Abstract
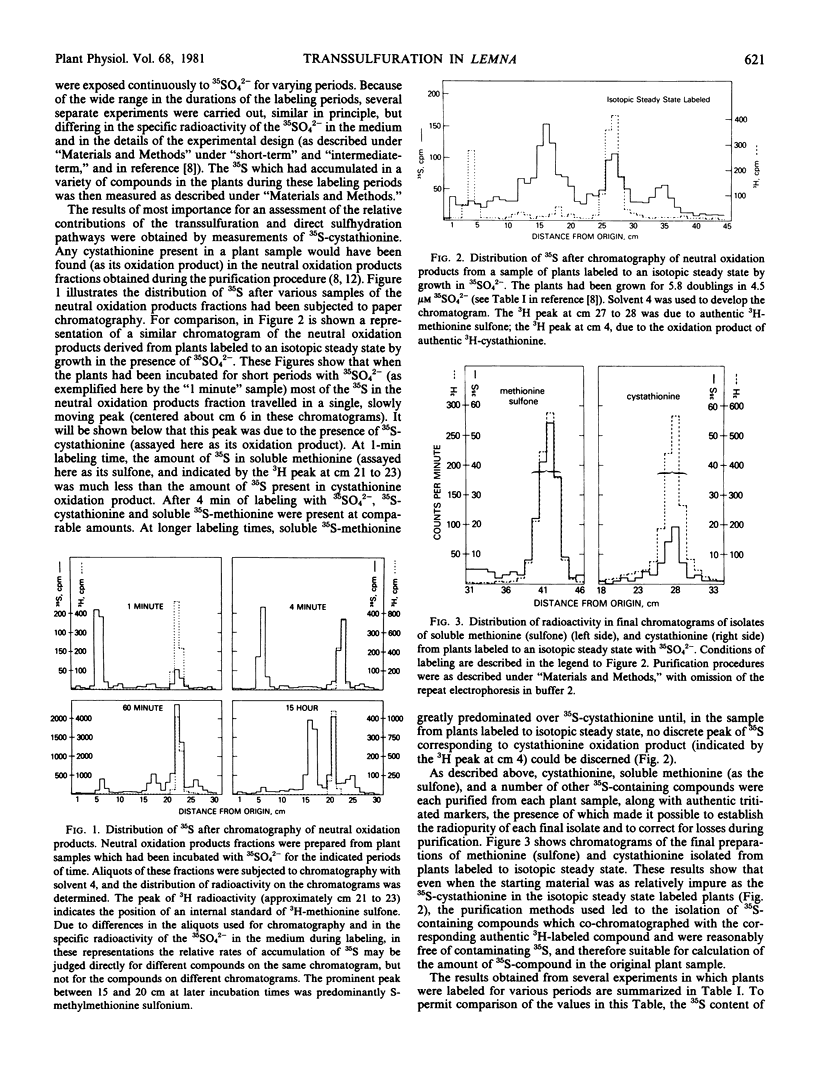
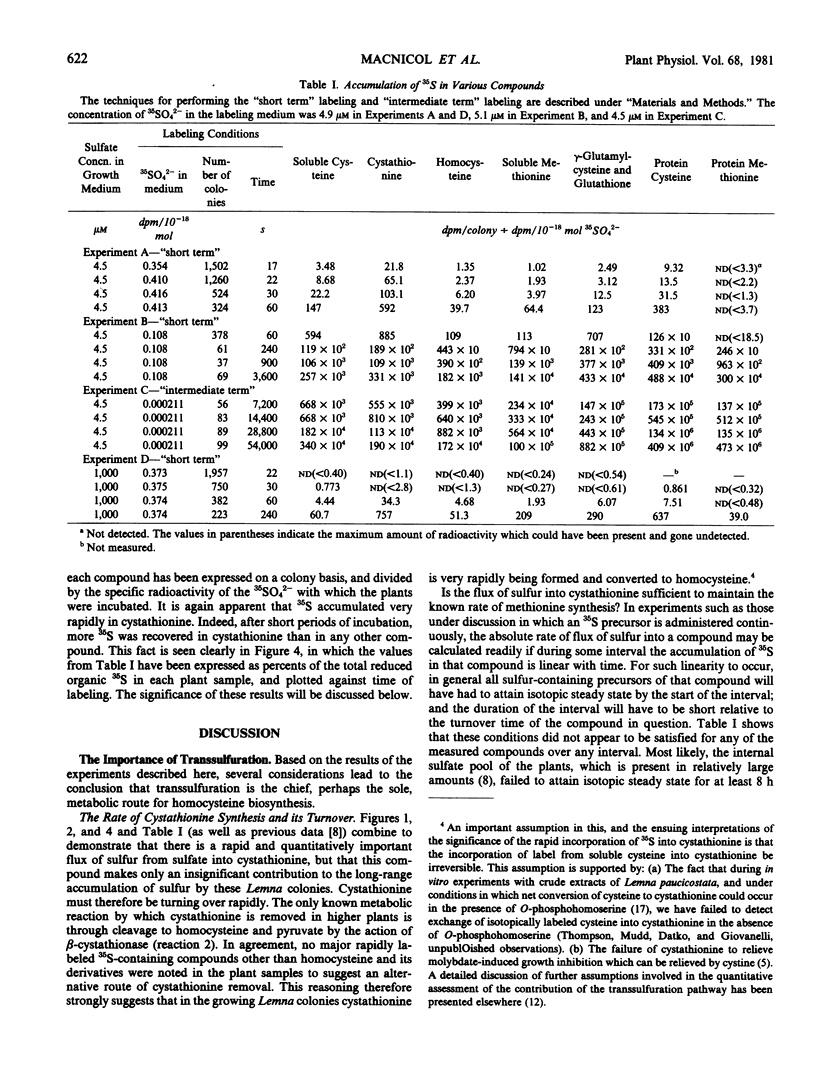
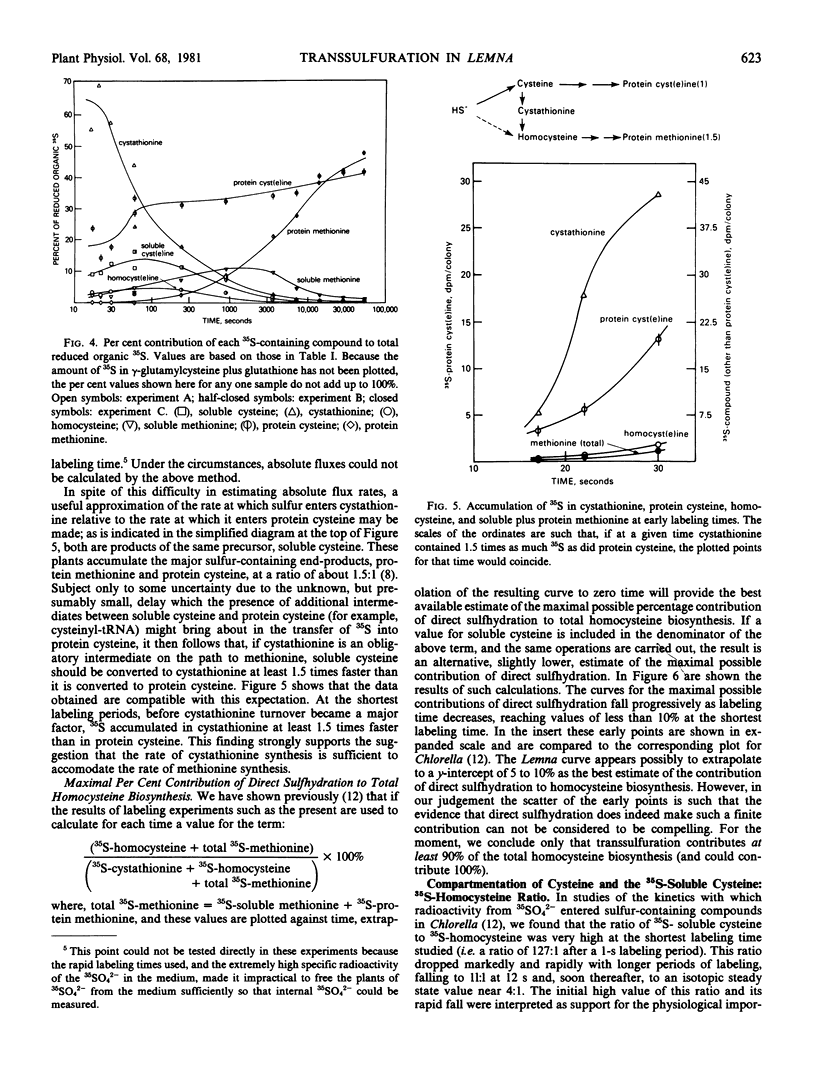
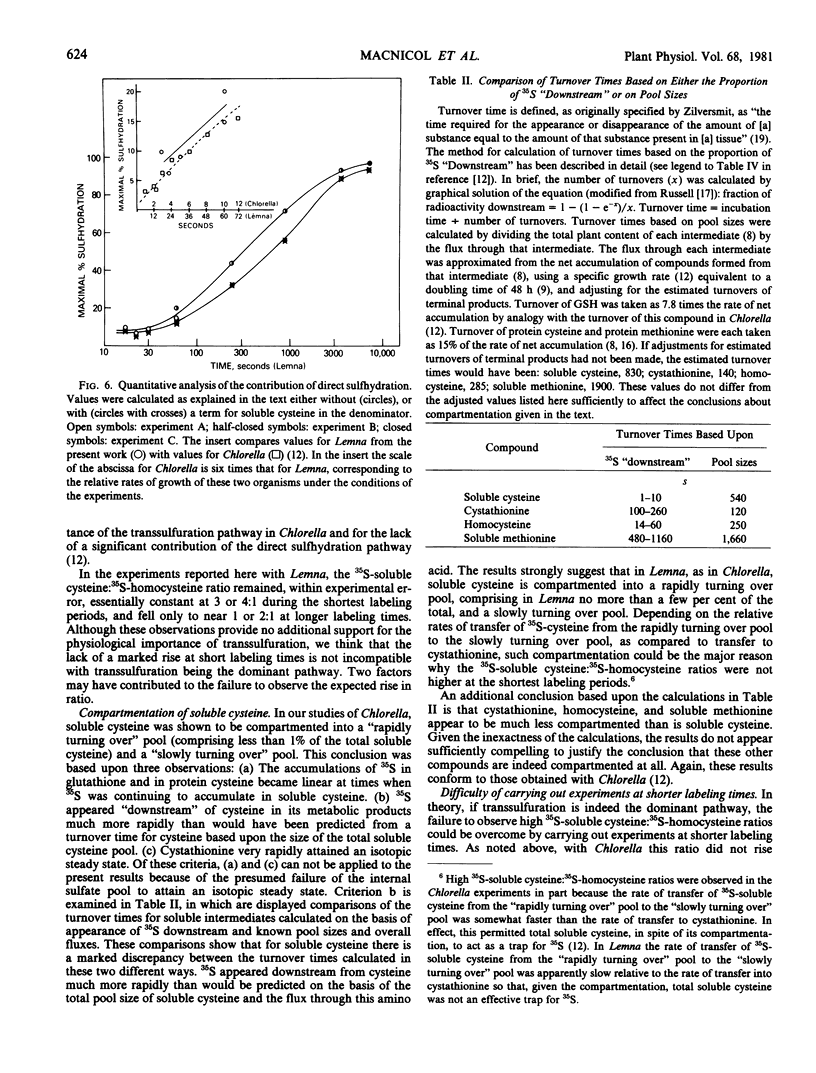
To permit an assessment of the relative contributions of the transsulfuration and the direct sulfhydration pathways for homocysteine biosynthesis, the time course of incorporation of 35S from 35SO42− into various sulfur-containing compounds in Lemna paucicostata has been determined. Plants were grown with either low (4.5 micromolar) or ample (1,000 micromolar) sulfate in the medium. At the shortest labeling times, 35S-cystathionine was the predominant 35S-containing organic sulfur compound. The flux of sulfur into cystathionine was sufficient to sustain the known rate of methionine biosynthesis. It was calculated that transsulfuration accounted for at least 90 and 85% of the total homocysteine synthesis in low and ample sulfate-grown plants, respectively (and may have accounted for 100%). No marked rise in the 35S-soluble cysteine:35S-homocysteine ratio was observed even at the shortest labeling times, but it is argued that this may be due to (a) the observed compartmentation of soluble cysteine, and (b) the impracticality of using labeling times shorter than 17 seconds. Additional evidence supporting the importance of transsulfuration in Lemna is briefly described.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brunold C. Regulation of Sulfate Assimilation in Plants: 7. Cysteine Inactivation of Adenosine 5'-Phosphosulfate Sulfotransferase in Lemna minor L. Plant Physiol. 1978 Mar;61(3):342–347. doi: 10.1104/pp.61.3.342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datka A. H., Mudd S. H., Giovanelli J. Homocysteine biosynthesis in green plants: studies of the homocysteine-forming sulfhydrylase. J Biol Chem. 1977 May 25;252(10):3436–3445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datko A. H., Giovanelli J., Mudd S. H. Homocysteine biosynthesis in green plants. O-Phosphorylhomoserine as the physiological substrate for cystathionine gamma-synthase. J Biol Chem. 1974 Feb 25;249(4):1139–1155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datko A. H., Mudd S. H., Giovanelli J. Lemna paucicostata Hegelm. 6746: LIFE CYCLE AND CHARACTERIZATION OF THE COLONY TYPES IN A POPULATION. Plant Physiol. 1980 May;65(5):913–923. doi: 10.1104/pp.65.5.913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datko A. H., Mudd S. H., Giovanelli J., Macnicol P. K. Sulfur-containing Compounds in Lemna perpusilla 6746 Grown at a Range of Sulfate Concentrations. Plant Physiol. 1978 Oct;62(4):629–635. doi: 10.1104/pp.62.4.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datko A. H., Mudd S. H., Macnicol P. K., Giovanelli J. Phytostat for the growth of lemna in semicontinuous culture with low sulfate. Plant Physiol. 1978 Oct;62(4):622–628. doi: 10.1104/pp.62.4.622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giovanelli J., Mudd S. H., Datko A. H. Homocysteine biosynthesis in green plants. Physiological importance of the transsulfuration pathway in Chlorella sorokiniana growing under steady state conditions with limiting sulfate. J Biol Chem. 1978 Aug 25;253(16):5665–5677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giovanelli J., Mudd S. H. Transsulfuration in higher plants. Partial purification and properties of beta-cystathionase of spinach. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Mar 10;227(3):654–670. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(71)90015-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giovanelli J., Owens L. D., Mudd S. H. beta-Cystathionase In Vivo Inactivation by Rhizobitoxine and Role of the Enzyme in Methionine Biosynthesis in Corn Seedlings. Plant Physiol. 1973 Mar;51(3):492–503. doi: 10.1104/pp.51.3.492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey T. J., Davies D. D. A sensitive method for measuring protein turnover based on the measurement of 2-3H-labelled amino acids in protein. Biochem J. 1976 Jun 15;156(3):561–568. doi: 10.1042/bj1560561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



