Abstract
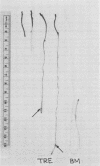
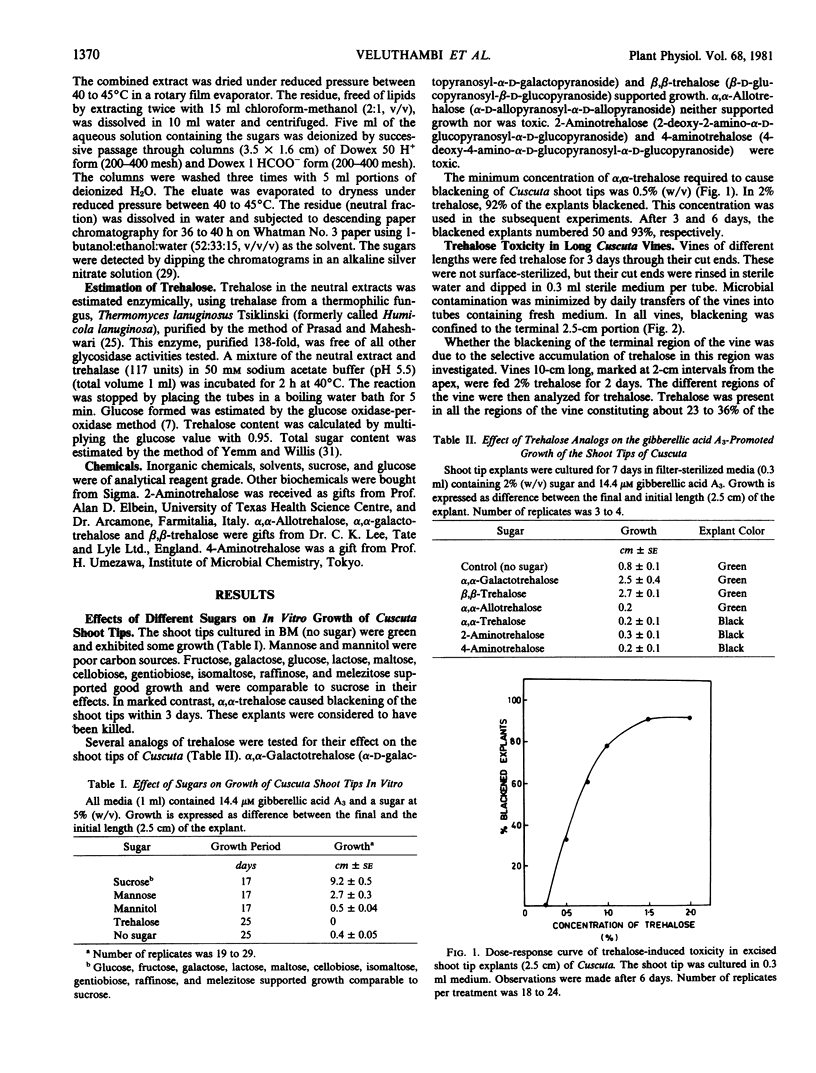
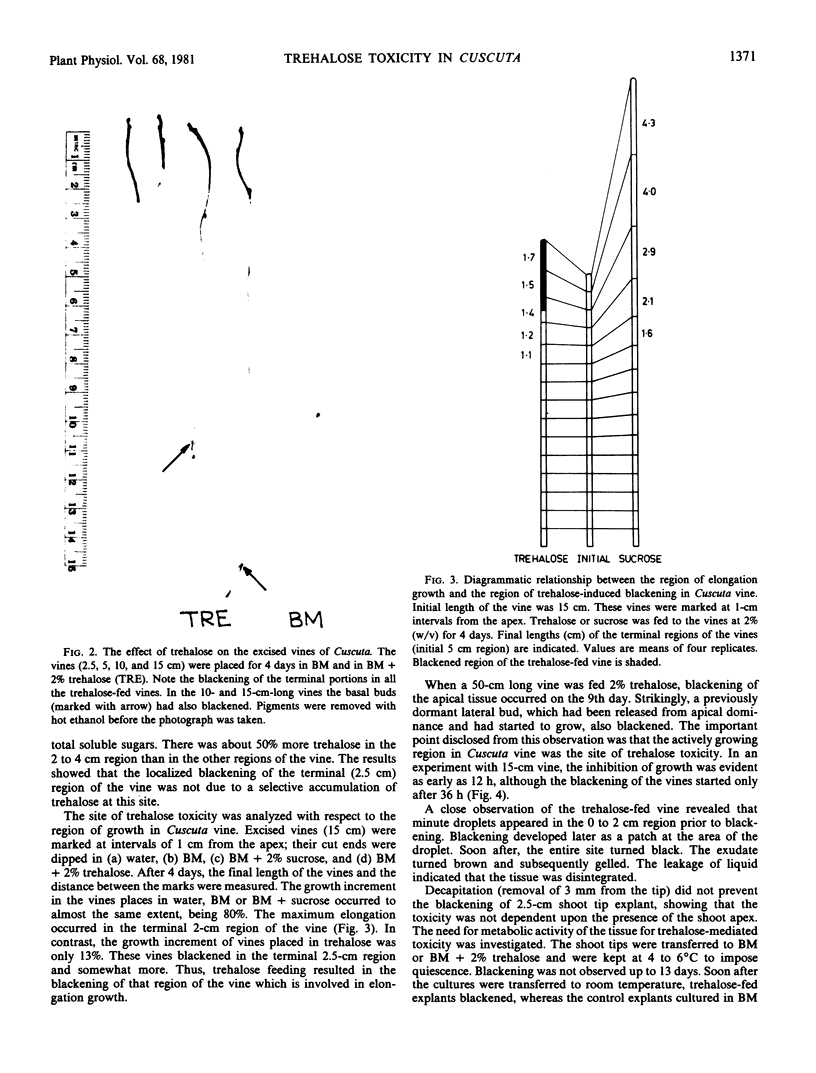
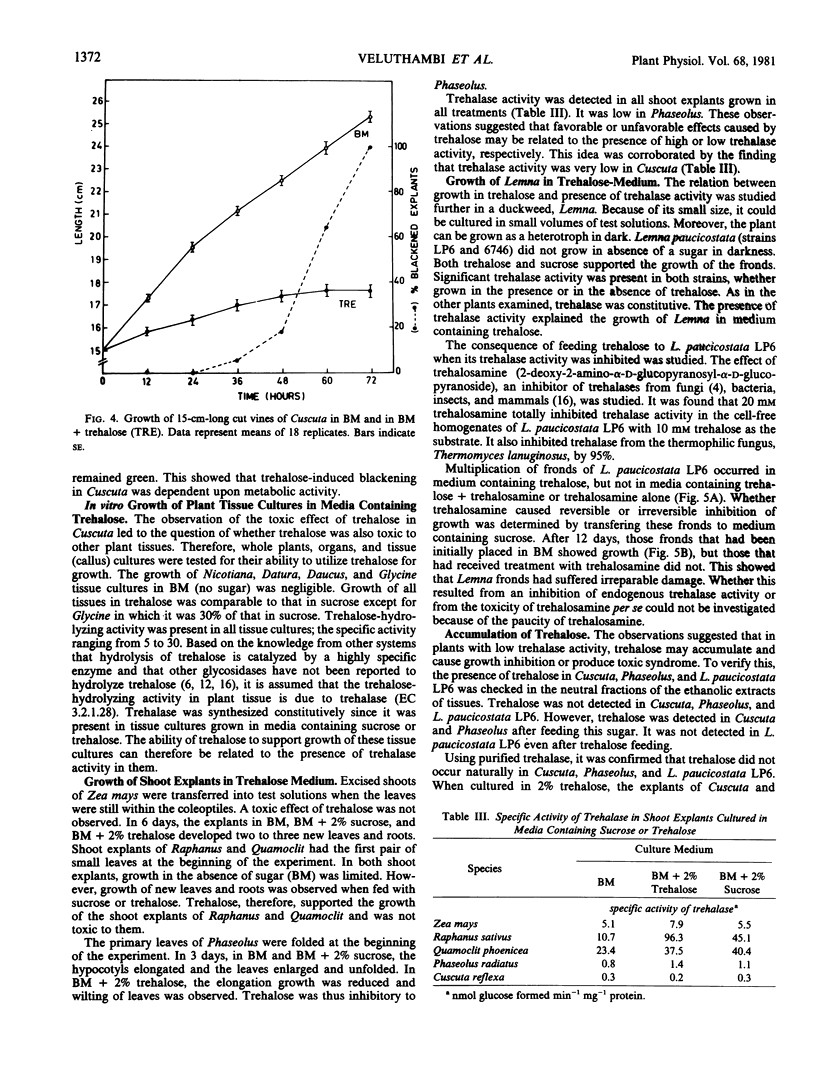
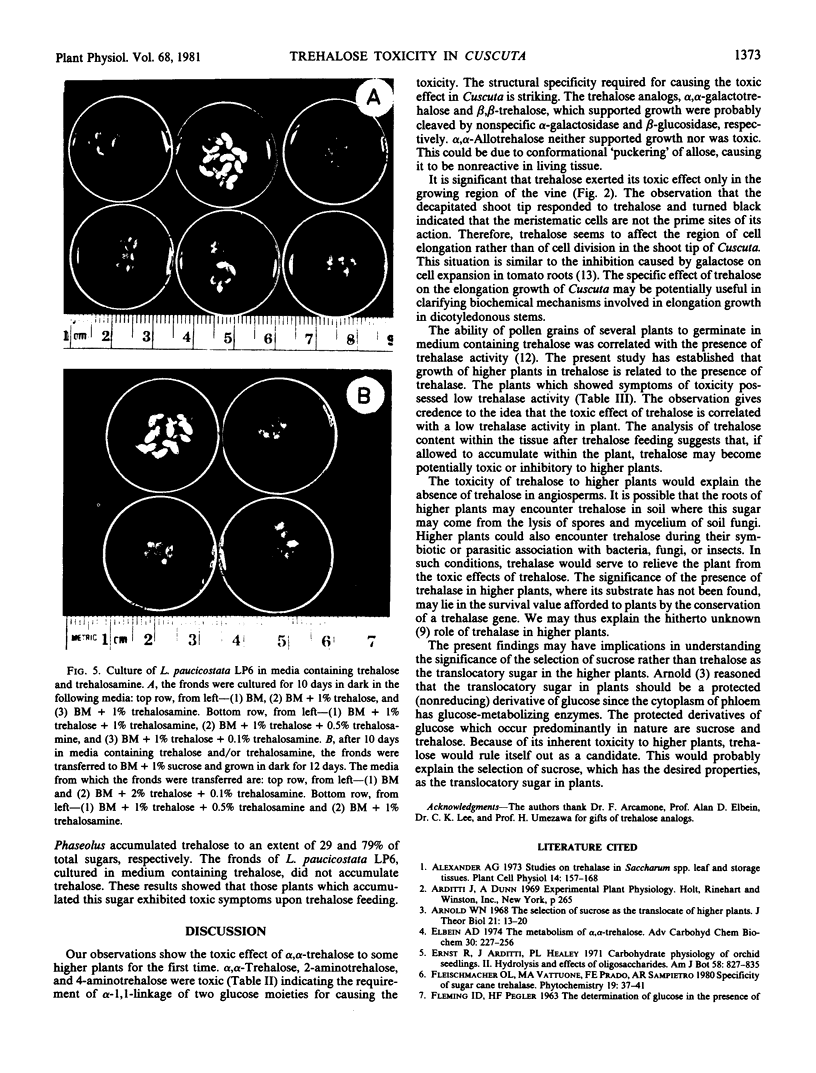
A toxic effect of α,α-trehalose in an angiospermic plant, Cuscuta reflexa (dodder), is described. This disaccharide and its analogs, 2-aminotrehalose and 4-aminotrehalose, induced a rapid blackening of the terminal region of the vine which is involved in elongation growth. From the results of in vitro growth of several angiospermic plants and determination of trehalase activity in them, it is concluded that the toxic effect of trehalose in Cuscuta is because of the very low trehalase activity in the vine. As a result, trehalose accumulates in the vine and interferes with some process closely associated with growth. The growth potential of Lemna (a duckweed) in a medium containing trehalose as the carbon source was irreversibly lost upon addition of trehalosamine, an inhibitor of trehalase activity. It is concluded that, if allowed to accumulate within the tissue, trehalose may be potentially toxic or inhibitory to higher plants in general. The presence of trehalase activity in plants, where its substrate has not been found to occur, is envisaged to relieve the plant from the toxic effects of trehalose which it may encounter in soil or during association with fungi or insects.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnold W. N. The selection of sucrose as the translocate of higher plants. J Theor Biol. 1968 Oct;21(1):13–20. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(68)90056-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elbein A. D. The metabolism of alpha,alpha-trehalose. Adv Carbohydr Chem Biochem. 1974;30:227–256. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2318(08)60266-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gussin A. E., McCormack J. H., Waung L. Y., Gluckin D. S. Trehalase: a new pollen enzyme. Plant Physiol. 1969 Aug;44(8):1163–1168. doi: 10.1104/pp.44.8.1163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keen N. T., Williams P. H. Translocation of sugars into infected cabbage tissues during clubroot development. Plant Physiol. 1969 May;44(5):748–754. doi: 10.1104/pp.44.5.748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labat-Robert J., Baumann F. C., Bar-Guilloux E., Robic D. Comparative specificities of trehalases from various species. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1978;61(1):111–114. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(78)90225-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maheshwari R., Shailini C., Veluthambi K., Mahadevan S. Interaction of Gibberellic Acid and Indole-3-acetic Acid in the Growth of Excised Cuscuta Shoot Tips in Vitro. Plant Physiol. 1980 Feb;65(2):186–192. doi: 10.1104/pp.65.2.186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marzullo G., Danforth W. F. Ethanol-soluble intermediates and products of acetate metabolism by Euglena gracilis var. bacillaris. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 Feb;55(2):257–266. doi: 10.1099/00221287-55-2-257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potty V. H. Determination of proteins in the presence of phenols and pectins. Anal Biochem. 1969 Jun;29(3):535–539. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90339-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prasad A. R., Maheshwari R. Purification and properties of trehalase from the thermophilic fungus Humicola lanuginosa. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jul 7;525(1):162–170. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(78)90210-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TREVELYAN W. E., PROCTER D. P., HARRISON J. S. Detection of sugars on paper chromatograms. Nature. 1950 Sep 9;166(4219):444–445. doi: 10.1038/166444b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma D. C., Dougall D. K. Influence of carbohydrates on quantitative aspects of growth and embryo formation in wild carrot suspension cultures. Plant Physiol. 1977 Jan;59(1):81–85. doi: 10.1104/pp.59.1.81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YEMM E. W., WILLIS A. J. The estimation of carbohydrates in plant extracts by anthrone. Biochem J. 1954 Jul;57(3):508–514. doi: 10.1042/bj0570508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]