Abstract
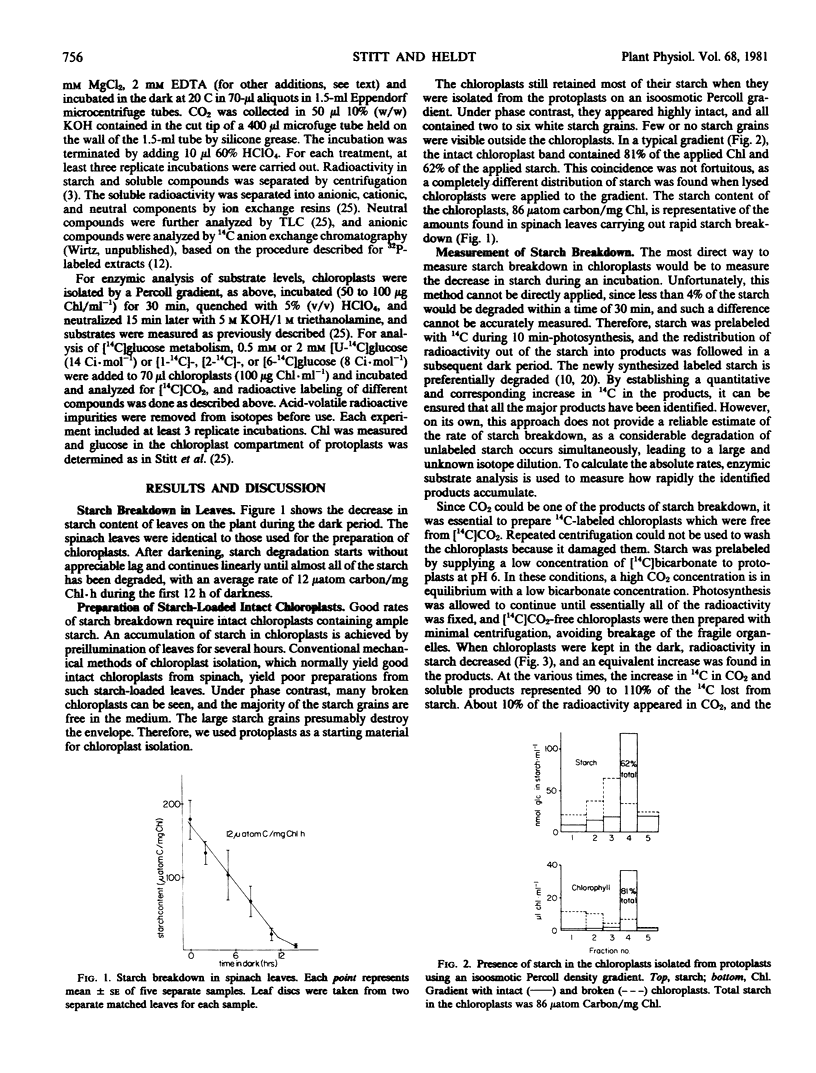
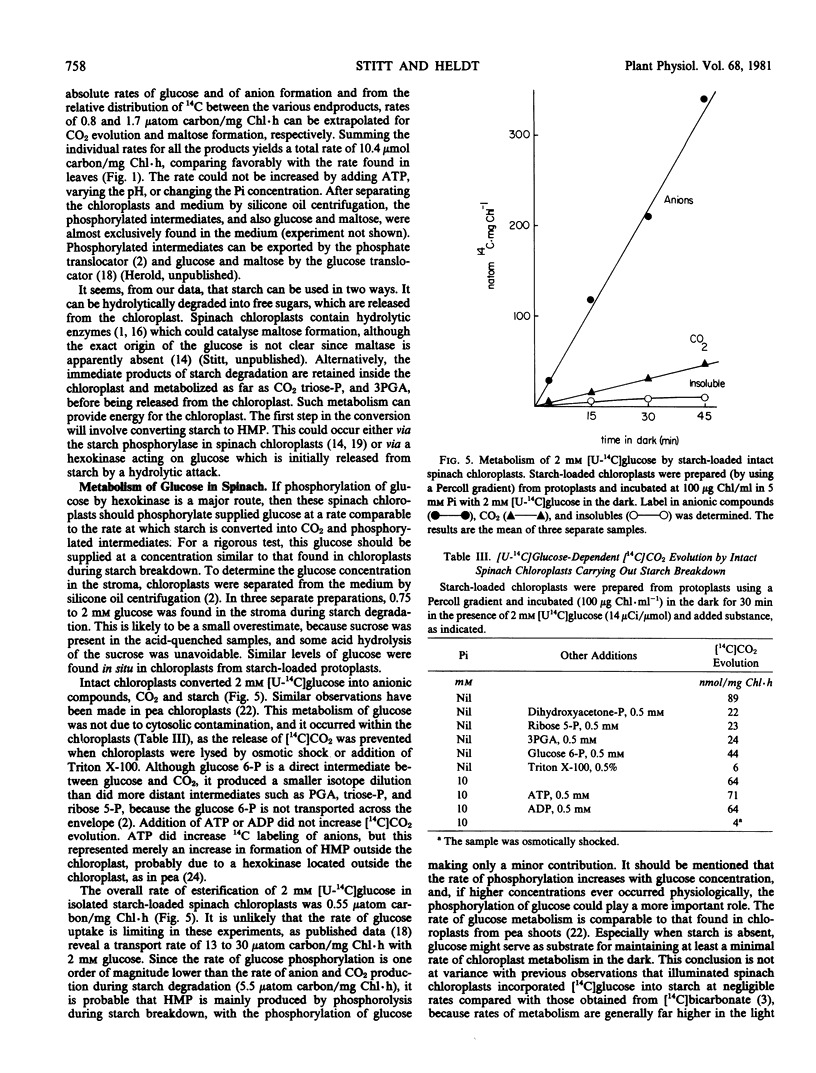
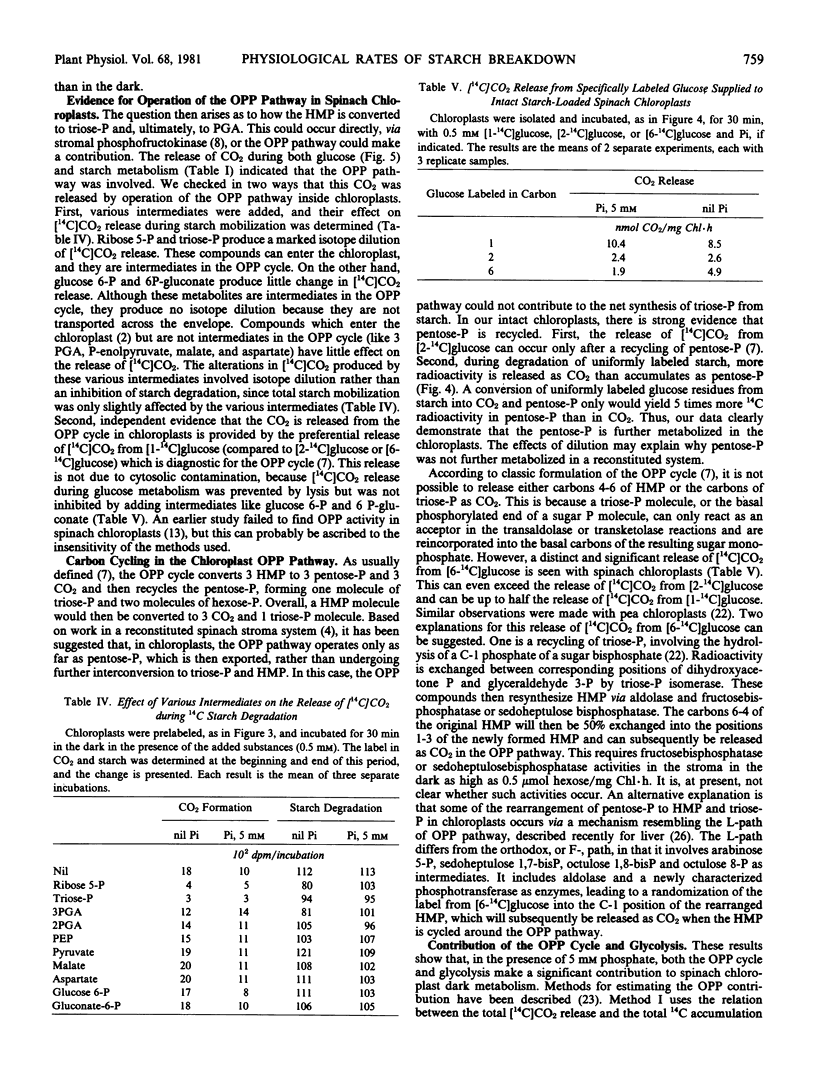
Starch breakdown with rates above 10 μatom carbon per mg chlorophyll per hour has been monitored in spinach chloroplasts and compares favorably with the rates in whole leaves. Intact starch-loaded chloroplasts were prepared from protoplasts to avoid rupture during mechanical homogenization and rapid centrifugation. Particular attention was paid to the identification of all the products of starch degradation and to measuring the actual rates of their accumulation. The products of starch breakdown included triose phosphate, 3-phosphoglycerate, CO2, glucose, and some maltose. Comparison of the rates of metabolism of added glucose and of the conversion of starch to phosphorylated intermediates showed that starch phosphorolysis was the major pathway leading to phosphorylated endproducts. From the results, the relative contribution of phosphorolysis and hydrolysis to starch breakdown and the contribution of glycolysis and the oxidative pentose phosphate cycle can be estimated. Phosphate has a large influence on the metabolism of the chloroplast in the dark.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Contractor S. F., Shane B. Purification and characterization of lysosomal -glucuronidase from human placenta. Biochem J. 1972 Jun;128(1):11–18. doi: 10.1042/bj1280011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fliege R., Flügge U. I., Werdan K., Heldt H. W. Specific transport of inorganic phosphate, 3-phosphoglycerate and triosephosphates across the inner membrane of the envelope in spinach chloroplasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 May 10;502(2):232–247. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(78)90045-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heldt H. W., Chon C. J., Maronde D. Role of orthophosphate and other factors in the regulation of starch formation in leaves and isolated chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 1977 Jun;59(6):1146–1155. doi: 10.1104/pp.59.6.1146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ J., WOOD H. G. The use of glucose-C14 for the evaluation of the pathways of glucose metabolism. J Biol Chem. 1960 Aug;235:2165–2177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz J., Landau B. R., Bartsch G. E. The pentose cycle, triose phosphate isomerization, and lipogenesis in rat adipose tissue. J Biol Chem. 1966 Feb 10;241(3):727–740. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly G. J., Latzko E. Chloroplast phosphofructokinase: I. Proof of phosphofructokinase activity in chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 1977 Aug;60(2):290–294. doi: 10.1104/pp.60.2.290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi C., Gibbs M. Starch degradation in isolated spinach chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 1976 Jun;57(6):933–935. doi: 10.1104/pp.57.6.933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi C., Preiss J. Amylopectin degradation in pea chloroplast extracts. Plant Physiol. 1978 Feb;61(2):218–220. doi: 10.1104/pp.61.2.218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilley R. M., Chon C. J., Mosbach A., Heldt H. W. The distribution of metabolites between spinach chloroplasts and medium during photosynthesis in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 May 11;460(2):259–272. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(77)90212-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilley R. M., Walker D. A. The reduction of 3-phosphoglycerate by reconstituted chloroplasts and by chloroplast extracts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Dec 19;368(3):269–278. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(74)90174-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okita T. W., Greenberg E., Kuhn D. N., Preiss J. Subcellular localization of the starch degradative and biosynthetic enzymes of spinach leaves. Plant Physiol. 1979 Aug;64(2):187–192. doi: 10.1104/pp.64.2.187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peavey D. G., Steup M., Gibbs M. Characterization of starch breakdown in the intact spinach chloroplast. Plant Physiol. 1977 Aug;60(2):305–308. doi: 10.1104/pp.60.2.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pongratz P., Beck E. Diurnal oscillation of amylolytic activity in spinach chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 1978 Nov;62(5):687–689. doi: 10.1104/pp.62.5.687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson S. P., Walker D. A. The site of sucrose synthesis in isolated leaf protoplasts. FEBS Lett. 1979 Nov 15;107(2):295–299. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80394-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schäfer G., Heber U. Glucose transport into spinach chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 1977 Aug;60(2):286–289. doi: 10.1104/pp.60.2.286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steup M., Peavey D. G., Gibbs M. The regulation of starch metabolism by inorganic phosphate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Oct 18;72(4):1554–1561. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(76)80191-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stitt M., Bulpin P. V., ap Rees T. Pathway of starch breakdown in photosynthetic tissues of Pisum sativum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Nov 15;544(1):200–214. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90223-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stitt M., Rees T. A. Carbohydrate breakdown by chloroplasts of Pisum sativum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jan 17;627(2):131–143. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(80)90315-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stitt M., Wirtz W., Heldt H. W. Metabolite levels during induction in the chloroplast and extrachloroplast compartments of spinach protoplasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Nov 5;593(1):85–102. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(80)90010-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



