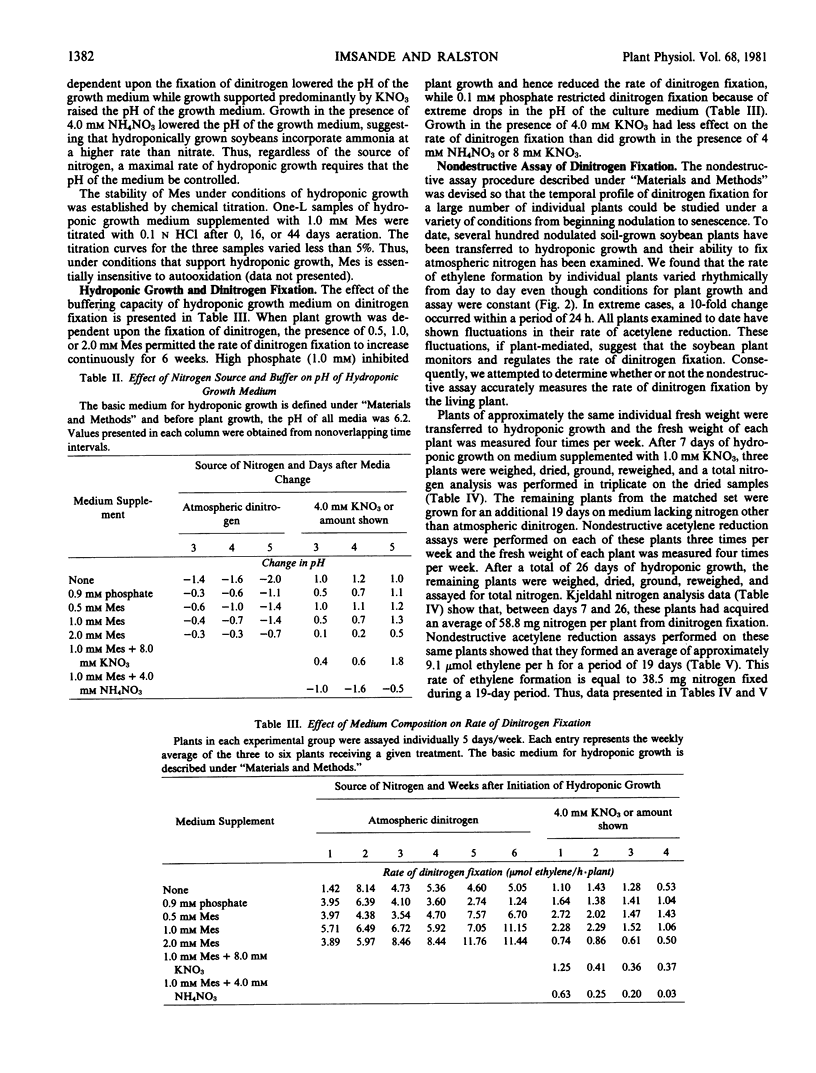
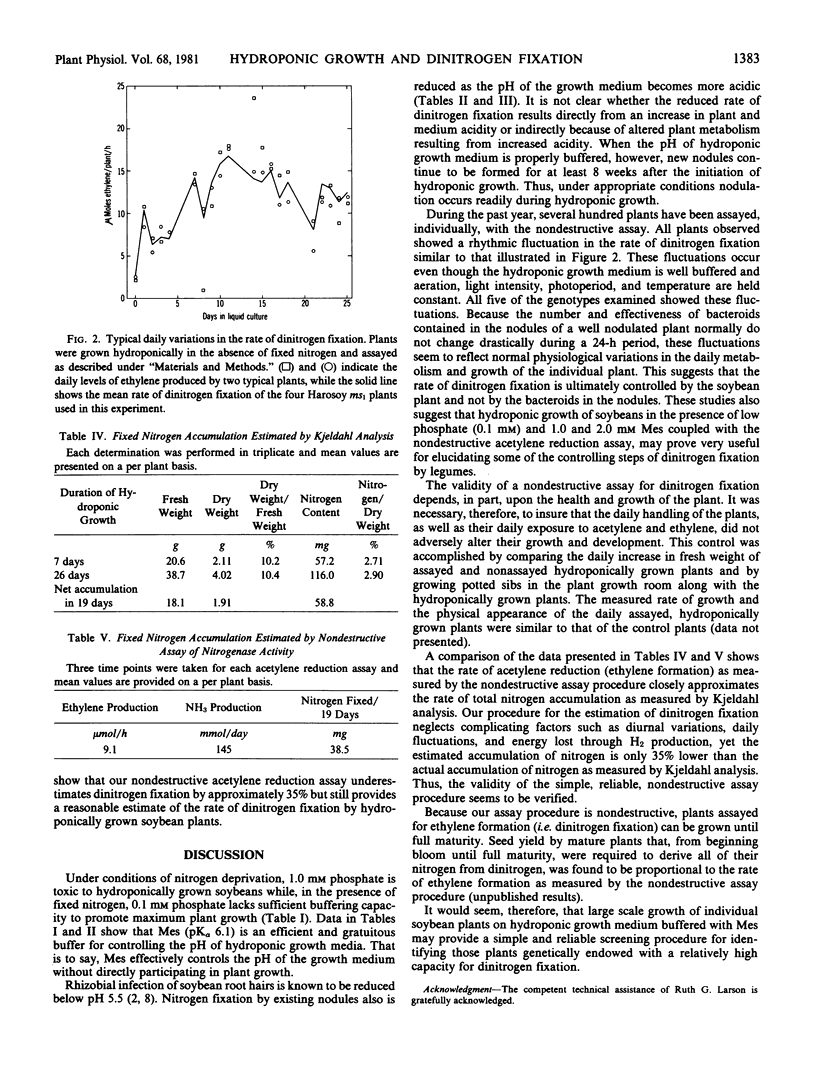
Abstract
Hydroponic growth medium must be well buffered if it is to support sustained plant growth. Although 1.0 millimolar phosphate is commonly used as a buffer for hydroponic growth media, at that concentration it is generally toxic to a soybean plant that derives its nitrogen solely from dinitrogen fixation. On the other hand, we show that 1.0 to 2.0 millimolar 2-(N-morpholino)ethanesulfonic acid, pKa 6.1, has excellent buffering capacity, and it neither interferes with nor contributes nutritionally to soybean plant growth. Furthermore, it neither impedes nodulation nor the assay of dinitrogen fixation. Hence, soybean plants grown hydroponically on a medium supplemented with 1.0 to 2.0 millimolar 2-(N-morpholino)ethanesulfonic acid and 0.1 millimolar phosphate achieve an excellent rate of growth and, in the absence of added fixed nitrogen, attain a very high rate of dinitrogen fixation. Combining the concept of hydroponic growth and the sensitive acetylene reduction technique, we have devised a simple, rapid, reproducible assay procedure whereby the rate of dinitrogen fixation by individual plants can be measured throughout the lifetime of those plants. The rate of dinitrogen fixation as measured by the nondestructive acetylene reduction procedure is shown to be approximately equal to the rate of total plant nitrogen accumulation as measured by Kjeldahl analysis. Because of the simplicity of the procedure, one investigator can readily assay 50 plants individually per day.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dilworth M. J. Acetylene reduction by nitrogen-fixing preparations from Clostridium pasteurianum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Oct 31;127(2):285–294. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90383-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy R. W., Holsten R. D., Jackson E. K., Burns R. C. The acetylene-ethylene assay for n(2) fixation: laboratory and field evaluation. Plant Physiol. 1968 Aug;43(8):1185–1207. doi: 10.1104/pp.43.8.1185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. Y., Boyer J. S., Vanderhoef L. N. Acetylene reduction (nitrogen fixation) and metabolic activities of soybean having various leaf and nodule water potentials. Plant Physiol. 1975 Aug;56(2):222–227. doi: 10.1104/pp.56.2.222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mederski H. J., Streeter J. G. Continuous, automated acetylene reduction assays using intact plants. Plant Physiol. 1977 Jun;59(6):1076–1081. doi: 10.1104/pp.59.6.1076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G. W., Brown J. C., Holmes R. S. Chlorosis in Soybean as Related to Iron, Phosphorus, Bicarbonate, and Cytochrome Oxidase Activity. Plant Physiol. 1960 Sep;35(5):619–625. doi: 10.1104/pp.35.5.619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweitzer L. E., Harper J. E. Effect of light, dark, and temperature on root nodule activity (acetylene reduction) of soybeans. Plant Physiol. 1980 Jan;65(1):51–56. doi: 10.1104/pp.65.1.51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart W. D., Fitzgerald G. P., Burris R. H. In situ studies on N2 fixation using the acetylene reduction technique. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Nov;58(5):2071–2078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.5.2071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zobel R. W., Del Tredici P., Torrey J. G. Method for growing plants aeroponically. Plant Physiol. 1976 Mar;57(3):344–346. doi: 10.1104/pp.57.3.344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


