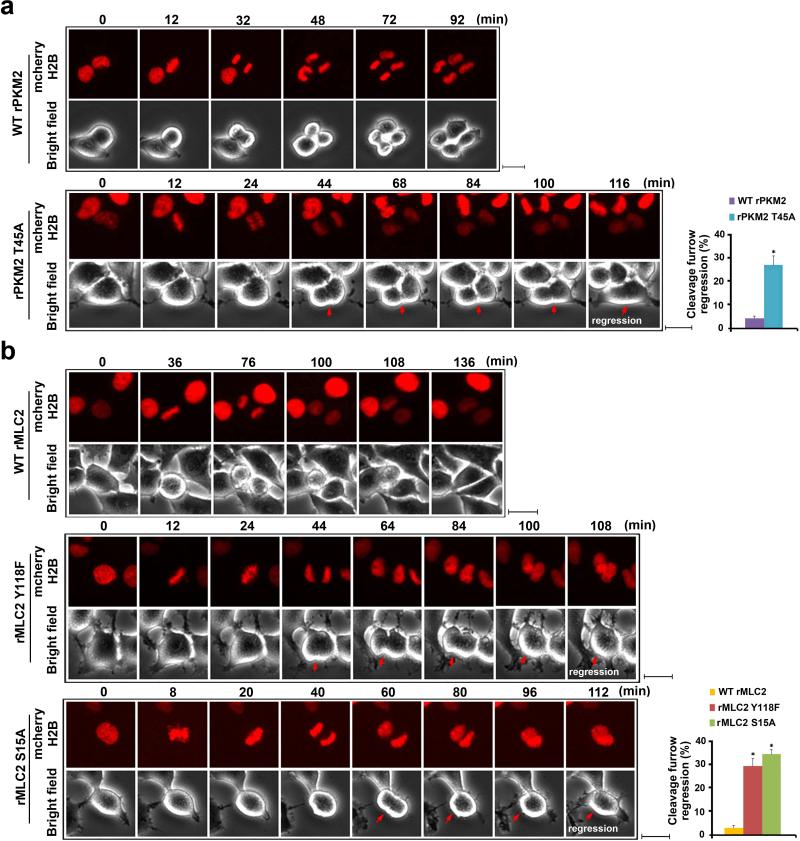
To determine the effect of PKM2-regulated MLC2 on cytokinesis progression, we evaluated live images of late-mitosis U87/EGFRvIII cells. These cells were infected with the lentivirus that co-expressed GFP and shRNA for PKM2 or MLC2 and the lentivirus that expressed RNAi-resistant WT rPKM2, rPKM2 T45A, WT rMLC2, rMLC2 Y118F, or rMLC2 S15A. High viral infection rates, efficient depletion of endogenous PKM2 or MLC2 (Supplementary Fig. 5a), and similar reconstituted expression levels were achieved (Supplementary Fig. 5b). Live cell analyses showed that the mitotic cells expressing WT rPKM2 (Fig. 5a and Supplementary Video 1) and WT rMLC2 (Fig. 5b and Supplementary Video 2) underwent normal and complete cell division. In contrast, a large percentage of cells with reconstituted expression of rPKM2 T45A (Fig. 5a and Supplementary Video 3), rMLC2 Y118F, and rMLC2 S15A failed to complete cytokinesis, with regression of cleavage furrow (Fig. 5b and Supplementary Videos 4 and 5). These results indicate that Aurora B-dependent PKM2 T45 phosphorylation and the subsequent PKM2 phosphorylation-primed MLC2 phosphorylation at S15 by ROCK2 are instrumental to cytokinesis in GBM cells.
Figure 5. MLC2 Phosphorylation by PKM2 Is Critical for Cytokinesis.
(a, b) U87/EGFRvIII cells with PKM2 depletion and reconstituted expression of WT rPKM2 or rPKM2 T45A (a) or with MLC2 depletion and reconstituted expression of WT rMLC2, rMLC2 Y118F, or rMLC2 S15A (b) were synchronized by double thymidine block (2 mM) for 43 h and released for 9 h. Imaging analyses were performed by using a DeltaVision deconvolution microscope with a 20×lens in a CO2 environment chamber. Pictures were taken at 4-min intervals. Selected time points are shown. Scale bars, 10 μm. Thirty cells from each cell line were analyzed. The data represent the mean ± SD of three independent experiments (right panel). *P<0.01: statistically significant value in relation to U87/EGFRvIII cells with reconstituted expression of WT rPKM2 (a) or WT rMLC2 (b), Student's t-test.
Oncogenic Signaling Promotes PKM2-regulated Cytokinesis
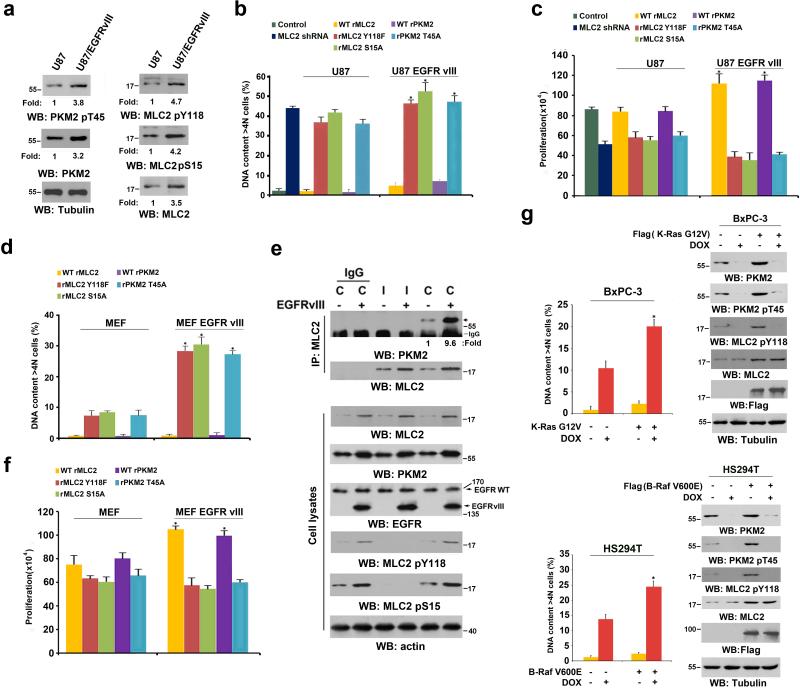
EGFR activation by EGF treatment or EGFRvIII mutant expression in GBM cells significantly upregulated the expression of both PKM2 22 and MLC2 (Fig. 1d). In addition, EGFRvIII expression in U87 cells increased the total phosphorylation levels of PKM2 T45, MLC2 Y118, and MLC2 S15 (Fig. 6a). We performed flow cytometry analyses of synchronized U87 cells with a double thymidine block and release. Fig. 6b shows that about 35%-40% of U87 cells with depleted endogenous PKM2 and MLC2 and with or without reconstituted expression of rPKM2 T45A, rMLC2 Y118F, or rMLC2 S15A had DNA content of more than 4N, indicating DNA replication in the absence of cell division. In addition, the expression of these PKM2 or MLC2 mutants and deletion of MLC2 inhibited U87 cell proliferation (Fig. 6c). In contrast, reconstituted expression of rPKM2 T45A, rMLC2 Y118F, or rMLC2 S15A in U87/EGFRvIII cells resulted in more profound defects in cytokinesis (Fig. 6b) and cell proliferation (Fig. 6c). Furthermore, flow cytometric analyses showed that the expression of rPKM2 T45A, rMLC2 Y118F, or rMCL2 S15A resulted in the accumulation of cells in the sub-G1 phase (an indication of apoptotic cells), with decreased number of cells in the G1/S phase (Supplementary Fig. 6a). Notably, overexpression of a phosphorylation-mimic MLC2 S15D mutant largely rescued the cytokinesis defects of rPKM2 T45A-expressed U87 cells, supporting the critical role of MLC2 phosphorylation in PKM2-regulated cytokinesis (Supplementary Fig. 6b). In line with the results from U87/EGFRvIII cells, EGFRvIII expression in HeLa cells also led to upregulated expression and phosphorylation levels of PKM2 and MLC2 and exacerbated the cytokinesis defect under the context of PKM2 depletion (Supplementary Fig. 6c). These results indicate that tumor cells with EGFRvIII-enhanced expression of PKM2 and MLC2 increase their dependence on PKM2's cytokinesis regulation.
Figure 6. Oncogenic Signaling Promotes PKM2-regulated Cytokinesis.
(a) U87 and U87/EGFRvIII cells, synchronized by thymidine double block (2 mM), were released for 10 h (anaphase). Immunoblotting analyses were performed with the indicated antibodies.
(b, c) U87 and U87/EGFRvIII cells with reconstituted expression of WT rPKM2, rPKM2 T45A, WT rMLC2, rMLC2 Y118F, or rMLC2 S15A were synchronized by double thymidine block (2 mM) for 43 h and released for 36 h. Flow cytometric analyses were performed (b). The cells (2 × 104) were plated and counted 7 days after being seeded in DMEM with 2% bovine calf serum (c). The data represent the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. *P<0.01: statistically significant value in relation to parental cells, Student's t-test.
(d) MEFs and EGFRvIII-expressing MEFs with reconstituted expression of WT rPKM2, rPKM2 T45A, WT rMLC2, rMLC2 Y118F, or rMLC2 S15A were synchronized by double thymidine block (2 mM) for 43 h and released for 36 h. Flow cytometric analyses were performed. The data represent the mean ± SD of three independent experiments.
(e) MEFs and EGFRvIII-expressing MEFs that had been synchronized by thymidine double block (2 mM) were unreleased or released for 10 h (anaphase). Immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting analyses were performed with the indicated antibodies. C, cytokinesis; I, interphase (no thymidine release).
(f) The indicated cells (2 × 104) were plated and counted 7 days after being seeded in DMEM with 2% bovine calf serum. The data represent the mean ± SD of three independent experiments.
(g) BxPC3 and K-Ras G12V-expressing BxPC3 cells (top panel) or HS294T and B-Raf V600E-expressing HS294T cells (bottom panel) were treated with doxycycline (500 ng/ml) for the indicated time periods, as shown in Fig. 1b, to induce PKM2 shRNA expression. Flow cytometric analyses were performed. The data represent the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. Immunoblotting analyses were performed with the indicated antibodies.
PKM2 is highly expressed during embryonic development 16. To determine whether the function of PKM2 in cytokinesis is also shared by rapidly proliferating embryonic cells, we depleted PKM2 or MLC2 from immortalized MEFs and reconstituted their expression with WT rPKM2, rPKM2 T45A, WT rMLC2, rMLC2 Y118F, or rMLC2 S15A (Supplementary Fig. 6d). Of note, endogenous expression levels of PKM2 and MLC2 in MEFs were lower than those in U87, U251, and U87/EGFRvIII GBM cells and GSC11 human primary GBM cells (Supplementary Fig. 6e), and the cytokinesis defect rate in MEFs with disrupted PKM2 regulation was significantly lower than that in U87 cells (Figs. 6b and 6d). Expression of the EGFRvIII mutant in MEFs greatly increased PKM2 and MLC2 expression levels, with an enhanced interaction between PKM2 and MLC2 and phosphorylation levels of MLC2 at Y118 and S15 (Fig. 6e). In addition, the reconstituted expression of rPKM2 T45A, rMLC2 Y118F, or rMLC2 S15A in MEFs/EGFRvIII cells (Supplementary Fig. 6f) heightened the defect of cytokinesis (Fig. 6d) and proliferation (Fig. 6f) in contrast to the expression of these mutants in parental MEFs.
Similar to MEFs, A549 human lung adenocarcinoma cells and HCT116 human colorectal carcinoma cells, which had lower expression levels of MLC2 and PKM2 than did the GBM cells (Supplementary Fig. 6e), had limited defects in cytokinesis and cell proliferation (Supplementary Fig. 6g) after doxycycline-induced PKM2 depletion (Supplementary Fig. 6h). These results suggest that these cells regulate cytokinesis mainly through other isoforms of RMLC protein.
To validate this hypothesis, we determined the role of MRLC1 in cytokinesis in HCT116 cells. We depleted MRLC1 and reconstituted the expression of rMRLC1 T18/S19 phosphorylation-dead mutant (T18/S19A) because T18/S19 phosphorylation of smooth muscle and non-muscle RMLC isoforms is important for actomyosin contraction 5, 6, 7 (Supplementary Fig. 6i, left panel). The expression of rMRLC1 T18/S19A, but not its WT counterpart, led to significant cytokinesis defects (Supplementary Fig. 6i, right panel), indicating that T18/S19 phosphorylation plays a major role in the cytokinesis of HCT116 cells. Reconstituted expression of MLC2 S15A and rMRLC1 T18/S19A in HCT116 cells with depleted MLC2 and MRLC1 (Supplementary Fig. 6j, left panel) had an added effect on the cytokinesis defect rate compared with that in HCT116 cells that expressed MLC2 S15A or rMRLC1 T18/S19A alone (Supplementary Fig. 6j, right panel). These findings indicate that MLC2 S15 and rMRLC1 T18/S19 phosphorylations have a non-overlapped function in regulation of cytokinesis progression. As expected, expression of EGFRvIII increased the phosphorylation levels of both PKM2 and MLC2 in a PKM2-dependent manner in A549 and HCT116 cells (Supplementary Fig. 6h). In addition, PKM2 depletion increased the cytokinesis defect rates of EGFRvIII-expressing A549 and HCT116 cells compared to those in their parental cells (Supplementary Fig. 6g). These results indicate that PKM2's limited effect on cytokinesis regulation in tumor cells with low PKM2 and MLC2 expression can be significantly altered after EGFR activation.
To determine whether our findings were limited to EGFR activation, we examined the role of PKM2 in the cytokinesis of tumor cells with K-Ras G12V and B-Raf V600E mutations, which occur in many types of cancer. Fig. 6g shows that overexpression of K-Ras G12V in BxPC-3 human pancreatic cancer cells (with no endogenous Ras mutation) (Fig. 6g, top panel) and B-Raf V600E in HS294T human melanoma cells (with no endogenous Raf mutation) (Fig. 6g, bottom panel) resulted in upregulation of PKM2 and MLC2 expression, PKM2 T45 phosphorylation, and PKM2-dependent MLC2 Y118 phosphorylation and exhibited PKM2 expression-dependent cytokinesis 40. These results suggest that K-Ras and B-Raf mutations increase the reliance of tumor cells on PKM2-regulated cell division.
MLC2 Phosphorylation by PKM2 Promotes Tumorigenesis
Abnormal cytokinesis affects cell growth and proliferation 3. Although multi-nucleated cells likely have an aberrant cell metabolism, an in vitro pyruvate kinase assay revealed that PKM2 T45A had similar glycolytic kinase activity to that of its WT counterpart (Supplementary Fig. 7a). In addition, compared with the expression of its WT counterpart, PKM2 T45A expression did not affect the glucose uptake and lactate production in U87/EGFRvIII cells arrested at the G1/S phase (Supplementary Fig. 7b), PKM2-regulated Bub3 Y207 phosphorylation (Supplementary Fig. 7c), chromatid alignment and segregation (Supplementary Fig. 7d), or EGF-induced and PKM2-dependent histone H3 T11 phosphorylation in U87 cells (Supplementary Fig. 7e). These results suggest that PKM2 T45 phosphorylation exerts a specific role in cytokinesis.
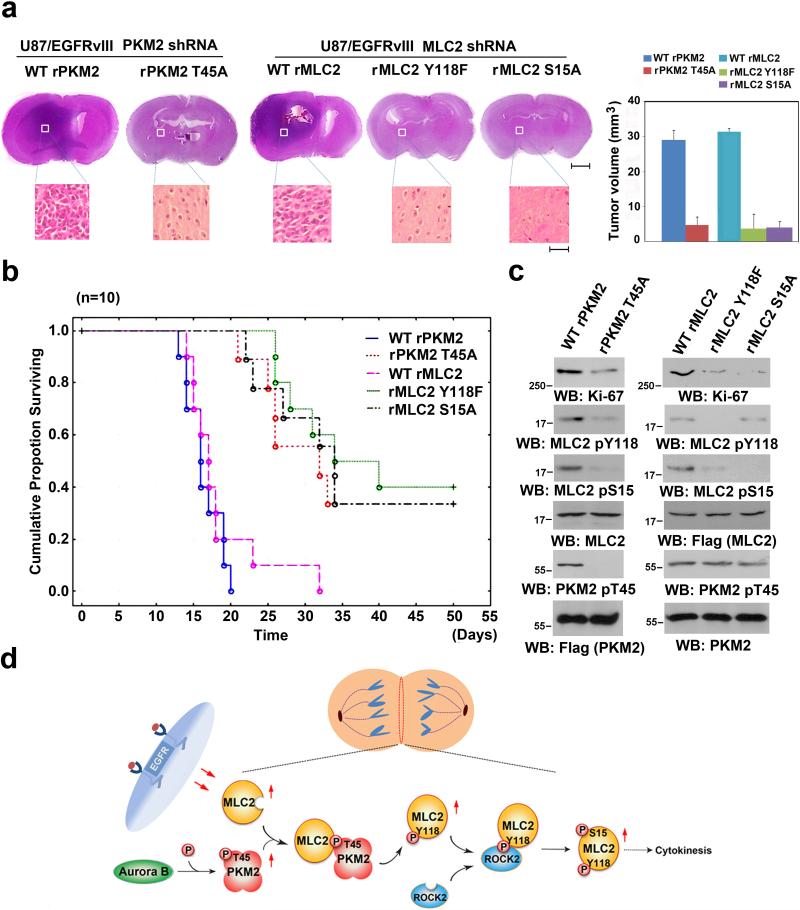
To determine the role of PKM2-regulated MLC2 phosphorylation in brain tumor development, we intracranially injected athymic nude mice with PKM2- or MLC2-depleted U87/EGFRvIII (Supplementary Fig. 5b) and GSC11 (Supplementary Fig. 7f) cells with reconstituted WT rPKM2, rPKM2 T45A, WT rMLC2, rMLC2 Y118F, or rMLC2 S15A expression. U87/EGFRvIII (Fig. 7a) and GSC11 (Supplementary Fig. 7g) cells that expressed WT rPKM2 or WT rMLC2 elicited rapid tumorigenesis. In contrast, rPKM2 T45A, rMLC2 Y118F, and rMLC2 S15A expression significantly inhibited brain tumor growth (Fig. 7a and Supplementary Fig. 7g) and prolonged mouse survival (Fig. 7b). The expression of Ki-67, a marker of cell proliferation, was reduced in tumor tissue that expressed these mutants (Fig. 7c). Furthermore, rPKM2 T45A expression reduced the phosphorylation levels of MLC2 Y118 and S15, and rMLC2 Y118F expression blocked MLC2 S15 phosphorylation in tumor tissue (Fig. 7c). These results indicate that PKM2-regulated MLC2 phosphorylation and cytokinesis are instrumental in brain tumor development.
Figure 7. MLC2 Phosphorylation by PKM2 Promotes Tumorigenesis.
(a, c) U87/EGFRvIII (5 × 105) cells with PKM2 depletion and reconstituted expression of WT rPKM2 or rPKM2 T45A or with MLC2 depletion and reconstituted expression of WT rMLC2, rMLC2 Y118F, or rMLC2 S15A were intracranially injected into athymic nude mice. The mice were sacrificed 14 days after injection of cells and examined for tumor growth. Hematoxylin-and-eosin-stained coronal brain sections show representative tumor xenografts. Scale bars for original images, 0.2 cm; Scale bars for amplified images, 50 μm. Tumor volumes were measured using length (a) and width (b) and calculated using the equation: V = ab2/2. The data represent the means ± SD of seven mice (right panel). The tumor tissues normalized with expression levels of Flag-tagged rPKM2 or rMLC2 were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies (c).
(b) U87/EGFRvIII (5 × 105) cells with PKM2 depletion and reconstituted expression of WT rPKM2 or rPKM2 T45A or with MLC2 depletion and reconstituted expression of WT rMLC2, rMLC2 Y118F, or rMLC2 S15A were intracranially injected into athymic nude mice. Data were presented by the Kaplan-Meier plots of 10 mice.
(d) A Mechanism of PKM2-regulated cytokinesis. Aurora B-phosphorylated PKM2 at T45 results in PKM2's localization and its interaction with MLC2 at the equator/contractile ring region of mitotic cells, where PKM2 phosphorylates MLC2 at Y118. MLC2 Y118 phosphorylation primes ROCK2's binding to MLC2, ROCK2-dependent MLC2 S15 phosphorylation, and subsequent cytokinesis progression.
DISCUSSION
PKM2 is known as a classic glycolytic enzyme and is upregulated by growth factor-induced and nuclear factor-κB-regulated PKM gene transcription in tumor cells 22. PKM2 has critical nuclear functions in directly controlling gene transcription by binding to transcriptional factors, such as β-catenin and hypoxia-inducible factor 1α, and phosphorylating histone H3 at T11, leading to histone H3 acetylation 19, 23. PKM2-dependent c-Myc and cyclin D1 expression regulate the Warburg effect and G1-S transition, respectively 21. In addition, PKM2 binds to and phosphorylates Bub3 and regulates correct kinetochore-microtubule attachment, the spindle-assembly checkpoint, and accurate chromosome segregation 26. However, the role of PKM2 in controlling other phases of the cell cycle remains unknown. In this report, we demonstrated that the activation of EGFR, K-Ras, and B-Raf resulted in enhanced expression of both PKM2 and MLC2. Importantly, PKM2 T45 is phosphorylated by Aurora B during cytokinesis. This phosphorylation is required for PKM2-dependent MLC2 phosphorylation at Y118, leading to the ROCK2-dependent phosphorylation of MLC2 at S15 and cytokinesis progression (Fig. 7d).
Several RMLC isoforms exist in tumor cells, and the phosphorylation of smooth muscle and non-muscle cell isoforms at T18/S19 (which are not conserved in MLC2) and MLC2 at S15 regulates actomyosin contraction by distinct mechanisms 5, 6, 7. The phosphorylation of smooth muscle and non-muscle cell RMLC isoforms results in a conformational change, with enhanced myosin ATPase activity and effects on actin filament formation 41. In contrast, MLC2 phosphorylation has no significant effect on myosin ATPase activity; instead, it modulates Ca2+-sensitivity and Ca2+/troponin-dependent force generation, influencing contraction properties 6. In contrast to the relatively well-studied RMLC S19 phosphorylation regulation, how MLC2 S15 phosphorylation is regulated in tumor cells is largely unknown. We found that MLC2 expression was significantly increased in tumor cells that expressed active EGFRvIII, K-Ras G12V, and B-Raf V600E mutants. In addition, the sequential interaction between PKM2 and MLC2 and the interaction between MLC2 and ROCK2 are dependent on the primed phosphorylation of PKM2 and MLC2, respectively. These results strongly suggest that phosphorylation-mediated structural changes of proteins or the creation of protein-binding motifs promotes subsequent protein interactions. PKM2 does not associate with ROCK2, suggesting that it disassociates from the ROCK2 and MLC2 complex after phosphorylating MLC2 Y118. These findings highlight the role of PKM2-involved protein posttranslational modifications in precisely controlling cytokinesis. The added effect of MLC2 S15A and rMRLC1 T18/S19A expression on blocking cytokinesis progression indicates that a coordinated regulation of different RMLC isoforms is required for the fully executed constriction of the contractile ring and cytokinesis completion.
Aurora kinase B localizes at both the contractile ring/cleavage furrow region and the central spindle area during cytokinesis 42. Intriguingly, PKM2 partially localizes at the contractile ring region as well as the central spindle area, suggesting that PKM2 is involved in both cytokinesis and spindle morphologic alteration.
Our results suggest that PKM2-regulated cytokinesis occurs in certain types of tumors. It is known that cell cycle progression and cell proliferation can be promoted by distinct signal transduction that is induced by oncogene activation, tumor suppressor gene deficiency, or both. Published evidence demonstrates that PKM2 regulation is signaling dependent, and the roles of PKM2 in tumorigenesis vary on the basis of the signaling context. For instance, recent reports showed that PKM2 deficiency in mice did not block Brca1 loss-driven mammary tumor formation but inhibited cyclin D1 expression and leukemia initiation induced by BCR-ABL and MLL-AF9 43, 44. These findings suggest that PKM2, which is not highly expressed in every type of human cancer, regulates tumor development in a signaling context-dependent manner. In line with these observations, we showed that expression of EGFRvIII in GBM cells, K-Ras G12V in pancreatic cancer cells, and B-Raf V600E in melanoma cells resulted in upregulation of PKM2 and MLC2 expression, Aurora B-mediated PKM2 T45 phosphorylation, PKM2-dependent MLC2 Y118 phosphorylation, and MLC2 Y118-dependent cytokinesis. These results suggest that tumor cells with activated EGFR, K-Ras, or B-Raf compared with other cells without activation of these oncogenes develop a new pattern of molecular signatures for regulating cell proliferation: enhanced PKM2 expression to regulate glycolysis and prepare building blocks for cell proliferation and enhanced PKM2 and MLC2 expression to govern the progression of cytokinesis. These changes in the molecular signature enable these tumor cells to coordinate their metabolism and cycle progression through PKM2 21, 23, 45, 46.
Human PKM2 is expressed in early fetal tissues and decreases immediately after birth. In many cancer cells, it is overexpressed 47, 48, 49. In this study, we found that it had a limited effect on cytokinesis in MEFs and tumor cells (such as HCT116 cells) with low levels of PKM2 expression, which is in line with the results of a report that PKM2 depletion in HCT116 cells has limited effect on tumor growth 50. Of note, cytokinesis of HCT116 cells is largely dependent on MRLC1 regulation. However, activation of EGFR increases the cells’ dependence on PKM2-regulated cytokinesis by increasing the expression levels of PKM2 and MLC2 and PKM2-mediated MLC2 phosphorylation. These results suggest that PKM2 participates in cytokinesis of certain types of normal and tumor cells in a manner dependent on the level and duration of activation of growth factor receptors, such as EGFR. Importantly, tumor cells with constitutively activated oncogenic signaling induced by EGFR, K-ras, and B-Raf significantly upregulate PKM2 and enhances the activity of upregulated MLC2. The disruption of PKM2-dependent MLC2 phosphorylation in GBM cells leads to polyploidy and inhibits tumor cell proliferation and tumor development.
Thus, in our study, we identified a novel regulatory mechanism for cell cycle progression. Our findings highlight the non-metabolic function of PKM2 as a protein kinase that controls cell division and may provide a molecular basis for improving the diagnosis and treatment of tumors with upregulated PKM2.
METHODS
Cell culture and synchronization
U87, U251, and MEFs, were from ATCC and were maintained in Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (DMEM) supplemented with 10% bovine calf serum (HyClone, Logan, UT). Human primary GSC11 glioblastoma cells were maintained in DMEM/F-12 50/50 supplemented with B27, EGF (10 ng/ml), and basic fibroblast growth factor (10 ng/ml).
Confluent cells (30%-40%) were washed twice with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), treated with 2 mM thymidine for 17 h, washed twice in PBS again, released in complete medium containing 10 μM deoxycytidine for 9 h, treated with 2 mM thymidine for 17 h, released in complete medium with 10 μM deoxycytidine, and assayed.
After the double thymidine block, cells were washed twice with PBS, released in complete medium for 9 h, and treated with MG132 (25 μM) for 1.5 h. Cells were arrested in metaphase.
Materials
Rabbit polyclonal antibodies that recognize MLC2 (1:500 for immunoblotting analyses [IB]), phospho-MLC2 S15 (1:400 for IB), phospho-MLC2 Y118 (1:400 for IB), PKM1 (1:1000 for IB), PKM2 (1:1000 for IB), and cyclin B1 (1:1000 for IB), were obtained from Signalway Antibody (College Park, MD). A mouse antibody that recognizes MLC2 (1:500 for IB, 1:100 for IP), was obtained from Santa Cruz (San Jose, CA). Antibodies that recognize Aurora B (1:500 for IB), ROCK2 (1:1000 for IB), MLC kinase (1:1000 for IB), and AMPK (1:1000 for IB) were purchased from Abcam (Boston, MA). Rabbit polyclonal antibodies against MRLC1 (MYL9) (1:1000 for IB), phospho-MRLC1 (MYL9) S19 (1:500 for IB), ACC, (1:1000 for IB) and phospho-ACC S79 (1:500 for IB) were from Cell Signaling Technology (Beverly, MA). GST-Purified ROCK2 protein, purified GST-Aurora B protein, thymidine, and mouse monoclonal antibodies for tubulin, Flag (1:5000 for IB, 1:500 for IP), GST (1:1000 for IB), and His (1:1000 for IB) were purchased from Sigma (St. Louis, MO). Hygromycin, puromycin, DNase-free RNase A, and propidium iodide were purchased from EMD Biosciences (San Diego, CA). DAPI (1:3000 for IB); Alexa Fluor 488 (1:400 for IF), 594 (1:400 for IF), and 633 goat anti-rabbit (1:400 for IF) antibodies; and Alexa Fluor 488 (1:400 for IF), 594 (1:400 for IF), and 633 goat anti-mouse (1:400 for IF) antibodies were from Molecular Probes (Eugene, OR). HyFect transfection reagent was from Denville Scientific (Metuchen, NJ). GelCode blue stain reagent was obtained from Pierce (Rockford, IL). GST-ROCK2 and GST-Aurora B were purchased from Sigma (St. Louis, MO).
Transfection
Cells were plated at a density of 4 × 105/60-mm dish 18 h prior to transfection. The transfection was performed using HyFect reagent (Denville Scientific) according to the vendor's instructions.
Mass spectrometry analysis
Aurora B-phosphorylated PKM2 and PKM2-phosphorylated MLC2 were acetone-precipitated in vitro at −20°C overnight and re-suspended in 50 mM ammonium bicarbonate buffer containing Rapigest (Waters Corp, MA). The sample was heated to 95°C for 10 minutes and allowed to cool before 100 ng of sequencing-grade modified trypsin (Promega, Madison, WI) was added. The digestion proceeded overnight at 37°C and was analyzed by LC-MS/MS using an Obitrap-Elite mass spectrometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA).
Proteins were identified by comparing the fragment spectra against those in the SwissProt protein database (EBI) using Mascot v.2.3 (Matrix Science, London, UK) and Sequest v.1.20 via Proteome Discoverer v.1.3 (Thermo Fisher Scientific) software. Phosphopeptide matches were analyzed using PhosphoRS via Proteome Discoverer and manually curated 51.
Immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting analysis
Proteins were extracted from cultured cells using a modified buffer, consisting of 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5), 1% Triton X-100, 150 mM NaCl, 1 mM dithiothreitol, 0.5 mM EDTA, 0.1 mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride, leupeptin (12 mg/ml), aprotinin (20 μg/ml), 100 μM sodium vanadate, 100 μM sodium pyrophosphate, and 1 mM sodium fluoride. Cell extracts were clarified by centrifugation at 12,000 rpm, and the supernatants were subjected to immunoprecipitation immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting with the corresponding antibodies 52. Representative original images of immunoblotting results for Figs. 1-3 are shown in Supplementary Figs. 8-10.
Cell proliferation assay
Cells (2×104) were plated and counted 7 days after being seeded in DMEM with 2% bovine calf serum. The data represent the mean ± standard deviation (SD) of three independent experiments.
DNA constructs and mutagenesis
pcDNA 3.1/hygro (+) MLC2 Y118F, Y152F, S15A, and PKM2 T45A were created using the QuikChange site-directed mutagenesis kit (Stratagene, Santa Clara, CA). The pGIPZ controls were generated with control oligonucleotide GCTTCTAACACCGGAGGTCTT or GCCCGAAAGGGTTCCAGCTTA. pGIPZ human PKM2 shRNA was generated with CATCTACCACTTGCAATTA oligonucleotide that targeted exon 10 of the PKM2 transcript. pGIPZ human MLC2 shRNA was generated with oligonucleotide ACATTGTGAGGAACACAGT. pGIPZ human MYL9 shRNA was generated with oligonucleotide TGAGGATGCGGGTGAACTC. Two pGIPZ human ROCK2 shRNAs were generated with oligonucleotides AGTAATAACAGATTCTTTG and AACTTGGCAGTCTCCAGCA. pGIPZ mouse PKM2 shRNA was generated with TCCTCGAATAGCTGCAAGT oligonucleotide that targeted exon 10 of the PKM2 transcript. pGIPZ mouse MLC2 shRNA was generated with oligonucleotide TGTGTGGTCAGCATCTCCC. PCR-amplified bacteria (Escherichia coli) PEPCK DNA was cloned into pCold vector between KpnI and EcoR I.
In vitro kinase assays
The kinase reactions were performed as described previously 53. In brief, bacterially purified recombinant PKM2 (200 ng) was incubated with MLC2 (100 ng) in kinase buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl [pH 7.5], 100 mM KCl, 50 mM MgCl2, 1 mM Na3VO4, 1 mM dithiothreitol, 5% glycerol, 0.5 mM 32P-PEP, and 0.05 mM fructose-1.6-bisphosphate in 25 μl at 25°C for 1 h. The reactions were terminated by adding sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) loading buffer and heating to 100°C.
Aurora B and ROCK2 kinase activity assays were performed using the HTScan Aurora B and ROCK2 kinase assay kit, following the manufacturer's instructions (Cell Signaling Technology, Beverly, MA).
32P-PEP preparation
The assays were performed with purified His-PEPCK in 0.05-ml volumes, which contained 160 μCi 32P-ATP, 20 mM oxaloacetate, 5 mM MgCl2, 50 mM potassium phosphate buffer (pH 7.5), 12.5 mM KF, and 2 mM dithioerythritol. Assays were carried out at 37°C for 0.5 h. 32P-PEP was separated from 32P-ATP using anion exchange chromatography. Bound product was washed with reaction buffer, and the 32P- labeled PEP eluted stepwise using 0.3 mM triethylammonium bicarbonate (TEAB) (pH 8.5). Determining ATP and PEP concentrations in each fraction confirmed the separation of PEP from ATP 54, 55.
The activity of bacterially purified WT PKM2 (0.1 μg) and PKM2 T45A (0.1 μg) toward PEP was measured using a pyruvate kinase assay (BioVision, Mountain View, CA), according to the manufacturer's instructions. The data represent the mean ± SD of three independent experiments.
Quantitative RT-PCR
A quantitative real-time PCR analysis was performed as described previously (Cell, Weiwei Yang) and was used to measure relative mRNA levels; the value was calculated according to the relative amount of internal control. The following primer pairs were used: human MYL2, 5’-ACCATTCTCAACGCATTCAA-3’ (forward) and 5’-CATCTGGTCAACCTCCTCCT-3’ (reverse); human MYL9, 5’-CTTCACCATGTTCCTCACCA-3’ (forward) and 5’-GGTCCTCATGGATGAAACCT-3’ (reverse); human MYL12A/B, 5’-TGCAACATCCAATGTGTTTG-3’ (forward) and 5’-CATGCAAATCTTCCTTGTCG-3’ (reverse); mouse MYL2, 5’-GTGTTCCTCACGATGTTTGG-3’ (forward) and 5’-AGTCAGCCTTCAGTGACCCT-3’ (reverse); mouse MYL9, 5’-GAGGGCTACGTCCAATGTCT-3’ (forward) and 5’-GTCGTGCAGGTCCTCCTTAT-3’ (reverse); and mouse MYL12A/B, 5’-CACCATCCAGGAGGATTACC-3’ (forward) and 5’-CTTCAGGATGCGTGTGAACT-3’ (reverse).
Flow cytometry analysis
Cells (1×106) were fixed in 70% ethanol on ice for 3 h, spun down, and incubated for 1 h at 37°C in PBS with DNase-free RNase A (100 μg/ml) and propidium iodide (50 μg/ml). Cells were then analyzed by fluorescence-activated cell sorting.
Recombinant protein purification
Wild-type and mutant GST-PKM2, His-PKM2, His-PKM1, His-MLC2, GST–MLC2, and His-PEPCK were expressed in bacteria. Bacteria cultures were grown at 37°C to an OD600 of ~ 0.6 before inducing with 0.4 mM IPTG for 3 h. Cell pellets were collected, resuspended in 9 ml lysis buffer (50 mM Tris-Cl pH 8.0, 120 mM NaCl, 1 mM DTT, 1 mM PMSF, 1 mM benzamidine, 20 μg/ml leupeptin, and 1.0 μg/ml aprotinin), and lysed by sonication. Triton X-100 was added to the lysates at a final concentration of 1% and left on ice for 20 min, before centrifugation at 10,000 rpm for 10 min (4°C). Cleared lysates were then bound to glutathione-agarose or Ni-NTA agarose for 1.0 h, with rolling at 4°C. Beads were washed extensively with lysis buffer before eluting for 20 mins in the lysis buffer (pH 7.5) with 20 mM glutathione for GST fusion proteins or in an elution buffer (0.5 mM imidazole, 0.5 M NaCl, 20 mM Tris-HCl pH 7.9) for His-tagged proteins. Eluted proteins were then dialyzed extensively against 20 mM Tris-Cl pH 8.0, 50 mM NaCl, 10% glycerol, and 1 mM DTT 56.
Immunofluorescence analysis
Cells were fixed and incubated with primary antibodies: Flag (1:3000), PKM2 (1:400 for IF), MLC2 (1:400), MLC2 pY118 (1:200), MLC2 pS15 (1:100), Alexa Fluor dye-conjugated secondary antibodies (1:400 for IF), and DAPI (1:3000), according to standard protocols. Cells were evaluated using a deconvolution microscope (Zeiss, Thornwood, NY) with a 63-Å oil immersion objective. Axio Vision software from Zeiss was used to de-convolute Z-series images. For live-cell time-lapse microscopy, we cultured cells in 35-mm glass-bottomed dishes. Cells were imaged using a DeltaVision deconvolution microscope or a Spin Disk confocal microscope with a 20 × lens in a CO2 environment chamber. Pictures were taken at 4-min intervals.
Immunohistochemical analysis
Mouse tumor tissues were fixed and stained with Mayer's hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) (Biogenex Laboratories, Fremont, CA). The slides were mounted using Fluorogel with Tris buffer (Electron Microscopy Sciences, Hatfield, PA).
Intracranial injection
We intracranially injected 4-week-old athymic nude mice with 1) 5×105 U87/EGFRvIII or GSC11 cells that expressed PKM2 shRNA with WT rPKM2 or rPKM2 T45A or 2) U87/EGFRvIII or GSC11 cells that expressed MLC2 shRNA with WT rMLC2, rMLC2 Y118F, or rMLC2 S15A (in 5 μl of DMEM per mouse). The injections were performed as described in a previous publication 19. We divided the mice into two groups. One group (7 mice for each subgroup) was used for immunoblotting or histochemical analyses, and the mice were sacrificed 2 weeks after glioma cell injection. The brain of each mouse was harvested, frozen by liquid nitrogen for immunoblotting analyses, or fixed in 4% formaldehyde for paraffin embedding. Protein expression levels in tumor tissues isolated from the center of the tumors were normalized by immunoblotting analyses with an anti-FLAG antibody. Tumor formation and phenotype were determined by a histological analysis of H&E-stained sections.
The other group (10 mice for each subgroup) was monitored for survival. The duration of mouse survival was analyzed by STATISTICA software and was represented by Kaplan-Meier plots.
The use of animal was approved by the institutional review board at MD Anderson Cancer Center.
Supplementary Material
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank Don Cleveland (Ludwig Institute for Cancer Research, University of California-San Diego, CA) for supplying the plasmids that expressed MRLC1, Bih-Fang Pan (MD Anderson Proteomics Facility) for technical assistance, and Ann Sutton for her critical reading of this manuscript.
This work was supported by National Cancer Institute grants 2R01 CA109035 (Z.L.), 1R0 CA169603 (Z.L.), and CA16672 (Cancer Center Support Grant); James S. McDonnell Foundation 21st Century Science Initiative in Brain Cancer Research Award 220020318 (Z.L.); and the Odyssey Fellowship from MD Anderson (J.Y.).
Footnotes
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
This study was conceived by Z.L.; Z.L. and Y.J. designed the study; Y.J., Y.W., T. W., D.H., Y.Z., and X.L. performed the experiments; Q.Z., E.B., S.M., D.L., and S.H. provided reagents and conceptual advice; and Z.L. wrote the paper, with comments from all authors.
Competing financial interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
REFERENCES
- 1.Pollard TD. Mechanics of cytokinesis in eukaryotes. Current opinion in cell biology. 2010;22:50–56. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2009.11.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Green RA, Paluch E, Oegema K. Cytokinesis in animal cells. Annual review of cell and developmental biology. 2012;28:29–58. doi: 10.1146/annurev-cellbio-101011-155718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Sagona AP, Stenmark H. Cytokinesis and cancer. FEBS letters. 2010;584:2652–2661. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2010.03.044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Glotzer M. The molecular requirements for cytokinesis. Science. 2005;307:1735–1739. doi: 10.1126/science.1096896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Matsumura F, Totsukawa G, Yamakita Y, Yamashiro S. Role of myosin light chain phosphorylation in the regulation of cytokinesis. Cell structure and function. 2001;26:639–644. doi: 10.1247/csf.26.639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Scruggs SB, Solaro RJ. The significance of regulatory light chain phosphorylation in cardiac physiology. Archives of biochemistry and biophysics. 2011;510:129–134. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2011.02.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Iwasaki T, Murata-Hori M, Ishitobi S, Hosoya H. Diphosphorylated MRLC is required for organization of stress fibers in interphase cells and the contractile ring in dividing cells. Cell structure and function. 2001;26:677–683. doi: 10.1247/csf.26.677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Matsumura F. Regulation of myosin II during cytokinesis in higher eukaryotes. Trends in cell biology. 2005;15:371–377. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2005.05.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Altenberg B, Greulich KO. Genes of glycolysis are ubiquitously overexpressed in 24 cancer classes. Genomics. 2004;84:1014–1020. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2004.08.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Majumder PK, et al. mTOR inhibition reverses Akt-dependent prostate intraepithelial neoplasia through regulation of apoptotic and HIF-1-dependent pathways. Nat Med. 2004;10:594–601. doi: 10.1038/nm1052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Noguchi T, Inoue H, Tanaka T. The M1- and M2-type isozymes of rat pyruvate kinase are produced from the same gene by alternative RNA splicing. The Journal of biological chemistry. 1986;261:13807–13812. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.David CJ, Chen M, Assanah M, Canoll P, Manley JL. HnRNP proteins controlled by c-Myc deregulate pyruvate kinase mRNA splicing in cancer. Nature. 2010;463:364–368. doi: 10.1038/nature08697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Christofk HR, et al. The M2 splice isoform of pyruvate kinase is important for cancer metabolism and tumour growth. Nature. 2008;452:230–233. doi: 10.1038/nature06734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Koppenol WH, Bounds PL, Dang CV. Otto Warburg's contributions to current concepts of cancer metabolism. Nature reviews Cancer. 2011;11:325–337. doi: 10.1038/nrc3038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Cairns RA, Harris IS, Mak TW. Regulation of cancer cell metabolism. Nature reviews Cancer. 2011;11:85–95. doi: 10.1038/nrc2981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Vander Heiden MG, Cantley LC, Thompson CB. Understanding the Warburg effect: the metabolic requirements of cell proliferation. Science. 2009;324:1029–1033. doi: 10.1126/science.1160809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Hsu PP, Sabatini DM. Cancer cell metabolism: Warburg and beyond. Cell. 2008;134:703–707. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.08.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Lv L, et al. Acetylation targets the M2 isoform of pyruvate kinase for degradation through chaperone-mediated autophagy and promotes tumor growth. Molecular cell. 2011;42:719–730. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2011.04.025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Yang W, et al. Nuclear PKM2 regulates beta-catenin transactivation upon EGFR activation. Nature. 2011;480:118–122. doi: 10.1038/nature10598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Lu Z. Nonmetabolic functions of pyruvate kinase isoform M2 in controlling cell cycle progression and tumorigenesis. Chinese journal of cancer. 2012;31:5–7. doi: 10.5732/cjc.011.10446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Yang W, et al. ERK1/2-dependent phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of PKM2 promotes the Warburg effect. Nature cell biology. 2012;14:1295–1304. doi: 10.1038/ncb2629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Yang W, et al. EGFR-induced and PKCepsilon monoubiquitylation-dependent NF-kappaB activation upregulates PKM2 expression and promotes tumorigenesis. Molecular cell. 2012;48:771–784. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2012.09.028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Yang W, et al. PKM2 phosphorylates histone H3 and promotes gene transcription and tumorigenesis. Cell. 2012;150:685–696. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.07.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Lu Z. PKM2 functions as a histone kinase. Cell Cycle. 2012;11:4101–4102. doi: 10.4161/cc.22325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Harris I, McCracken S, Mak TW. PKM2: a gatekeeper between growth and survival. Cell research. 2012;22:447–449. doi: 10.1038/cr.2011.203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Jiang Y, et al. PKM2 Regulates Chromosome Segregation and Mitosis Progression of Tumor Cells. Molecular cell. 2013 doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2013.11.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Kuan CT, Wikstrand CJ, Bigner DD. EGF mutant receptor vIII as a molecular target in cancer therapy. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2001;8:83–96. doi: 10.1677/erc.0.0080083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Potapova TA, et al. The reversibility of mitotic exit in vertebrate cells. Nature. 2006;440:954–958. doi: 10.1038/nature04652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Bohnert KA, Gould KL. On the cutting edge: post-translational modifications in cytokinesis. Trends in cell biology. 2011;21:283–292. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2011.01.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Christofk HR, Vander Heiden MG, Wu N, Asara JM, Cantley LC. Pyruvate kinase M2 is a phosphotyrosine-binding protein. Nature. 2008;452:181–186. doi: 10.1038/nature06667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Gao X, Wang H, Yang JJ, Liu X, Liu ZR. Pyruvate kinase M2 regulates gene transcription by acting as a protein kinase. Molecular cell. 2012;45:598–609. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2012.01.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Lu Z, Hunter T. Ubiquitylation and proteasomal degradation of the p21(Cip1), p27(Kip1) and p57(Kip2) CDK inhibitors. Cell Cycle. 2010;9:2342–2352. doi: 10.4161/cc.9.12.11988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Sanbe A, et al. Abnormal cardiac structure and function in mice expressing nonphosphorylatable cardiac regulatory myosin light chain 2. The Journal of biological chemistry. 1999;274:21085–21094. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.30.21085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Scruggs SB, et al. Ablation of ventricular myosin regulatory light chain phosphorylation in mice causes cardiac dysfunction in situ and affects neighboring myofilament protein phosphorylation. The Journal of biological chemistry. 2009;284:5097–5106. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M807414200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Thaiparambil JT, Eggers CM, Marcus AI. AMPK regulates mitotic spindle orientation through phosphorylation of myosin regulatory light chain. Molecular and cellular biology. 2012;32:3203–3217. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00418-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Banko MR, et al. Chemical genetic screen for AMPKalpha2 substrates uncovers a network of proteins involved in mitosis. Molecular cell. 2011;44:878–892. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2011.11.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Matsumura F, Yamakita Y, Yamashiro S. Myosin light chain kinases and phosphatase in mitosis and cytokinesis. Archives of biochemistry and biophysics. 2011;510:76–82. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2011.03.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Riento K, Ridley AJ. Rocks: multifunctional kinases in cell behaviour. Nature reviews Molecular cell biology. 2003;4:446–456. doi: 10.1038/nrm1128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Lowery DM, et al. Proteomic screen defines the Polo-box domain interactome and identifies Rock2 as a Plk1 substrate. The EMBO journal. 2007;26:2262–2273. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Anastasiou D, et al. Inhibition of pyruvate kinase M2 by reactive oxygen species contributes to cellular antioxidant responses. Science. 2011;334:1278–1283. doi: 10.1126/science.1211485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Craig R, Woodhead JL. Structure and function of myosin filaments. Current opinion in structural biology. 2006;16:204–212. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2006.03.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Goto H, et al. Aurora-B regulates the cleavage furrow-specific vimentin phosphorylation in the cytokinetic process. The Journal of biological chemistry. 2003;278:8526–8530. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M210892200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Israelsen WJ, et al. PKM2 isoform-specific deletion reveals a differential requirement for pyruvate kinase in tumor cells. Cell. 2013;155:397–409. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.09.025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Wang YH, et al. Cell-state-specific metabolic dependency in hematopoiesis and leukemogenesis. Cell. 2014;158:1309–1323. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.07.048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Tani K, Singer-Sam J, Munns M, Yoshida A. Molecular cloning and structure of an autosomal processed gene for human phosphoglycerate kinase. Gene. 1985;35:11–18. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90152-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Yaffe MB, et al. Sequence-specific and phosphorylation-dependent proline isomerization: a potential mitotic regulatory mechanism. Science. 1997;278:1957–1960. doi: 10.1126/science.278.5345.1957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Mazurek S. Pyruvate kinase type M2: a key regulator within the tumour metabolome and a tool for metabolic profiling of tumours. Ernst Schering Found Symp Proc. 2007:99–124. doi: 10.1007/2789_2008_091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Dombrauckas JD, Santarsiero BD, Mesecar AD. Structural basis for tumor pyruvate kinase M2 allosteric regulation and catalysis. Biochemistry. 2005;44:9417–9429. doi: 10.1021/bi0474923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Mazurek S, Boschek CB, Hugo F, Eigenbrodt E. Pyruvate kinase type M2 and its role in tumor growth and spreading. Semin Cancer Biol. 2005;15:300–308. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2005.04.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Cortes-Cros M, et al. M2 isoform of pyruvate kinase is dispensable for tumor maintenance and growth. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2013;110:489–494. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1212780110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Taus T, et al. Universal and confident phosphorylation site localization using phosphoRS. Journal of proteome research. 2011;10:5354–5362. doi: 10.1021/pr200611n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Lu Z, Liu D, Hornia A, Devonish W, Pagano M, Foster DA. Activation of protein kinase C triggers its ubiquitination and degradation. Molecular and cellular biology. 1998;18:839–845. doi: 10.1128/mcb.18.2.839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Fang D, et al. Phosphorylation of beta-catenin by AKT promotes beta-catenin transcriptional activity. The Journal of biological chemistry. 2007;282:11221–11229. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M611871200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Mattoo RL, Waygood EB. An enzymatic method for [32P]phosphoenolpyruvate synthesis. Analytical biochemistry. 1983;128:245–249. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90372-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Vander Heiden MG, et al. Evidence for an alternative glycolytic pathway in rapidly proliferating cells. Science. 2010;329:1492–1499. doi: 10.1126/science.1188015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Xia Y, Wang J, Liu TJ, Yung WK, Hunter T, Lu Z. c-Jun downregulation by HDAC3-dependent transcriptional repression promotes osmotic stress-induced cell apoptosis. Molecular cell. 2007;25:219–232. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2007.01.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.