Abstract
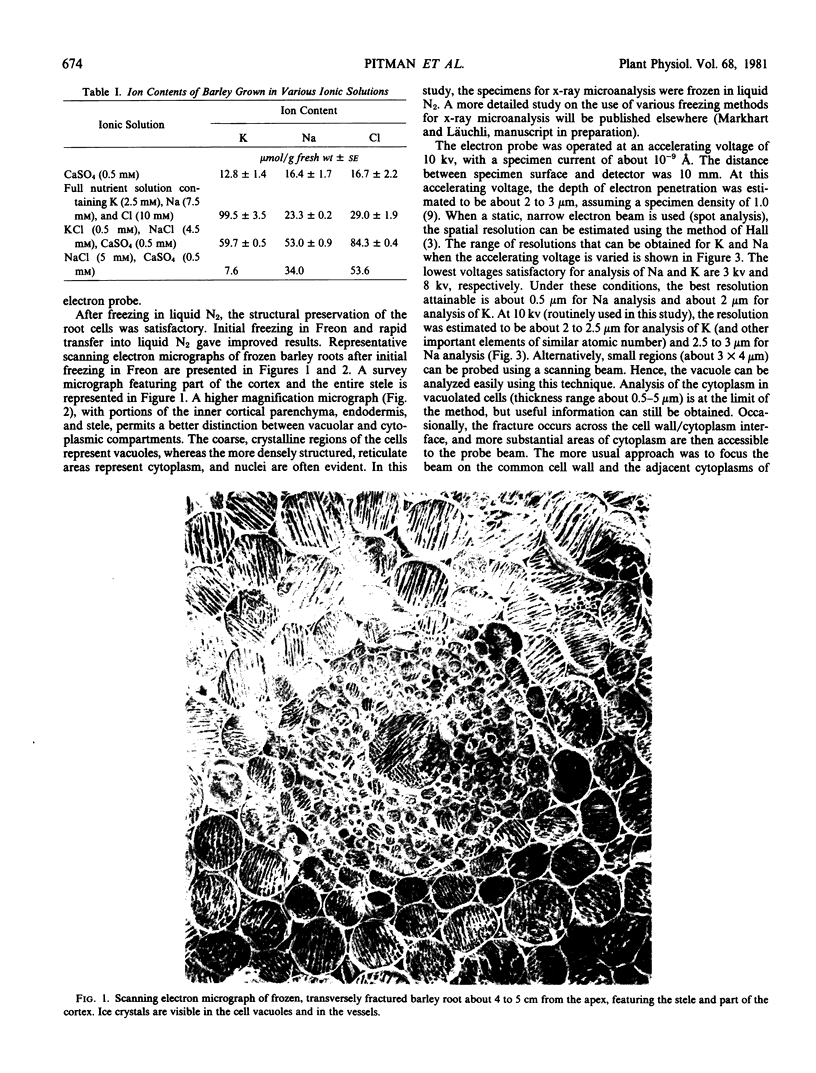
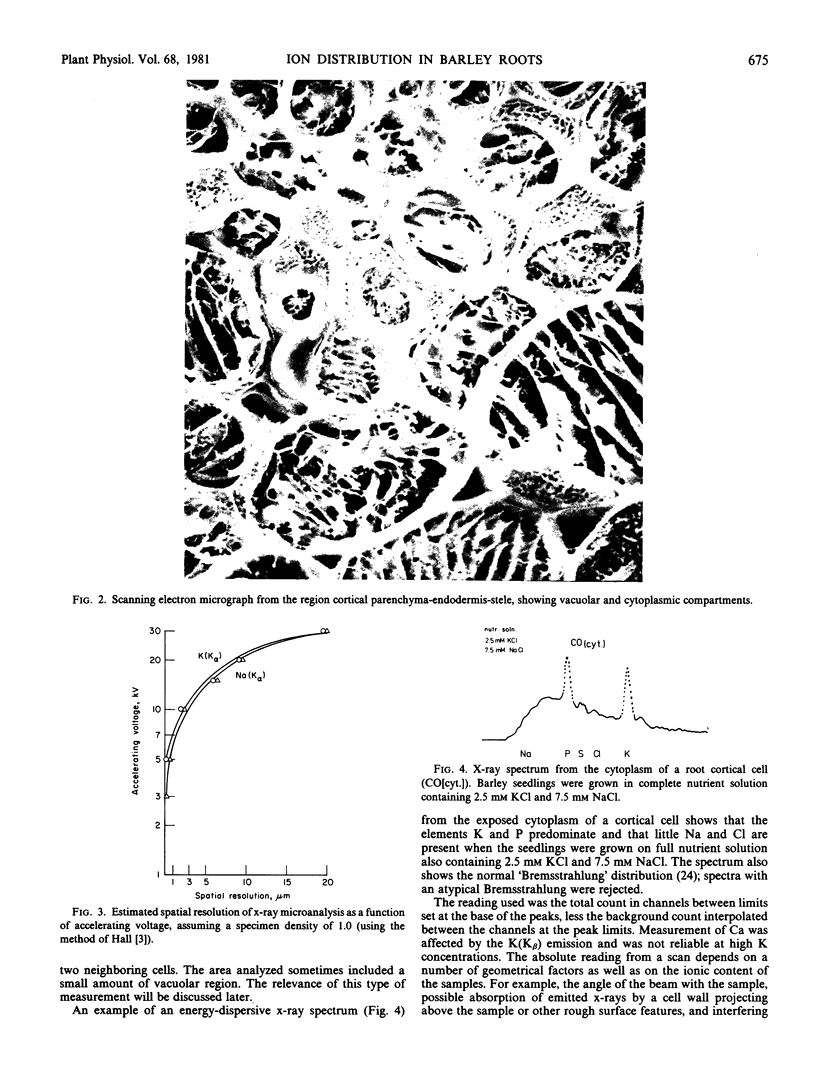
The distribution of ions, particularly K and Na, was studied in roots of barley seedlings grown on various ionic solutions. Analyses were made by means of electron probe x-ray microanalysis using frozen, fractured bulk specimens. By this technique, it was demonstrated that there can be variability in the ratio K/Na measured in the vacuoles of cortical cells, with this ratio often being lower in epidermal cells of the root than in the inner cortex. A sharp difference in the K/Na ratio was also found between cells of the endodermis and those of the adjacent cortex, and generally higher ratios of K/Na occurred in the stele than in the cortex. Estimation of the concentrations in the cytoplasm was at the limit of resolution of this technique, but it can be shown that the K/Na ratio in the cytoplasm was higher than that in the vacuole. In low salt roots, the K concentration in the cytoplasm was higher than that in the vacuoles. The results with the x-ray microprobe confirm other measurements based on flux analysis or analysis of small samples of the root.
Full text
PDF
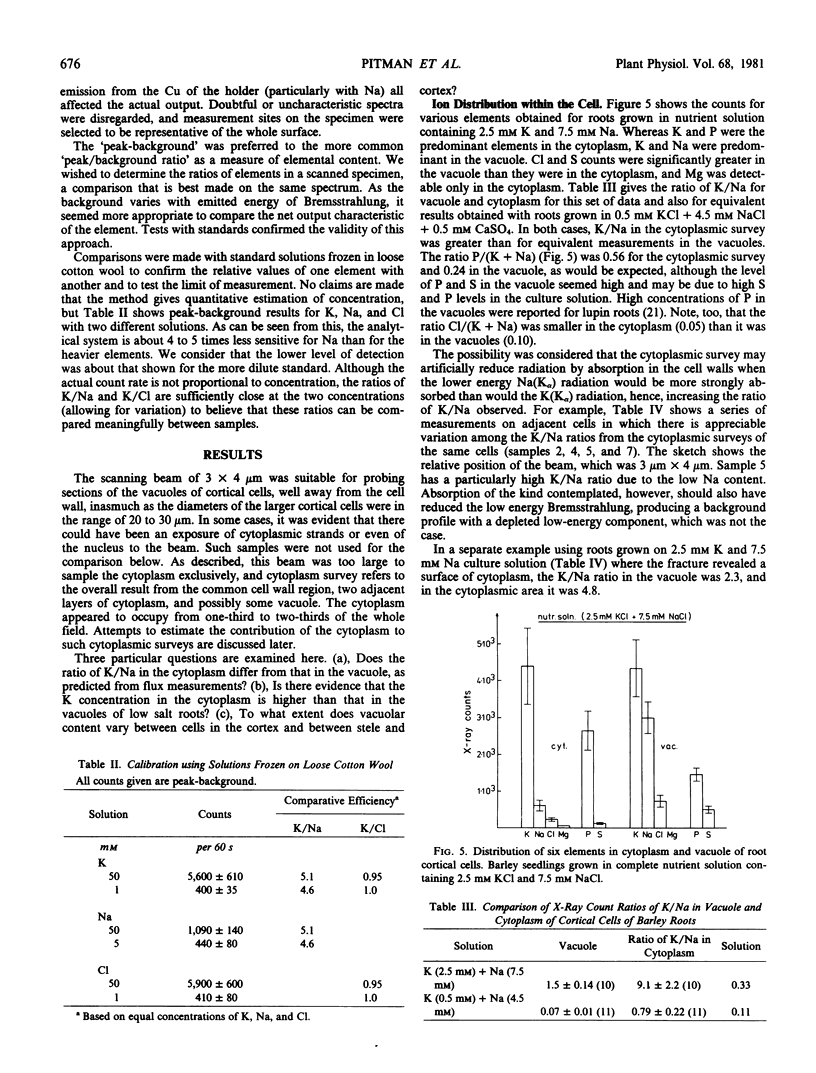

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Etherton B. Steady State Sodium and Rubidium Effluxes in Pisum sativum Roots. Plant Physiol. 1967 May;42(5):685–690. doi: 10.1104/pp.42.5.685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etherton B. Vacuolar and Cytoplasmic Potassium Concentrations in Pea Roots in Relation to Cell-to-Medium Electrical Potentials. Plant Physiol. 1968 May;43(5):838–840. doi: 10.1104/pp.43.5.838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitman M. G., Saddler H. D. Active sodium and potassium transport in cells of barley roots. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jan;57(1):44–49. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.1.44. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]