Abstract
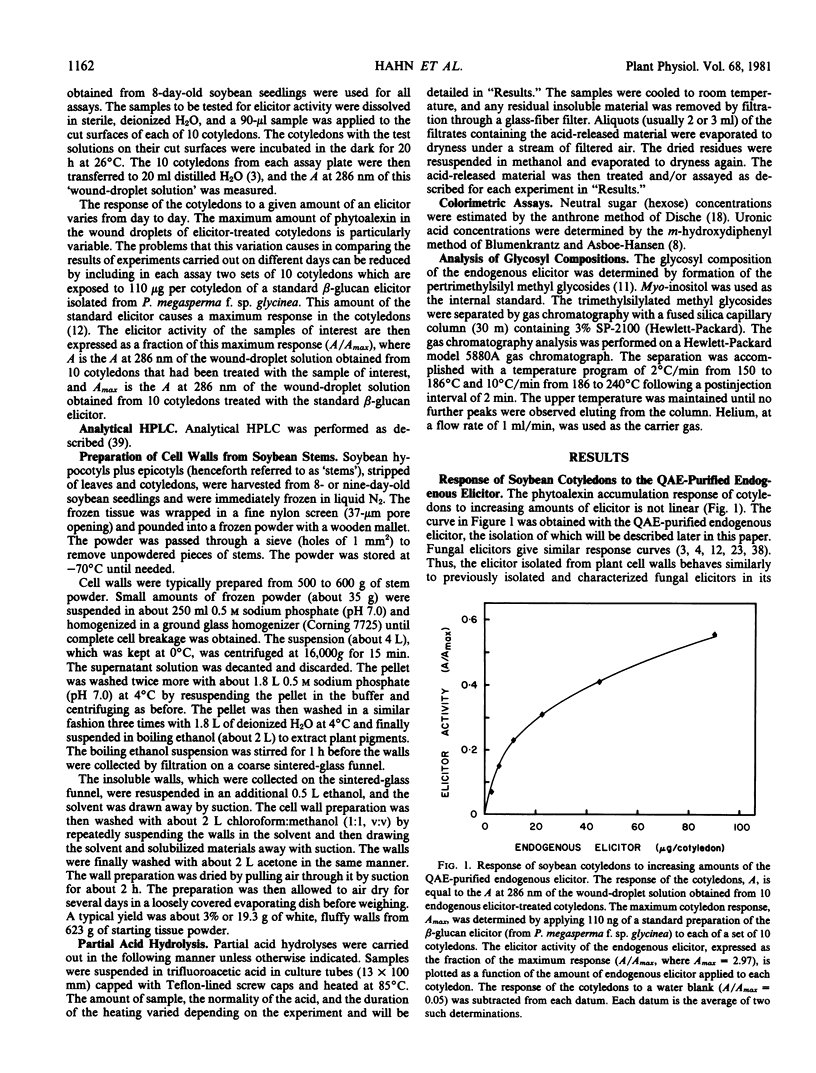
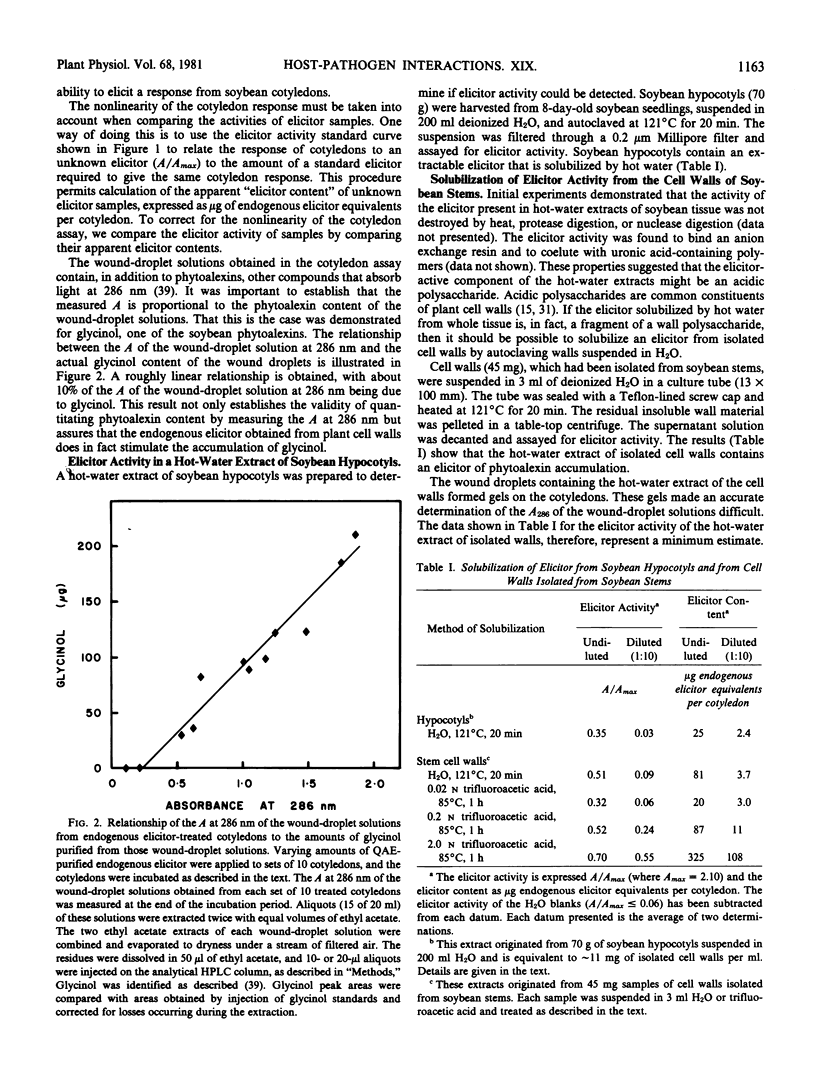
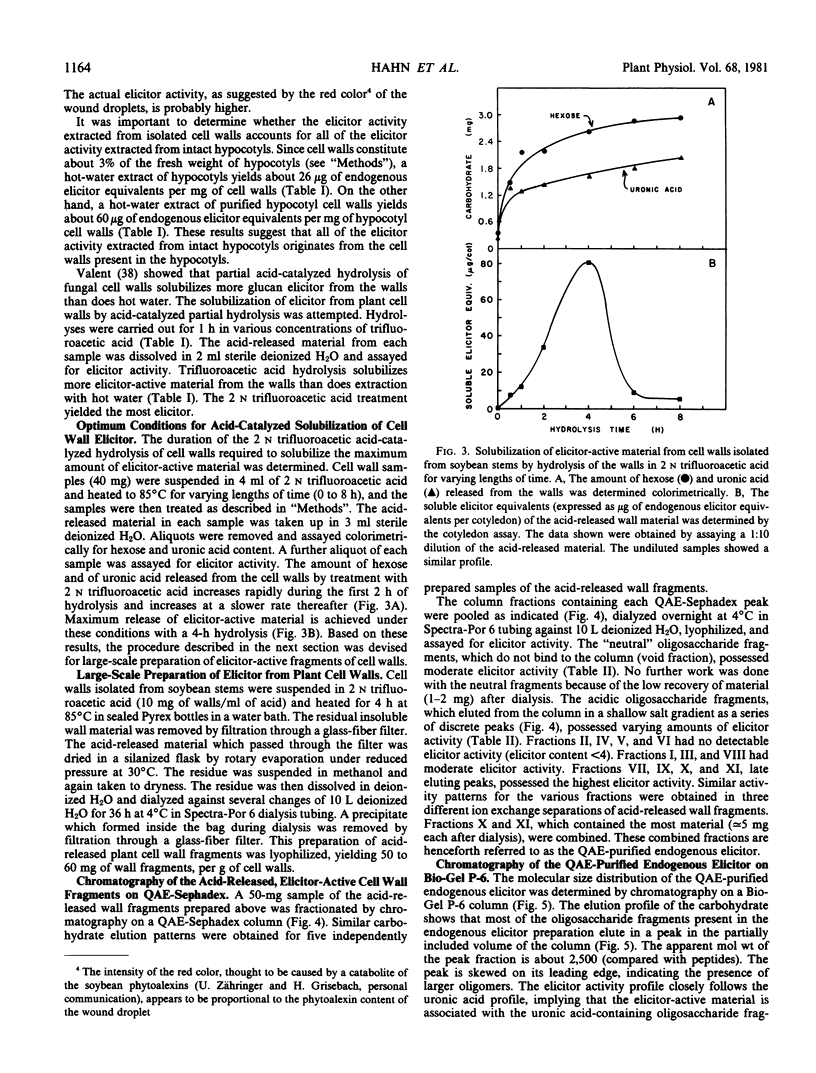
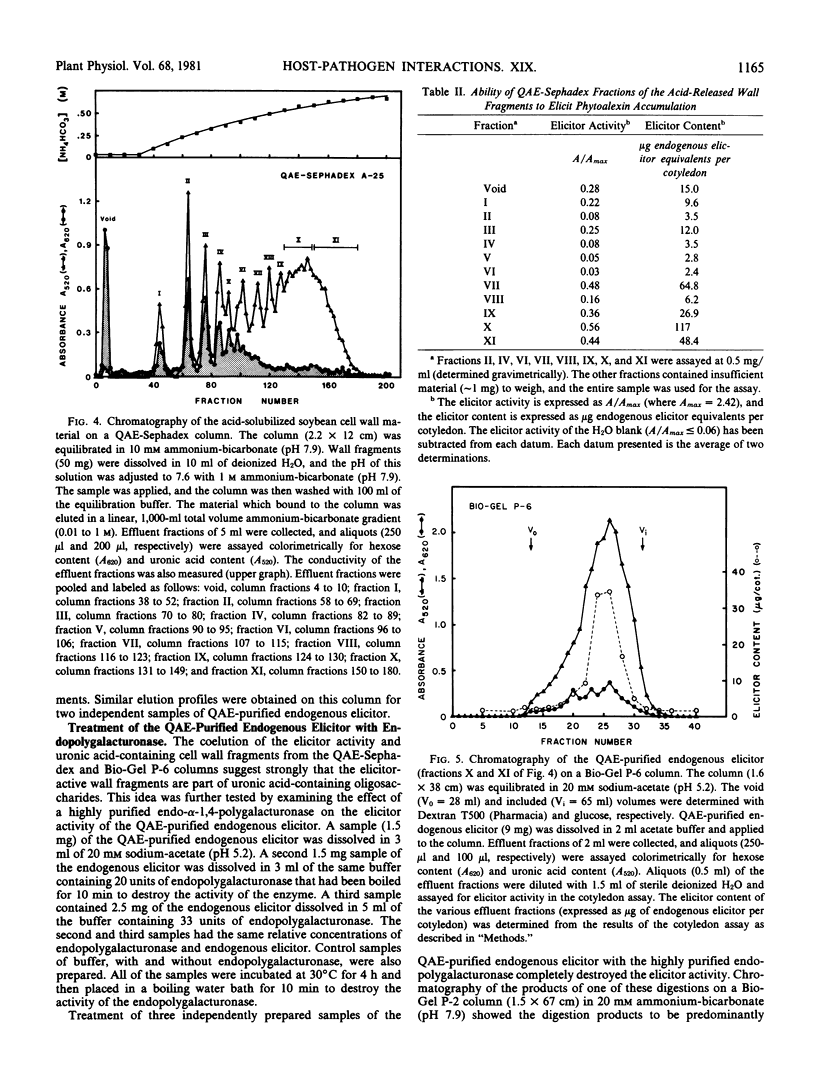
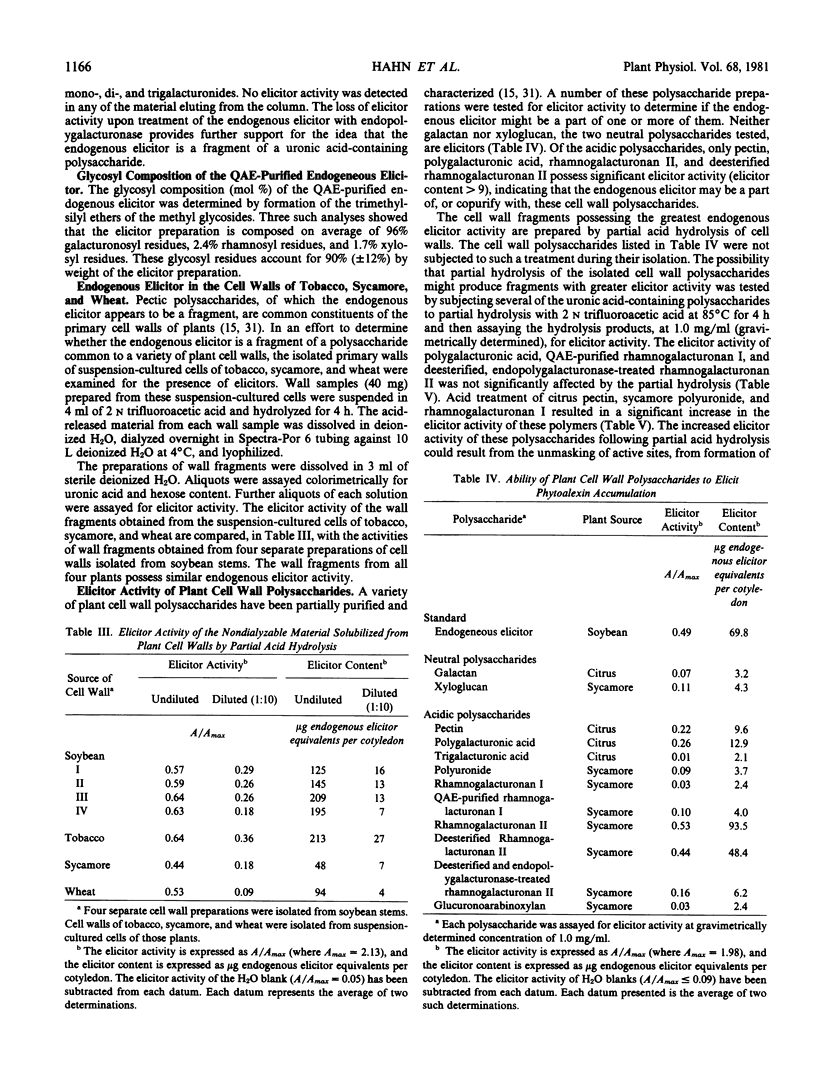
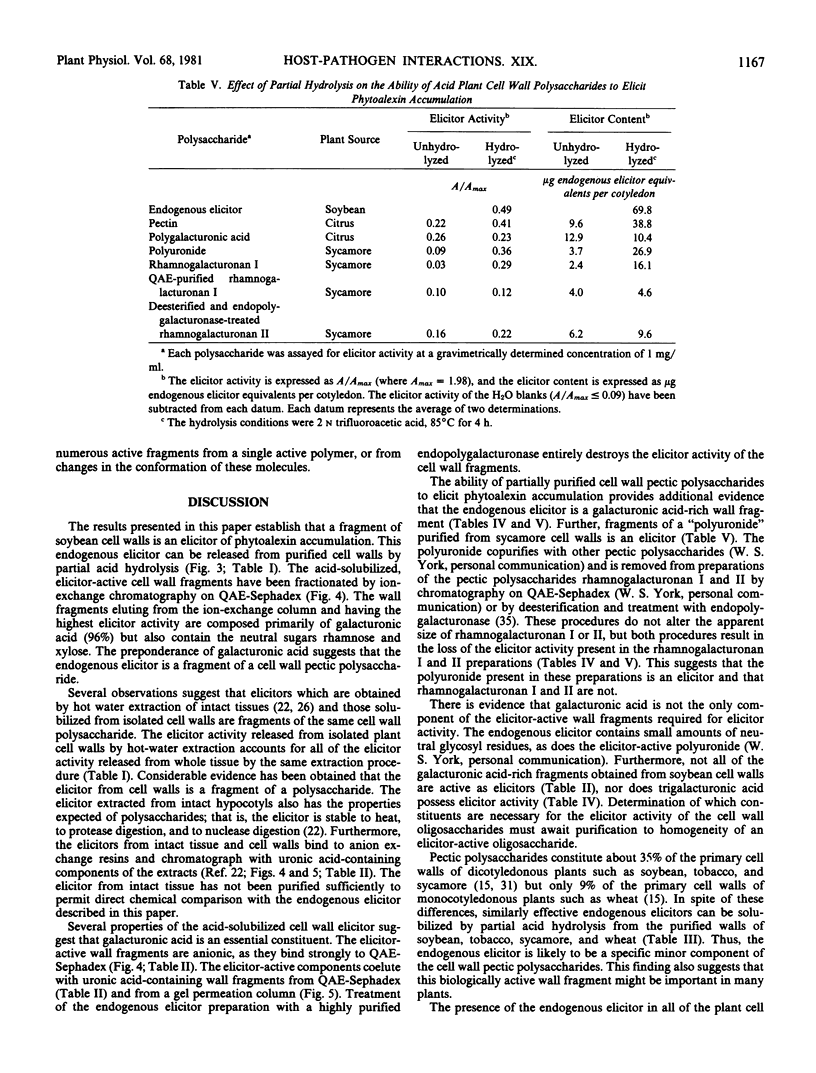
An elicitor of phytoalexin accumulation (endogenous elicitor) is solubilized from purified cell walls of soybean (Glycine max [L.] Merr., cv. Wayne) by extracting the walls with hot water or by subjecting the walls to partial acid hydrolysis. The endogenous elicitor obtained from soybean cell walls binds to an anion exchange resin. The elicitor-active material released from the resin contains oligosaccharides rich in galacturonic acid; small amounts of rhamnose and xylose are also present. The preponderance of galacturonic acid in the elicitor-active fragments suggests that the elicitor is, in fact, a fragment of a pectic polysaccharide. This possibility is supported by the observation that treatment of the wall fragments with a highly purified endopolygalacturonase destroys their ability to elicit phytoalexin accumulation. This observation, together with other evidence presented in this paper, suggests that galacturonic acid is an essential constituent of the elicitor-active wall fragments. Endogenous elicitors were also solubilized by partial hydrolysis from cell walls of suspension-cultured tobacco, sycamore, and wheat cells.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ayers A. R., Ebel J., Finelli F., Berger N., Albersheim P. Host-Pathogen Interactions: IX. Quantitative Assays of Elicitor Activity and Characterization of the Elicitor Present in the Extracellular Medium of Cultures of Phytophthora megasperma var. sojae. Plant Physiol. 1976 May;57(5):751–759. doi: 10.1104/pp.57.5.751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayers A. R., Ebel J., Valent B., Albersheim P. Host-Pathogen Interactions: X. Fractionation and Biological Activity of an Elicitor Isolated from the Mycelial Walls of Phytophthora megasperma var. sojae. Plant Physiol. 1976 May;57(5):760–765. doi: 10.1104/pp.57.5.760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayers A. R., Valent B., Ebel J., Albersheim P. Host-Pathogen Interactions: XI. Composition and Structure of Wall-released Elicitor Fractions. Plant Physiol. 1976 May;57(5):766–774. doi: 10.1104/pp.57.5.766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer W. D., Talmadge K. W., Keegstra K., Albersheim P. The Structure of Plant Cell Walls: II. The Hemicellulose of the Walls of Suspension-cultured Sycamore Cells. Plant Physiol. 1973 Jan;51(1):174–187. doi: 10.1104/pp.51.1.174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenkrantz N., Asboe-Hansen G. New method for quantitative determination of uronic acids. Anal Biochem. 1973 Aug;54(2):484–489. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90377-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers R. E., Clamp J. R. An assessment of methanolysis and other factors used in the analysis of carbohydrate-containing materials. Biochem J. 1971 Dec;125(4):1009–1018. doi: 10.1042/bj1251009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline K., Albersheim P. Host-Pathogen Interactions : XVII. HYDROLYSIS OF BIOLOGICALLY ACTIVE FUNGAL GLUCANS BY ENZYMES ISOLATED FROM SOYBEAN CELLS. Plant Physiol. 1981 Jul;68(1):221–228. doi: 10.1104/pp.68.1.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darvill A. G., McNeil M., Albersheim P. Structure of Plant Cell Walls: VIII. A New Pectic Polysaccharide. Plant Physiol. 1978 Sep;62(3):418–422. doi: 10.1104/pp.62.3.418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darvill J. E., McNeil M., Darvill A. G., Albersheim P. Structure of Plant Cell Walls: XI. GLUCURONOARABINOXYLAN, A SECOND HEMICELLULOSE IN THE PRIMARY CELL WALLS OF SUSPENSION-CULTURED SYCAMORE CELLS. Plant Physiol. 1980 Dec;66(6):1135–1139. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.6.1135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- English P. D., Maglothin A., Keegstra K., Albersheim P. A Cell Wall-degrading Endopolygalacturonase Secreted by Colletotrichum lindemuthianum. Plant Physiol. 1972 Mar;49(3):293–298. doi: 10.1104/pp.49.3.293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadwiger L. A., Schwochau M. E. Ultraviolet Light-induced Formation of Pisatin and Phenylalanine Ammonia Lyase. Plant Physiol. 1971 Apr;47(4):588–590. doi: 10.1104/pp.47.4.588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn M. G., Albersheim P. Host-Pathogen Interactions: XIV. Isolation and Partial Characterization of an Elicitor from Yeast Extract. Plant Physiol. 1978 Jul;62(1):107–111. doi: 10.1104/pp.62.1.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. C., West C. A. Polygalacturonase from Rhizopus stolonifer, an Elicitor of Casbene Synthetase Activity in Castor Bean (Ricinus communis L.) Seedlings. Plant Physiol. 1981 Apr;67(4):633–639. doi: 10.1104/pp.67.4.633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. C., West C. A. Properties of Rhizopus stolonifer Polygalacturonase, an Elicitor of Casbene Synthetase Activity in Castor Bean (Ricinus communis L.) Seedlings. Plant Physiol. 1981 Apr;67(4):640–645. doi: 10.1104/pp.67.4.640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeil M., Darvill A. G., Albersheim P. Structure of Plant Cell Walls: X. RHAMNOGALACTURONAN I, A STRUCTURALLY COMPLEX PECTIC POLYSACCHARIDE IN THE WALLS OF SUSPENSION-CULTURED SYCAMORE CELLS. Plant Physiol. 1980 Dec;66(6):1128–1134. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.6.1128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plant J., Wood E. C. E.D. involvement grows in audit activities, rape treatment. Hospitals. 1977 Apr 1;51(7):107-8, 110,112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein L. I., Hahn M. G., Albersheim P. Host-Pathogen Interactions : XVIII. ISOLATION AND BIOLOGICAL ACTIVITY OF GLYCINOL, A PTEROCARPAN PHYTOALEXIN SYNTHESIZED BY SOYBEANS. Plant Physiol. 1981 Aug;68(2):358–363. doi: 10.1104/pp.68.2.358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


