Abstract
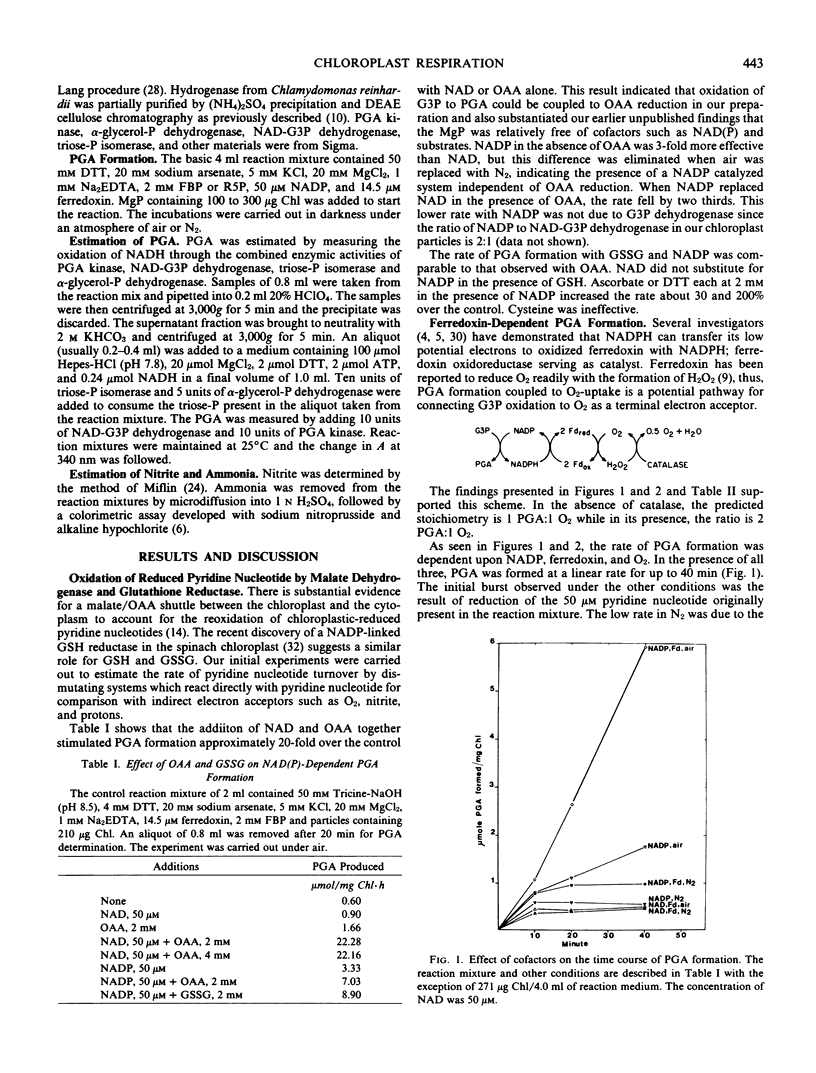
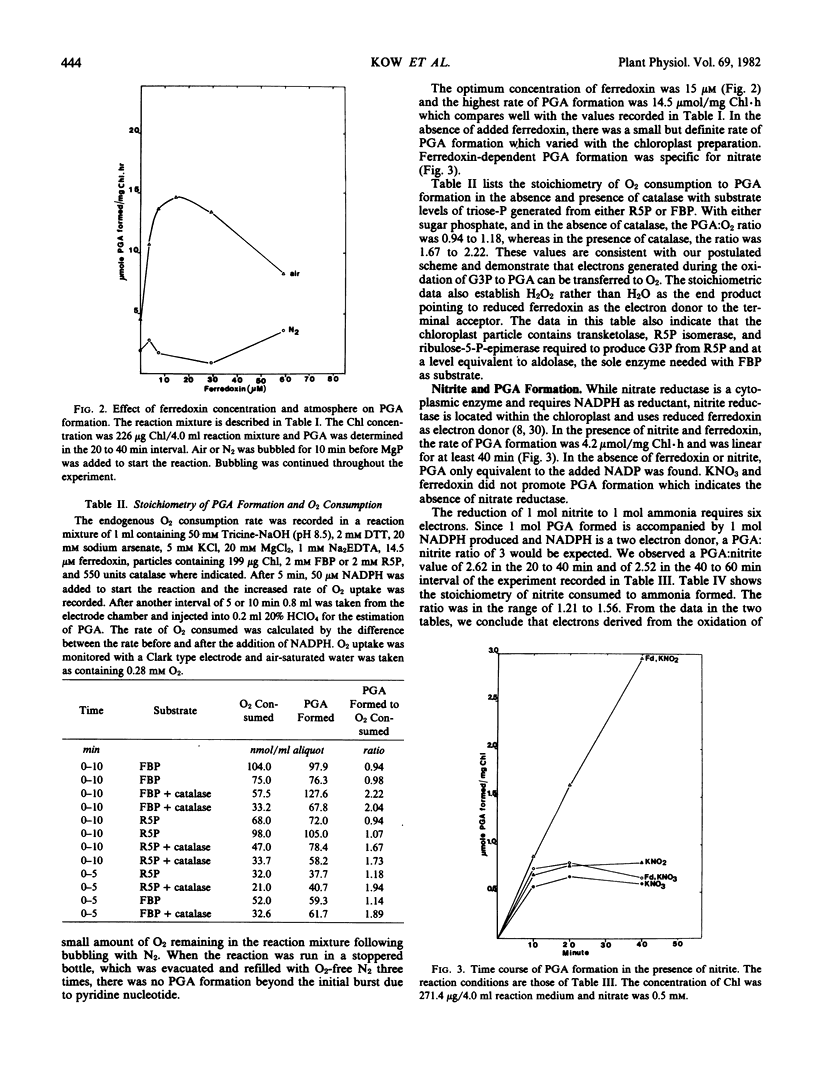
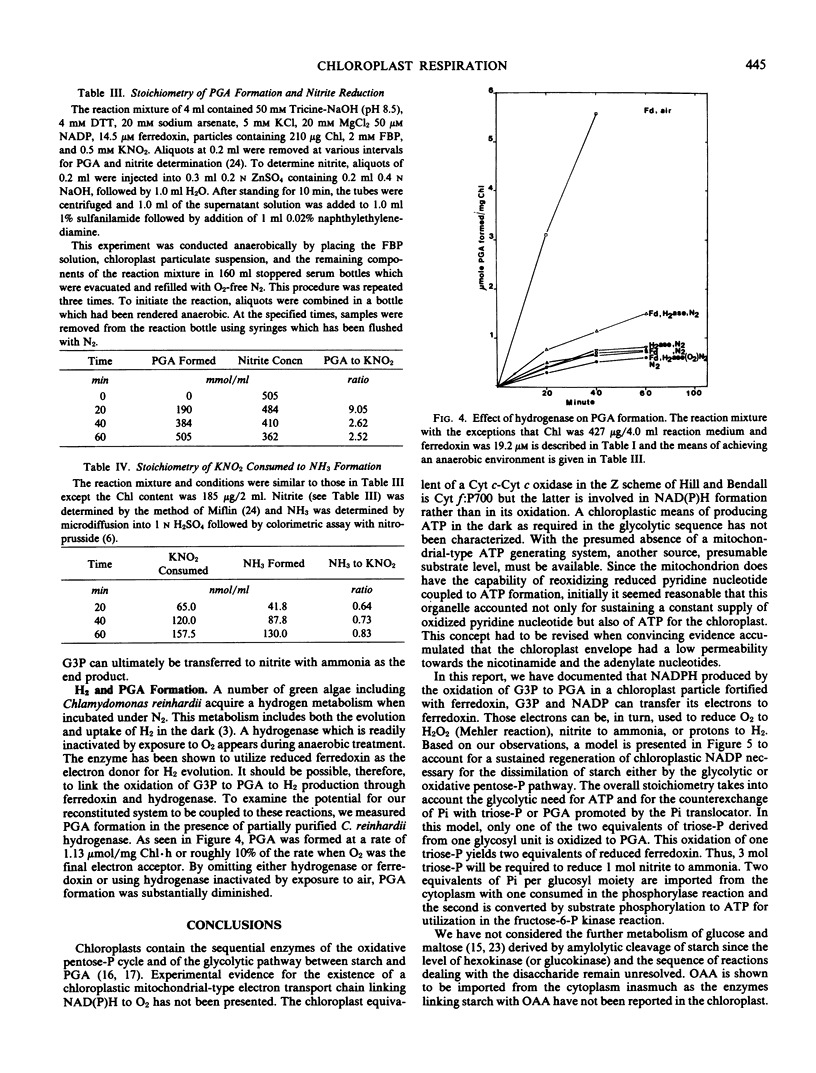
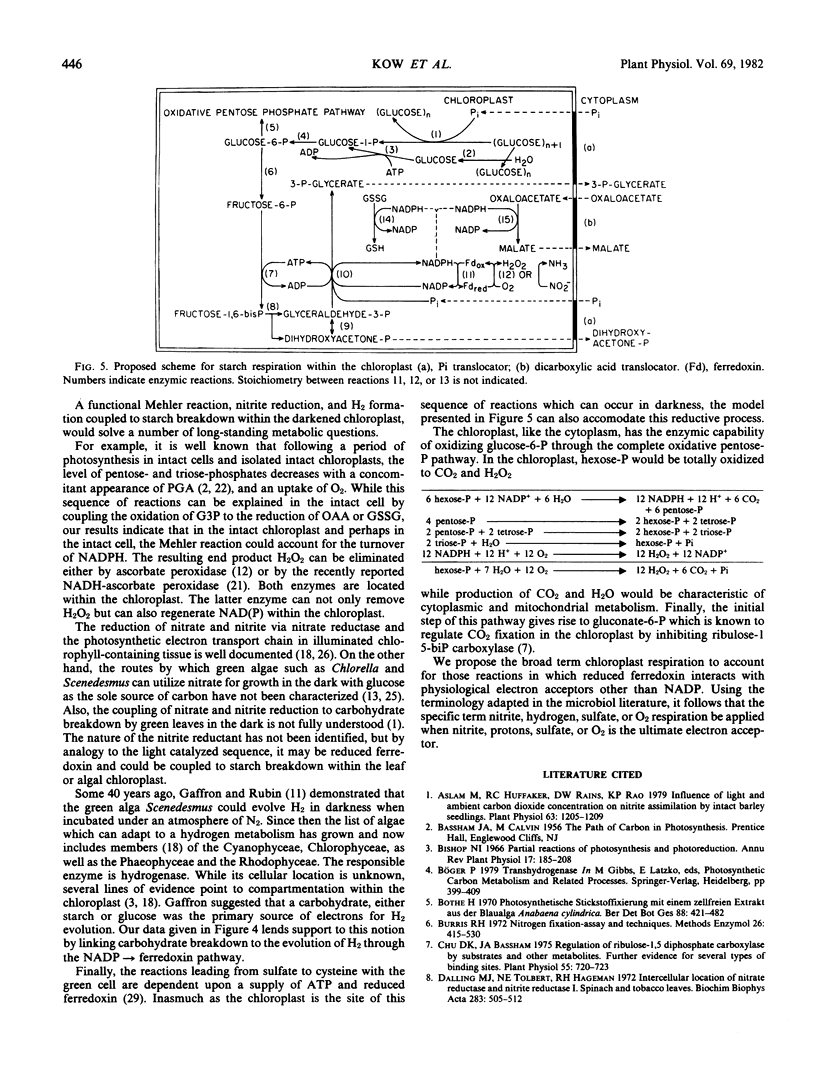
A spinach (Spinacia oleracia var. America) chloroplast particle fortified with ferredoxin, fructose-1,6-bisphosphate, or ribose-5-phosphate and NADP has been shown to generate NADPH by the oxidation of glyceraldehyde-3 phosphate to glycerate-3-phosphate (PGA) and to reduce ferredoxin with the NADPH. The resulting reduced ferredoxin can reduce O2 to H2O2, nitrite to ammonia, or protons to H2. Hydrogen production was the result of adding hydrogenase from Chlamydomonas reinhardii to the chloroplast preparation. The predicted stoichiometry of 1 PGA:1 O2 in the absence of and 2 PGA:1 O2 in the presence of catalase was observed indicating H2O2 as the end product of O2 reduction. The predicted stoichiometry of 3 PGA:1 nitrite:1 ammonia was also observed. A scheme is presented to account for a sustained generation of NADP and ATP necessary for the dissimilation of starch in the darkened chloroplast. The unifying term chloroplast respiration is introduced to account for those reactions in which reduced ferredoxin interacts with physiological acceptors other than NADP or nitrite, hydrogen, or O2 respiration when nitrite, protons, or O2 is the ultimate electron acceptor.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aslam M., Huffaker R. C., Rains D. W., Rao K. P. Influence of light and ambient carbon dioxide concentration on nitrate assimilation by intact barley seedlings. Plant Physiol. 1979 Jun;63(6):1205–1209. doi: 10.1104/pp.63.6.1205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burris R. H. Nitrogen fixation--assay methods and techniques. Methods Enzymol. 1972;24:415–431. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(72)24088-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu D. K., Bassham J. A. Regulation of ribulose 1,5-diphosphate carboxylase by substrates and other metabolites: further evidence for several types of binding sites. Plant Physiol. 1975 Apr;55(4):720–726. doi: 10.1104/pp.55.4.720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalling M. J., Tolbert N. E., Hageman R. H. Intracellular location of nitrate reductase and nitrite reductase. I. Spinach and tobacco leaves. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Dec 14;283(3):505–512. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(72)90266-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erbes D. L., King D., Gibbs M. Inactivation of Hydrogenase in Cell-free Extracts and Whole Cells of Chlamydomonas reinhardi by Oxygen. Plant Physiol. 1979 Jun;63(6):1138–1142. doi: 10.1104/pp.63.6.1138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groden D., Beck E. H2O2 destruction by ascorbate-dependent systems from chloroplasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jun 5;546(3):426–435. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(79)90078-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrero M. G., Rivas J., Paneque A., Losada M. Mechanism of nitrate and nitrate reduction in Chlorella cells grown in the dark. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Oct 1;45(1):82–89. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90053-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heldt H. W., Chon C. J., Maronde D. Role of orthophosphate and other factors in the regulation of starch formation in leaves and isolated chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 1977 Jun;59(6):1146–1155. doi: 10.1104/pp.59.6.1146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latzko E., Gibbs M. Level of photosynthetic intermediates in isolated spinach chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 1969 Mar;44(3):396–402. doi: 10.1104/pp.44.3.396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi C., Gibbs M. Starch degradation in isolated spinach chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 1976 Jun;57(6):933–935. doi: 10.1104/pp.57.6.933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neyra C. A., Hageman R. H. Dependence of nitrite reduction on electron transport chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 1974 Oct;54(4):480–483. doi: 10.1104/pp.54.4.480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peavey D. G., Steup M., Gibbs M. Characterization of starch breakdown in the intact spinach chloroplast. Plant Physiol. 1977 Aug;60(2):305–308. doi: 10.1104/pp.60.2.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAN PIETRO A., LANG H. M. Photosynthetic pyridine nucleotide reductase. I. Partial purification and properties of the enzyme from spinach. J Biol Chem. 1958 Mar;231(1):211–229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiller H., Bookjans G., Böger P. The influence of oxygen on nitrite reduction in a reconstituted system. Z Naturforsch C. 1976 Sep-Oct;31(9-10):565–568. doi: 10.1515/znc-1976-9-1015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steup M., Peavey D. G., Gibbs M. The regulation of starch metabolism by inorganic phosphate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Oct 18;72(4):1554–1561. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(76)80191-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



