Abstract
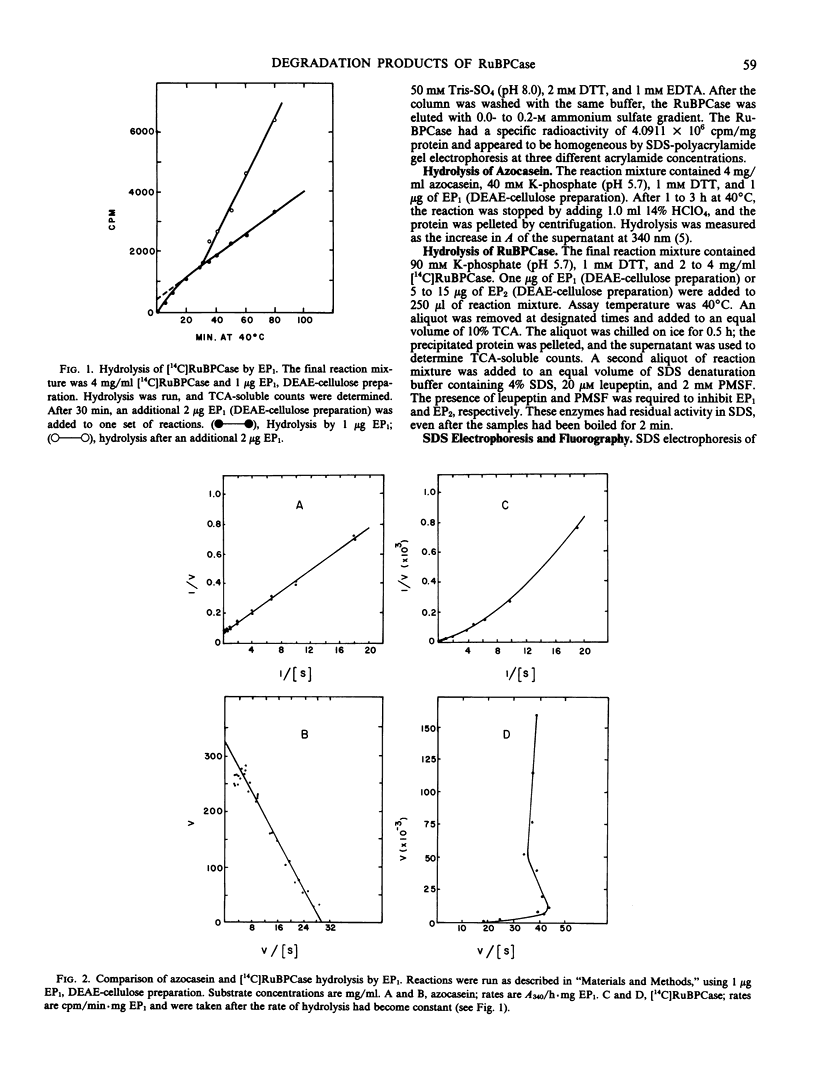
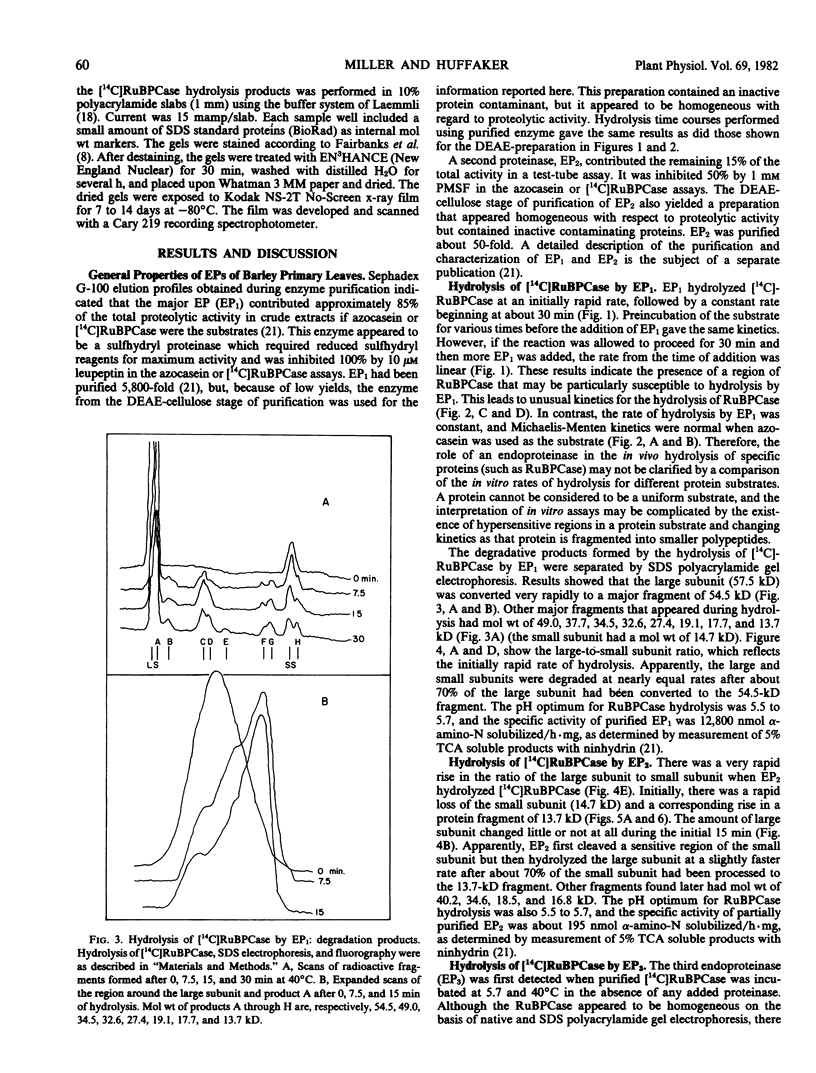
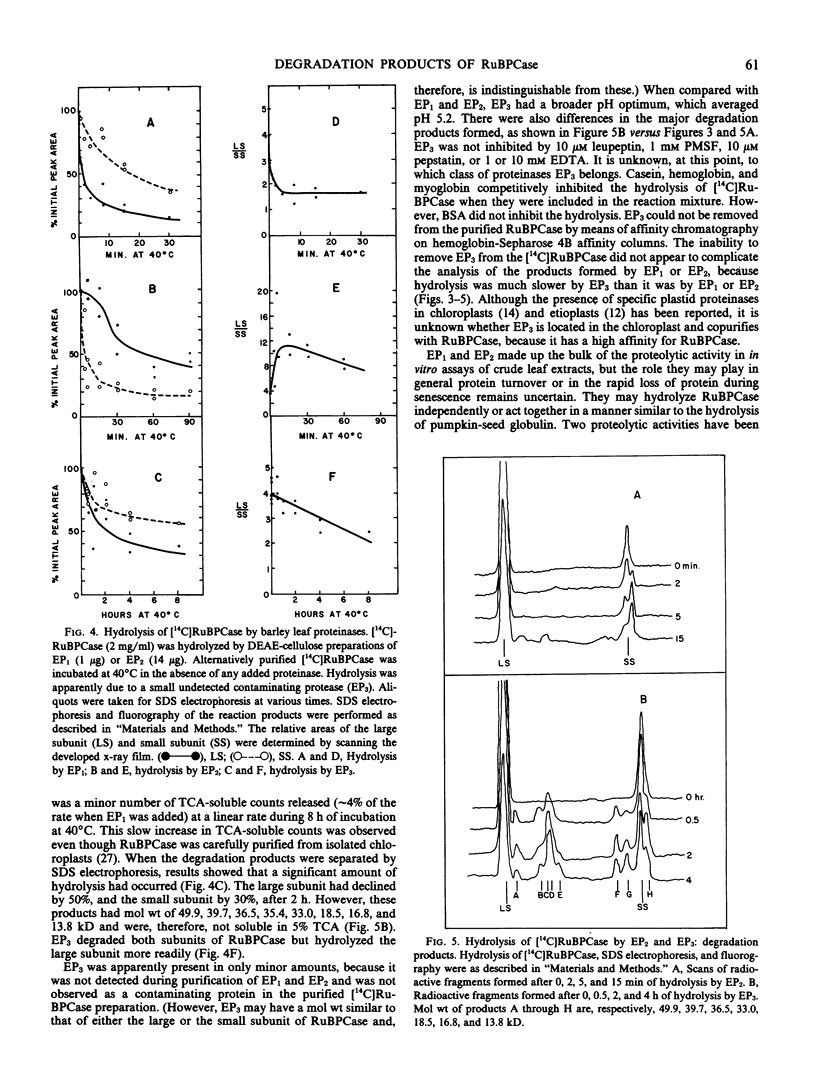
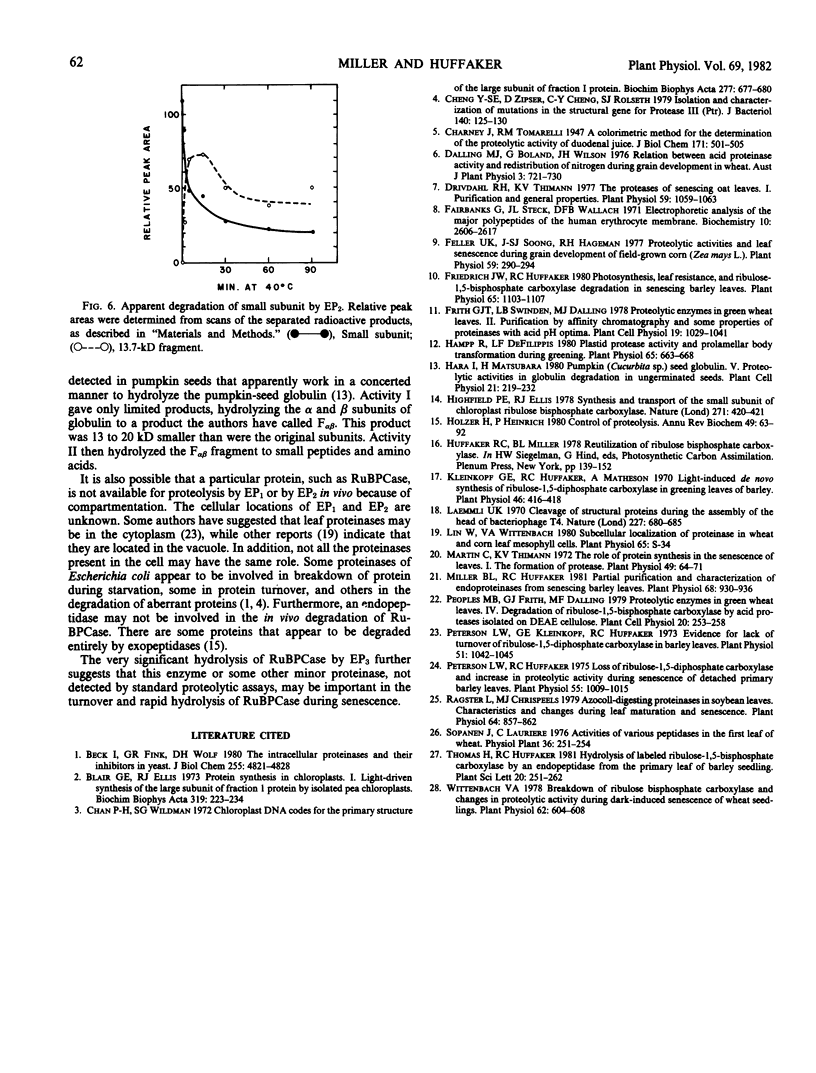
The hydrolysis of 14C-labeled ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase (RuBPCase) by two partially purified endoproteinases from senescing barley (Hordeum vulgare v. Numar) leaves is described. The major thiol proteinase, EP1, exhibits biphasic kinetics which appear to be caused by a region of the large subunit of RuBPCase that is highly sensitive to attack by EP1. This proteinase further hydrolyzes both the large and small subunit to smaller peptides. A second proteinase, EP2, appears to convert the small subunit of RuBPCase rapidly to a 13.7-kilodalton fragment during initial stages of hydrolysis and then to degrade both this fragment and the large subunit. The presence of a third endoproteinase, EP3, was discovered when [14C]RuBPCase, which appeared to be homogeneous by sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide electrophoresis, seemed to undergo very low but significant rates of “autolysis.” The large molecular weight fragments produced by EP3 were different from those of EP1 and EP2.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blair G. E., Ellis R. J. Protein synthesis in chloroplasts. I. Light-driven synthesis of the large subunit of fraction I protein by isolated pea chloroplasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Aug 24;319(2):223–234. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(73)90013-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan P. H., Wildman S. G. Chloroplast DNA codes for the primary structure of the large subunit of fraction I protein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Sep 14;277(3):677–680. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90115-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y. S., Zipser D., Cheng C. Y., Rolseth S. J. Isolation and characterization of mutations in the structural gene for protease III (ptr). J Bacteriol. 1979 Oct;140(1):125–130. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.1.125-130.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drivdahl R. H., Thimann K. V. Proteases of senescing oat leaves: I. Purification and general properties. Plant Physiol. 1977 Jun;59(6):1059–1063. doi: 10.1104/pp.59.6.1059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feller U. K., Soong T. S., Hageman R. H. Leaf Proteolytic Activities and Senescence during Grain Development of Field-grown Corn (Zea mays L.). Plant Physiol. 1977 Feb;59(2):290–294. doi: 10.1104/pp.59.2.290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedrich J. W., Huffaker R. C. Photosynthesis, leaf resistances, and ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase degradation in senescing barley leaves. Plant Physiol. 1980 Jun;65(6):1103–1107. doi: 10.1104/pp.65.6.1103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampp R., De Filippis L. F. Plastid Protease Activity and Prolamellar Body Transformation during Greening. Plant Physiol. 1980 Apr;65(4):663–668. doi: 10.1104/pp.65.4.663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzer H., Heinrich P. C. Control of proteolysis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:63–91. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.000431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinkopf G. E., Huffaker R. C., Matheson A. Light-induced de Novo Synthesis of Ribulose 1,5-Diphosphate Carboxylase in Greening Leaves of Barley. Plant Physiol. 1970 Sep;46(3):416–418. doi: 10.1104/pp.46.3.416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin C., Thimann K. V. The role of protein synthesis in the senescence of leaves: I. The formation of protease. Plant Physiol. 1972 Jan;49(1):64–71. doi: 10.1104/pp.49.1.64. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller B. L., Huffaker R. C. Partial purification and characterization of endoproteinases from senescing barley leaves. Plant Physiol. 1981 Oct;68(4):930–936. doi: 10.1104/pp.68.4.930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson L. W., Huffaker R. C. Loss of Ribulose 1,5-Diphosphate Carboxylase and Increase in Proteolytic Activity during Senescence of Detached Primary Barley Leaves. Plant Physiol. 1975 Jun;55(6):1009–1015. doi: 10.1104/pp.55.6.1009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson L. W., Kleinkopf G. E., Huffaker R. C. Evidence for lack of turnover of ribulose 1,5-diphosphate carboxylase in barley leaves. Plant Physiol. 1973 Jun;51(6):1042–1045. doi: 10.1104/pp.51.6.1042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ragster L. V., Chrispeels M. J. Azocoll-digesting Proteinases in Soybean Leaves: Characteristics and Changes during Leaf Maturation and Senescence. Plant Physiol. 1979 Nov;64(5):857–862. doi: 10.1104/pp.64.5.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittenbach V. A. Breakdown of Ribulose Bisphosphate Carboxylase and Change in Proteolytic Activity during Dark-induced Senescence of Wheat Seedlings. Plant Physiol. 1978 Oct;62(4):604–608. doi: 10.1104/pp.62.4.604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



