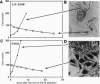
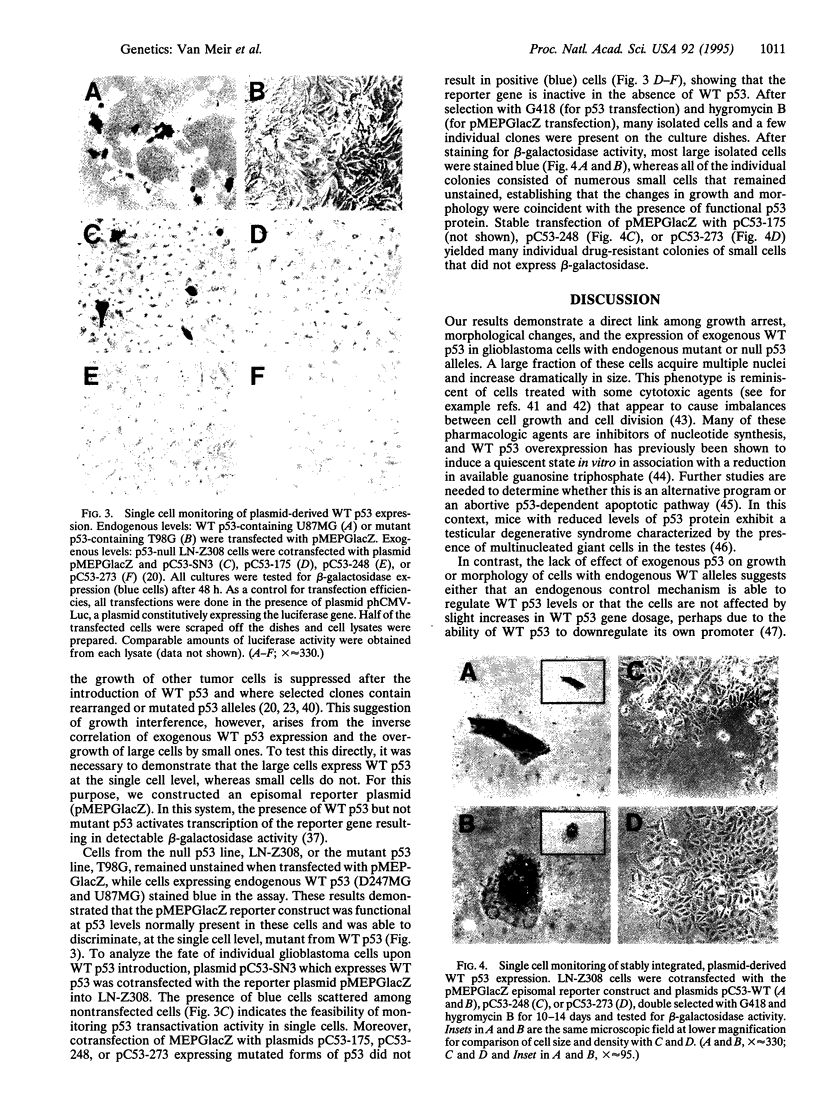
Abstract
Mutation of the p53 tumor suppressor gene is one of the earliest identified genetic lesions during malignant progression of human astrocytomas. To assess the functional significance of these mutations, wild-type (WT) p53 genes were introduced into glioblastoma cell lines having mutant, WT, or null endogenous p53 alleles. Populations of cells with mutant or null endogenous p53 alleles and exogenous WT p53 were spontaneously selected in culture for cells expressing only mutant p53 or no p53, which then displayed a growth and tumorigenic phenotype identical to the parental cells. To determine the phenotypic consequences of WT p53 expression before the occurrence of mutations, we developed a single cell assay to monitor WT p53-dependent transcription activity. Transfer and expression of exogenous WT p53 genes to cells with endogenous mutant or deleted, but not WT, p53 alleles caused growth arrest and morphological changes, including increased cell size and acquisition of multiple nuclei. This supports the hypothesis that genetic lesions of the p53 gene play an important role in the genesis of astrocytomas. Furthermore, the high sensitivity of the episomal single cell reporter strategy developed here has potential clinical applications in the rapid screening of patients for germ-line mutations of the p53 gene or any other gene with known targets for transcriptional transactivation.
Full text
PDF
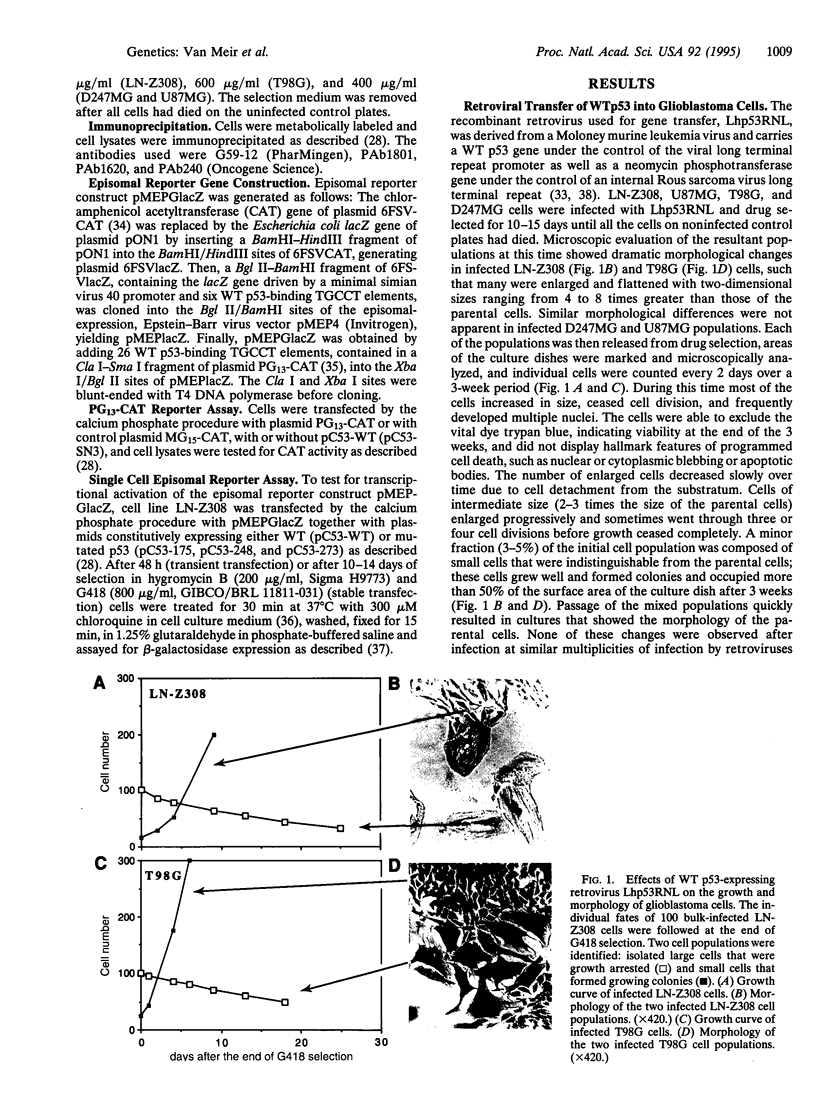


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker S. J., Markowitz S., Fearon E. R., Willson J. K., Vogelstein B. Suppression of human colorectal carcinoma cell growth by wild-type p53. Science. 1990 Aug 24;249(4971):912–915. doi: 10.1126/science.2144057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bigner D. D., Bigner S. H., Pontén J., Westermark B., Mahaley M. S., Ruoslahti E., Herschman H., Eng L. F., Wikstrand C. J. Heterogeneity of Genotypic and phenotypic characteristics of fifteen permanent cell lines derived from human gliomas. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1981 May;40(3):201–229. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198105000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bigner S. H., Mark J., Burger P. C., Mahaley M. S., Jr, Bullard D. E., Muhlbaier L. H., Bigner D. D. Specific chromosomal abnormalities in malignant human gliomas. Cancer Res. 1988 Jan 15;48(2):405–411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cajot J. F., Anderson M. J., Lehman T. A., Shapiro H., Briggs A. A., Stanbridge E. J. Growth suppression mediated by transfection of p53 in Hut292DM human lung cancer cells expressing endogenous wild-type p53 protein. Cancer Res. 1992 Dec 15;52(24):6956–6960. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey G., Lo-Hsueh M., Lopez M. E., Vogelstein B., Stanbridge E. J. Growth suppression of human breast cancer cells by the introduction of a wild-type p53 gene. Oncogene. 1991 Oct;6(10):1791–1797. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavenee W. K., Scrable H. J., James C. D. Molecular genetics of human cancer predisposition and progression. Mutat Res. 1991 Apr;247(2):199–202. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(91)90015-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng J., Yee J. K., Yeargin J., Friedmann T., Haas M. Suppression of acute lymphoblastic leukemia by the human wild-type p53 gene. Cancer Res. 1992 Jan 1;52(1):222–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diller L., Kassel J., Nelson C. E., Gryka M. A., Litwak G., Gebhardt M., Bressac B., Ozturk M., Baker S. J., Vogelstein B. p53 functions as a cell cycle control protein in osteosarcomas. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):5772–5781. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.5772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dittmer D., Pati S., Zambetti G., Chu S., Teresky A. K., Moore M., Finlay C., Levine A. J. Gain of function mutations in p53. Nat Genet. 1993 May;4(1):42–46. doi: 10.1038/ng0593-42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon E. R., Vogelstein B. A genetic model for colorectal tumorigenesis. Cell. 1990 Jun 1;61(5):759–767. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90186-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frebourg T., Barbier N., Kassel J., Ng Y. S., Romero P., Friend S. H. A functional screen for germ line p53 mutations based on transcriptional activation. Cancer Res. 1992 Dec 15;52(24):6976–6978. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimoto M., Fults D. W., Thomas G. A., Nakamura Y., Heilbrun M. P., White R., Story J. L., Naylor S. L., Kagan-Hallet K. S., Sheridan P. J. Loss of heterozygosity on chromosome 10 in human glioblastoma multiforme. Genomics. 1989 Feb;4(2):210–214. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90302-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fults D., Pedone C. A., Thomas G. A., White R. Allelotype of human malignant astrocytoma. Cancer Res. 1990 Sep 15;50(18):5784–5789. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fults D., Tippets R. H., Thomas G. A., Nakamura Y., White R. Loss of heterozygosity for loci on chromosome 17p in human malignant astrocytoma. Cancer Res. 1989 Dec 1;49(23):6572–6577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsberg D., Mechta F., Yaniv M., Oren M. Wild-type p53 can down-modulate the activity of various promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):9979–9983. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.9979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper J. W., Adami G. R., Wei N., Keyomarsi K., Elledge S. J. The p21 Cdk-interacting protein Cip1 is a potent inhibitor of G1 cyclin-dependent kinases. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):805–816. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90499-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey D. M., Levine A. J. p53 alteration is a common event in the spontaneous immortalization of primary BALB/c murine embryo fibroblasts. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12B):2375–2385. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12b.2375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi Y., Yamashita J., Yamaguchi K. Timing and role of p53 gene mutation in the recurrence of glioma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Oct 31;180(2):1145–1150. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81186-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollstein M., Sidransky D., Vogelstein B., Harris C. C. p53 mutations in human cancers. Science. 1991 Jul 5;253(5015):49–53. doi: 10.1126/science.1905840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishioka C., Frebourg T., Yan Y. X., Vidal M., Friend S. H., Schmidt S., Iggo R. Screening patients for heterozygous p53 mutations using a functional assay in yeast. Nat Genet. 1993 Oct;5(2):124–129. doi: 10.1038/ng1093-124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James C. D., Carlbom E., Dumanski J. P., Hansen M., Nordenskjold M., Collins V. P., Cavenee W. K. Clonal genomic alterations in glioma malignancy stages. Cancer Res. 1988 Oct 1;48(19):5546–5551. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James C. D., Carlbom E., Nordenskjold M., Collins V. P., Cavenee W. K. Mitotic recombination of chromosome 17 in astrocytomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2858–2862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James C. D., He J., Carlbom E., Nordenskjold M., Cavenee W. K., Collins V. P. Chromosome 9 deletion mapping reveals interferon alpha and interferon beta-1 gene deletions in human glial tumors. Cancer Res. 1991 Mar 15;51(6):1684–1688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P., Gray D., Mowat M., Benchimol S. Expression of wild-type p53 is not compatible with continued growth of p53-negative tumor cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):1–11. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern S. E., Pietenpol J. A., Thiagalingam S., Seymour A., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. Oncogenic forms of p53 inhibit p53-regulated gene expression. Science. 1992 May 8;256(5058):827–830. doi: 10.1126/science.1589764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köpf-Maier P., Hermann G. Cytologic observations on the effects of metallocene dichlorides on human fibroblasts cultivated in vitro. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1984;47(2):107–122. doi: 10.1007/BF02890193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine A. J., Momand J., Finlay C. A. The p53 tumour suppressor gene. Nature. 1991 Jun 6;351(6326):453–456. doi: 10.1038/351453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libermann T. A., Nusbaum H. R., Razon N., Kris R., Lax I., Soreq H., Whittle N., Waterfield M. D., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Amplification, enhanced expression and possible rearrangement of EGF receptor gene in primary human brain tumours of glial origin. Nature. 1985 Jan 10;313(5998):144–147. doi: 10.1038/313144a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe S. W., Schmitt E. M., Smith S. W., Osborne B. A., Jacks T. p53 is required for radiation-induced apoptosis in mouse thymocytes. Nature. 1993 Apr 29;362(6423):847–849. doi: 10.1038/362847a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu X., Park S. H., Thompson T. C., Lane D. P. Ras-induced hyperplasia occurs with mutation of p53, but activated ras and myc together can induce carcinoma without p53 mutation. Cell. 1992 Jul 10;70(1):153–161. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90541-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matozaki T., Sakamoto C., Suzuki T., Matsuda K., Uchida T., Nakano O., Wada K., Nishisaki H., Konda Y., Nagao M. p53 gene mutations in human gastric cancer: wild-type p53 but not mutant p53 suppresses growth of human gastric cancer cells. Cancer Res. 1992 Aug 15;52(16):4335–4341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercer W. E., Shields M. T., Amin M., Sauve G. J., Appella E., Romano J. W., Ullrich S. J. Negative growth regulation in a glioblastoma tumor cell line that conditionally expresses human wild-type p53. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6166–6170. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mietz J. A., Unger T., Huibregtse J. M., Howley P. M. The transcriptional transactivation function of wild-type p53 is inhibited by SV40 large T-antigen and by HPV-16 E6 oncoprotein. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(13):5013–5020. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05608.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Momand J., Zambetti G. P., Olson D. C., George D., Levine A. J. The mdm-2 oncogene product forms a complex with the p53 protein and inhibits p53-mediated transactivation. Cell. 1992 Jun 26;69(7):1237–1245. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90644-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan L. M., Matlashewski G. J., Scrable H. J., Cavenee W. K. Mechanisms of p53 loss in human sarcomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5863–5867. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigro J. M., Baker S. J., Preisinger A. C., Jessup J. M., Hostetter R., Cleary K., Bigner S. H., Davidson N., Baylin S., Devilee P. Mutations in the p53 gene occur in diverse human tumour types. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):705–708. doi: 10.1038/342705a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliner J. D., Kinzler K. W., Meltzer P. S., George D. L., Vogelstein B. Amplification of a gene encoding a p53-associated protein in human sarcomas. Nature. 1992 Jul 2;358(6381):80–83. doi: 10.1038/358080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross D. W. Unbalanced cell growth and increased protein synthesis induced by chemotherapeutic agents. Blood Cells. 1983;9(1):57–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotter V., Schwartz D., Almon E., Goldfinger N., Kapon A., Meshorer A., Donehower L. A., Levine A. J. Mice with reduced levels of p53 protein exhibit the testicular giant-cell degenerative syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 1;90(19):9075–9079. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.19.9075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherley J. L. Guanine nucleotide biosynthesis is regulated by the cellular p53 concentration. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 25;266(36):24815–24828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidransky D., Mikkelsen T., Schwechheimer K., Rosenblum M. L., Cavanee W., Vogelstein B. Clonal expansion of p53 mutant cells is associated with brain tumour progression. Nature. 1992 Feb 27;355(6363):846–847. doi: 10.1038/355846a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein G. H. T98G: an anchorage-independent human tumor cell line that exhibits stationary phase G1 arrest in vitro. J Cell Physiol. 1979 Apr;99(1):43–54. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040990107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugawa N., Ekstrand A. J., James C. D., Collins V. P. Identical splicing of aberrant epidermal growth factor receptor transcripts from amplified rearranged genes in human glioblastomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8602–8606. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabuchi K., Fukuyama K., Mineta T. [Cytogenetic diagnosis of brain tumors]. No To Shinkei. 1992 Oct;44(10):871–879. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tounekti O., Pron G., Belehradek J., Jr, Mir L. M. Bleomycin, an apoptosis-mimetic drug that induces two types of cell death depending on the number of molecules internalized. Cancer Res. 1993 Nov 15;53(22):5462–5469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich S. J., Mercer W. E., Appella E. Human wild-type p53 adopts a unique conformational and phosphorylation state in vivo during growth arrest of glioblastoma cells. Oncogene. 1992 Aug;7(8):1635–1643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Meir E. G., Kikuchi T., Tada M., Li H., Diserens A. C., Wojcik B. E., Huang H. J., Friedmann T., de Tribolet N., Cavenee W. K. Analysis of the p53 gene and its expression in human glioblastoma cells. Cancer Res. 1994 Feb 1;54(3):649–652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong A. J., Bigner S. H., Bigner D. D., Kinzler K. W., Hamilton S. R., Vogelstein B. Increased expression of the epidermal growth factor receptor gene in malignant gliomas is invariably associated with gene amplification. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6899–6903. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeargin J., Cheng J., Haas M. Role of the p53 tumor suppressor gene in the pathogenesis and in the suppression of acute lymphoblastic T-cell leukemia. Leukemia. 1992;6 (Suppl 3):85S–91S. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin Y., Tainsky M. A., Bischoff F. Z., Strong L. C., Wahl G. M. Wild-type p53 restores cell cycle control and inhibits gene amplification in cells with mutant p53 alleles. Cell. 1992 Sep 18;70(6):937–948. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90244-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Azouzi M., Chung R. Y., Farmer G. E., Martuza R. L., Black P. M., Rouleau G. A., Hettlich C., Hedley-Whyte E. T., Zervas N. T., Panagopoulos K. Loss of distinct regions on the short arm of chromosome 17 associated with tumorigenesis of human astrocytomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):7186–7190. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.7186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Deiry W. S., Tokino T., Velculescu V. E., Levy D. B., Parsons R., Trent J. M., Lin D., Mercer W. E., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. WAF1, a potential mediator of p53 tumor suppression. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):817–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90500-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]