Abstract
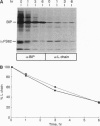
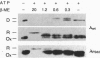
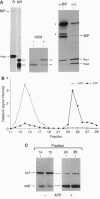
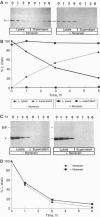
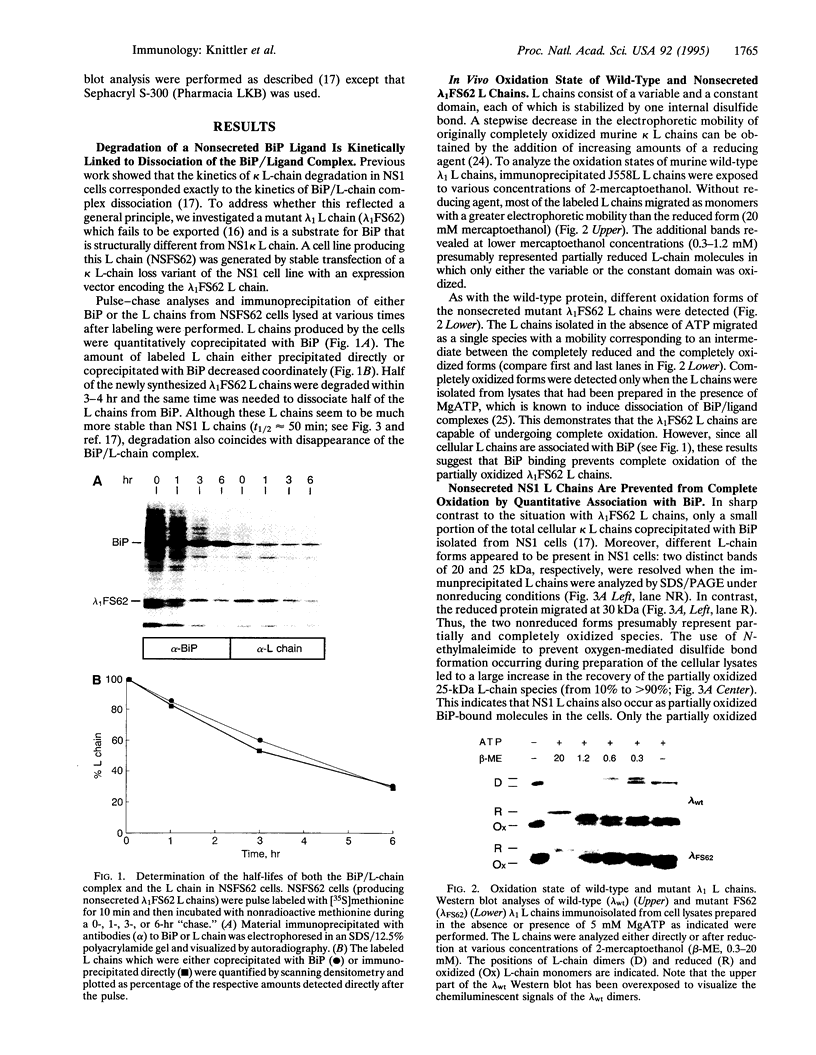
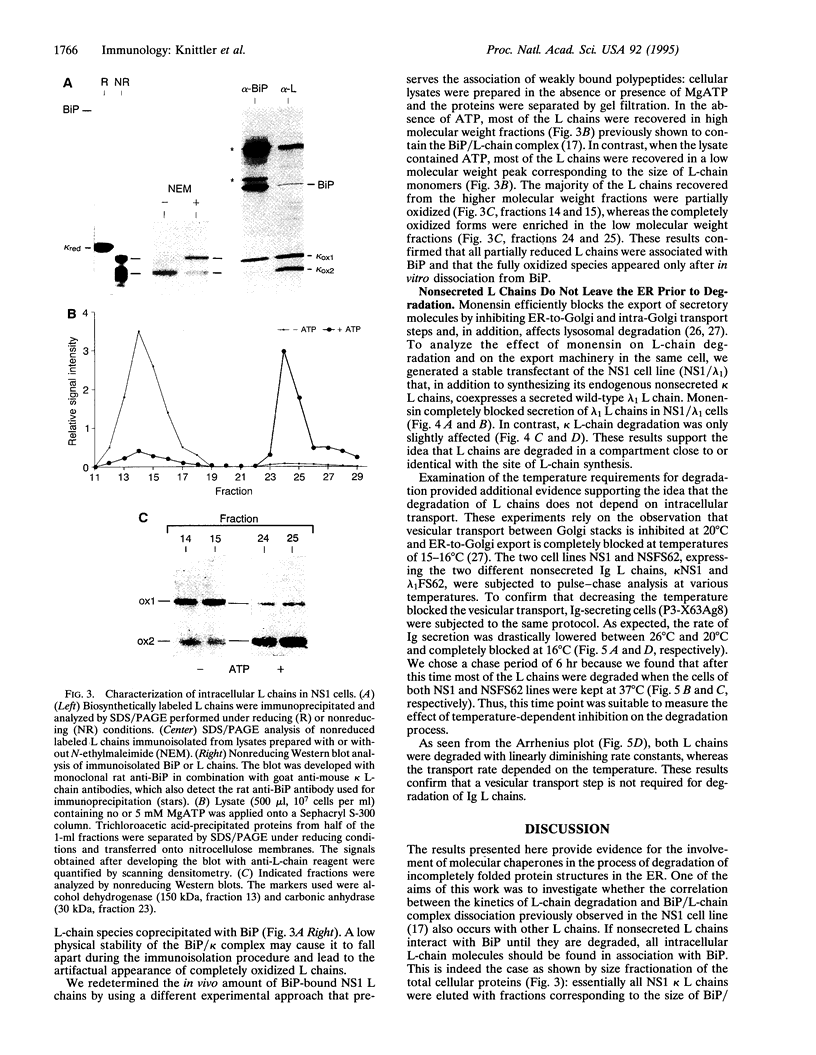
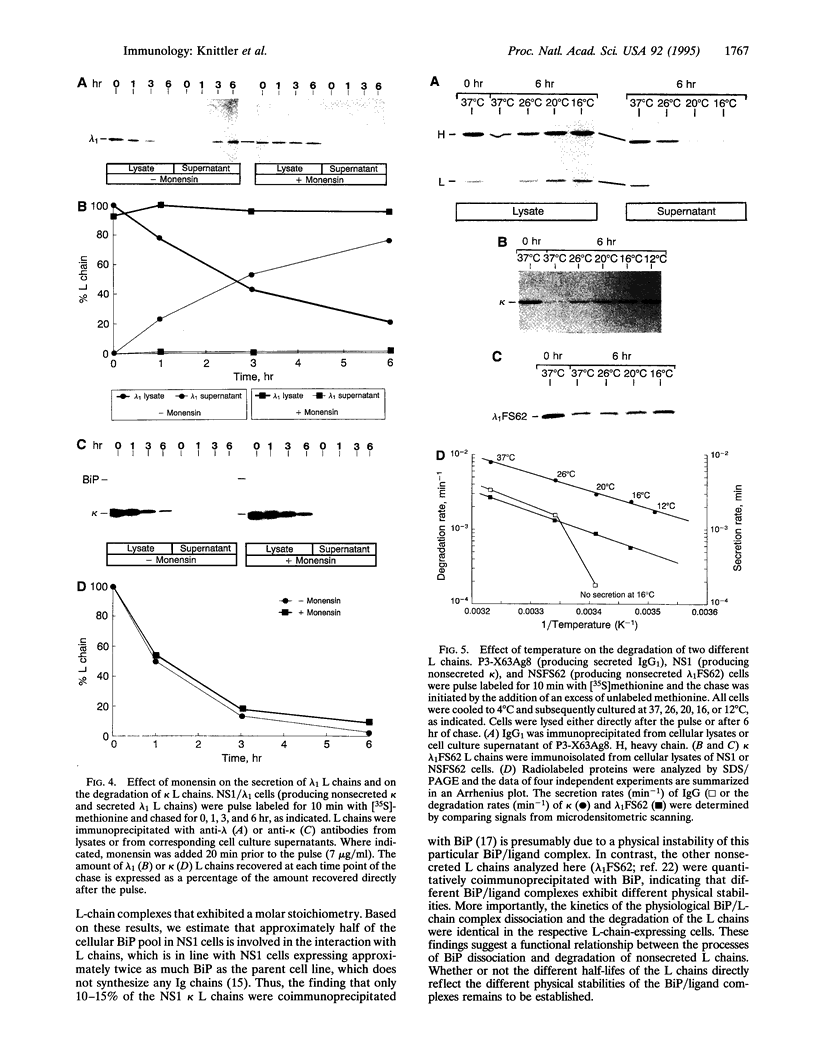
In the absence of immunoglobulin heavy-chain expression, some immunoglobulin light (L) chains are retained and degraded within the cell. We investigated the fate of two different nonsecreted murine L chains which exhibit different half-lives (50 min and 3-4 hr). Our results demonstrate that both nonsecreted L chains are quantitatively bound to BiP as partially oxidized molecules. The kinetics of L-chain degradation coincided with those of L-chain dissociation from BiP, which suggests that these two processes are functionally related. L-chain degradation does not depend on vesicular transport, indicating that these soluble proteins are degraded in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). In contrast, secreted L chains, which interact only transiently with BiP, are completely oxidized and are not degraded even when they are artificially retained in the ER. Our data support the model that, by means of BiP interaction, the ER degradation mechanism has the potential to discriminate between partially and completely folded molecules.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen D., Simon T., Sablitzky F., Rajewsky K., Cumano A. Antibody engineering for the analysis of affinity maturation of an anti-hapten response. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):1995–2001. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03038.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amara J. F., Lederkremer G., Lodish H. F. Intracellular degradation of unassembled asialoglycoprotein receptor subunits: a pre-Golgi, nonlysosomal endoproteolytic cleavage. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 2):3315–3324. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.3315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonifacino J. S., Suzuki C. K., Lippincott-Schwartz J., Weissman A. M., Klausner R. D. Pre-Golgi degradation of newly synthesized T-cell antigen receptor chains: intrinsic sensitivity and the role of subunit assembly. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;109(1):73–83. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.1.73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Bonifacino J. S., Yuan L. C., Klausner R. D. Selective degradation of T cell antigen receptor chains retained in a pre-Golgi compartment. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 1):2149–2161. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dul J. L., Argon Y. A single amino acid substitution in the variable region of the light chain specifically blocks immunoglobulin secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):8135–8139. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.8135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner A. M., Aviel S., Argon Y. Rapid degradation of an unassembled immunoglobulin light chain is mediated by a serine protease and occurs in a pre-Golgi compartment. J Biol Chem. 1993 Dec 5;268(34):25940–25947. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jäck H. M., Sloan B., Grisham G., Reason D., Wabl M. Large cytoplasmic inclusion body kappa-chain has unusual intrachain disulfide bonding. J Immunol. 1993 Jun 1;150(11):4928–4933. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jäntti J., Kuismanen E. Effect of caffeine and reduced temperature (20 degrees C) on the organization of the pre-Golgi and the Golgi stack membranes. J Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;120(6):1321–1335. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.6.1321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klausner R. D., Lippincott-Schwartz J., Bonifacino J. S. The T cell antigen receptor: insights into organelle biology. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1990;6:403–431. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.06.110190.002155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klausner R. D., Sitia R. Protein degradation in the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):611–614. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90104-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knittler M. R., Haas I. G. Interaction of BiP with newly synthesized immunoglobulin light chain molecules: cycles of sequential binding and release. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1573–1581. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05202.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krämer H., Deger A., Koch R., Rapp R., Hinz M., Weber U. Generation of oligomeric insulin receptor forms by intramolecular sulfhydryl-disulfide exchange. Involvement of masked sulfhydryl groups. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1987 May;368(5):471–479. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1987.368.1.471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Howe S. C., Milstein C. Fusion between immunoglobulin-secreting and nonsecreting myeloma cell lines. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Apr;6(4):292–295. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau M. M., Neufeld E. F. A frameshift mutation in a patient with Tay-Sachs disease causes premature termination and defective intracellular transport of the alpha-subunit of beta-hexosaminidase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 15;264(35):21376–21380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin H. Y., Masso-Welch P., Di Y. P., Cai J. W., Shen J. W., Subjeck J. R. The 170-kDa glucose-regulated stress protein is an endoplasmic reticulum protein that binds immunoglobulin. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Nov;4(11):1109–1119. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.11.1109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippincott-Schwartz J., Bonifacino J. S., Yuan L. C., Klausner R. D. Degradation from the endoplasmic reticulum: disposing of newly synthesized proteins. Cell. 1988 Jul 15;54(2):209–220. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90553-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melnick J., Aviel S., Argon Y. The endoplasmic reticulum stress protein GRP94, in addition to BiP, associates with unassembled immunoglobulin chains. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 25;267(30):21303–21306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro S., Pelham H. R. An Hsp70-like protein in the ER: identity with the 78 kd glucose-regulated protein and immunoglobulin heavy chain binding protein. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):291–300. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90746-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakaki T., Deans R. J., Lee A. S. Enhanced transcription of the 78,000-dalton glucose-regulated protein (GRP78) gene and association of GRP78 with immunoglobulin light chains in a nonsecreting B-cell myeloma line (NS-1). Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):2233–2238. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.2233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oi V. T., Morrison S. L., Herzenberg L. A., Berg P. Immunoglobulin gene expression in transformed lymphoid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):825–829. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saraste J., Palade G. E., Farquhar M. G. Temperature-sensitive steps in the transport of secretory proteins through the Golgi complex in exocrine pancreatic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6425–6429. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shin J., Lee S., Strominger J. L. Translocation of TCR alpha chains into the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum and their degradation. Science. 1993 Mar 26;259(5103):1901–1904. doi: 10.1126/science.8456316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon T., Rajewsky K. 'Enhancer-constitutive' vectors for the expression of recombinant antibodies. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 11;16(1):354–354. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.1.354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sitia R., Neuberger M. S., Milstein C. Regulation of membrane IgM expression in secretory B cells: translational and post-translational events. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):3969–3977. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02739.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoller T. J., Shields D. The propeptide of preprosomatostatin mediates intracellular transport and secretion of alpha-globin from mammalian cells. J Cell Biol. 1989 May;108(5):1647–1655. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.5.1647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartakoff A. M. Perturbation of vesicular traffic with the carboxylic ionophore monensin. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1026–1028. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90286-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsao Y. S., Ivessa N. E., Adesnik M., Sabatini D. D., Kreibich G. Carboxy terminally truncated forms of ribophorin I are degraded in pre-Golgi compartments by a calcium-dependent process. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;116(1):57–67. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.1.57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikström L., Lodish H. F. Nonlysosomal, pre-Golgi degradation of unassembled asialoglycoprotein receptor subunits: a TLCK- and TPCK-sensitive cleavage within the ER. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;113(5):997–1007. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.5.997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikström L., Lodish H. F. Unfolded H2b asialoglycoprotein receptor subunit polypeptides are selectively degraded within the endoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 5;268(19):14412–14416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wileman T., Carson G. R., Concino M., Ahmed A., Terhorst C. The gamma and epsilon subunits of the CD3 complex inhibit pre-Golgi degradation of newly synthesized T cell antigen receptors. J Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;110(4):973–986. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.4.973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]